
blog dedicated to my work with the planet Jupiter
96 posts
Latest Posts by jovian-witch - Page 3

Spell Circle
Purpose: To sanctify and maintain a space
Recommended Casting Type: Altar
Recommended Anchor: Wood
Outer Ring Translation: “Sanctify this space. Only my circle of spirits and gods may enter.”
Language: English
Script: Woevian
Planetary Correspondences: Sun/Jupiter/Saturn
Directional Correspondences: Center
Color Correspondences: Silver
Numerology: 0/1/3
The Planets and Their Correspondences: Jupiter

zodiac:
pisces
day:
thursday
element:
fire, water
gemstones:
amethyst, lapis lazuli, sapphire, diamond, jacinth, coral, pearl
body parts:
liver, digestion, metabolism, anabolic processes, nourishment, hips, thighs, legs, feet
colors:
violet, bright blue, yellow, green, amethyst, sea green, crimson, pinkish brown
plants:
anise, barley, beet, black walnut, brazil nut, catnip, chamomile, chestnut, chicory, ginseng, coconut, corn, dandelion root, echinacea root, fig, gobo, grape stem, tulip, valerian, yarrow, willow, nutmeg, magnolia, hydrangea
Tarot:
wheel of fortune, temperance
Essential oils/incense:
copaiba balsam, lime, magnolia, mint, norway spruce, nutmeg, oak, rose, red sandalwood, saffron, sage, carnation, heliotrope
Influences:
abundance, business, expansion, fame, gambling, greed, growth, honor, leadership, money, parties, politics, power, responsibilities, royalty, success, visions, wealth
Link to the Masterpost
Uncommon Correspondences: Jupiter 🌼

🌼 Abundance | amplification | exaggeration | expansion | “larger than…”
🌼 Affluence | benefactors | charity
🌼 Judgment | Attorneys and lawyers | courts | church officials | religion
🌼 Philosophy | professional people | professors and one’s education
🌼 Books | publishing
🌼 Celebrations | ceremonies | joviality | luck | optimism | prosperity
🌼 Fat metabolism | weight | arteries
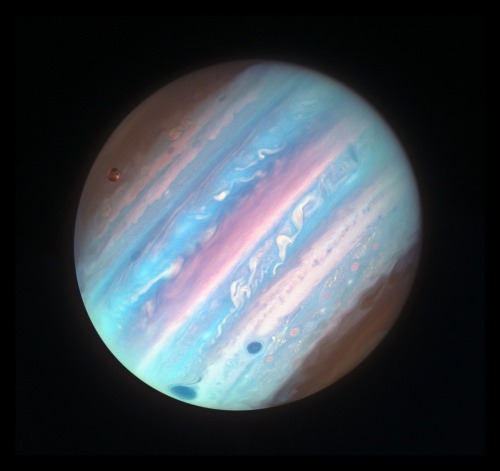



Jupiter (filtered) by Judith Schmidt.

For Jupiter and its limitless expansion.
Real stoked with how this one came out 💪🏻

Jupiter is considered to be a planet of luck, representing wealth of both knowledge and of monetary value, skills and talent development, courage, confidence, duty, and success, as well as self-improvement and developing one’s own individuality.
This spread is to shed light on how Jupiter can help you:
An aspect of yours that Jupiter asks you to focus on
How to remove or overcome any barriers that may get in the way of you expressing or developing this aspect
How you can share this trait with others/How this may help others and yourself
How you can develop this aspect/How Jupiter can help you harmonize with this aspect



Io as seen by the Voyager 1 spacecraft on March 4, 1979 | A triple eclipse on Jupiter: Moons Io, Ganymede & Callisto cast shadows on the planet simultaneously, by NASA, 2004 | Callisto.

