This Is Me
This is me
i dab every morning when i wake up
More Posts from Inter-stellxr-blog and Others
What’s Enceladus?
Before we tell you about Enceladus, let’s first talk about our Cassini spacecraft…
Our Cassini mission to Saturn is one of the most ambitious efforts in planetary space exploration ever mounted. Cassini is a sophisticated robotic spacecraft orbiting the ringed planet and studying the Saturnian system in detail.

Cassini completed its initial four-year mission to explore the Saturn System in June 2008. It has also completed its first mission extension in September 2010. Now, the health spacecraft is making exciting new discoveries in a second extension mission!
Enceladus

Enceladus is one of Saturn’s many moons, and is one of the brightest objects in our solar system. This moon is about as wide as Arizona, and displays at least five different types of terrain. The surface is believed to be geologically “young”, possibly less than 100 million years old.
Cassini first discovered continually-erupting fountains of icy material on Enceladus in 2005. Since then, the Saturn moon has become one of the most promising places in the solar system to search for present-day habitable environments.

Scientists found that hydrothermal activity may be occurring on the seafloor of the moon’s underground ocean. In September, it was announced that its ocean –previously thought to only be a regional sea – was global!
Since Cassini is nearing the end of its mission, we are able to make a series of three close encounters with Enceladus, one of Saturn’s moons.
Close Encounters
On Oct. 14, Cassini performed a mid-range flyby of Enceladus, but the main event will take place on Oct. 28, when Cassini will come dizzyingly close to the icy moon. During this flyby, the spacecraft will pass a mere 30 miles above the moon’s south polar region!

This will be the deepest-ever dive through the moon’s plume of icy spray, where Cassini can collect images and valuable data about what’s going on beneath the frozen surface.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
"Oh alright," the young adult responded. Tadashi had never really told Hiro that he wasn't allowed to because he really cared about his brother and only wanted the best for him. youneedsomeupgrades
hamada-tadashii
Hiro woke, rubbing his eyes and staring at the dark ceiling, slowly sitting up and dangling his feet off the bed. His eyes scanned the room searching for his sound asleep brother. As his eyes found him he tiredly stood out of bed and almost drunkly walked over to the bed, setting his hands on the bed, closing his eyes. “Dashi.. Tadashi, you awake?”




T-51 days (October 14) - OA-4 Cygnus service module arrives at KSC Marking a major milestone in its prelaunch processing flow, the service module for the Cygnus spacecraft’s return to flight arrived at Kennedy Space Center earlier this week. The pressurized cargo module for the OA-4 mission arrived at Kennedy in early August, and technicians have been checking out the module ahead of cargo stowing. OA-4 marks a significant shift in the Cygnus program, not just because it is the spacecraft’s return to flight, but also the first flight of the Enhanced Cygnus. The cargo module is 3.9 feet longer than the initial Standard Cygnus, allowing the spacecraft to transport over 3,300 extra pounds of cargo. The Service Module also boasts new Orbital ATK-made Ultraflex solar arrays, which are lighter than the original rectangular arrays made by DutchSpace. The image below shows a comparison between the two versions of the spacecraft, with the Enhanced Cygnus on the right.

Final assembly and cargo stowage is expected to occur in late October and early November. Encapsulation inside an Atlas V 400-series payload fairing will occur in mid November, followed by rollout to SLC-41 and vehicle integration in late November. Currently, the launch of OA-4 is scheduled for December 3, though that date may move up or be pushed back depending on various factors. It will be the first flight of the spacecraft since an October 29, 2014 launch failure that destroyed the spacecraft and subsequently grounded the program. The enhanced Antares 200 rocket is undergoing final integration and assembly at Wallops Island, Virginia, and Orbital ATK teams are preparing for a period of pad testing. The next flight of Cygnus on an Antares is scheduled for some time in the first half of 2016. Until then, Orbital ATK purchased two Atlas V 401 rockets to launch their enhanced Cygnus spacecraft; these missions are designated OA-4 and OA-5. The second flight is slated for sometime in spring of 2016.

