@i-can-taste-the-sun
@i-can-taste-the-sun
I CANT STOP LAUGHING
More Posts from Inter-stellxr-blog and Others

The mission objective of the Voyager Interstellar Mission (VIM) is to extend the NASA exploration of the solar system beyond the neighborhood of the outer planets to the outer limits of the Sun’s sphere of influence, and possibly beyond. This extended mission is continuing to characterize the outer solar system environment and search for the heliopause boundary, the outer limits of the Sun’s magnetic field and outward flow of the solar wind.



clouds on mars, photographed by mars express, 16th january 2014.
around 43°s 258°e, one the eastern icaria planum. details from a sequence of 5 monochrome images, colourized with a bit of art and a bit of science.
image credit: esa. animation & colourization: ageofdestruction.










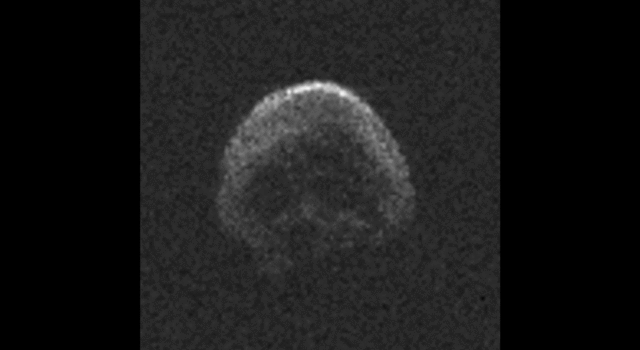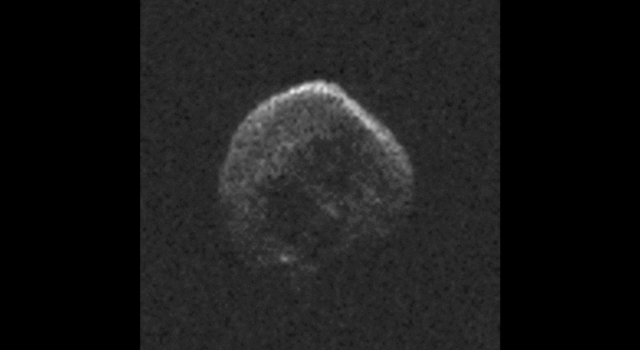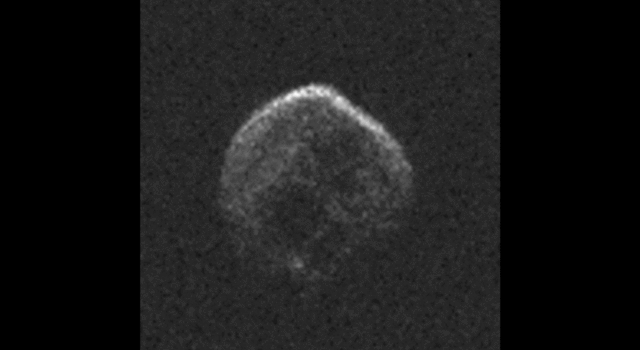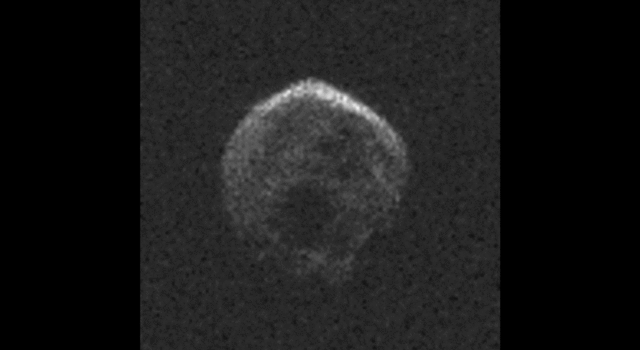
The large space rock that will zip past Earth this Halloween is most likely a dead comet that, fittingly, bears an eerie resemblance to a skull.
These first radar images from the National Science Foundation’s 1,000-foot (305-meter) Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico, indicate the near-Earth object is spherical in shape and approximately 2,000 feet (600 meters) in diameter. The radar images were taken on Oct. 30, 2015.
Scientists observing asteroid 2015 TB145 with NASA’s Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF) on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, have determined that the celestial object is more than likely a dead comet that has shed its volatiles after numerous passes around the sun.
For more information, click here.
Image Credit: NAIC-Arecibo/NSF