main: @a-exsists



Jupiter’s Big Red
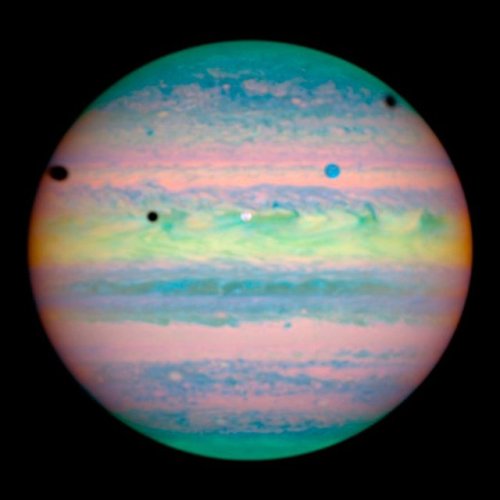

In this composite image from near-infrared light, two of Jupiter’s moons are visible against the planet. The white circle in the middle of Jupiter is Io, and the blue circle at upper right is Ganymede. The three black spots are shadows cast by Io, Ganymede, and another moon, Callisto.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, and E. Karkoschka (University of Arizona)
Solar System 10 Things: Two Years of Juno at Jupiter
Our Juno mission arrived at the King of Planets in July 2016. The intrepid robotic explorer has been revealing Jupiter’s secrets ever since.
Here are 10 historic Juno mission highlights:

1. Arrival at a Colossus
After an odyssey of almost five years and 1.7 billion miles (2.7 billion kilometers), our Juno spacecraft fired its main engine to enter orbit around Jupiter on July 4, 2016. Juno, with its suite of nine science instruments, was the first spacecraft to orbit the giant planet since the Galileo mission in the 1990s. It would be the first mission to make repeated excursions close to the cloud tops, deep inside the planet’s powerful radiation belts.

2. Science, Meet Art
Juno carries a color camera called JunoCam. In a remarkable first for a deep space mission, the Juno team reached out to the general public not only to help plan which pictures JunoCam would take, but also to process and enhance the resulting visual data. The results include some of the most beautiful images in the history of space exploration.

