Codependence






Codependence
Natural selection breeds competition, but it can also lead to sophisticated cooperation. The Glass Colligatio is what is known as a composite organism—a creature comprised of members of multiple species that share critical biological processes between them. The larger swimmer provides mobility, while its multi-legged symbiont feeds more efficiently than it could alone. Through the interspecies junction—a specialized dual orifice connecting the creatures—they share nutrients and oxygen, each specializing in what it does best while providing for the needs of the whole.
More Posts from Exobiotica and Others






In the waters of a lowland swamp, a dramatic scene unfolds in miniature. The skeletal remains of a long-deceased creature have been colonized by a gelatinous, rather fluffy organism known as Rugosa. Covering any available real estate like a crumpled, spreading blanket, this filter feeder removes organic particulates from the surrounding water. Swamps with high levels of Rugosa growth maintain a more transparent water column, hosting more autotrophs and greater biodiversity. Firmly attached to this ensconced matrix is the decaying husk of a once mobile Flame Diversoma. Its last dying act was to serve as a shelter for its numerous offspring, which are now developed enough to disperse en masse. The coordinated timing of this exodus is critical, for a slow diffusion of these larvae would make them easy prey for the surrounding cadre of predators, who have gathered in anticipation of this event. The most successful hunter thus far is the Spotted Spearmouth, which relies on its harpoon-like proboscis to stab the passing swimmers and drag them into its maw. A vast swarm of semi-transparent Swamp Pearls paddles along slowly, unaware of the violence unfolding nearby. Having little in the way of visual sensors or situational awareness, their lives are consumed by chasing the flow of nutrients and favorable conditions in this tangled aquatic realm.






A Universe Below
Almost no sunlight penetrates the thick canopy of the glow forest. As a result, organisms in this ancient biome have evolved a massive array of survival strategies using bioluminescence. Some emit light to attract mates or warn against predators. And some, strangely, illuminate themselves in order to be eaten.
You are one of my biggest inspirations for creature design. Your aliens are beautiful and unique, and when I look at your art it feels like I’m actually there! Your art is beautiful
Thank you so much! I’m honored to be an inspiration for you.





Life in the Dark
In the murky blackness of the deep sea, creatures are spread out over immense distances. To find each other, many use biologically-generated light. But what appears to be a potential mate might instead be a lurking predator.

This is the native habitat of the megamyriapod (at center). This slow-moving, placid beast is about twenty feet tall and feeds primarily on the purple wave carpet organism that is spread across the floor of this scene- gathering it up with its anterior grasping appendages (at left). Other creatures lurk here, including the greenish motile floating feather duster gourds, the yellow/teal walking platter life-forms, and the purple pilantir balls. Growing around and above these smaller living things are the gargantuan lineated gold air-sponges - the megaflora that constitute the main physical features in this environment. All these creatures obtain energy from a combination of photosynthesis and physical consumption of soil nutrients or living tissue. Basically, the strict division of heterotroph/autotroph (plant/animal) that is exhibited by Earth-life simply does not apply here. Rather there is a gradient between those creatures who gain energy exclusively from light, and those who must consume others to survive. The majority of creatures here utilize both approaches.






Interwoven
Like a giant pink warship, the Rosy Frigate punctuates the endless sea of tendrils. It hosts a crew of disk-shaped ravenous eating-machines called orbics. It is the orbics’ duty to keep the creeping tendrils from strangling and overtaking their home. Fading daylight signals their departure from the safe cluster beneath their giant companion to begin the night’s work of clearing new growth in the near vicinity. Each orbic can consume half its body weight in tube-carpet flesh every night, ensuring they will always have a place to return to at dawn. A Dwarf Blue Cortina observes the melee in confusion. Anything larger than an orbic will send it leaping away for cover, as its curiosity is matched only by its caution. The stoic quartet of Reponos standing solemnly in the background is incapable of seeing or hearing the events taking place nearby. Their role in this ecosystem turns out to be rather bizarre…

A new environment with some new species here.
This is the first look into this particular biome- hopefully with more to come. All creatures depicted have a photosynthetic component to them - least of all the large plodding walkers, who rely most heavily on grazing for their energy intake. The creatures that resemble flowers are motile, but move less frequently. The long rope-like organism grows at a rapid pace to stake its claim over as much ground area as possible. The large round textures semi-spheres are not phased by this tactic, as they employ an electro-chemical defense over their outer surface to keep the strident ropes at bay.
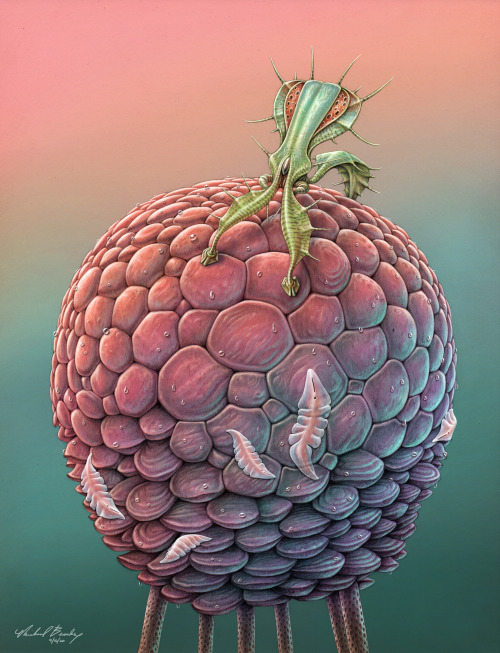