How Big is our Solar System Infographic - http://astronomyisawesome.com/infographics/how-big-is-our-solar-system/
Tadashi was unaware of what Hiro was doing, since he had fallen back asleep in under five minutes. He couldn't feel any movement, though he would wake up to the slightest sounds. youneedsomeupgrades
hamada-tadashii
Hiro woke, rubbing his eyes and staring at the dark ceiling, slowly sitting up and dangling his feet off the bed. His eyes scanned the room searching for his sound asleep brother. As his eyes found him he tiredly stood out of bed and almost drunkly walked over to the bed, setting his hands on the bed, closing his eyes. “Dashi.. Tadashi, you awake?”
IF YOU HAVE NOT SEEN 50 SHADES OF GRAY OR AMERICAN SNIPER AND HAVE NO INTENTIONS OF DOING SO, REBLOG THIS
I’m following all of you
The Martian Movie and Our Real Journey to Mars
The Martian movie is set 20 years in the future, but here at NASA we are already developing many of the technologies that appear in the film. The movie takes the work we’re doing and extends it into fiction set in the 2030s, when NASA astronauts are regularly traveling to Mars and living on the surface. Here are a few ways The Martian movie compares to what we’re really doing on our journey to Mars:
Analog Missions

MOVIE: In the film, Astronaut Mark Watney is stranded on the Red Planet.
REALITY: In preparation for sending humans to Mars, we have completed one of the most extensive isolation missions in Hawaii, known as HI-SEAS. The goal of this study was to see how isolation and the lack of privacy in a small group affects social aspects of would-be explorers. The most recent simulation was eight months long, and the next mission is planned to last a year.
Spaceport

MOVIE: The Martian movie launches astronauts on the Aries missions from a refurbished and state of the art space center.
REALITY: Currently, the Ground Systems Development and Operations’ primary objective is to prepare the center to process and launch the next-generation vehicles and spacecraft designed to achieve our goals for space exploration. We are not only working to develop new systems, but also refurbishing and upgrading infrastructure to meet future demands.
Deep Space Propulsion

MOVIE: In the film, the astronauts depart the Red Planet using a propulsion system know as the Mars Ascent Vehicle (MAV).
REALITY: We are currently developing the most powerful rocket we’ve ever built, our Space Launch System (SLS). Once complete, this system will enable astronauts to travel deeper into the solar system than ever before! The RS-25 engines that will be used on the SLS, were previously utilized as the main engine on our space shuttles. These engines have proven their reliability and are currently being refurbished with updated and improved technology for our journey to Mars.
Mission Control

MOVIE: In the movie, Mission Control operations support the Aries 3 crew.
REALITY: On our real journey to Mars, Mission Control in Houston will support our Orion spacecraft and the crew onboard as they travel into deep space.
Habitat

MOVIE: The artificial living habitat on Mars in The Martian movie is constructed of industrial canvas and contains an array of life support systems.
REALITY: The Human Exploration Research Analog (HERA), formerly known as the Deep Space Habitat, is a three-story module that was designed and created through a series of university competitions. Studies conducted in habitat mockups will allow us to evolve this technology to create a reliable structures for use on Mars.
Rover

MOVIE: The characters in the film are able to cruise around the Red Planet inside the Mars Decent Vehicle (MDV).
REALITY: We are currently developing a next generation vehicle for space exploration. Our Mars Exploration Vehicle (MEV) is designed to be flexible depending on the destination. It will have a pressurized cabin, ability to house two astronauts for up to 14 days and will be about the size of a pickup truck.
Harvest

