Solar Power Explorers

Solar Power Explorers
More Posts from Curiositytherover and Others

DJI’s drone safety system has you signing up to fly in some areas

Can You Tell if Your Therapist Has Empathy?
New software developed by researchers detects a person’s ability to understand or share feelings in therapy sessions.
The research is in PLOS ONE. (full open access)

One of the physicists who helped find the Higgs boson, Elina Berglund, has spent the past three years working on something completely different - a fertility app that tells women when they’re fertile or not.
It’s not the first fertility app out there, but Berglund’s app works so well that it’s been shown to help women avoid pregnancy with 99.5 percent reliability - an efficacy that puts it right up there with the pill and condoms.
Best of all, the app doesn’t have any side effects, and just requires women to input their temperature daily to map their fertility throughout the month.
Back in 2012, Berglund was working at CERN on the Large Hadron Collider experiment to find the famous Higgs boson. But after the discovery of the particle, she felt it was time to work on something completely different.
“I wanted to give my body a break from the pill,” she told Daniela Walker from Wired, “but I couldn’t find any good forms of natural birth control, so I wrote an algorithm for myself.”
The resulting app is called Natural Cycles, and so far, it’s had pretty promising results.
Continue Reading.
Gravity, who needs it
Houston TX (SPX) Nov 20, 2015 What happens to your body in space? NASA’s Human Research Program has been unfolding answers for over a decade. Space is a dangerous, unfriendly place. Isolated from family and friends, exposed to radiation that could increase your lifetime risk for cancer, a diet high in freeze-dried food, required daily exercise to keep your muscles and bones from deteriorating, a carefully scripted high-tempo Full article

Roller Coaster Physics.
The principle that underlies the working of a roller coaster is simple. As you ascent to the top, your potential energy builds up. ( i.e the higher you go, longer the distance that the force of gravity can act upon)
This built up Potential energy gets released as kinetic energy downhill. ( Kinetic energy is the energy of motion- linear and rotational).
Now what Roller Coaster Engineers do is abuse this principle to engineering perfection.

One thing we’re always doing as a species is expanding our knowledge of the heavens. We send out probes, robots, satellites, spacecraft, all to map out and add to our ever-expanding picture of what the Universe looks like.
But what if that picture suddenly became smaller? That is exactly what happened when new data from the Planck satellite tightened our previous notions of the observable universe, shrinking its area by 0.7%.
If you’ve never realized, we don’t actually see all of the stars in the Universe. If we did, night time sky would be a whole lot brighter. Instead, we see everything within a particular radius, the particle horizon. Any particle of light emitted outside that particle horizon is too far to have reached us.
So if we want to know just how large the observable universe is, we just have to figure out the distance between us and that particle horizon, right?
As it turns out, not quite.
The universe, specifically spacetime, is continuously expanding, with points in the universe moving further apart. This not only changes the distance between objects but also how fast light is moving in the universe.
The movement of spacetime has an effect on which photons reach us and can be observed.
So how do you calculate the radius? Back in 2003, scientists came up with an equation that took an event called “the recombination” as a reference point in the universe’s history. They combined that with the rate of the expansion of the universe and several other factors, in the end coming up with a number.
Back in 2003, that number was a radius of 45.66 billion light-years. Now, new data revealed a far more accurate number: 45.34 billion light-years.
“A difference of 320 million light-years might be peanuts on the cosmic scale, but it does make our knowable universe a little bit cozier,” Nick Tomasello from the University of the Sciences in Philadelphia writes over at Medium.
The study has been accepted for publication in an upcoming edition of Advances in Astrophysics.



