Emerald Moths To Improve Your Day - 3: Common Emerald

Emerald moths to improve your day - 3: common emerald
Called common, but for me at least it's an infrequent visitor. Its caterpillars eat a similar range of shrubby plants and trees to the light emerald. They're also very good twig mimics and you can see in these photos by Kjeld Brem (find the originals here and here on Flickr)

Look at it's adorable little mush!

Such a good moth. I hope I get some more visit this year.

More Posts from Goblin-in-the-rain and Others
“This is your daily, friendly reminder to use commas instead of periods during the dialogue of your story,” she said with a smile.

Range: Costa Rica, Panama, & Colombia.

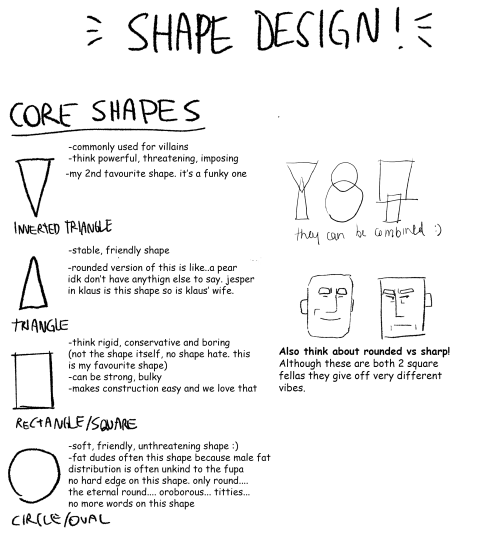
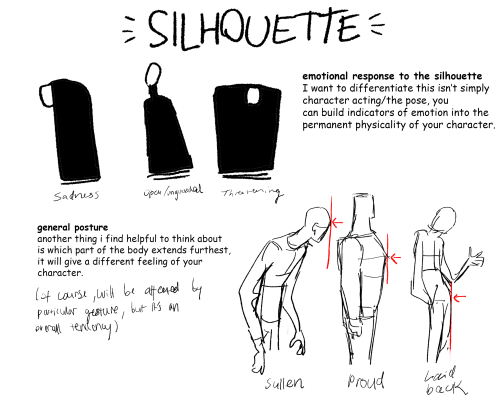
Part 2 of cino art tips is some basic tips on shape and silhouette design which are also principles I think about a lot :)
(also i'm so sorry i chose comic sans to write this in idk what i was thinking but i already flattened the layers)
i don't have any other obvious tips off the top of my head rn but feel free to ask anything you are curious about! i love getting asks uwu




Valentino at Paris Fashion Week Fall 2005

So cute
Made by https://paperbeatsscissors.tumblr.com/
not exactly using the ask box correctly here but shshshshshsh just wanted to share with the class incase anyone was curious! cats actually can have "skunk stripe" patterns like cashew

