A Dream

a dream
More Posts from Copperfingertips and Others
Why did we as a society ever stop making Jugend style architecture?
That should honestly be something we bring back for Solarpunk. The nature inspired and geometric designs feel like they should be right up that particular alley.


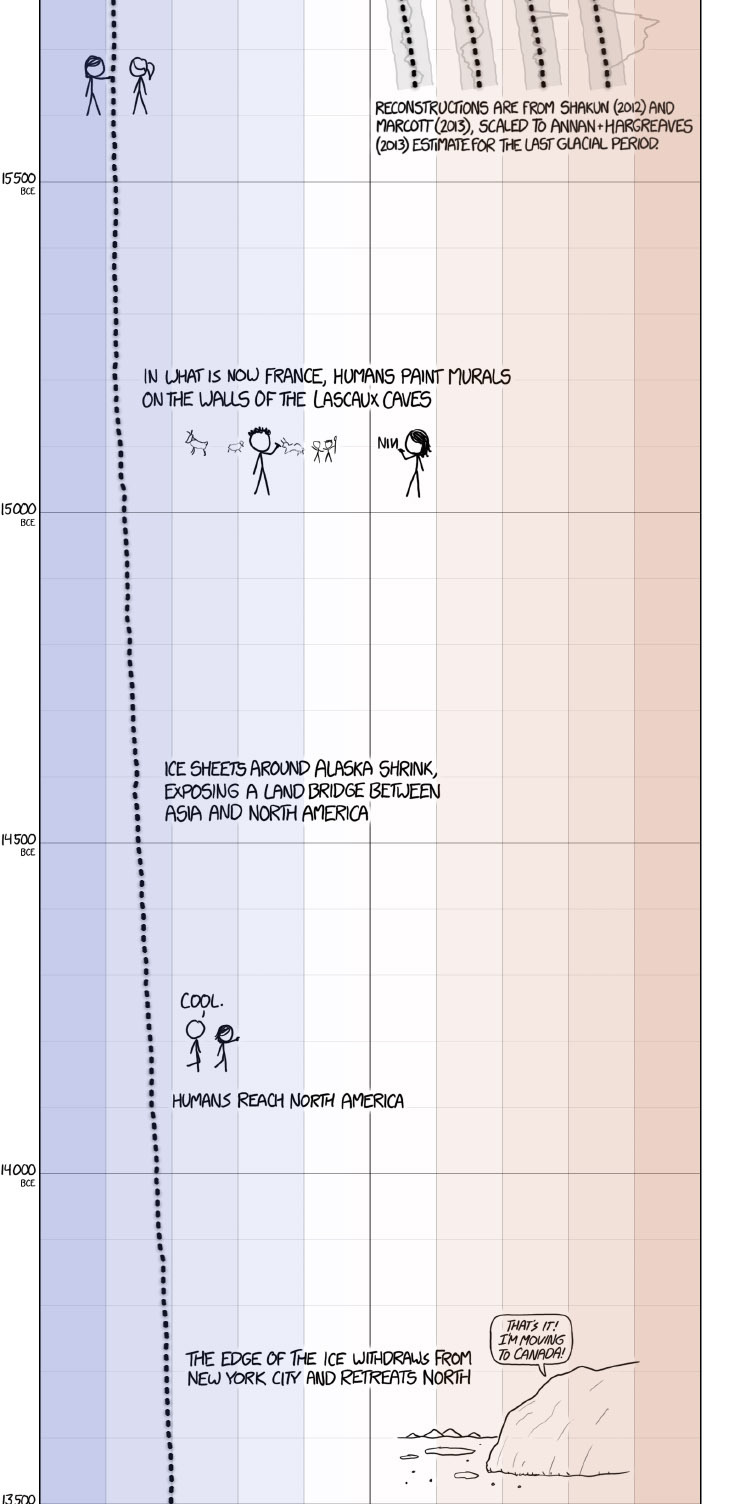



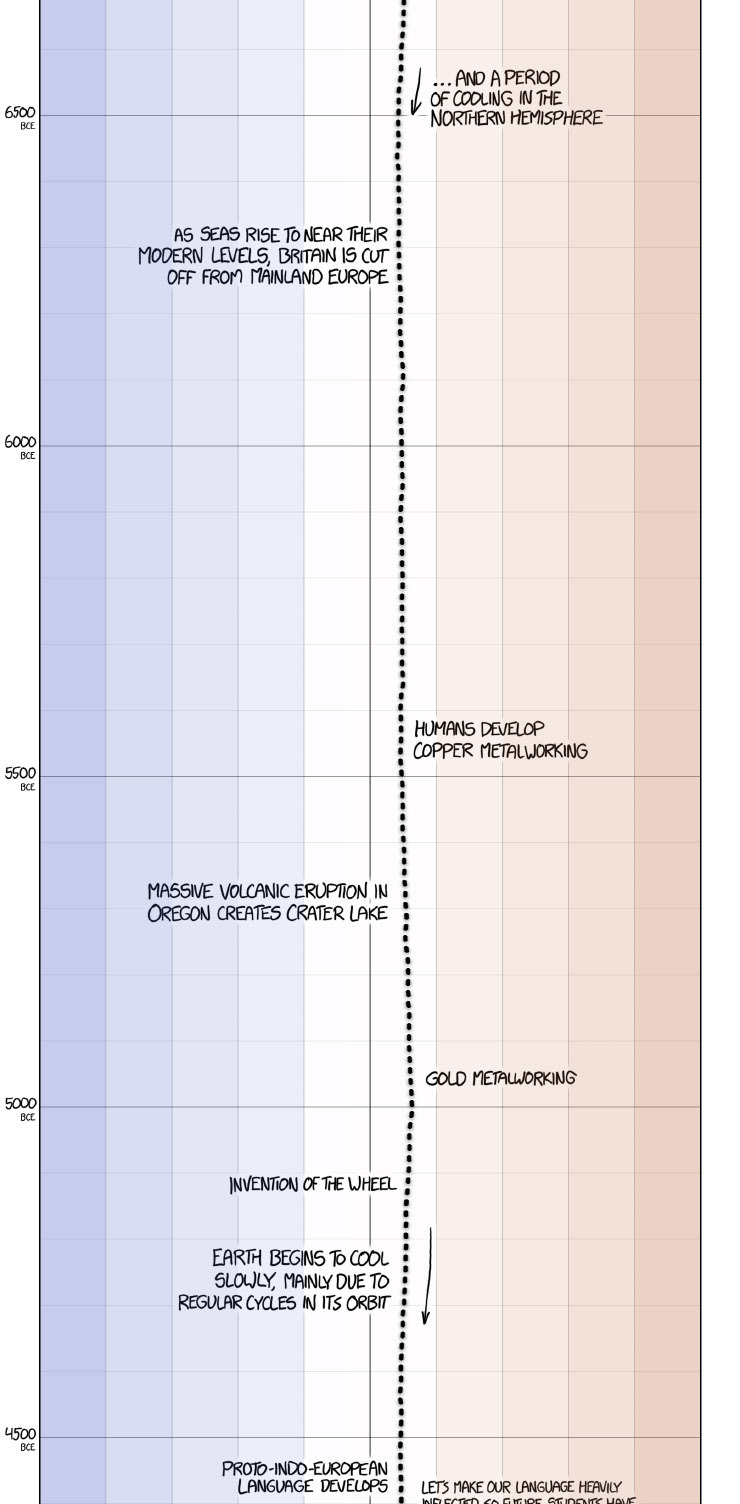
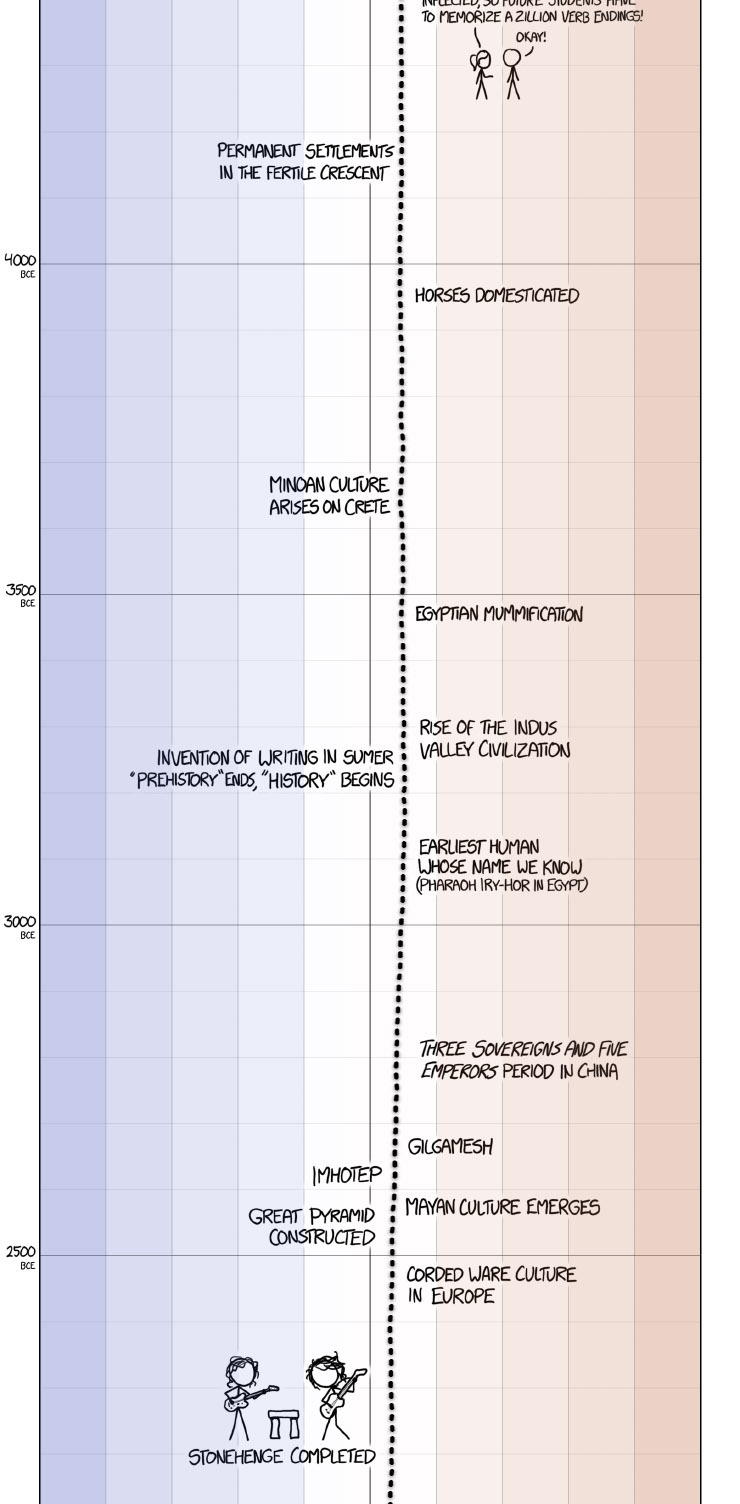


