Celebrate The Saturn V’s Birthday By Watching The Largest Rocket In History Fly

Celebrate the Saturn V’s Birthday by Watching the Largest Rocket in History Fly
The Saturn V rocket is objectively the most badass vehicle ever made. Screw your SR-71 Blackbirds. To hell with your Maglev trains. Shove your hoverboards up your butt. The Saturn V, flagship of the Apollo Moon landings, has them all beat for style, performance, and historical impact, hands-down, end of story.
No doubt the launches were even more incredible to witness in person, but this visual mosaic of all 13 blast-offs is bound to give you a contact high nonetheless. Watch on, and pay your respects to this masterpiece of engineering, which repeatedly burned up in the atmosphere so that we didn’t have to.
You heard it right: That’s Walter Cronkite, arguably the most unflappable newsman in history, losing his shit over the raw power of the Saturn V.
“My God, our building’s shaking here,” he says with palpable delight. “Oh it’s terrific, the building’s shaking! This big blast window is shaking! We’re holding it with our hands! Look at that rocket go into the clouds at 3,000 feet! Oh, the roar is terrific!”
We feel you, Walter. A lot of rockets have come and gone since the Saturn V was retired in 1973, but none have ever exceeded the sheer explosive wonder of this Apollo Age champ. It remains the largest and most powerful rocket of all time, standing 36 stories high and weighing about 6.2 million pounds when fully fueled. For comparison, SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy, slated for its first flight next year, will stand 22 stories high.

“It has more capability than any vehicle in history,” Elon Musk said of the Falcon Heavy, “apart from the Saturn V.”
Alas, the Saturn V rockets were also expendable launch vehicles, meaning that only the tiny command modules carrying the returning Apollo astronauts ever made it back to Earth. But though we don’t have many physical remains of the beasts that gave us our first boosts to another world, we have plenty of nostalgically sepia-toned footage recording their pyrotechnic departures from our planet.
Mad props, Saturn V. You’re the real MVP.
Source: @vicemag [x]
More Posts from Inter-stellxr-blog and Others

Andromeda Rising over the Alps
Tadashi was unaware of what Hiro was doing, since he had fallen back asleep in under five minutes. He couldn't feel any movement, though he would wake up to the slightest sounds. youneedsomeupgrades
hamada-tadashii
Hiro woke, rubbing his eyes and staring at the dark ceiling, slowly sitting up and dangling his feet off the bed. His eyes scanned the room searching for his sound asleep brother. As his eyes found him he tiredly stood out of bed and almost drunkly walked over to the bed, setting his hands on the bed, closing his eyes. “Dashi.. Tadashi, you awake?”


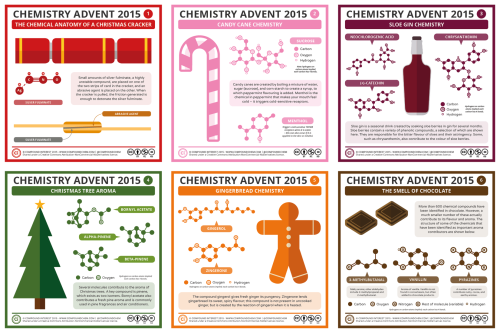
Six days into the Chemistry Advent Calendar! Missed any so far? Catch up here: http://www.compoundchem.com/2015advent/
his voice sounds so animated and he’s so cute i want to hug him for a long time

The mission objective of the Voyager Interstellar Mission (VIM) is to extend the NASA exploration of the solar system beyond the neighborhood of the outer planets to the outer limits of the Sun’s sphere of influence, and possibly beyond. This extended mission is continuing to characterize the outer solar system environment and search for the heliopause boundary, the outer limits of the Sun’s magnetic field and outward flow of the solar wind.
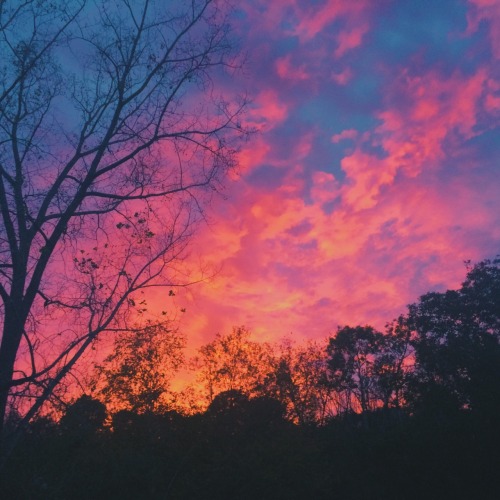
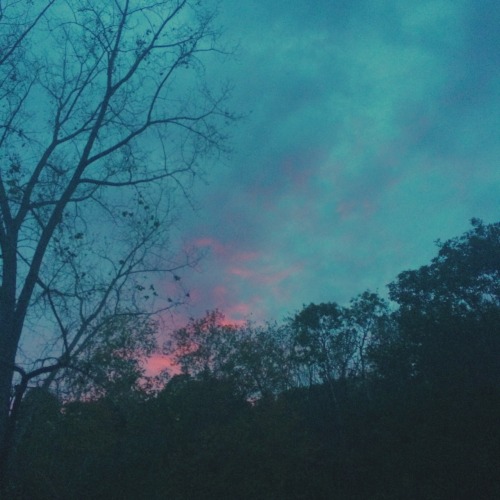