images from http://messybeast.com/bicolours.htm it's not the prettiest site but it's got alot of info + images of cats with really funky patterns! great design inspo don't mind me, i just think these kitties look cool
Aww pretty cats! It's nice to know that my ridiculous sparklecat designs have some kind of basis in reality.
Writing Deaf Characters
I am making this a series now so pls drop requests if there is something you’re curious about!
Disclaimer: This is all based on personal experience and research, all of which relate to the American Deaf experience. It’s not perfect, nor is it representative of a global experience of d/Deafness. If you plan to write a d/Deaf or hard of hearing character, please do your own research! This is intended to give people a few ideas about where to start.
Vocab
Deaf = Refers to the cultural experience of being deaf and immersed in Deaf communities.
deaf = Inability to hear some or all sound.
Profoundly deaf = Inability to hear almost all or all sound.
d/Deafblind = Inability to hear some or all sound and as well as having some level (usually high) of visual impairment.
Hard of hearing or HOH = A person whose inability to hear may not rise to the level of deafness or profound deafness, or simply may not identify with the term.
Deaf of deaf = A Deaf child born to Deaf parents.
CODA = Child Of Deaf Adults. This refers to hearing children, not d/Deaf children.
Manualism = Refers to the belief that d/Deaf children should be taught only sign language and should not be taught or expected to learn to speak.
Oralism = Refers to the belief that d/Deaf children should be taught only to speak and should be discouraged from learning or using sign language.
Bilingual-bicultural or bi-bi education = A school of thought that combines oral and manual education for d/Deaf children.
Mainstreaming = The belief that d/Deaf children should be educated in the same schools and classrooms as hearing students. (More widely refers to the belief that disabled students in general should be educated in the same schools and classrooms as nondisabled students.)
Deaf gain = The Deaf community’s answer to the term “hearing loss.” Rather than losing hearing, a person is said to be gaining Deafness.
Cochlear implant/CI = A medical device implanted into the inner ear which (debatably) produces sensation that is (somewhat) analogous to hearing.
American Sign Language or ASL = An American system of communication consisting of hand shapes, hand movements, body language, facial expressions, and occasionally, vocalizations.
Signed Exact English or SEE = A manner of communicating that directly translates English words into signed equivalents.
Home sign(s) = Signed communication that is specific to the signer’s home or community, which may not exist or be recognized in the wider world.
Identity First Language or IFL = A system in which someone is described first by an identifier that they choose and feel strongly connected to. Examples include describing someone as an Autistic woman, a disabled individual, or a Deaf man.
Key Elements of Deaf History
Can’t emphasize this enough - this is a VERY abbreviated list! It is also not in order. Sorry. That being said:
For a long time in America, Deaf children were not educated, nor was it considered possible to educate them. When this did change, American deaf children were educated in institutions, where they lived full-time. These children were often taken from their families young, and some never regained contact with their families. Some died and were buried at these institutions, all without their families’ knowledge.
In the early 20th century, oralism became popular among American deaf schools. This mode of teaching required lip reading and speech, no matter how difficult this was for students, and punished those who used or attempted to use sign language. Pure oralism is now widely considered inappropriate, outdated, and offensive.
Hopefully you’ve gleaned this from the above points, but d/Deaf schooling, education, and the hearing world’s involvement are a very sensitive subject. Proceed with caution. It’s unlikely your d/Deaf character would have a neutral relationship with schooling.
Helen Keller is probably the most famous deafblind person in America. In her time, she was also known for being a socio-political activist, a socialist, and a vaudeville actress. There are dozens of other famous d/Deaf people who are a quick Google search away. Give your Deaf character Deaf heroes, please.
The Americans with Disabilities Act, or ADA, was passed in 1991, and represented a landmark victory for disabled activists in America. Among its provisions were closed captioning for Deaf individuals, ASL interpreters for public services, and the right for d/Deaf children to attend accessible, accommodating public schools. The ADA is a HUGE deal. It’s also not perfect.
In 1961, cochlear implants were invented. I was going to write more about cochlear implants here, but it’s too long. New section.
Cochlear Implants
Massively massively massively controversial in the Deaf community. Always have been, potentially always will be. For people who strongly identify with Deafness and the Deaf community, CIs are an attack on their identity, their personhood, and their community’s right to exist.