XKCD’s excellent presentation on historical global temperature and anthropogenic global warming.
[After setting your car on fire] “Listen, your car’s temperature has changed before.”


After finding out recently that most gift wrap isn’t recyclable I decided to wrap my holiday gifts in the least amount of material possible. No tape, no waste. It’s the little things sometimes. ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀
[Image description: Two simply wrapped gifts in brown paper bags and red string.]⠀⠀⠀
⠀#zerowaste #giftwrap #diy #solarpunk #holidays #genretomovement




Fall Arrangement Flowers

Can't afford to buy things for your garden?
*Re-posting, with new information
A store-bought bag of topsoil, a roll of landscaping fabric, or a bag of cedar chips doesn’t go very far if you have a large garden or a very limited budget. Here are some ways to create the materials you need for a beautiful, organic, productive garden, by both re-directing household waste, and foraging in your local area. I use a lot of these tricks in my garden to make it almost completely free for me to continue growing new things, and expanding the workable area every year!
For soil
Save your food scraps to create a rich compost for growing veggies and amending your soil. There are numerous options for every size of dwelling and yard. Small space solutions such as Bokashi and vermicompost work indoors and don’t produce bad smells, so you can keep them underneath the sink.Worm towers, compost heaps, and outdoor compost bins are a great solution if you have more space. The more you add, the more rich, nutritious material you can make for your garden. I like composting because it means I don’t have gross smelly garbage bags to deal with, because food waste is diverted. It seems like a lot of work at first, but it actually saves time, money, and transportation.
Seaweed or kelp is one of the best things for your garden, with over 70 essential nutrients, and acting as a weed barrier and a moisture-retentive mulch. I collect seaweed nearby on the beach with my bike trailer, or, when I go for a walk I bring a little home with me each time. It’s an absolute miracle for your soil.