the sunset was violently sudden & spectacular tonight. these pictures were taken abt 2 minutes apart
Water on Mars!

Did you hear? New findings from our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) provide the strongest evidence yet that liquid water flows intermittently on present-day Mars.
Using an imaging spectrometer on MRO, we found hydrated minerals on slopes where mysterious streaks are seen on Mars. One thing that researchers noticed was that the darkish streaks appear to ebb and flow over time. During warm seasons, they darken and then fade in cooler seasons.

When discovered in 2010, these downhill flows known as recurring slope lineae (RSL) were thought to be related to liquid water. With the recent spectral detection of molecular water, we’re able to say it’s likely a shallow subsurface flow explains the darkening.
Mars is so cold, how could liquid water flow there? Great question! Since this liquid water is briny, the freezing point would be lower than that of pure water. Also, these saline slopes appear on Mars when temperatures are above minus 10 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 23 Celsius).
The dark, narrow streaks flowing downhill in the below image are roughly the length of a football field.

So there’s water, but how much? Currently we think this area has a very small amount of water, probably just enough to wet the top layer of the surface of Mars. The streaks are around four to five meters wide and 200 to 300 meters long.
Could humans drink this water? The salts in the water appear to be perchlorates, so you probably wouldn’t want to drink the water. It would most likely be very salty and would need to be purified before human consumption.
Perchlorate…What is that? A perchlorate is a salt that absorbs water from the air. Learn more about how it’s helping us unlock the mysteries of Mars in this video:
What’s next? We want to look for more locations where brine flows may occur. We have only covered 3% of Mars at resolutions high enough to see these features.
For more information on the Mars announcement, visit our Journey to Mars landing page. There is also a full recap of the press conference HERE, and a short recap below.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Supermoon Total Lunar Eclipse and Lightning Storm
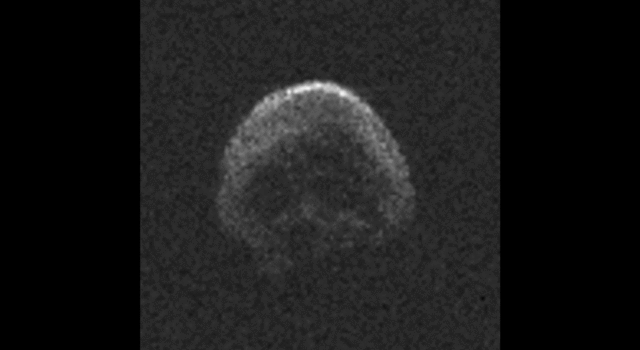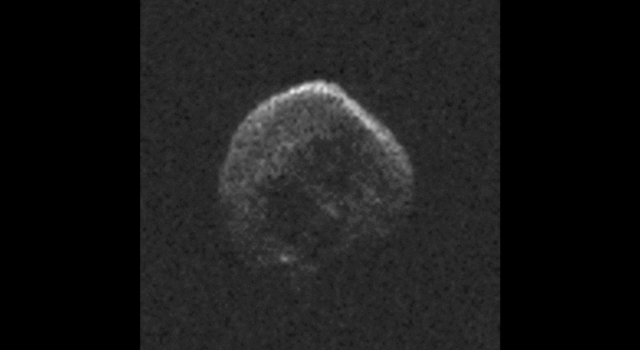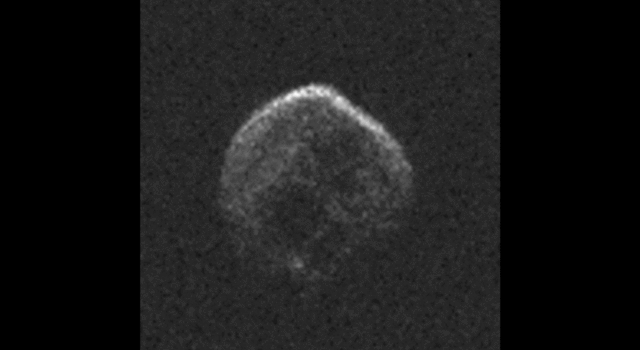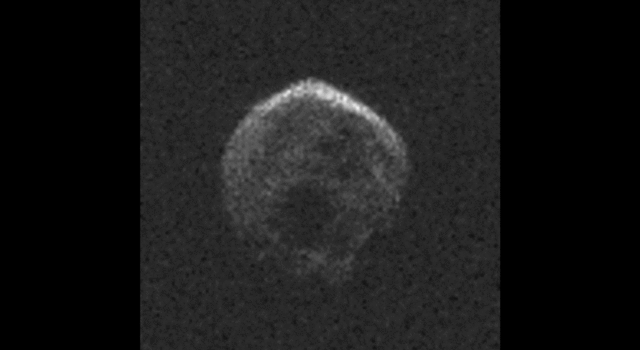
The large space rock that will zip past Earth this Halloween is most likely a dead comet that, fittingly, bears an eerie resemblance to a skull.
These first radar images from the National Science Foundation’s 1,000-foot (305-meter) Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico, indicate the near-Earth object is spherical in shape and approximately 2,000 feet (600 meters) in diameter. The radar images were taken on Oct. 30, 2015.
Scientists observing asteroid 2015 TB145 with NASA’s Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF) on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, have determined that the celestial object is more than likely a dead comet that has shed its volatiles after numerous passes around the sun.
For more information, click here.
Image Credit: NAIC-Arecibo/NSF
-
 ill-fudgin-kill-ya liked this · 8 years ago
ill-fudgin-kill-ya liked this · 8 years ago -