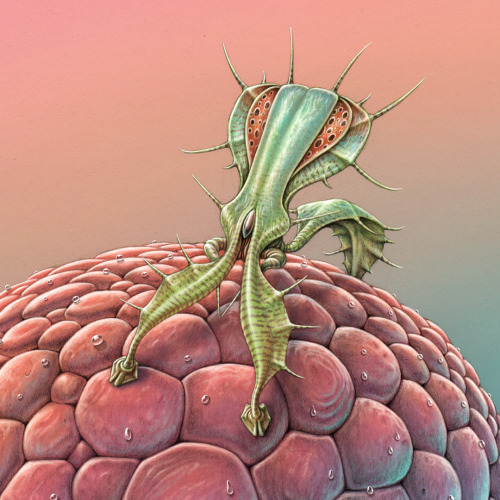
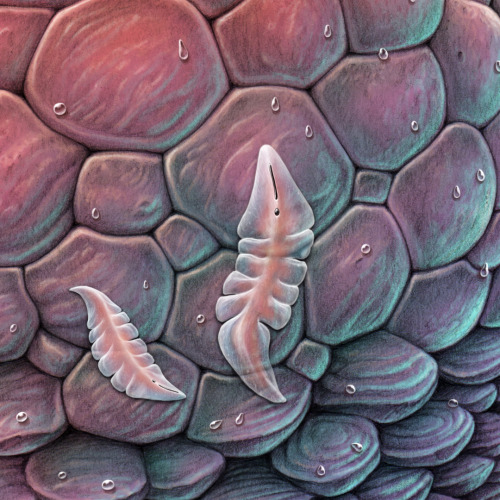
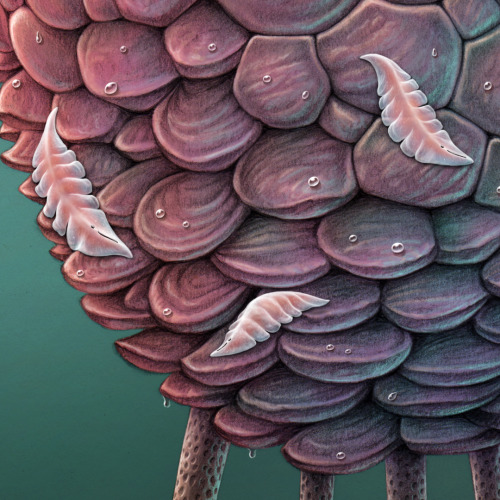
Guardian
On Veteris, it is common for creatures to obtain energy from multiple sources. The large round, multifaceted autotroph angles its plates to face the light at any given time of day. It also feeds on decomposing organic matter it obtains by moving slowly on its long spindly legs. Conversely, the spiny guardian on top originally evolved to hunt the semi-transparent flat creatures that feed on the autotroph, but came to rely on them exclusively. Over many generations, individuals that allowed some prey items to live and reproduce eventually outlasted the more aggressive hunters, and now their style of subsistence is closer to farming. The guardians now protect the entire micro-system – each large round walker and its flock of parasites is topped by a spiny guardian who has the dual task of defending against predators as well as keeping the herd numbers in check. A round walker without a guardian slowly succumbs to parasite overpopulation. Occasionally huge numbers of walkers congregate in vast gently-swaying miniature forests, each crowned by a flamboyant spiny guardian defending its small world.






Life on the Seafloor
Some habitats are very consistent from planet to planet across the universe. The bottoms of deep oceans generally experience similar conditions—extremely high water pressure, zero sunlight, and a constant rain of organic debris known as marine snow. Thus, organisms on the deep sea floor of Veteris developed common traits in parallel to their counterparts on Earth. The darkness eliminates the need for most pigments, so most creatures are rather drab. In order to grab bits of food from the water column, many utilize grasping appendages covered in sticky setae. For every scrap of nourishment that can be found here, there is a creature that has evolved to exploit it. Far from being a desolate wasteland, this seemingly inhospitable environment is full of bizarre, perfectly-adapted inhabitants.