Worm tower
Fertiliser
There are three things that are essential for plant growth. These are nitrogen for leaves and vegetation (N), phosphorus for roots and shoots (P), and potassium for water movement, flowering, and fruiting (K). Commercial fertilisers will give the relative concentrations of each of these compounds with and “NPK” rating. Plants like tomatoes also need calcium to produce healthy fruit. You can create amendments for your garden and soil at home so that you do not have to purchase fertiliser.
For nitrogen
Grass clippings contain 4% nitrogen, 1% phosphorus, and 2% potassium (NPK = 4-1-2).
Human urine contains 12% nitrogen, and it’s sterile. Dilute before adding directly to plants.
Legumes such as beans, clover, peanuts, and alfalfa fix inorganic nitrogen into the soil with mycorrhizal organisms and nodules on their root systems. Plant these crops every few years in rotation with others to renew the soil organically.
For phosphorus
Human urine is also a great source of phosphorous and trace amounts of potassium.
Ground up bones or shells add a slow-release phosphorous to the soil
Had a baby recently? Bury the placenta in the garden.
For potassium
Hardwood ashes
Composted banana peels
For calcium
Break down all of your eggshells, or seashells you have found, in a plastic bucket, using vinegar. This creates a soluble calcium solution you can add to a watering can.
Soil Acidity/Alkalinity
Many plants are particular about what the soil pH should be.
To make soil more acidic: add oak leaves, pine needles, leaf mulch, urine, coffee grounds or sphagnum.
To make soil more alkaline: add wood ash, shell, or bone.
Mulch
Mulch is decomposing organic matter that adds nutrition to the soil, while simultaneously keeping out weed growth and retaining moisture. It also attracts worms, fungi and other beneficial creatures to your soil. Free sources of mulch include:
Leaves
Garden waste
Grass clippings
Straw (often straw bales are given away after being used for decoration in the fall. You can also plant vegetables directly in straw bales using a technique called straw bale gardening).
Wood chips (if you can borrow a wood chipper after you’ve collected some wood you can have attractive wood mulch for free)

Straw bale garden
Landscaping fabric
When mulch isn’t enough to keep the weeds down, many people opt for landscaping fabric. It can be quite expensive and inorganic-looking. Free solutions that both attract worms and can be replaced in small segments as they break down include:
Newspaper*
Cardboard*
Egg cartons*
Printer paper, looseleaf, etc. in thick layers*
*try to make sure you are using paper that has vegetable-based dyes, so you aren’t leeching toxins into the soil.
Soil density/drainage
If your soil is compacted and you have plants that require low levels of water, or excellent drainage, add sand. I don’t recommend stealing it from the beach, but ask around and you’d be surprised at how easy it is to get for free. Sawdust also improves drainage. Adding organic matter and mulch encourages worms, who also till and aerate compacted soil.
If the area still needs drainage, dig a hole and fill it with bricks or rocks to create a “dry well”
For drainage in pots, add crushed bricks, terra cotta pot fragments, packing peanuts, small stones, marbles, orsand to the bottom under the soil layer. I find these in construction sites, on craigslist, or at flea markets.
Pots and growing containers
If you have space, raised beds are a great no-dig way to establish growing space. If you are pressed for space (like working on a balcony) there are many cheap or free options for container gardens.
Creating raised beds allows you to build up the soil without digging. Free ways to do this include using rocks or lumber (like my DIY “lasagna garden” made with the sheet composting technique), using the “wattle“ method with sticks and posts you have found, using discarded straw bales, old bricks,paving stones, cinder blocks or really anything else you have lying around.
Hugelkutur raised beds, which fix carbon and provide drainage, can be made by stacking sticks and untreated wood, and then piling soil or compost over it. (Thanks milos-garden)
Rubber tire gardens retain heat in the night and allow for great drainage. They can also be painted in fun ways.
Herb spirals (here is mine: 1, 2, 3) can be built with stones, bricks, and other found materials.
I often use old cooking pots, barbecues, teapots, or other found objects as planters.
Making wooden planters is easy, and scrap or salvaged wood is also easy to come by. I’m not a fan of using wooden pallets for DIY projects, but they are also a free source of lumber for things like planters.
If you can track down peat moss, cement, and vermiculite, you can make an easy Hypertufa planter in whatever shape you would like, provided you have a form in which it can dry.
I’ve made hanging gardens out of soda cans.
You can build a self-watering container with a 2L pop bottle.
Start seeds in eggshells
Make biodegradable pots out of newspapers.
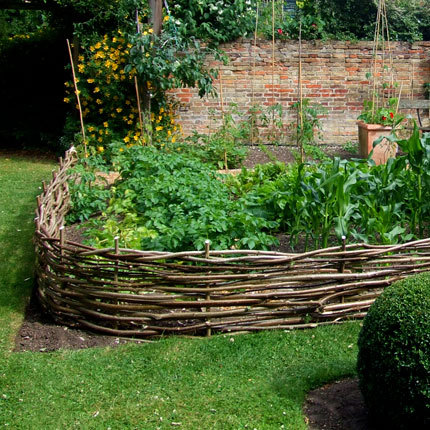