 monkeychops84 liked this · 8 years ago
monkeychops84 liked this · 8 years ago -
 therock47 liked this · 8 years ago
therock47 liked this · 8 years ago -
 harbingerwolf liked this · 8 years ago
harbingerwolf liked this · 8 years ago -
 davesnothere liked this · 8 years ago
davesnothere liked this · 8 years ago -
 thedreamingmoon liked this · 8 years ago
thedreamingmoon liked this · 8 years ago -
 darkdraggon liked this · 8 years ago
darkdraggon liked this · 8 years ago -
 snowness liked this · 8 years ago
snowness liked this · 8 years ago -
 somecallmetracy liked this · 8 years ago
somecallmetracy liked this · 8 years ago -
 somecallmetracy reblogged this · 8 years ago
somecallmetracy reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 akoan liked this · 8 years ago
akoan liked this · 8 years ago -
 soulless-blunder reblogged this · 8 years ago
soulless-blunder reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 finder-of-things liked this · 8 years ago
finder-of-things liked this · 8 years ago -
 pitchsilent liked this · 8 years ago
pitchsilent liked this · 8 years ago -
 cheesewhizexpress reblogged this · 8 years ago
cheesewhizexpress reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 my-stellar-escape reblogged this · 8 years ago
my-stellar-escape reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 starhasarrived liked this · 9 years ago
starhasarrived liked this · 9 years ago -
 honeybug99-blog liked this · 9 years ago
honeybug99-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 hopeology liked this · 9 years ago
hopeology liked this · 9 years ago -
 flightandbasketball liked this · 9 years ago
flightandbasketball liked this · 9 years ago -
 calibratedoddity reblogged this · 9 years ago
calibratedoddity reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 calibratedoddity liked this · 9 years ago
calibratedoddity liked this · 9 years ago -
 patrick42h reblogged this · 9 years ago
patrick42h reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tomtenadia reblogged this · 9 years ago
tomtenadia reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tomtenadia liked this · 9 years ago
tomtenadia liked this · 9 years ago -
 parkjimindotjpg liked this · 9 years ago
parkjimindotjpg liked this · 9 years ago -
 angstorm123 liked this · 9 years ago
angstorm123 liked this · 9 years ago -
 gorgongrin reblogged this · 9 years ago
gorgongrin reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 schwootermcgavin liked this · 9 years ago
schwootermcgavin liked this · 9 years ago -
 rhlounge liked this · 9 years ago
rhlounge liked this · 9 years ago -
 wander2theedge reblogged this · 9 years ago
wander2theedge reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 petro1986 liked this · 9 years ago
petro1986 liked this · 9 years ago -
 quakeponi reblogged this · 9 years ago
quakeponi reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 quakeponi liked this · 9 years ago
quakeponi liked this · 9 years ago -
 105northtower liked this · 9 years ago
105northtower liked this · 9 years ago -
 sheriffdeputy liked this · 9 years ago
sheriffdeputy liked this · 9 years ago -
 sixthrangerknight reblogged this · 9 years ago
sixthrangerknight reblogged this · 9 years ago
"I don't know who will read this. I guess someone will find it eventually. Maybe in a hundred years or so." -Mark Watney
174 posts