3. A Whole New Jupiter
It didn’t take long for Juno—and the science teams who hungrily consumed the data it sent home—to turn theories about how Jupiter works inside out. Among the early findings: Jupiter’s poles are covered in Earth-sized swirling storms that are densely clustered and rubbing together. Jupiter’s iconic belts and zones were surprising, with the belt near the equator penetrating far beneath the clouds, and the belts and zones at other latitudes seeming to evolve to other structures below the surface.
4. The Ultimate Classroom
The Goldstone Apple Valley Radio Telescope (GAVRT) project, a collaboration among NASA, JPL and the Lewis Center for Educational Research, lets students do real science with a large radio telescope. GAVRT data includes Jupiter observations relevant to Juno, and Juno scientists collaborate with the students and their teachers.
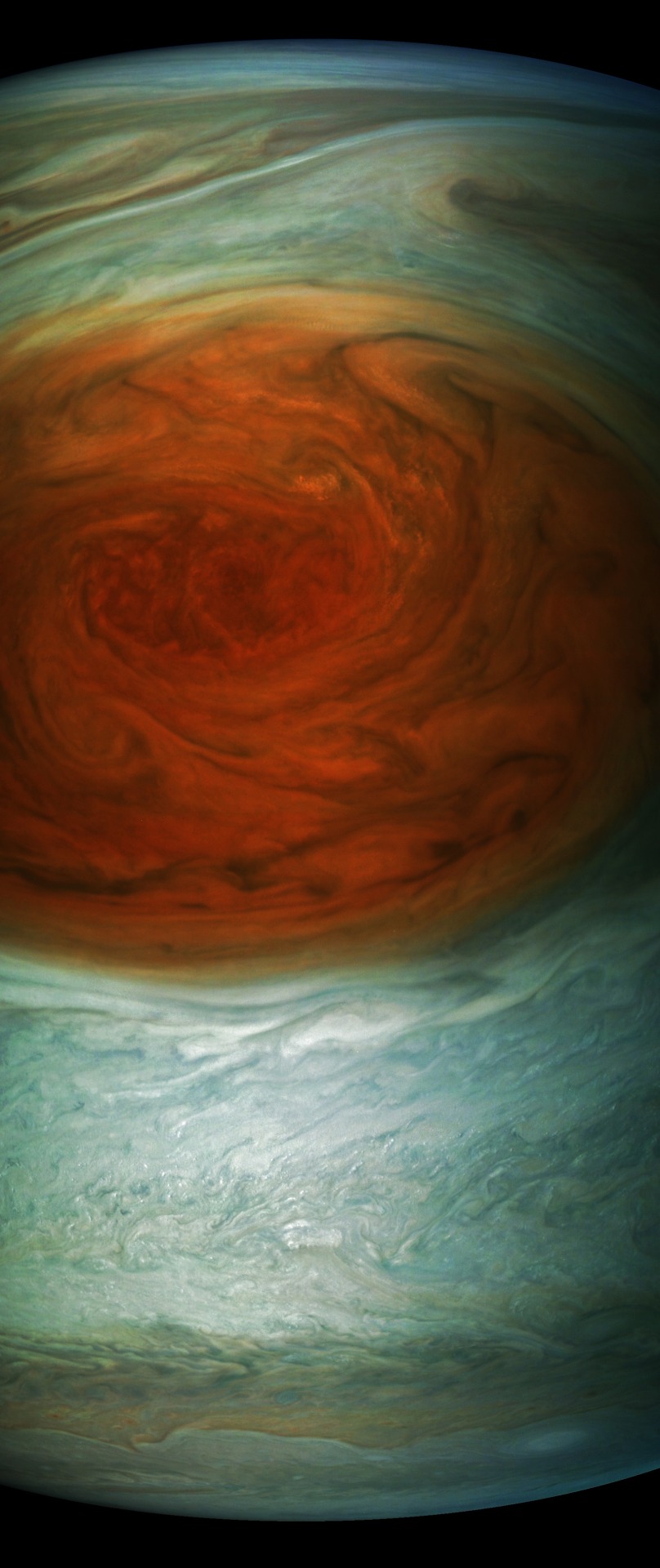

5. Spotting the Spot
Measuring in at 10,159 miles (16,350 kilometers) in width (as of April 3, 2017) Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is 1.3 times as wide as Earth. The storm has been monitored since 1830 and has possibly existed for more than 350 years. In modern times, the Great Red Spot has appeared to be shrinking. In July 2017, Juno passed directly over the spot, and JunoCam images revealed a tangle of dark, veinous clouds weaving their way through a massive crimson oval.
“For hundreds of years scientists have been observing, wondering and theorizing about Jupiter’s Great Red Spot,” said Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator from the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio. “Now we have the best pictures ever of this iconic storm. It will take us some time to analyze all the data from not only JunoCam, but Juno’s eight science instruments, to shed some new light on the past, present and future of the Great Red Spot.”

6. Beauty Runs Deep
Data collected by the Juno spacecraft during its first pass over Jupiter’s Great Red Spot in July 2017 indicate that this iconic feature penetrates well below the clouds. The solar system’s most famous storm appears to have roots that penetrate about 200 miles (300 kilometers) into the planet’s atmosphere.