Saturn V Cutaway ~ This fascinating Saturn V cutaway drawing is by far the most detailed I’ve ever come across. It’s an original, official Boeing engineering breakdown by Don Sprague and includes everything you ever wanted to know about the Saturn V’s internal workings – right down to millimetre accurate measurements …
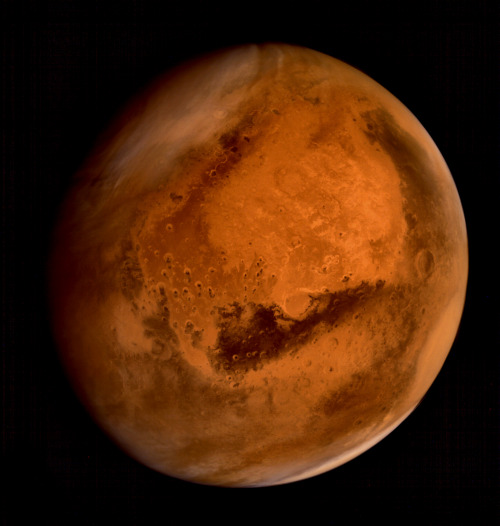
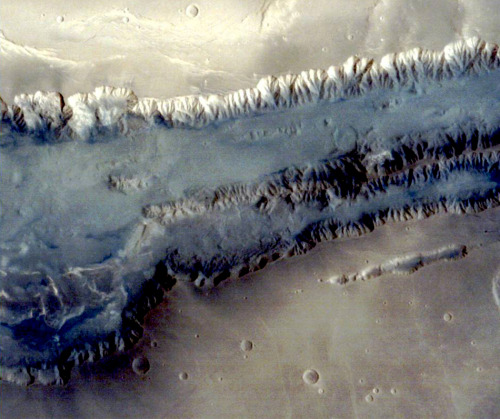
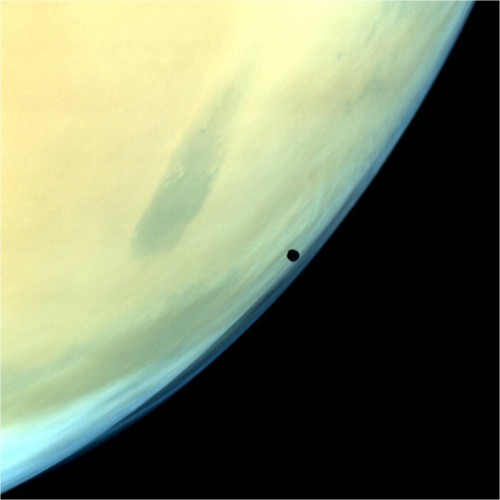



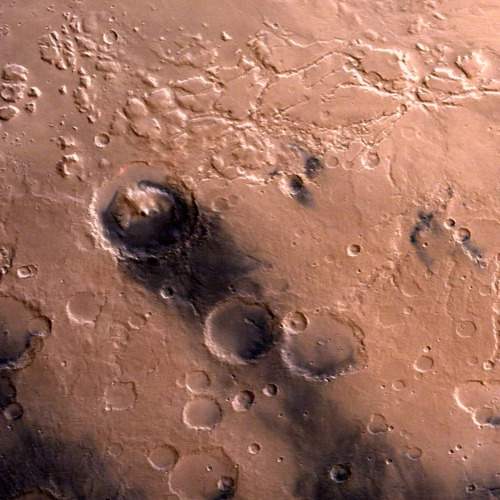
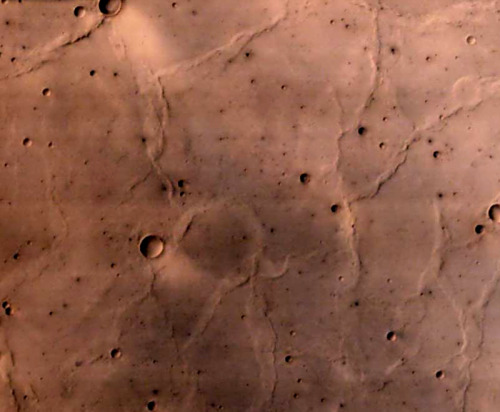
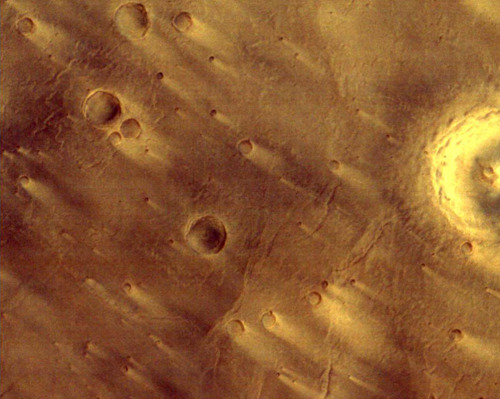


