Latest Posts by exobiotica - Page 2
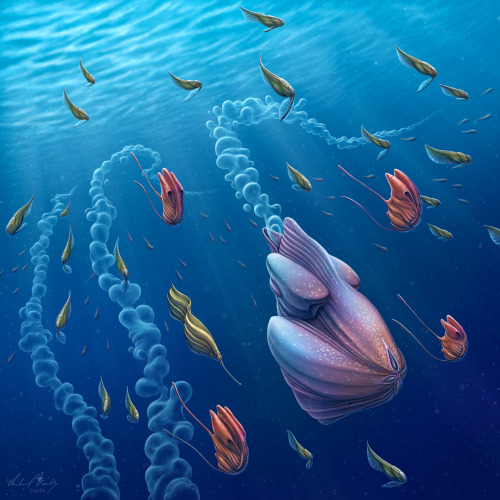
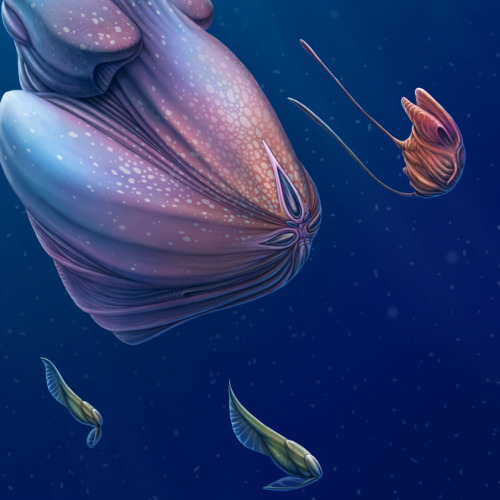
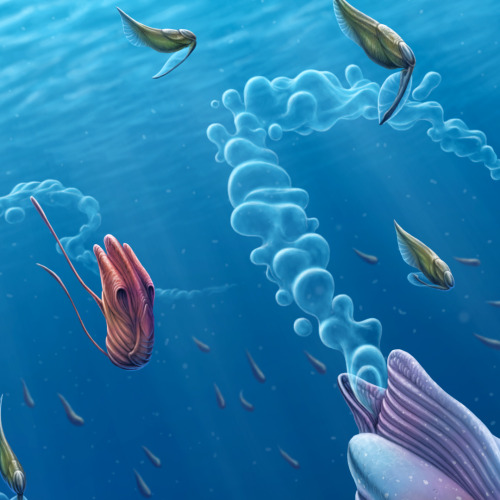
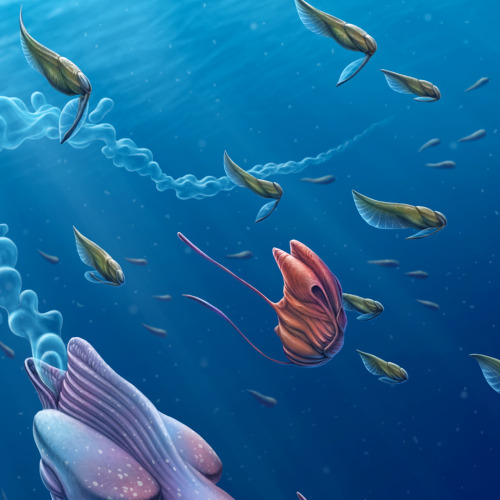




Back to the Depths
An entourage of opportunistic creatures accompanies the deep-sea behemoths during their brief ascent to the surface. Releasing their gelatinous strings of embryos here in the sunlight has a significant benefit - there's far more visibility. The swarm of followers are here in search of a quick meal in the form of the gelatin, which is full of valuable protiens and nutrients. After the feast however, the recipients of this apparent windfall become unwitting hosts for the behemoth's multitudinous offspring, which were embedded in the gel. Adapted to develop inside a wide variety of pelagic creatures, the young grow internally - and sometimes even on the surface of - their hosts until such time as they detach and sink back into the darkness. For most host species, this seems to be a mutually-beneficial symbiosis. At the beginning they receive a large and valuable meal, and usually incur very little detriment due to their temporary parasites. The young behemoths will hide in the dark depths for many years until attaining the size necessary to return to the light and repeat the ancient cycle again.

Passengers
The Purple Slow Walker is primarily photosynthetic, but occasionally it must travel to acquire additional resources. It retracts its mobile roots, extends its tube legs, and begins the tedious journey to better feeding grounds. Groups of slow walkers congregate around a large carcass, exogenously digesting the flesh and absorbing the coctail through their extended roots. This is the opportunity the passengers have been waiting for. Not only do they rely on the walker for shelter and free transport, but also as a source of pre-digested nutrients they can pilfer from their host's method of carrion consumption. Whether the passengers provide the walker anything in return for its efforts is unclear.

Veteris-42820 C
Finally a planet to house (most of) the creatures I've designed so far. A terrestrial planet with about 2/3 the mass of Earth, it orbits its K-type star, Veteris, within the habitable zone. This system is around 8 billion years old - about twice that of ours, hence the name Veteris, which is Latin for "old". It sits at the outskirts of the nebula behind it, which will still be busy birthing star systems for billions of years to come. Veteris is a good analog for earth- it has a similar chemical composition (including its atmosphere, which is slightly more dense - at about 1.5 atm) so it's a good place to begin our journey.