7. Powerful Auroras, Powerful Mysteries
Scientists on the Juno mission observed massive amounts of energy swirling over Jupiter’s polar regions that contribute to the giant planet’s powerful auroras – only not in ways the researchers expected. Examining data collected by the ultraviolet spectrograph and energetic-particle detector instruments aboard Juno, scientists observed signatures of powerful electric potentials, aligned with Jupiter’s magnetic field, that accelerate electrons toward the Jovian atmosphere at energies up to 400,000 electron volts. This is 10 to 30 times higher than the largest such auroral potentials observed at Earth.
Jupiter has the most powerful auroras in the solar system, so the team was not surprised that electric potentials play a role in their generation. What puzzled the researchers is that despite the magnitudes of these potentials at Jupiter, they are observed only sometimes and are not the source of the most intense auroras, as they are at Earth.
8. Heat from Within
Juno scientists shared a 3D infrared movie depicting densely packed cyclones and anticyclones that permeate the planet’s polar regions, and the first detailed view of a dynamo, or engine, powering the magnetic field for any planet beyond Earth (video above). Juno mission scientists took data collected by the spacecraft’s Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument and generated a 3D fly-around of the Jovian world’s north pole.
Imaging in the infrared part of the spectrum, JIRAM captures light emerging from deep inside Jupiter equally well, night or day. The instrument probes the weather layer down to 30 to 45 miles (50 to 70 kilometers) below Jupiter’s cloud tops.

9. A Highly Charged Atmosphere
Powerful bolts of lightning light up Jupiter’s clouds. In some ways its lightning is just like what we’re used to on Earth. In other ways,it’s very different. For example, most of Earth’s lightning strikes near the equator; on Jupiter, it’s mostly around the poles.

10. Extra Innings
In June, we approved an update to Juno’s science operations until July 2021. This provides for an additional 41 months in orbit around. Juno is in 53-day orbits rather than 14-day orbits as initially planned because of a concern about valves on the spacecraft’s fuel system. This longer orbit means that it will take more time to collect the needed science data, but an independent panel of experts confirmed that Juno is on track to achieve its science objectives and is already returning spectacular results. The spacecraft and all its instruments are healthy and operating nominally.
Read the full web version of this week’s ‘Solar System: 10 Things to Know’ article HERE.
For regular updates, follow NASA Solar System on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
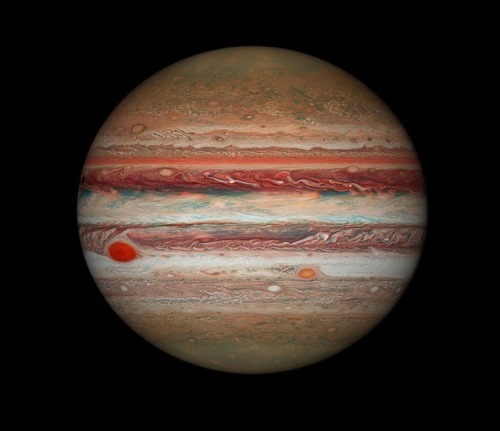

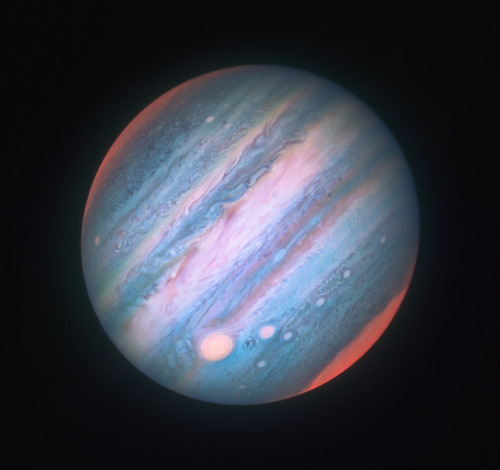
Hubble’s Jupiter and the Shrinking Great Red Spot
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble, OPAL Program, STScI; Processing: Karol Masztalerz