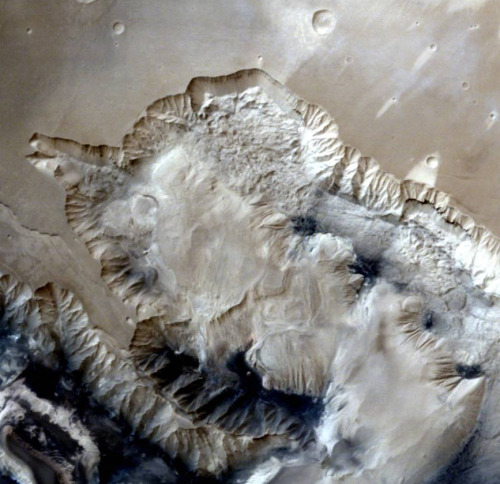
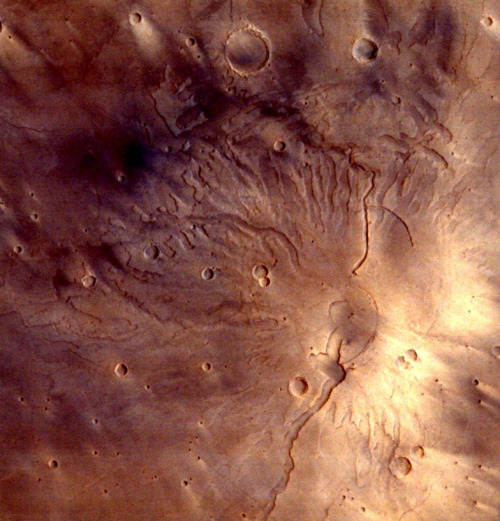

Photographs of Mars taken by the Indian Mars Orbiter Mission, which has been orbiting the planet since September 2014. Can you imagine our descendants colonizing this world?
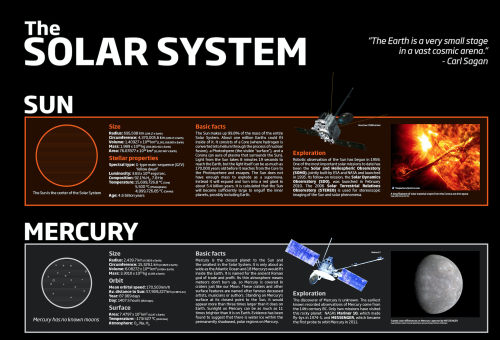





The Solar System

Landing site recommended for ExoMars 2018
Oxia Planum has been recommended as the primary candidate for the landing site of the ExoMars 2018 mission.
ExoMars 2018, comprising a rover and surface platform, is the second of two missions making up the ExoMars programme, a joint endeavour between ESA and Russia’s Roscosmos. Launch is planned for May 2018, with touchdown on the Red Planet in January 2019.
The main goal for the rover is to search for evidence of martian life, past or present, in an area with ancient rocks where liquid water was once abundant. A drill is capable of extracting samples from up to 2 m below the surface. This is crucial, because the present surface of Mars is a hostile place for living organisms owing to the harsh solar and cosmic radiation. By searching underground, the rover has more chance of finding preserved evidence.
Read full article.