MOVIE: Astronaut Mark Watney grows potatoes on Mars in The Martian movie.
REALITY: We’re already growing and harvesting lettuce on the International Space Station in preparation for deep space exploration. Growing fresh food in space will provide future pioneers with a sustainable food supplement, and could also be used for recreational gardening during deep space missions.
Spacesuit

MOVIE: The spacesuit worn by astronauts in the film allows them to work and function on the surface of Mars, while protecting them from the harsh environment.
REALITY: Prototypes of our Z-2 Exploration Suit are helping to develop the technologies astronauts will use to live and work on the the Martian surface. Technology advances in this next generation spacesuit would shorten preparation time, improve safety and boost astronaut capabilities during spacewalks and surface activities.
-
 solarsaurus-rex liked this · 9 years ago
solarsaurus-rex liked this · 9 years ago -
 midnightsnack125 liked this · 9 years ago
midnightsnack125 liked this · 9 years ago -
 midnightsnack125 reblogged this · 9 years ago
midnightsnack125 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 varietydivision liked this · 9 years ago
varietydivision liked this · 9 years ago -
 koibo-i liked this · 9 years ago
koibo-i liked this · 9 years ago -
 davepetraque liked this · 9 years ago
davepetraque liked this · 9 years ago -
 vespren reblogged this · 9 years ago
vespren reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 anydecentnameistaken liked this · 9 years ago
anydecentnameistaken liked this · 9 years ago -
 beelijah reblogged this · 9 years ago
beelijah reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 sweetasblackcoffee reblogged this · 9 years ago
sweetasblackcoffee reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 ahihcu00 liked this · 9 years ago
ahihcu00 liked this · 9 years ago -
 tamagosalad reblogged this · 9 years ago
tamagosalad reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 liquidcaramel reblogged this · 9 years ago
liquidcaramel reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 thatonequietvampire-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
thatonequietvampire-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 iwasyoungandnew reblogged this · 9 years ago
iwasyoungandnew reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 fucking-fandom-trash reblogged this · 9 years ago
fucking-fandom-trash reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 fucking-fandom-trash liked this · 9 years ago
fucking-fandom-trash liked this · 9 years ago -
 mollymawks liked this · 9 years ago
mollymawks liked this · 9 years ago -
 mm-0912 liked this · 9 years ago
mm-0912 liked this · 9 years ago -
 scarlett-dragon reblogged this · 9 years ago
scarlett-dragon reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 scarlett-dragon liked this · 9 years ago
scarlett-dragon liked this · 9 years ago -
 gltichyspams reblogged this · 9 years ago
gltichyspams reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 gltichyspams liked this · 9 years ago
gltichyspams liked this · 9 years ago -
 13thseeker reblogged this · 9 years ago
13thseeker reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 13thseeker liked this · 9 years ago
13thseeker liked this · 9 years ago -
 beanlamps reblogged this · 9 years ago
beanlamps reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 beanlamps liked this · 9 years ago
beanlamps liked this · 9 years ago -
 psp2i liked this · 9 years ago
psp2i liked this · 9 years ago -
 ellie-pofficial liked this · 9 years ago
ellie-pofficial liked this · 9 years ago -
 liina-puff reblogged this · 9 years ago
liina-puff reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 liina-puff liked this · 9 years ago
liina-puff liked this · 9 years ago -
 kaigalaticus reblogged this · 9 years ago
kaigalaticus reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 kaigalaticus liked this · 9 years ago
kaigalaticus liked this · 9 years ago -
 malay-spiruss reblogged this · 9 years ago
malay-spiruss reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 malay-spiruss liked this · 9 years ago
malay-spiruss liked this · 9 years ago -
 saltycollectionpersonfan liked this · 9 years ago
saltycollectionpersonfan liked this · 9 years ago -
 n1ghts1ash liked this · 9 years ago
n1ghts1ash liked this · 9 years ago -
 alh1597 reblogged this · 9 years ago
alh1597 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 pyralspi reblogged this · 9 years ago
pyralspi reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 lionsmug liked this · 9 years ago
lionsmug liked this · 9 years ago
"I don't know who will read this. I guess someone will find it eventually. Maybe in a hundred years or so." -Mark Watney
174 posts