Do not allow people to “hear.” The input that a person receives from CI can, with physical therapy, training, and time, be understood and processed in a similar way to sound. This does not mean it would be recognizable to a hearing person as sound. It is often described by people who have them as being metallic, buzzy, or robotic. YouTube is a great resource for sound references.
In order for a cochlear implant to be effective, a personal will have to participate in years of training and therapy to correct process, understand, and interpret the feedback given by the CI. This is not negotiable. Even if your character just lost their hearing in an accident last week, a CI will not allow them to instantaneously regain that hearing. Nothing that currently exists in the real world will do that.
CIs, to be most effective, are almost always implanted when the recipient is very young. This decision is often made by hearing parents. This, again, is massively controversial, as Deaf activists argue that it violates the child’s bodily autonomy and is inherently anti-Deaf.
A cochlear implant, once placed, irreparably destroys any residual hearing that the recipient may have had. This is because it penetrates the inner ear in order to function. This residual hearing cannot be regained, even if the cochlear implant is not used.
Deaf people do choose to get cochlear implants of their own accord. Many d/Deaf people are very happy with their cochlear implants! It is still a highly charged choice in light of the political history surrounding d/Deafness and hearing.
Notes About American Sign Language
ASL is not a signed version of English. It is a distinct language, with its own vocabulary, slang, and grammar. Just a sentence would not be constructed the same way in Russian, Spanish, or Tagalog, a sentence in ASL would not be a direct translation of its English equivalent.
Deaf people have historically lower rates of literacy. This is not due to a lack of intelligence; it is because ASL and English are two different languages. ASL has no written equivalent. In order to be able to read or write, d/Deaf children must learn an entirely different language. This means that it is not realistic to always be able to communicate with d/Deaf people through writing.
As ASL is a visual language, many signs started out as very literal gestures. This means that many older signs are continuously being phased out as they or their roots are recognized as stereotypical or offensive. Please be careful in researching signs. I recommend Handspeak or Signing Savvy for accurate, relatively up-to-date information.
Many online “teachers” do not have credentials to teach ASL, and especially due to the prevalence of “baby sign,” home signs, invented signs, or false information spreads unchecked. If you see multiple different signs advertised for the same English word, please be diligent in checking your sources.
Not every English word has a distinct signed equivalent, and not every sign has an English equivalent.
SEE is almost never used by Deaf people. It’s rarely used and is generally thought of as a “lesser” version of both English and ASL.
ASL is a complete, complex, nuanced language. A character would not switch into SEE for a technical conversation or really any reason. Complex ideas, technical terms, and even poetry can all be expressed in American Sign Language.
Just like in English, there are some signs that are only considered appropriate for certain people to use. For example, the sign for “Black” when referring to a Black person has a modified version that is only used by Black signers. This does not mean it is a slur or the equivalent of a slur. It is a sign reserved for Black signers referring to other Black people.
Things to Consider/Avoid/Be Aware Of
I hesitate to tell anyone to avoid anything, because I don’t think I have that authority. That being said:
The Deaf community has a complicated history and relationship with cochlear implants and the concept of being “cured.” What message are you sending when you write a story in which a d/Deaf character is “cured” of their d/Deafness?
Generally speaking, d/Deaf people do not identify with the “disabled” label. Each person has their own preferences, and those preferences should always be respected. Your character(s) may choose differently than their real life community, but you should put thought into why that is.
Generally speaking, d/Deaf people use IFL. This means that a majority of d/Deaf people in America would describe themselves as d/Deaf people, rather than people with deafness, people with hearing loss, people that are hard of hearing, etc.
Okay I lied I’m going to tell you what to do here: Do not use words like mute, deaf-mute, or dumb when describing d/Deaf people. Hearing impaired is also not ideal but is considered outdated, rather than outright offensive.
The best lip readers are judged to be able to catch 30% of the words people say. How realistic is it to have a character that relies 100% on lipreading? What do you gain when you write a character that lipreads, and what do you lose?
Yes, Deaf people can drive. I don’t know why so many people wonder about this. It’s okay if you didn’t know, but please don’t come into my ask box about it.
Assistive Devices/Aids
Cochlear implants ^ see above