Colors of Jupiter
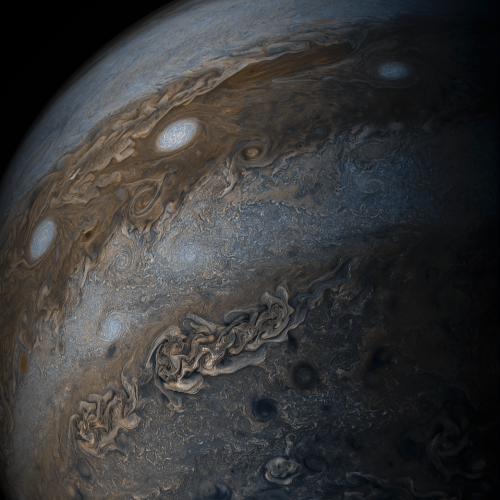

Swirling bands of light and dark clouds on Jupiter are seen in this image made by citizen scientists using data from our Juno spacecraft. Each of the alternating light and dark atmospheric bands in this image is wider than Earth, and each rages around Jupiter at hundreds of miles (km) per hour. The lighter areas are regions where gas is rising, and the darker bands are regions where gas is sinking. This image was acquired on May 19, 2017 from about 20,800 miles (33,400km) above Jupiter’s cloud tops. Learn more
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Gerald Eichstädt /Seán Doran
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Crescent Moon, Jupiter and four of its moons.
Incoming! We’ve Got Science from Jupiter!
Our Juno spacecraft has just released some exciting new science from its first close flyby of Jupiter!

In case you don’t know, the Juno spacecraft entered orbit around the gas giant on July 4, 2016…about a year ago. Since then, it has been collecting data and images from this unique vantage point.

Juno is in a polar orbit around Jupiter, which means that the majority of each orbit is spent well away from the gas giant. But once every 53 days its trajectory approaches Jupiter from above its north pole, where it begins a close two-hour transit flying north to south with its eight science instruments collecting data and its JunoCam camera snapping pictures.

Space Fact: The download of six megabytes of data collected during the two-hour transit can take one-and-a-half days!

Juno and her cloud-piercing science instruments are helping us get a better understanding of the processes happening on Jupiter. These new results portray the planet as a complex, gigantic, turbulent world that we still need to study and unravel its mysteries.
So what did this first science flyby tell us? Let’s break it down…
1. Tumultuous Cyclones

Juno’s imager, JunoCam, has showed us that both of Jupiter’s poles are covered in tumultuous cyclones and anticyclone storms, densely clustered and rubbing together. Some of these storms as large as Earth!

These storms are still puzzling. We’re still not exactly sure how they formed or how they interact with each other. Future close flybys will help us better understand these mysterious cyclones.

Seen above, waves of clouds (at 37.8 degrees latitude) dominate this three-dimensional Jovian cloudscape. JunoCam obtained this enhanced-color picture on May 19, 2017, at 5:50 UTC from an altitude of 5,500 miles (8,900 kilometers). Details as small as 4 miles (6 kilometers) across can be identified in this image.

An even closer view of the same image shows small bright high clouds that are about 16 miles (25 kilometers) across and in some areas appear to form “squall lines” (a narrow band of high winds and storms associated with a cold front). On Jupiter, clouds this high are almost certainly comprised of water and/or ammonia ice.
2. Jupiter’s Atmosphere
Juno’s Microwave Radiometer is an instrument that samples the thermal microwave radiation from Jupiter’s atmosphere from the tops of the ammonia clouds to deep within its atmosphere.

Data from this instrument suggest that the ammonia is quite variable and continues to increase as far down as we can see with MWR, which is a few hundred kilometers. In the cut-out image below, orange signifies high ammonia abundance and blue signifies low ammonia abundance. Jupiter appears to have a band around its equator high in ammonia abundance, with a column shown in orange.

Why does this ammonia matter? Well, ammonia is a good tracer of other relatively rare gases and fluids in the atmosphere…like water. Understanding the relative abundances of these materials helps us have a better idea of how and when Jupiter formed in the early solar system.
This instrument has also given us more information about Jupiter’s iconic belts and zones. Data suggest that the belt near Jupiter’s equator penetrates all the way down, while the belts and zones at other latitudes seem to evolve to other structures.
3. Stronger-Than-Expected Magnetic Field

Prior to Juno, it was known that Jupiter had the most intense magnetic field in the solar system…but measurements from Juno’s magnetometer investigation (MAG) indicate that the gas giant’s magnetic field is even stronger than models expected, and more irregular in shape.

