Goblin-in-the-rain - Meta

More Posts from Goblin-in-the-rain and Others




a couple extremely handsome carpet beeltes, Anthrenus lepidus and Anthrenus scrophulariae
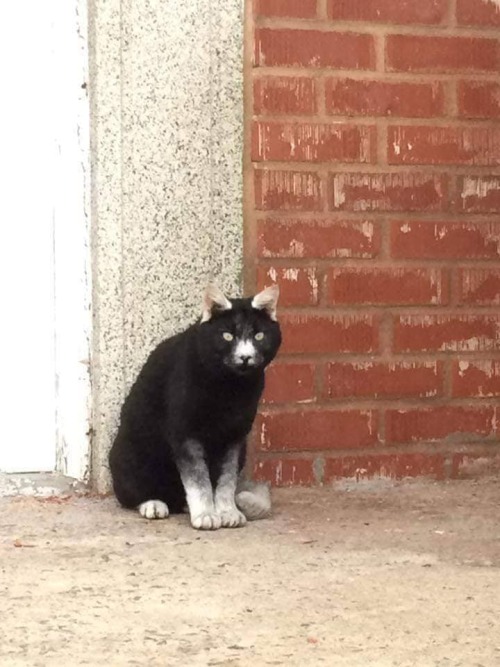




Unusual cat gene that seems to occur naturally in Poland and Romania. This gene is called Karpati. More can be read here
Me: oh yeah, if you think school photography is hard now, try imagining doing this with film.
The new girl: what’s film?
Me: … film. Like… film that goes in a film camera.
New girl: what’s that mean?
Me: … before cameras were digital.
New girl: how did you do it before digital?
Me:… with film? I haven’t had enough coffee for this conversation



㋡🥀
dried flowers..





I'm currently doing an online art school program and I thought I'd share some notes on clothing pieces for anyone else whose like me and for some reason can't understand objects with free from lol I hope you find some of these observations/ notes useful for any of your art journeys!
I'd love to hear more about what makes the wings of the stylops so unique! Wings are always fascinating to me
Almost all insects with wings normally have four of them, except that in beetles, the front wings became the shields we call Elytra:

And in the true flies (diptera), the HIND wings became little vibrating knobs we call halteres, which are organic gyroscopes for collecting information about air pressure, direction and elevation, easiest to see on larger flies like this crane fly:

So, the male Strepsiptera is actually the only insect other than flies to have evolved halteres, but the Strepsiptera's halteres are evolved from the FRONT wings:

Their hind wings are odd enough too; simple "fans" unlike the intricately veined wings of other insects, but still not as unusual as forewing halteres. It's thought to be convergent evolution, and that they may have once been elytra like the beetles have. A connection to beetles is also suggested by the fact that a few beetle groups have larvae very similar to those of the strepsipterans, which look like this:

Lovably nasty larvae! They jump, and they're all spiny, and they actually use an acid secretion to melt their way into their first host.
There's one other insect group that incidentally evolved elytra shields, earwigs!
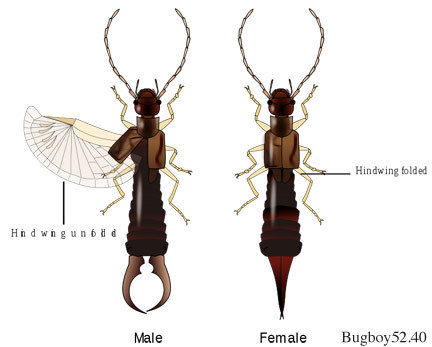
But earwigs can't be ancestral to either beetles or strepsiptera, because earwigs don't go through a larval stage, which the big evolutionary divide for insects; all the insects with larvae are thought to have just one common ancestor, splitting off from the other insects fairly early.



I've found this nifty reference website for artists called www.dimensions.com that has a database of exact measurements for various objects, plants, and animals
They have a premium version with 3D models that I haven't tried yet, but it's definitely very informative if you're trying to get the anatomy and proportions for different species of animals right!

Claude Rains ~ 1930 Broadway Portrait ~
The Common Green Lacewing: these tiny insects pupate within loosely-woven cocoons that measure just 3-6mm (about 1/8 to 1/4 inch) in diameter

The lacewing will spend about 5 days maturing within its cacoon, before it cuts an opening in the top and emerges as a fully-developed adult.

The larvae of the green lacewing (family Chrysopidae) are also known as "aphid lions," due to their skill/appetite when it comes to hunting aphids. They're widely used in agricultural contexts to help eradicate pests, because they are voracious predators that also commonly prey upon caterpillars, leafhoppers, planthoppers, thrips, spiders, mites, and insect eggs.
As it nears the end of its larval stage, a lacewing will spin a small cacoon out of silk and then tuck itself inside, allowing the pupal phase to begin; its tiny green body is often partially visible through the thin, loosely-woven walls of the cacoon.
These breathtaking photos of a lacewing climbing out of its cacoon were taken by a Danish photographer named Frederik Leck Fischer.