Interpreters. Will have gone to school for years, might have specific training for certain environments or technical terms, etc. For instance, an interpreter that works with Deaf people that have mental illnesses would be fully fluent in ASL as well as having requisite mental health training in order to interpret for them. Interpreters could be a whole other post actually, but I won’t tackle that now.
Closed captions. Self-explanatory.
Alarm clocks, fire alarms, and doorbells that use light instead of sound. This is sometimes a typical flashing light, but particularly fire alarms in predominantly d/Deaf spaces can be overwhelmingly bright. Bright like you’ve never seen before. Bright enough to wake someone from a dead sleep.
Some assistive devices also use sensation - alarms that actually shake bedframes exist and are the best choice for some people!
Service dogs - can alert people to sounds like the above - fire alarms, doorbells, knocking, etc.
Hearing aids. Generally not controversial in the way that CIs are. Only effective if people have residual hearing. Do not really expand the range of sounds people can hear, just amplify sounds in that range. Very, very expensive.
Microphones. If a d/Deaf or HOH person is in a crowd/lecture setting, the speaker will want to use a microphone. If this is a frequent occurrence, the microphone may be linked to a small personal speaker or earbud used by the d/Deaf or HOH person.
TTY: Much less frequent now that everyone can text and email, but stands for Text Telephone Device and was/is a way to send written communication over a telephone line. The message is sent, the phone rings, and a robot voice reads the message. Obviously, this is not effective for d/Deaf people communicating with other d/Deaf people, but it was often used to communicate with hearing people/hearing establishments, as when setting up appointments.
Media About/Including Deafness
No media is perfect and unproblematic, but here are somethings I have seen that I can verify do at least a pretty good job -
CODA is a movie that features Deaf actors, ASL, and a story about growing up, family, and independence vs. interdependence.
The Sound of Metal is a movie that features ASL and a story about identity, recovery, and hearing loss/Deaf gain.
A Quiet Place is a movie features ASL and Deaf actors, although Deafness itself is not necessarily integral to the story.
BUG: Deaf Identity and Internal Revolution by Christopher Heuer is a collection of essays by a Deaf man that discuss a wide range of topics. This book is not always up to modern standards of political correctness.
Train Go Sorry by Leah Hager Cohen is a memoir by the granddaughter of a Deaf man, which discusses the intersections of the hearing and Deaf worlds.
Far From the Tree by Andrew Solomon is a research book about the effect of horizontal identity on parent/child relationships and features a chapter on d/Deafness. This is a good look at how d/Deafness can impact familial relationships. Some aspects of the book are outdated, and it was written by a hearing author, albeit one who extensively interviewed Deaf and hearing parents of Deaf children.
If you made it this far, congratulations! Thank you so much for taking the time to read through my lil/not so lil primer :) If you have any questions, comments, concerns, or feedback, please feel free to hit me up! If you have any requests for a diagnosis or a disability you’d like me to write about next, I’d love to hear it. Happy writing!
[Image IDs: All the images are photos of clouds at sunset/rise, with beautiful high-contrast orange and dark blue color palettes. In all of them the moon is visible and there are airplanes with long, lit up contrails.
ID1: In this one the clouds are huge thunderheads clustered mostly in the bottom half of the image and to the left. The moon is a waning crescent in the close to the center of the image. The contrails of the airplane cut through the higher clouds on the left, moving diagonally up and to the right, ending just under the moon. There are stars in the sky.
ID2: Just the top of a large thunderhead is pictured in this one, with a very bright waxing crescent moon just above it. The airplane is this one is a bit bigger and more visible than the others, its contrails cutting across the image to the right/top diagonally, disappearing behind the cloud. The sky is a slightly lighter blue in this one, but there are still stars in the sky.
ID3: This is the only image that shows the ground, which is hard to see because of the low light, but appears to be an parking lot overlook on the top of a mountain with a city below and to the right. The clouds in this one are more scattered and wispy, but are still huge and cover most of the sky. The sky is bright yellow near the horizon, turning to a rich, starless blue at the top of the image. The contrails strikingly travel straight up from the horizon, behind the clouds and up to the moon; which is a thin waxing crescent.
ID4: Dark clouds billow up and to the left, a dimmer contrail cutting through the peak of them diagonally up and left. The moon is a bright waxing crescent. It’s so bright the shadowed side is still visible, and it’s also off-center, resting just above the highest point of the clouds. The 3 stars of Orion’s Belt are the only ones visible.
/End IDs]