At 7.766 Gauss, it is about 10 times stronger than the strongest magnetic field found on Earth! What is Gauss? Magnetic field strengths are measured in units called Gauss or Teslas. A magnetic field with a strength of 10,000 Gauss also has a strength of 1 Tesla.

Juno is giving us a unique view of the magnetic field close to Jupiter that we’ve never had before. For example, data from the spacecraft (displayed in the graphic above) suggests that the planet’s magnetic field is “lumpy”, meaning its stronger in some places and weaker in others. This uneven distribution suggests that the field might be generated by dynamo action (where the motion of electrically conducting fluid creates a self-sustaining magnetic field) closer to the surface, above the layer of metallic hydrogen. Juno’s orbital track is illustrated with the black curve.
4. Sounds of Jupiter
Juno also observed plasma wave signals from Jupiter’s ionosphere. This movie shows results from Juno’s radio wave detector that were recorded while it passed close to Jupiter. Waves in the plasma (the charged gas) in the upper atmosphere of Jupiter have different frequencies that depend on the types of ions present, and their densities.
Mapping out these ions in the jovian system helps us understand how the upper atmosphere works including the aurora. Beyond the visual representation of the data, the data have been made into sounds where the frequencies and playback speed have been shifted to be audible to human ears.
5. Jovian “Southern Lights”

The complexity and richness of Jupiter’s “southern lights” (also known as auroras) are on display in this animation of false-color maps from our Juno spacecraft. Auroras result when energetic electrons from the magnetosphere crash into the molecular hydrogen in the Jovian upper atmosphere. The data for this animation were obtained by Juno’s Ultraviolet Spectrograph.

During Juno’s next flyby on July 11, the spacecraft will fly directly over one of the most iconic features in the entire solar system – one that every school kid knows – Jupiter’s Great Red Spot! If anybody is going to get to the bottom of what is going on below those mammoth swirling crimson cloud tops, it’s Juno.

Stay updated on all things Juno and Jupiter by following along on social media: Twitter | Facebook | YouTube | Tumblr
Learn more about the Juno spacecraft and its mission at Jupiter HERE.



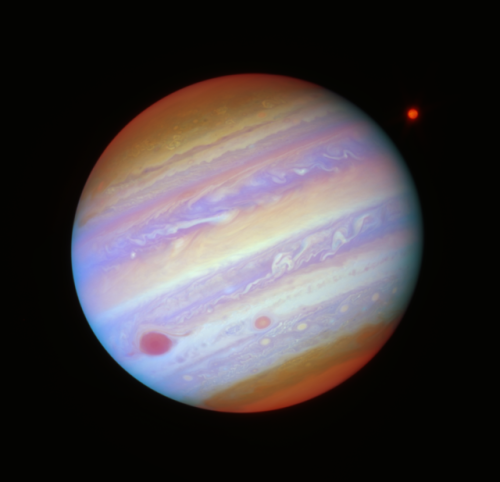
Voyager’s Jupiter and Io
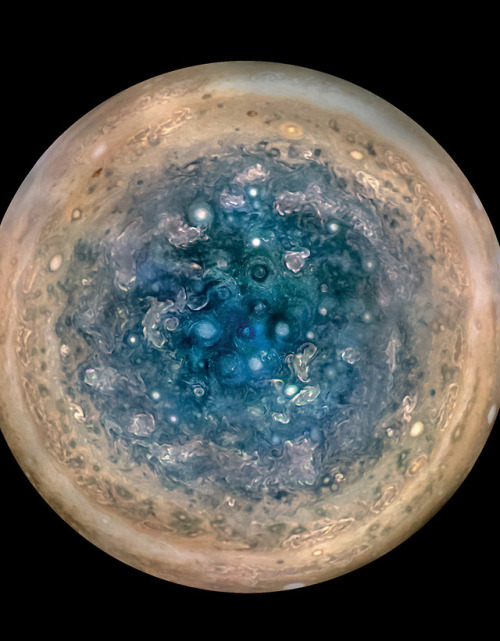
This image shows an enhanced colour, daytime and stereographic image of Jupiter’s south pole.
It was imaged by NASA’s Juno spacecraft from an altitude of 32,000 miles (52,000 kilometers). The oval features are cyclones, up to 600 miles (1,000 kilometers) in diameter.