The simple discovery that a piece of wire mesh can stop a flame in its tracks saved the lives of thousands of miners.
This demonstration shows how a simple lamp made of gauze could contain the open candle flames that miners used before 1815. With the safety lamp, any potential explosions would stay contained and never escalate to dangerous levels (although mining remained an extremely dangerous occupation).
Watch the whole demo and hear the full story here.
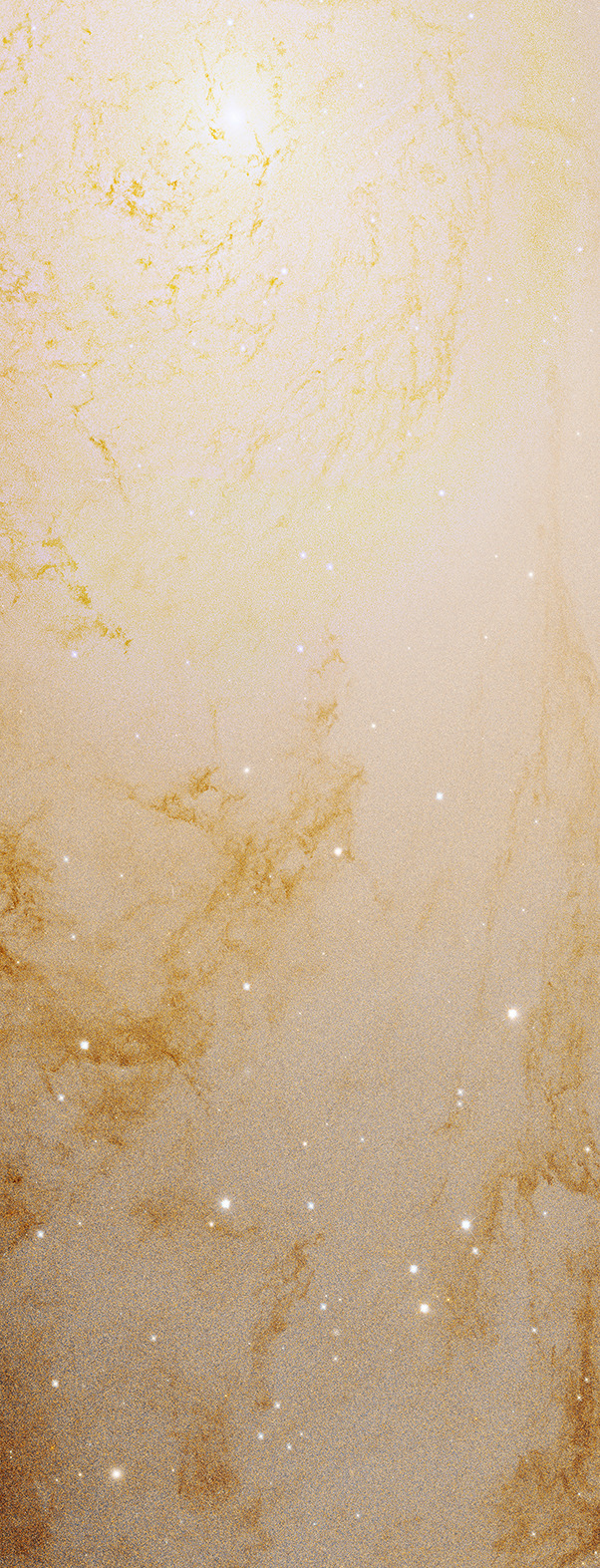
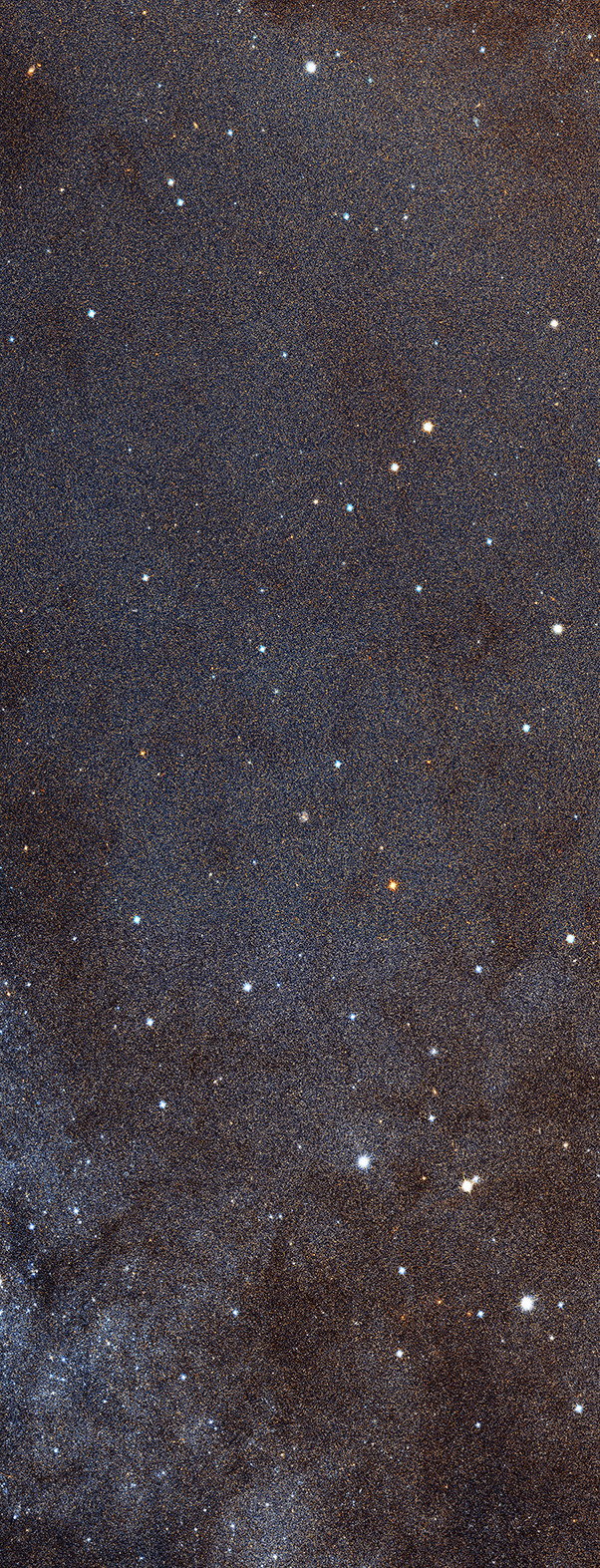




You just scrolled over a high-res segment of the Andromeda galaxy. How does NASA get its photos to look so spectacular? The same way as everyone else.

