What Have We Learned About Pluto?
What Have We Learned About Pluto?
Earlier this year on July 14, our New Horizons spacecraft successfully flew by Pluto. During this encounter, it collected more than 1,200 images of the dwarf planet and tens of gigabits of data. The intensive downlinking of this information began on Sept. 5, and will continue for around a year. With the information being returned for the duration of a year, we still have a lot more to learn about Pluto. Here are a few things we’ve discovered so far:
Pluto’s Heart

An image captured by New Horizons around 16 hours before closest approach displays Pluto’s “heart”. This stunning image of one of the planet’s most dominate features shows us that the heart’s diameter is about the same distance as from Denver to Chicago. This image also showed us that Pluto is a complex world with incredible geological diversity.
Icy Plains

Pluto’s vast icy plain, informally called Sputnik Planum, resembles frozen mud cracks on Earth. It has a broken surface of irregularly-shaped segments, bordered by what appear to be shallow troughs. In other areas, the surface appears to be etched by fields of small pits that may have formed by a process called sublimation, which is when ice turns directly from solid to gas, just as dry ice does on Earth.
Majestic Mountains

Images from the spacecraft display chaotically jumbled mountains that only add to the complexity of Pluto’s geography. The rugged, icy mountains are as tall as 11,000 feet high.
Color Variations

This high-resolution enhanced color view of Pluto combines, blue red and infrared images taken by the New Horizons spacecraft. The surface of the dwarf planet has a remarkable range of subtle color variations. Many landforms have their own distinct colors, telling a complex geological and climatological story of the planet.
Foggy Haze and Blue Atmosphere

Images returned from the New Horizons spacecraft have also revealed that Pluto’s global atmospheric haze has many more layers than scientists realized. The haze even creates a twilight effect that softly illuminates nightside terrain near sunset, which makes them visible to the cameras aboard the spacecraft. Today, a new announcement was made about Pluto’s atmosphere after the most recent image returned from New Horizons showed that Pluto’s hazes are blue. The haze particles themselves are likely gray or red, but they way they scatter blue light has created this tint.
Water Ice

In another finding announced today, New Horizons has detected numerous small, exposed regions of water ice on Pluto. Scientists are eager to understand why water appears exactly where it does, and not in other places.
Stay updated on New Horizons findings by visiting the New Horizons page. You can also keep track of Pluto News on the New Horizons Blog.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Inter-stellxr-blog and Others


Wernher von Braun’s space station concept in Collier’s, March 22, 1952 - (source)









The ruins of the Soviet space shuttle program captured by photographer Ralph Mirebs

Meteorite Shower Over McCloud Falls, California
js

October 13, 1966 – Gemini 12 astronaut Buzz Aldrin undergoes zero-gravity training aboard an Air Force KC-135 vomit comet. (NASA)
10 Intriguing Worlds Beyond Our Solar System
In celebration of the 20th anniversary of the first confirmed planet around a sun-like star (aka exoplanet), a collection of some interesting exoplanets has been put together. Some of these are rocky, some are gaseous and some are very, very cold. But there’s one thing each these strange new worlds have in common: All have advanced scientific understanding of our place in the cosmos. Check out these 10 exoplanets, along with artist’s concepts depicting what they might look like. For an extended list of 20 exoplanets, go HERE.
1. Kepler-186f

Kepler-186f was the first rocky planet to be found within the habitable zone – the region around the host star where the temperature is right for liquid water. This planet is also very close in size to Earth. Even though we may not find out what’s going on at the surface of this planet anytime soon, it’s a strong reminder of why new technologies are being developed that will enable scientists to get a closer look at distance worlds.
More Info
2. HD 209458 b (nickname “Osiris”)

The first planet to be seen in transit (crossing its star) and the first planet to have it light directly detected. The HD 209458 b transit discovery showed that transit observations were feasible and opened up an entire new realm of exoplanet characterization.
More info
3. Kepler-11 system

This was the first compact solar system discovered by Kepler, and it revealed that a system can be tightly packed, with at least five planets within the orbit of Mercury, and still be stable. It touched off a whole new look into planet formation ideas and suggested that multiple small planet systems, like ours, may be common.
More info
4. Kepler-16b