Monolith
The seasonal rains have come to the high desert. Among the first to respond is the monolith. It sends out hose-like tendrils to siphon water and turns on its biolights to attract flying symbionts.



Tripodal Plains Runner
An agile and fast herd-dwelling inhabitor of the open plains, this creature posesses no true jointed appendages. Its legs and periscope are comprised of rigid, yet flexible hydraulic tubes. Sensory organs are clustered on the top of its upward-pointing appendage to give maximum perspective even during more vulnerable moments like feeding.





Sunworshipper
By our terrestrial standards, the coloration on this creature may seem vivacious or even gaudy, but in its native habitat it actually serves as cryptic camouflage. Its planet orbits a star with different color output than our own, and photosynthetic systems have adapted to reflect a different color than our earthly green plants. The sunworshipper, like many other mobile creatures here, receives a portion of its energy from photosynthesis - as evidenced by the specially-adapted appendages radiating from its body.
Absolutely incredible work! Do you post anywhere else?
Thank you! Yes I’m on Instagram @exobiotica





The Challenger
A new competitor has entered the misty valley. Attracted by ample food supply, the hopeful newcomer will have to contend with the reigning resident of this territory. In times of scarcity, populations begrudgingly coexist in shrinking pockets of such favorable habitat, but rain and sun have been plentiful lately, so a battle seems imminent.



A few marker sketches from last year's Inktober
I haven't posted in a while, so I'll be adding some of the work I've been doing for the last couple years.

Egg Chamber
In some environments, it's hard to tell the difference between genders and species. Organisms share genetic material more easily on this planet, and that leads to some complicated taxonomy. In this case, we see a group of aquatic creatures acting as nurses for a seemingly endless field of eggs. But the network of underwater chambers in which they reside is in fact another living creature. By some categorizations, it would be considered the female of the species - it produces and to some extent nourishes the field of eggs, some of which mature to be gigantic network-chambers themselves. Whether this is an extreme example of sexual dimorphism, or the result of some sort of horizontal gene transfer is a matter of conjecture at this point.



Curiosity
A massive predator on the ocean floor lures in its next naive dinner guest. The smaller creatures that surround it have been waiting for this moment.

New Lands

A new environment with some new species here.
This is the first look into this particular biome- hopefully with more to come. All creatures depicted have a photosynthetic component to them - least of all the large plodding walkers, who rely most heavily on grazing for their energy intake. The creatures that resemble flowers are motile, but move less frequently. The long rope-like organism grows at a rapid pace to stake its claim over as much ground area as possible. The large round textures semi-spheres are not phased by this tactic, as they employ an electro-chemical defense over their outer surface to keep the strident ropes at bay.

Quick personal promo!
When not drawing aliens, I'm a web/graphic designer. Here's my new portfolio site: michaelpbeaudry.com . Check it out if you are interested in other creative stuff I do.
I'm also on Instagram, DeviantArt, and Behance.
Ok, sorry- back to alien stuff now!

Part of a color study for the next painting I plan to start this week.

Quick sketch I hope to make into a full painting later.

I've decided to start posting sketches more often, as they comprise over 90% of my artistic time. This is the Greater Parvasalia. It travels in large groups, is about the size of a hamster, and is generally non-aggressive. More details as they are developed.



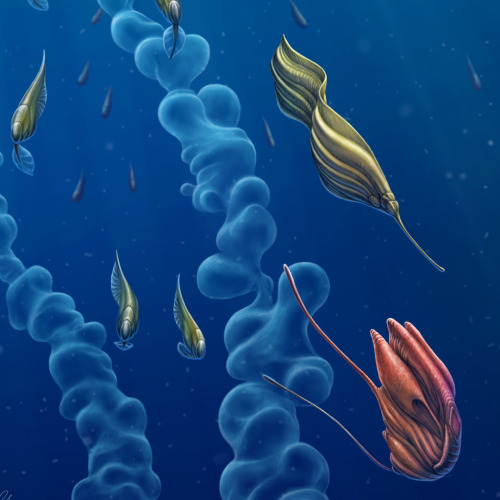
Placid Segmaris
Caelumbestiae placidus
The Placid Segmaris is the sole food source of the Sky Shepherd. They are essentially floating livestock that are nurtured, herded, and protected until such time as the shepherds need to consume them. The tri-part symbiosis between the Sky Shepherds, the Segmaris, and their large floating counterpart (partially visible as the reddish-brown creature on the right side of the image) is rather complicated, and will be the subject of further works. Helpless on their own, the Segmaris relies on its symbionts for neary everything- protection, reproduction, much of their locomotion, and Hydrogen. The only thing it is capable of accomplishing by itself is the acquisition of food- which is does by filtering particles and small microfauna from the dense atmosphere where it lives. Adults are around 50 feet long at maximum, young start out around a foot long.