Geophysicists call it the new core paradox: They can’t quite explain how the ancient Earth could have sustained a magnetic field billions of years ago, as it was cooling from its fiery birth.
Now, two scientists have proposed two different ways to solve the paradox. Each relies on minerals crystallizing out of the molten Earth, a process that would have generated a magnetic field by churning the young planet’s core. The difference between the two explanations comes in which particular mineral does the crystallizing.
Silicon dioxide is the choice of Kei Hirose, a geophysicist at the Tokyo Institute of Technology who runs high-pressure experiments to simulate conditions deep within the Earth. “I’m very confident in this,” he reported on 17 December at a meeting of the American Geophysical Union in San Francisco, California.
But David Stevenson, a geophysicist at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, says that magnesium oxide — not silicon dioxide — is the key to solving the problem. In unpublished work, Stevenson proposes that magnesium oxide, settling out of the molten early Earth, could have set up the buoyancy differences that would drive an ancient geodynamo.
The core paradox arose in 2012, when several research teams reported that Earth’s core loses heat at a faster rate than once thought1, 2. More heat conducting away from the core means less heat available to churn the core’s liquid. That’s important because some studies suggest Earth could have had a magnetic field more than 4 billion years ago — just half a billion years after it coalesced from fiery debris swirling around the newborn Sun. “We need a dynamo more or less continuously,” Peter Driscoll, a geophysicist at the Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington DC, said at the meeting.
Continue Reading.
-
 fulltimesapphic liked this · 1 week ago
fulltimesapphic liked this · 1 week ago -
 itsoveranakin-ihavethehighground reblogged this · 1 week ago
itsoveranakin-ihavethehighground reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 mrs-flood reblogged this · 1 week ago
mrs-flood reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 cobra-nova liked this · 1 week ago
cobra-nova liked this · 1 week ago -
 vivalamanberg reblogged this · 1 week ago
vivalamanberg reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 vivalamanberg liked this · 1 week ago
vivalamanberg liked this · 1 week ago -
 itspetrovichworld liked this · 1 week ago
itspetrovichworld liked this · 1 week ago -
 berryblu-arts liked this · 1 week ago
berryblu-arts liked this · 1 week ago -
 renzanix liked this · 1 week ago
renzanix liked this · 1 week ago -
 technologicallyme-reblogs reblogged this · 1 week ago
technologicallyme-reblogs reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 pygmaeum reblogged this · 1 week ago
pygmaeum reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 silvercloudsaregay liked this · 1 week ago
silvercloudsaregay liked this · 1 week ago -
 amu-unfortunate liked this · 1 week ago
amu-unfortunate liked this · 1 week ago -
 alfazed liked this · 1 week ago
alfazed liked this · 1 week ago -
 pirate-captain-froggy reblogged this · 1 week ago
pirate-captain-froggy reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 winteriine reblogged this · 1 week ago
winteriine reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 talltransman liked this · 1 week ago
talltransman liked this · 1 week ago -
 blockbee reblogged this · 1 week ago
blockbee reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 postmanlinksbootyshorts reblogged this · 1 week ago
postmanlinksbootyshorts reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 ace-of-arthropods reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
ace-of-arthropods reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 boo-mite liked this · 2 weeks ago
boo-mite liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 s0apsuds liked this · 2 weeks ago
s0apsuds liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 dragonmaker1 liked this · 2 weeks ago
dragonmaker1 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 septicsoldier13 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
septicsoldier13 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 septicsoldier13 liked this · 2 weeks ago
septicsoldier13 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 kataang36 liked this · 2 weeks ago
kataang36 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 slugtime reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
slugtime reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 dainobones reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
dainobones reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 babey liked this · 2 weeks ago
babey liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 silencelistening reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
silencelistening reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 cheshirekittin9090 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
cheshirekittin9090 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 cheshirekittin9090 liked this · 2 weeks ago
cheshirekittin9090 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 pkmn-trainer-touko-tajiri reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
pkmn-trainer-touko-tajiri reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 adagast2024 liked this · 2 weeks ago
adagast2024 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 driftveilcity liked this · 3 weeks ago
driftveilcity liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 alola03 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
alola03 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 mallow-marsh liked this · 3 weeks ago
mallow-marsh liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 these-bees-r18 liked this · 3 weeks ago
these-bees-r18 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 venusararara liked this · 3 weeks ago
venusararara liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 raylaandcallum liked this · 3 weeks ago
raylaandcallum liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 bevydev reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
bevydev reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 gayboy-derogatory reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
gayboy-derogatory reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 bigdumbdumbjuice reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
bigdumbdumbjuice reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 melancholystarry liked this · 3 weeks ago
melancholystarry liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 salander-san reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
salander-san reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 clicketywack liked this · 3 weeks ago
clicketywack liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 demons-main-hell reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
demons-main-hell reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 markachii liked this · 3 weeks ago
markachii liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 notsoheterosapien liked this · 3 weeks ago
notsoheterosapien liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 victorianboyonrollerskates liked this · 3 weeks ago
victorianboyonrollerskates liked this · 3 weeks ago
"I don't know who will read this. I guess someone will find it eventually. Maybe in a hundred years or so." -Mark Watney
174 posts