A real-life “Tatooine,” this planet was Kepler’s first discovery of a planet that orbits two stars – what is known as a circumbinary planet.
More info
5. 51 Pegasi b

This giant planet, which is about half the mass of Jupiter and orbits its star every four days, was the first confirmed exoplanet around a sun-like star, a discovery that launched a whole new field of exploration.
More info
6. CoRoT 7b

The first super-Earth identified as a rocky exoplanet, this planet proved that worlds like the Earth were indeed possible and that the search for potentially habitable worlds (rocky planets in the habitable zone) might be fruitful.
More info
7. Kepler-22b

A planet in the habitable zone and a possible water-world planet unlike any seen in our solar system.
More info
8. Kepler-10b

Kepler’s first rocky planet discovery is a scorched, Earth-size world that scientists believe may have a lava ocean on its surface.
More info
9. Kepler-444 system

The oldest known planetary system has five terrestrial-sized planets, all in orbital resonance. This weird group showed that solar systems have formed and lived in our galaxy for nearly its entire existence.
More info
10. 55 Cancri e

Sauna anyone? 55 Cancri e is a toasty world that rushes around its star every 18 hours. It orbits so closely – about 25 times closer than Mercury is to our sun – that it is tidally locked with one face forever blistering under the heat of its sun. The planet is proposed to have a rocky core surrounded by a layer of water in a “supercritical” state, where it is both liquid and gas, and then the whole planet is thought to be topped by a blanket of steam.
More info

NASA in the 1970s expected to process the Space Shuttle after flights quickly, like an airliner. It didn’t work out that way.
Keep reading