Wattle raised beds

Rubber tire gardens

Hugelkultur

An herb spiral
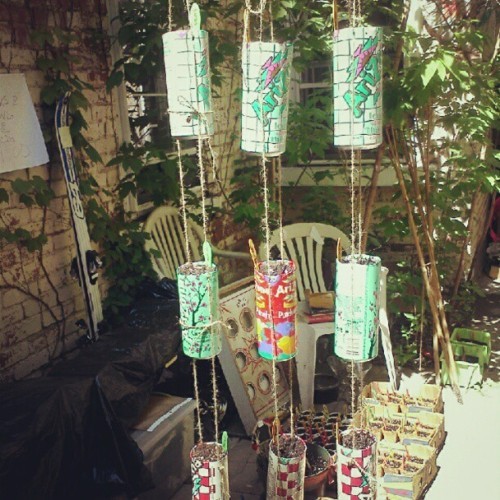
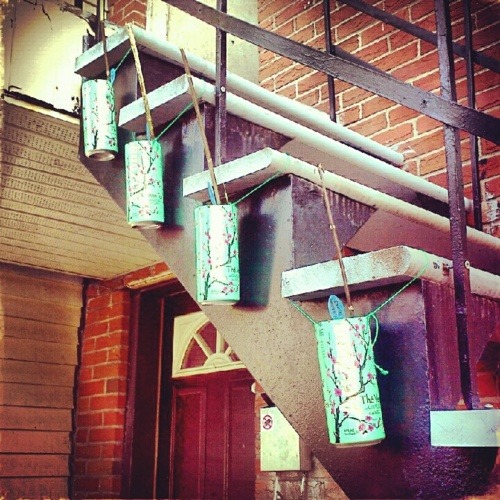


Hanging gardens in cans (2)
Trellises and supports
Many plants need external support, such as stakes of trellises, to thrive.
Rebar can almost always be salvaged cheaply or free and makes a great trellis, arch, or purgola
Build trellises and supports out of the pliable young stems of plants like willow

Rebar trellis/arch

Living willow arch/trellis
Paving
Paving often requires a foundation of sand or another stable and well-drained substrate, and a covering of stones, bricks, or other weatherproof elements. Slowly collect stones over time, or free paving stone fragments to create a mosaic-type walkway. Often people give these things away on craigslist. I made a patio and fireplace out of free salvaged bricks, for example.

Salvaged garden walkway
Greenhouses and cold frames
Here is a gallery of greenhouses made out of salvaged windows and doors
A cold frame is easy to make with salvaged lumber, and plastic sheeting.