When a lacewing first emerges from a cacoon, its wings are still compactly folded down against its body; the wings then gradually begin to expand until they have reached their full size, which usually takes about an hour or two.

Fischer's photographs provide an excellent account of this entire process.

Here are just a few other images of the common green lacewing:

Sources & More Info
University of California's Integrated Pest Management Program: The Green Lacewing
Texas A&M's Field Guide to the Insects of Texas: Green Lacewings
Washington State University: Lacewings
Tennessee State University: Fact Sheet on the Green Lacewing (PDF download)
Pacific Pests & Pathogens: Green Lacewings/Biocontrol
-
 712220 reblogged this · 2 months ago
712220 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 koalatattoo liked this · 2 months ago
koalatattoo liked this · 2 months ago -
 sadlilpanda liked this · 2 months ago
sadlilpanda liked this · 2 months ago -
 raindancejodi reblogged this · 2 months ago
raindancejodi reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 raindancejodi liked this · 2 months ago
raindancejodi liked this · 2 months ago -
 donttouchthestache reblogged this · 2 months ago
donttouchthestache reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 donttouchthestache liked this · 2 months ago
donttouchthestache liked this · 2 months ago -
 bong-bones reblogged this · 2 months ago
bong-bones reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 burkezurk reblogged this · 3 months ago
burkezurk reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 burkezurk liked this · 3 months ago
burkezurk liked this · 3 months ago -
 adorable-animals-daily reblogged this · 3 months ago
adorable-animals-daily reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 neferlene liked this · 3 months ago
neferlene liked this · 3 months ago -
 ravensbyte reblogged this · 3 months ago
ravensbyte reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 justanotherlilly reblogged this · 3 months ago
justanotherlilly reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 consultingdalekhunter reblogged this · 3 months ago
consultingdalekhunter reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 crowharpy liked this · 3 months ago
crowharpy liked this · 3 months ago -
 no-longer-mine reblogged this · 3 months ago
no-longer-mine reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 hotsoup1969 liked this · 3 months ago
hotsoup1969 liked this · 3 months ago -
 sorryaboutthelean liked this · 3 months ago
sorryaboutthelean liked this · 3 months ago -
 typeonetrend liked this · 3 months ago
typeonetrend liked this · 3 months ago -
 churchyardgrim reblogged this · 3 months ago
churchyardgrim reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 xhazzz liked this · 3 months ago
xhazzz liked this · 3 months ago -
 heir-of-the-founders liked this · 3 months ago
heir-of-the-founders liked this · 3 months ago -
 tintheelvenking reblogged this · 3 months ago
tintheelvenking reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 fellwar-finch reblogged this · 3 months ago
fellwar-finch reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 fellwar-finch liked this · 3 months ago
fellwar-finch liked this · 3 months ago -
 auri-holmes reblogged this · 3 months ago
auri-holmes reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 mossandb0nes liked this · 3 months ago
mossandb0nes liked this · 3 months ago -
 thanager liked this · 3 months ago
thanager liked this · 3 months ago -
 wiifit reblogged this · 3 months ago
wiifit reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 sirenangle liked this · 3 months ago
sirenangle liked this · 3 months ago -
 silkmori reblogged this · 3 months ago
silkmori reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 silkmori liked this · 3 months ago
silkmori liked this · 3 months ago -
 lislis80 liked this · 3 months ago
lislis80 liked this · 3 months ago -
 fnvbennygecko liked this · 3 months ago
fnvbennygecko liked this · 3 months ago -
 faernwei reblogged this · 3 months ago
faernwei reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 bugmage reblogged this · 3 months ago
bugmage reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 haunteddollsgeorg reblogged this · 4 months ago
haunteddollsgeorg reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 aro-ace-attorney reblogged this · 4 months ago
aro-ace-attorney reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 aro-ace-attorney liked this · 4 months ago
aro-ace-attorney liked this · 4 months ago -
 anticupid16 reblogged this · 4 months ago
anticupid16 reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 hammalo liked this · 4 months ago
hammalo liked this · 4 months ago -
 raccoonlover64 liked this · 4 months ago
raccoonlover64 liked this · 4 months ago -
 prognostic-santhanas reblogged this · 4 months ago
prognostic-santhanas reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 prognostic-santhanas liked this · 4 months ago
prognostic-santhanas liked this · 4 months ago -
 artsy-n-smartsy liked this · 4 months ago
artsy-n-smartsy liked this · 4 months ago -
 starlos-soulmate liked this · 4 months ago
starlos-soulmate liked this · 4 months ago -
 cervinae-canine reblogged this · 4 months ago
cervinae-canine reblogged this · 4 months ago

Hi it’s me puddleorganism if you’re confused why you got a billion hoops from me
298 posts