FAA: No, you won’t need to pay someone to register your drone
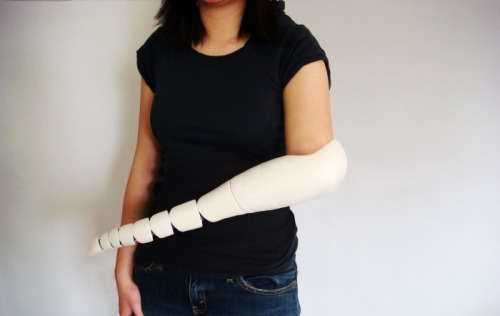


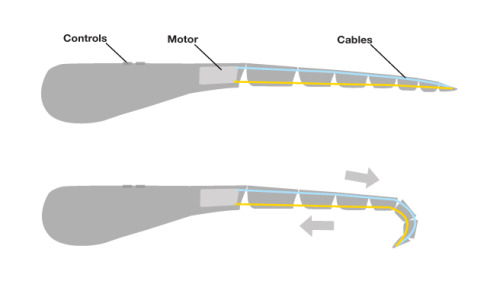
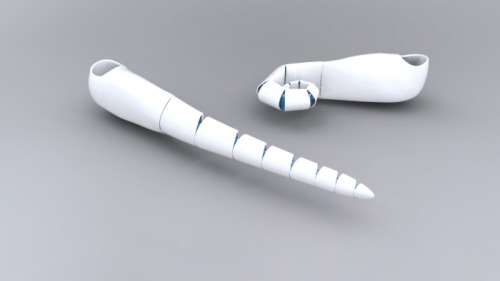
-
 1mores liked this · 8 years ago
1mores liked this · 8 years ago -
 tech-no-logic-bb reblogged this · 9 years ago
tech-no-logic-bb reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 lastleyuniverse reblogged this · 9 years ago
lastleyuniverse reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tampongrease reblogged this · 9 years ago
tampongrease reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tampongrease liked this · 9 years ago
tampongrease liked this · 9 years ago -
 infographic-maker-blog liked this · 9 years ago
infographic-maker-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 blue2224 reblogged this · 9 years ago
blue2224 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 blue2224 liked this · 9 years ago
blue2224 liked this · 9 years ago -
 oceanofemptiness reblogged this · 9 years ago
oceanofemptiness reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 sunsetorangeee liked this · 9 years ago
sunsetorangeee liked this · 9 years ago -
 queen-ayisha liked this · 9 years ago
queen-ayisha liked this · 9 years ago -
 go-john-blr liked this · 9 years ago
go-john-blr liked this · 9 years ago -
 lea-schenkova-blog liked this · 9 years ago
lea-schenkova-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 jamaicanjasta reblogged this · 9 years ago
jamaicanjasta reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 cosmicflowpoetry liked this · 9 years ago
cosmicflowpoetry liked this · 9 years ago -
 tryingtorunintraffic reblogged this · 9 years ago
tryingtorunintraffic reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 ana1266 liked this · 9 years ago
ana1266 liked this · 9 years ago -
 destopia liked this · 9 years ago
destopia liked this · 9 years ago -
 quietlonersoul reblogged this · 9 years ago
quietlonersoul reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 twytchy liked this · 9 years ago
twytchy liked this · 9 years ago -
 ttruxell liked this · 9 years ago
ttruxell liked this · 9 years ago -
 curiositytherover reblogged this · 9 years ago
curiositytherover reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 rationnels-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
rationnels-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 madangel1992 liked this · 9 years ago
madangel1992 liked this · 9 years ago -
 adelewolf-blog liked this · 9 years ago
adelewolf-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 starhasarrived reblogged this · 9 years ago
starhasarrived reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 starhasarrived liked this · 9 years ago
starhasarrived liked this · 9 years ago -
 lonesomewatcher-blog liked this · 9 years ago
lonesomewatcher-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 55132f liked this · 9 years ago
55132f liked this · 9 years ago -
 itisinmyremains liked this · 9 years ago
itisinmyremains liked this · 9 years ago -
 victor-manuel96 liked this · 9 years ago
victor-manuel96 liked this · 9 years ago -
 thoths-foundry-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
thoths-foundry-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 calibratedoddity liked this · 9 years ago
calibratedoddity liked this · 9 years ago -
 lovemetals liked this · 9 years ago
lovemetals liked this · 9 years ago -
 papabear33 reblogged this · 9 years ago
papabear33 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 area12 reblogged this · 9 years ago
area12 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 stuckinpermafrost reblogged this · 9 years ago
stuckinpermafrost reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 stuckinpermafrost liked this · 9 years ago
stuckinpermafrost liked this · 9 years ago -
 itsjeisahoe liked this · 9 years ago
itsjeisahoe liked this · 9 years ago -
 maraudingcaptain-archive reblogged this · 9 years ago
maraudingcaptain-archive reblogged this · 9 years ago