Window greenhouse

Palet cold-frame
Seeds and plants
Swap seeds with other gardeners
If you see a plant you like at someone’s house, ask for seeds or cuttings
Save seeds every year and build a library of options. Here is a great guide to seed saving.
Save seeds from foods you like from the grocery store: consider growing peanuts, ginger, garlic, peppers, or a walnut tree: all of these and more can be planted from store-bought produce.
Learn to take cuttings. There is a tonne of info on the web about basic cutting propagation, layering, (like I do with rhododendrons) air layering, and numerous other techniques to take clones of plants you like. This saves going to a nursery and shelling out big bucks for all the variety you want.
For cuttings, willow tea and honey are great rooting hormones/antiseptics/anti-fungal agents, which can save you $40 if you were thinking of buying commercial rooting hormone.
You can root cuttings in a potato! (See my methods for rooting “borrowed” plants here)
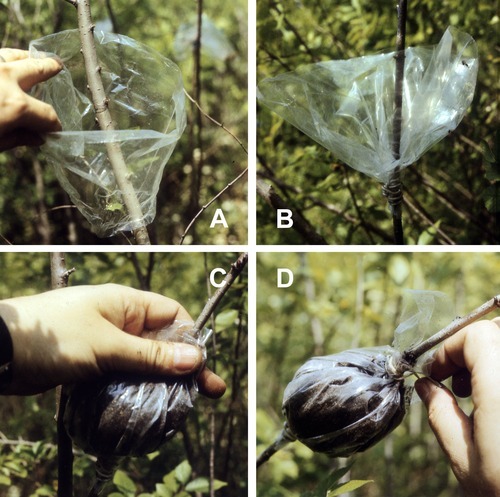

Air layering

Rooting cuttings in potatoes
—-
I hope this helps you build your garden outside of the usual capitalist channels! It can be a cheap or free hobby if you are willing to think outside the box, and maybe put up with things that don’t look as clean or crisp as a hardware store catalogue. If you have any further ideas, please add them! The more information the better.