Veteris-42820 C
Finally a planet to house (most of) the creatures I've designed so far. A terrestrial planet with about 2/3 the mass of Earth, it orbits its K-type star, Veteris, within the habitable zone. This system is around 8 billion years old - about twice that of ours, hence the name Veteris, which is Latin for "old". It sits at the outskirts of the nebula behind it, which will still be busy birthing star systems for billions of years to come. Veteris is a good analog for earth- it has a similar chemical composition (including its atmosphere, which is slightly more dense - at about 1.5 atm) so it's a good place to begin our journey.
-
 intoner8 liked this · 2 months ago
intoner8 liked this · 2 months ago -
 a-peculiar-potoo reblogged this · 4 months ago
a-peculiar-potoo reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 alienworlds reblogged this · 4 months ago
alienworlds reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 chaotic-taco14 liked this · 4 months ago
chaotic-taco14 liked this · 4 months ago -
 goldymove liked this · 6 months ago
goldymove liked this · 6 months ago -
 lemotjuste-tx reblogged this · 6 months ago
lemotjuste-tx reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 kaznata liked this · 7 months ago
kaznata liked this · 7 months ago -
 tv1977 liked this · 7 months ago
tv1977 liked this · 7 months ago -
 deadsearisen liked this · 7 months ago
deadsearisen liked this · 7 months ago -
 verins-little-notebook liked this · 8 months ago
verins-little-notebook liked this · 8 months ago -
 grokkensgrumblings liked this · 8 months ago
grokkensgrumblings liked this · 8 months ago -
 remyjf reblogged this · 8 months ago
remyjf reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 remyjf liked this · 8 months ago
remyjf liked this · 8 months ago -
 tundragravedigger reblogged this · 8 months ago
tundragravedigger reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 tundragravedigger liked this · 8 months ago
tundragravedigger liked this · 8 months ago -
 crimnsontroll liked this · 9 months ago
crimnsontroll liked this · 9 months ago -
 verdelacosaesa liked this · 10 months ago
verdelacosaesa liked this · 10 months ago -
 cunnnilinguist liked this · 10 months ago
cunnnilinguist liked this · 10 months ago -
 ara6gir liked this · 10 months ago
ara6gir liked this · 10 months ago -
 garbagewriter liked this · 10 months ago
garbagewriter liked this · 10 months ago -
 lamehandle liked this · 10 months ago
lamehandle liked this · 10 months ago -
 14-lizards-in-a-trenchcoat liked this · 10 months ago
14-lizards-in-a-trenchcoat liked this · 10 months ago -
 lowcountry-gothic liked this · 11 months ago
lowcountry-gothic liked this · 11 months ago -
 jayjayzzzzzz liked this · 1 year ago
jayjayzzzzzz liked this · 1 year ago -
 dipthong-dumping-ground reblogged this · 1 year ago
dipthong-dumping-ground reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 haru-dipthong liked this · 1 year ago
haru-dipthong liked this · 1 year ago -
 surrendertomywill reblogged this · 1 year ago
surrendertomywill reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 pinelimehypergiant reblogged this · 1 year ago
pinelimehypergiant reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 erinmccomics liked this · 1 year ago
erinmccomics liked this · 1 year ago -
 kingofthecobras liked this · 1 year ago
kingofthecobras liked this · 1 year ago -
 idontwannaliveinasociety liked this · 1 year ago
idontwannaliveinasociety liked this · 1 year ago -
 neddalian liked this · 1 year ago
neddalian liked this · 1 year ago -
 crepuscular-girlthing liked this · 1 year ago
crepuscular-girlthing liked this · 1 year ago -
 moths-in-a-sweater liked this · 1 year ago
moths-in-a-sweater liked this · 1 year ago -
 batterymaster01 liked this · 1 year ago
batterymaster01 liked this · 1 year ago -
 astravis liked this · 1 year ago
astravis liked this · 1 year ago -
 equibo liked this · 1 year ago
equibo liked this · 1 year ago -
 foxmaskwoman reblogged this · 1 year ago
foxmaskwoman reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 paradichlorosocksy liked this · 1 year ago
paradichlorosocksy liked this · 1 year ago -
 justgoji reblogged this · 1 year ago
justgoji reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 justgoji liked this · 1 year ago
justgoji liked this · 1 year ago -
 seven-eyes-048 liked this · 1 year ago
seven-eyes-048 liked this · 1 year ago -
 sanemeks liked this · 1 year ago
sanemeks liked this · 1 year ago -
 calzoneifornia liked this · 1 year ago
calzoneifornia liked this · 1 year ago -
 troythecatfish liked this · 1 year ago
troythecatfish liked this · 1 year ago