The Key to Colonizing Mars Could Be These Tiny Green Microbes
Long ago, a clan of hardy microbes called cyanobacteria helped terraform the lifeless Earth into a vibrant biosphere. Today, the very same critters could be the key to colonizing Mars.
Plants are going to have a tough time on the Red Planet’s hostile surface, but cyanobacteria have coped with extreme environments for eons. A paper led by astrobiologist Lynn Rothschild of NASA’s Ames Research Institute argues that we can harness these tiny photosynthesis machines to produce many of the resources we’ll need to survive, from food and oxygen to metals and medicine. Here are all the ways cyanobacteria can help us build a Martian colony.
Continue reading via Gizmodo and introduce yourself to biomining.
abusive parents can buy their children nice things
abusive parents can provide food, shelter and other necessaries
abusive parents can be nice to their children at times
abusive parents can seem like the most loving parents in the world
You don’t know what goes on behind closed doors.
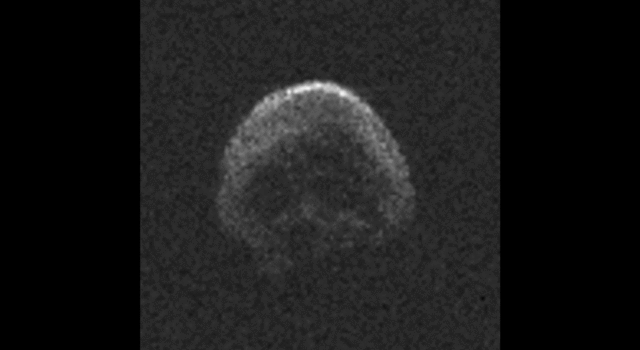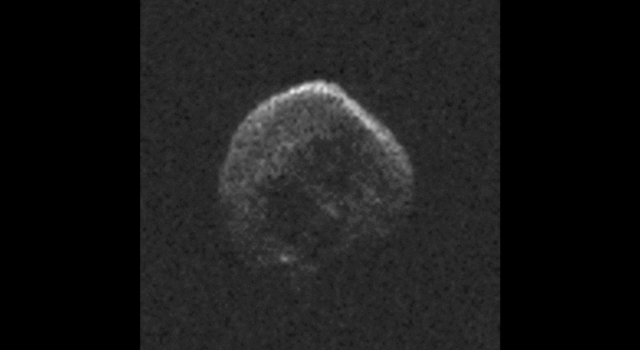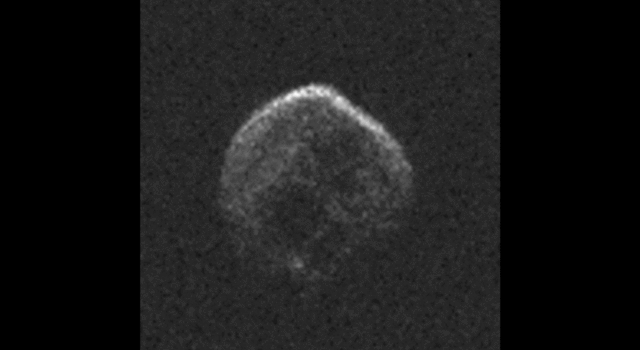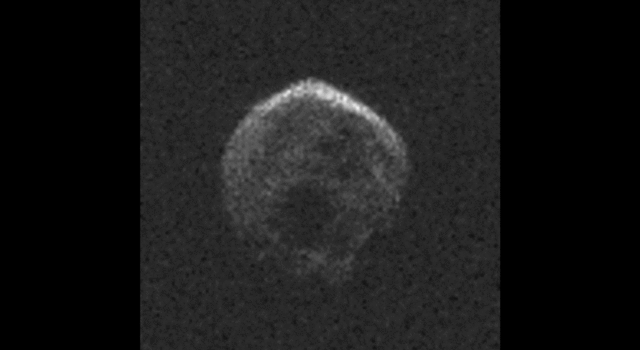
The large space rock that will zip past Earth this Halloween is most likely a dead comet that, fittingly, bears an eerie resemblance to a skull.
These first radar images from the National Science Foundation’s 1,000-foot (305-meter) Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico, indicate the near-Earth object is spherical in shape and approximately 2,000 feet (600 meters) in diameter. The radar images were taken on Oct. 30, 2015.
Scientists observing asteroid 2015 TB145 with NASA’s Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF) on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, have determined that the celestial object is more than likely a dead comet that has shed its volatiles after numerous passes around the sun.
For more information, click here.
Image Credit: NAIC-Arecibo/NSF
-
 annahpmn8 liked this · 6 months ago
annahpmn8 liked this · 6 months ago -
 majesticleon liked this · 1 year ago
majesticleon liked this · 1 year ago -
 chanzero liked this · 1 year ago
chanzero liked this · 1 year ago -
 feech reblogged this · 1 year ago
feech reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 feech liked this · 1 year ago
feech liked this · 1 year ago -
 austinwehaveaproblem reblogged this · 1 year ago
austinwehaveaproblem reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 arocrows42 reblogged this · 1 year ago
arocrows42 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 arocrows42 liked this · 1 year ago
arocrows42 liked this · 1 year ago -
 lovelyyellowdress liked this · 2 years ago
lovelyyellowdress liked this · 2 years ago -
 tt-squid reblogged this · 3 years ago
tt-squid reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 espectrode-luz liked this · 5 years ago
espectrode-luz liked this · 5 years ago -
 thelostlenoir reblogged this · 6 years ago
thelostlenoir reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 phootyraskel reblogged this · 6 years ago
phootyraskel reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 hoolahoopsmcgee reblogged this · 6 years ago
hoolahoopsmcgee reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 hoolahoopsmcgee liked this · 6 years ago
hoolahoopsmcgee liked this · 6 years ago -
 replicant1955 liked this · 6 years ago
replicant1955 liked this · 6 years ago -
 angelic-girl liked this · 6 years ago
angelic-girl liked this · 6 years ago -
 kindwarrior liked this · 6 years ago
kindwarrior liked this · 6 years ago -
 dragonkinglover liked this · 6 years ago
dragonkinglover liked this · 6 years ago -
 a-golden-bear reblogged this · 6 years ago
a-golden-bear reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 a-golden-bear liked this · 6 years ago
a-golden-bear liked this · 6 years ago -
 nyzale liked this · 6 years ago
nyzale liked this · 6 years ago
"I don't know who will read this. I guess someone will find it eventually. Maybe in a hundred years or so." -Mark Watney
174 posts