High Above Saturn This portrait looking down on Saturn and its rings was created from images obtained by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft on Oct. 10, 2013. It was made by amateur image processor and Cassini fan Gordan Ugarkovic. This image has not been geometrically corrected for shifts in the spacecraft perspective and still has some camera artifacts.The mosaic was created from 12 image footprints with red, blue and green filters from Cassini’s imaging science subsystem. Ugarkovic used full color sets for 11 of the footprints and red and blue images for one footprint.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute/G. Ugarkovic

Sky Shepherds
Caelumopilio pictoratus
This work serves as the official kickoff for my illustration project called "Exobiotica". The creature pictured is a Sky Shepherd. As its name implies, it carries on an aerial existence - maintaining neutral buoyancy via internal hydrogen compartments. The front appendages serve two functions- they are used to physically herd or corral the species of floating creature they subsist on, and also they are equipped with color-changing tissue that is used as communication between members of their group. Like them, most of their predators and prey are essentially floating gas bags which are highly susceptible to rupture. Thus, the Sky Shepherd evolved sharp appendages for use in attack and defense. Propulsion in any direction is achieved by the intake of air at the ventral posterior end, and then subsequent directional exhalation of the air through any of the four siphons. The next work will I produce will feature these creatures and their prey in their aerial environment.





Cloud Grazers
Nubes comedenti
A family of Cloud Grazers seeks shelter from strong winds on the leeward side of a sheer rock face several hundred feet above the ground. Thanks to a lightweight body structure and internal hydrogen gas sacs, they are completely neutrally buoyant. Propelled by air jets on their sides, they are most at home at high altitude amongst the cliffs and mountain tops where they can hide from harsh weather and fierce predators. Most of their nutriment is obtained by way of their anterior filtration organs, which they extend while flying to sweep the sky of aerial biota - a sort of sky plankton.

This is the native habitat of the megamyriapod (at center). This slow-moving, placid beast is about twenty feet tall and feeds primarily on the purple wave carpet organism that is spread across the floor of this scene- gathering it up with its anterior grasping appendages (at left). Other creatures lurk here, including the greenish motile floating feather duster gourds, the yellow/teal walking platter life-forms, and the purple pilantir balls. Growing around and above these smaller living things are the gargantuan lineated gold air-sponges - the megaflora that constitute the main physical features in this environment. All these creatures obtain energy from a combination of photosynthesis and physical consumption of soil nutrients or living tissue. Basically, the strict division of heterotroph/autotroph (plant/animal) that is exhibited by Earth-life simply does not apply here. Rather there is a gradient between those creatures who gain energy exclusively from light, and those who must consume others to survive. The majority of creatures here utilize both approaches.

This was a colored-pencil rendering of the creatures involved in the ecosystem portrayed in the "Aglow" piece. The pancake creatures on the floor are mobile decomposers. The floating lanterns are semi-autotrophic creatures that travel in groups. They travel by spouting air directionally through their vents which are visible along the middle of their bodies.




Here is a nocturnal view of a habitat in which the inhabitants have evolved extreme forms of bioluminescence. The vertical glowing blobs are the reproductive bulb form of a species with a complex life cycle (to be elucidated in following artworks). The groove-backed, ravenous creatures at the bottom are of the same species as the glowing blobs, but at a different life stage. At center is a rather placid, slow-moving consumer of the bulbs- one who has incorporated its own form of bioluminescence into its respiratory apparatus as a means of camouflage. Names and descriptions will come as soon as possible.

Luminous Oppugno
Submarinus luminare
Named for the Latin word for 'attack', the Luminous Oppugno is a crafty aquatic predator. Primarily nocturnal, it uses its bioluminescent-tipped rods to attract prey. Once within range, the main grasping appendage shoots out and arrests the unsuspecting victim with vigorous tenacity. Being fully aquatic (dwelling rather deeply at that) as well as nocturnal, the oppugno rarely comes into contact with sunlight, and thus has lost the capability of its ancestors to harness energy from photons. Thus, the creature must rely exclusively on its skill as a predator to meet its energy requirements. An adult oppugno usually tops out at around 5 feet long.

Grandulus
Trifasciatus grandulus
I should preface the description of this creature by giving a short statement about the natural history of its home planet. Early in its evolutionary history, life on this world did not split into such rigidly defined taxa as it did on Earth. For example, the majority of multicellular earth-life is divided into autotrophic creatures (plants) which are immobile, and the highly mobile heterotrophs (animals). On grandulus’s planet, the peculiar biochemistry allows for a much higher rate of horizontal gene transfer and endocytosis. This means that instead of a taxonomic “tree of life” like on Earth, their evolutionary history looks more like a web. In short, this allows for a wide array of photosynthetic, yet mobile creatures. The grandulus is one of these. It moves around slowly with its sticky appendages and positions itself in a spot with maximum sunlight to unfold its inflatable photosynthetic organ from its posterior shell. It also feeds on the internal fluids of metaflora, as well as decaying organic matter. Its many species range in size from that of a quarter to the size of a hippo.

This is an aerial ecosystem inhabited by floating creatures that utilize gas sacs within their bodies to stay aloft.