-
 vieille-femme-moisie liked this · 10 months ago
vieille-femme-moisie liked this · 10 months ago -
 thugdove liked this · 1 year ago
thugdove liked this · 1 year ago -
 hawkpartys reblogged this · 1 year ago
hawkpartys reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 moth-queer reblogged this · 2 years ago
moth-queer reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 fonzie44 liked this · 2 years ago
fonzie44 liked this · 2 years ago -
 kissmewithyourmouth liked this · 2 years ago
kissmewithyourmouth liked this · 2 years ago -
 moth-queer liked this · 2 years ago
moth-queer liked this · 2 years ago -
 bug-maniac reblogged this · 2 years ago
bug-maniac reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 use1pc liked this · 2 years ago
use1pc liked this · 2 years ago -
 shriveledradish liked this · 2 years ago
shriveledradish liked this · 2 years ago -
 celerybeast reblogged this · 2 years ago
celerybeast reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 darkkdeity liked this · 2 years ago
darkkdeity liked this · 2 years ago -
 bootesstar liked this · 2 years ago
bootesstar liked this · 2 years ago -
 bugsmoocher liked this · 2 years ago
bugsmoocher liked this · 2 years ago -
 mantischildren reblogged this · 2 years ago
mantischildren reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 burntmlk liked this · 2 years ago
burntmlk liked this · 2 years ago -
 cedar-trees liked this · 2 years ago
cedar-trees liked this · 2 years ago -
 barbiemonamie liked this · 2 years ago
barbiemonamie liked this · 2 years ago -
 calou12 liked this · 2 years ago
calou12 liked this · 2 years ago -
 washimbembe reblogged this · 2 years ago
washimbembe reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 thesewersofparis liked this · 2 years ago
thesewersofparis liked this · 2 years ago -
 beralbluebat liked this · 2 years ago
beralbluebat liked this · 2 years ago -
 joserosblog liked this · 2 years ago
joserosblog liked this · 2 years ago -
 cerberus-ink reblogged this · 2 years ago
cerberus-ink reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 cosmic-affinities liked this · 2 years ago
cosmic-affinities liked this · 2 years ago -
 hydrostatic-exoskeleton liked this · 2 years ago
hydrostatic-exoskeleton liked this · 2 years ago -
 shianu reblogged this · 2 years ago
shianu reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 shianu liked this · 2 years ago
shianu liked this · 2 years ago -
 huget0ad liked this · 2 years ago
huget0ad liked this · 2 years ago -
 bobagrub liked this · 2 years ago
bobagrub liked this · 2 years ago -
 rosifer liked this · 2 years ago
rosifer liked this · 2 years ago -
 sillymisdreavus liked this · 2 years ago
sillymisdreavus liked this · 2 years ago -
 softmousse liked this · 2 years ago
softmousse liked this · 2 years ago -
 ipswitch-north liked this · 2 years ago
ipswitch-north liked this · 2 years ago -
 indecisive-ire liked this · 2 years ago
indecisive-ire liked this · 2 years ago -
 0rientations liked this · 2 years ago
0rientations liked this · 2 years ago -
 bathynomus239 reblogged this · 2 years ago
bathynomus239 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 bathynomus239 liked this · 2 years ago
bathynomus239 liked this · 2 years ago -
 potatoes-have-no-gender liked this · 2 years ago
potatoes-have-no-gender liked this · 2 years ago -
 punky-funky liked this · 2 years ago
punky-funky liked this · 2 years ago -
 rc-dragons liked this · 2 years ago
rc-dragons liked this · 2 years ago -
 snails-exe liked this · 2 years ago
snails-exe liked this · 2 years ago -
 forestbeast liked this · 2 years ago
forestbeast liked this · 2 years ago -
 silverwhiteraven liked this · 2 years ago
silverwhiteraven liked this · 2 years ago

Hi it’s me puddleorganism if you’re confused why you got a billion hoops from me
298 posts
