Hubble Sees A Star Called HBC 672 And The Bat Shadow : A Young Star’s Unseen, Planet-forming Disk Casts

Hubble Sees a Star Called HBC 672 and the Bat Shadow : A young star’s unseen, planet-forming disk casts a huge shadow across a more distant cloud in a star-forming region. (via NASA)
More Posts from Epic-flight and Others

Space Fragments - 230211

🌕 Lemat Moon 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13🌗 Twinkle Night27 3 17 / instagram / Adobe Behance🌑✨

‘jump’







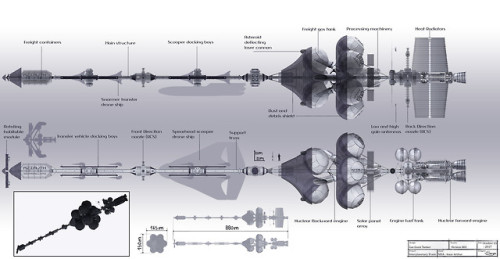
Wells-class interplanetary vehicle - Sergio Botero
“By the dawn of the XXII century, humanity’s thirst for Deuterium and Anti-Deuterium became so immense that companies began harvesting raw Hydrogen from the gas and ice giant planets. For that purpose, thousands of interplanetary spaceship tankers that work as refineries were built in order to transport the collected gas from the atmospheres of those planets to space stations over Earth, the Moon and other locations in the Solar System.“

Rick Sternbach’s 1976 cover for Under Pressure, by Frank Herbert

Richard Bizley

A selection orbs of the Solar System: Mercury, Venus, Earth (and Moon), Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. The spacecraft responsible for these images are as follows:
Mercury was photographed by Mariner 10.
Venus was imaged by the Magellan spacecraft’s radar.
Earth and its Moon were photographed by Galileo.
Mars Global Surveyor took the image of Mars.
Jupiter was photographed by Cassini as it traveled to Saturn.
Saturn, Uranus and Neptune images were taken by the twin Voyager spacecraft.
(NASA)

Another beautiful space painting from my friend Steve R Dodd. ‘The Beacon’. Originally displayed in NASA’s 25th anniversary art show, Cleveland Museum of Natural History (1980s)

SPARTH Collapsing Empire - Preliminary Sketch Digital

Wispy remains of a supernova explosion hide a possible ‘survivor.’ Of all the varieties of exploding stars, the ones called Type Ia are perhaps the most intriguing. Their predictable brightness lets astronomers measure the expansion of the universe, which led to the discovery of dark energy. Yet the cause of these supernovae remains a mystery. Do they happen when two white dwarf stars collide? Or does a single white dwarf gorge on gases stolen from a companion star until bursting? If the second theory is true, the normal star should survive. Astronomers used the Hubble Space Telescope to search the gauzy remains of a Type Ia supernova in a neighboring galaxy called the Large Magellanic Cloud. They found a sun-like star that showed signs of being associated with the supernova. Further investigations will be needed to learn if this star is truly the culprit behind a white dwarf’s fiery demise.
This supernova remnant is located 160,000 light-years from Earth. The actual supernova remnant is the irregular shaped dust cloud, at the upper center of the image. The gas in the lower half of the image and the dense concentration of stars in the lower left are the outskirts of a star cluster.
Image credit: NASA, ESA and H.-Y. Chu (Academia Sinica, Taipei)
-
 selfkaiharness liked this · 9 months ago
selfkaiharness liked this · 9 months ago -
 qualitymoonsuit reblogged this · 1 year ago
qualitymoonsuit reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 treasureplanetlove reblogged this · 1 year ago
treasureplanetlove reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 werewoofs liked this · 3 years ago
werewoofs liked this · 3 years ago -
 focusas reblogged this · 3 years ago
focusas reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 confusedwhiteperson liked this · 3 years ago
confusedwhiteperson liked this · 3 years ago -
 kibellah reblogged this · 3 years ago
kibellah reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 kibellah liked this · 3 years ago
kibellah liked this · 3 years ago -
 buttzklauser reblogged this · 3 years ago
buttzklauser reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ryssabrin reblogged this · 3 years ago
ryssabrin reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 isaactheastronaut reblogged this · 3 years ago
isaactheastronaut reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 s-t-y-x liked this · 3 years ago
s-t-y-x liked this · 3 years ago -
 antwone51 liked this · 3 years ago
antwone51 liked this · 3 years ago -
 oni-ino liked this · 3 years ago
oni-ino liked this · 3 years ago -
 celamity reblogged this · 3 years ago
celamity reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 celamity liked this · 3 years ago
celamity liked this · 3 years ago -
 wolfsong-the-bloody-beast reblogged this · 3 years ago
wolfsong-the-bloody-beast reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 theymightbebipeds liked this · 3 years ago
theymightbebipeds liked this · 3 years ago -
 katherinneheikolorenz liked this · 3 years ago
katherinneheikolorenz liked this · 3 years ago -
 pinkbabby liked this · 3 years ago
pinkbabby liked this · 3 years ago -
 unsigneddreams reblogged this · 3 years ago
unsigneddreams reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 unapparent-summer-air liked this · 3 years ago
unapparent-summer-air liked this · 3 years ago -
 xarnaskin reblogged this · 3 years ago
xarnaskin reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 daolemutt2 liked this · 4 years ago
daolemutt2 liked this · 4 years ago -
 alwaysacurious1 liked this · 4 years ago
alwaysacurious1 liked this · 4 years ago -
 spacefrog23 reblogged this · 4 years ago
spacefrog23 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 spacefrog23 liked this · 4 years ago
spacefrog23 liked this · 4 years ago -
 neuvirtualoasis reblogged this · 4 years ago
neuvirtualoasis reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 epic-flight reblogged this · 4 years ago
epic-flight reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 voronah liked this · 4 years ago
voronah liked this · 4 years ago -
 zephyrus77 reblogged this · 4 years ago
zephyrus77 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 myblueirony liked this · 4 years ago
myblueirony liked this · 4 years ago -
 kenvas liked this · 4 years ago
kenvas liked this · 4 years ago -
 bodhisattva-mosura liked this · 4 years ago
bodhisattva-mosura liked this · 4 years ago -
 quantum-light reblogged this · 4 years ago
quantum-light reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 doccywhomst liked this · 4 years ago
doccywhomst liked this · 4 years ago -
 medusagi liked this · 4 years ago
medusagi liked this · 4 years ago -
 miloutic reblogged this · 4 years ago
miloutic reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 wizardimpersonator reblogged this · 4 years ago
wizardimpersonator reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 rico-hyuuga reblogged this · 4 years ago
rico-hyuuga reblogged this · 4 years ago