~ the pondering muse🌙
Where have all the bugs gone? That’s what this post tries to answer and if you’re like me and hadn’t really noticed the lack of bugs recently, you’ll understand why this is such a big deal after reading the article. However, before we dive into this article, I want to share with you what I’ve noticed.
I’ve lived in Missouri for almost 19 years now, about a decade ago I remember windshields so full of bug splats that you couldn’t see out of it while driving down the highway and cringing at the *thump* of especially large bugs when they hit. I remember a season where when I rode my bike around town I couldn’t not hit a grasshopper because there were more than I could count all over the roads and fields. Last summer however? I remember pulling a single butterfly from the grill of my dad’s truck. That’s it… There were no more bugs. …
Here’s how plentiful our world used to be. We tend to think that the environmental conditions that we are born into are normal, but it is anything but normal.
“In “The Once and Future World,” the journalist J.B. MacKinnon cites records from recent centuries that hint at what has only just been lost: “In the North Atlantic, a school of cod stalls a tall ship in midocean; off Sydney, Australia, a ship’s captain sails from noon until sunset through pods of sperm whales as far as the eye can see. … Pacific pioneers complain to the authorities that splashing salmon threaten to swamp their canoes.” There were reports of lions in the south of France, walruses at the mouth of the Thames, flocks of birds that took three days to fly overhead, as many as 100 blue whales in the Southern Ocean for every one that’s there now. “These are not sights from some ancient age of fire and ice,” MacKinnon writes. “We are talking about things seen by human eyes, recalled in human memory.”“
So, when you read the above article, please understand how dire these circumstances are for us and our planet. Ok, so what are the highlights of the article?
“A 2013 paper in Nature, which modeled both natural and computer-generated food webs, suggested that a loss of even 30 percent of a species’ abundance can be so destabilizing that other species start going fully, numerically extinct — in fact, 80 percent of the time it was a secondarily affected creature that was the first to disappear.”
- Drastic drops in insect populations have been recorded globally.
- World’s largest king penguin colony shrank by 88%.
- Blue-fin Tuna populations have shrunk 97%.
- 60% decrease in total wild land animal populations.
- 96% of the planet’s biomass now is humans and livestock. Wild animals represent less than 4%. …
- 10-60% less arthropod biomass in Puerto Rico.
- 50-80% drops in partridges from France due to the lack of insects they eat.
- 50% of all farmland birds in Europe are gone.
- Birds which rely on insects may be starving to death due to their collapse.
These are some drastic decreases and we tend to forget that all species are connected. When we loose one species, we can loose all the species that rely on it. We need to recognize what is happening around us with our environment and our planet. We need to know, that what we are seeing today, isn’t normal.
-
 dragononymous liked this · 2 months ago
dragononymous liked this · 2 months ago -
 unlikelywitchmiracle liked this · 2 months ago
unlikelywitchmiracle liked this · 2 months ago -
 thoraugusta liked this · 2 months ago
thoraugusta liked this · 2 months ago -
 firstrainybitch101 liked this · 2 months ago
firstrainybitch101 liked this · 2 months ago -
 happyk44 reblogged this · 2 months ago
happyk44 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 inspiresandagii reblogged this · 3 months ago
inspiresandagii reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 umbairnatrium reblogged this · 3 months ago
umbairnatrium reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 kaispiral liked this · 3 months ago
kaispiral liked this · 3 months ago -
 andron-temporis reblogged this · 3 months ago
andron-temporis reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 the-fallen-sky liked this · 3 months ago
the-fallen-sky liked this · 3 months ago -
 wasnotafraid liked this · 3 months ago
wasnotafraid liked this · 3 months ago -
 pinkandprose liked this · 3 months ago
pinkandprose liked this · 3 months ago -
 usernamegobrrrrr liked this · 3 months ago
usernamegobrrrrr liked this · 3 months ago -
 silent-weightlessness reblogged this · 3 months ago
silent-weightlessness reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 silent-weightlessness liked this · 3 months ago
silent-weightlessness liked this · 3 months ago -
 distinguishedsandwichcreator liked this · 3 months ago
distinguishedsandwichcreator liked this · 3 months ago -
 veluni reblogged this · 3 months ago
veluni reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 khey-s reblogged this · 3 months ago
khey-s reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 khey-s liked this · 3 months ago
khey-s liked this · 3 months ago -
 deadleypotatoes reblogged this · 3 months ago
deadleypotatoes reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 henrycavillsfleshjack liked this · 4 months ago
henrycavillsfleshjack liked this · 4 months ago -
 by96days liked this · 4 months ago
by96days liked this · 4 months ago -
 ai-meems liked this · 5 months ago
ai-meems liked this · 5 months ago -
 fablenaught reblogged this · 5 months ago
fablenaught reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 aaas98 liked this · 6 months ago
aaas98 liked this · 6 months ago -
 demichrising liked this · 6 months ago
demichrising liked this · 6 months ago -
 russenoire liked this · 7 months ago
russenoire liked this · 7 months ago -
 fckyourthoughts reblogged this · 7 months ago
fckyourthoughts reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 jernon liked this · 7 months ago
jernon liked this · 7 months ago -
 essenceofinn reblogged this · 7 months ago
essenceofinn reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 youwillperishinflame reblogged this · 7 months ago
youwillperishinflame reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 thetownpornographer reblogged this · 7 months ago
thetownpornographer reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 marimbista reblogged this · 7 months ago
marimbista reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 dazedquasars reblogged this · 7 months ago
dazedquasars reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 basementofthearchmage liked this · 7 months ago
basementofthearchmage liked this · 7 months ago -
 lucky-lesbian reblogged this · 7 months ago
lucky-lesbian reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 ineffable-iridescence reblogged this · 7 months ago
ineffable-iridescence reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 quintessential-ethereal reblogged this · 7 months ago
quintessential-ethereal reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 ineffable-iridescence liked this · 7 months ago
ineffable-iridescence liked this · 7 months ago -
 spookytsukki reblogged this · 7 months ago
spookytsukki reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 spookytsukki liked this · 7 months ago
spookytsukki liked this · 7 months ago -
 hulklinging reblogged this · 7 months ago
hulklinging reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 crowstalker liked this · 8 months ago
crowstalker liked this · 8 months ago -
 mj037 liked this · 8 months ago
mj037 liked this · 8 months ago -
 lextrangera liked this · 8 months ago
lextrangera liked this · 8 months ago -
 marclar0314 liked this · 9 months ago
marclar0314 liked this · 9 months ago -
 resonance432hz liked this · 9 months ago
resonance432hz liked this · 9 months ago -
 sweet--candy reblogged this · 9 months ago
sweet--candy reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 bdbeady liked this · 10 months ago
bdbeady liked this · 10 months ago -
 midnightwerewoolf reblogged this · 10 months ago
midnightwerewoolf reblogged this · 10 months ago