Everyone is familiar with Jupiter’s great red spot, but did you know Jupiter also has a series of smaller white storms called pearls? Currently there are 8, but anywhere between 6-9 of them have been witnessed over the last three decades. Pretty cool, right?

Imagine yourself in space
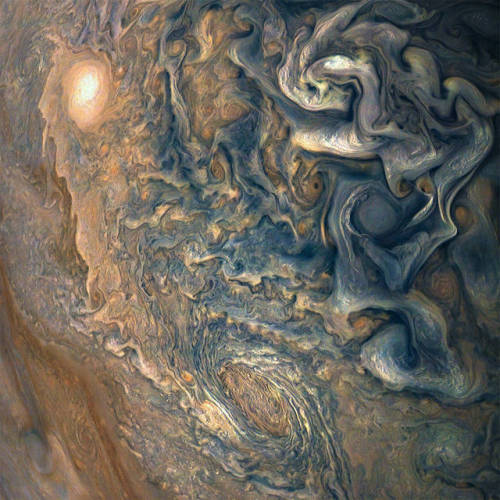
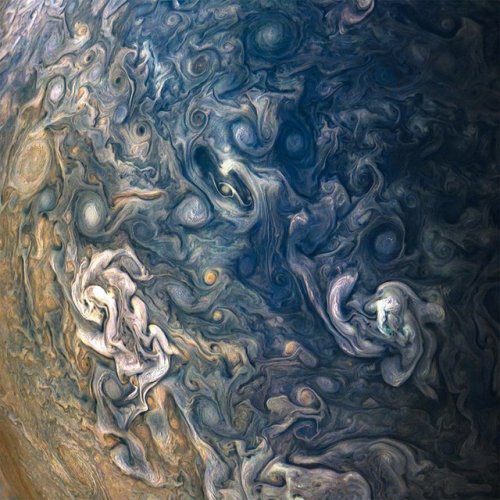






Swirls of Jupiter
Jupiter is a very stormy, turbulent, violent planet. The planet completes a day (or one complete rotation) within roughly 10 hours, which creates massive winds, producing these swirls, and violent storms. The fast rotation coupled with the fact that the planet is nothing but gas greatly multiplies the Coriolis effect. Earth too has a Coriolis effect, this creates the characteristic hurricane shapes and also contributes to the fact that storms will spin the opposite direction in different hemispheres. Luckily, our rotation is slower - our storms are less frequent and less violent than they would be if our days were shorter.
The above images come from the recent Juno mission by NASA.




Jupiter has 12 newly discovered moons!! I really relate to Valetudo, for some reason…



Jupiter’s surface looks like it came from a dream



Jupiter (filtered) by Judith Schmidt.
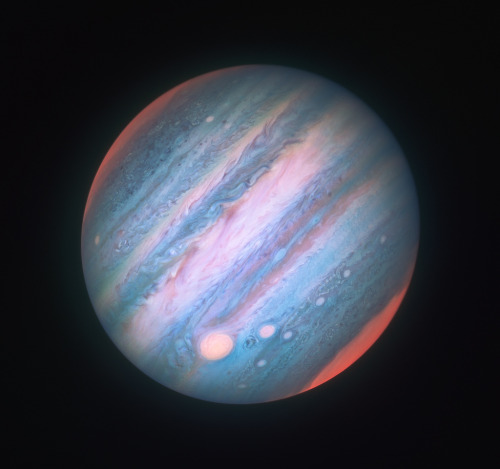
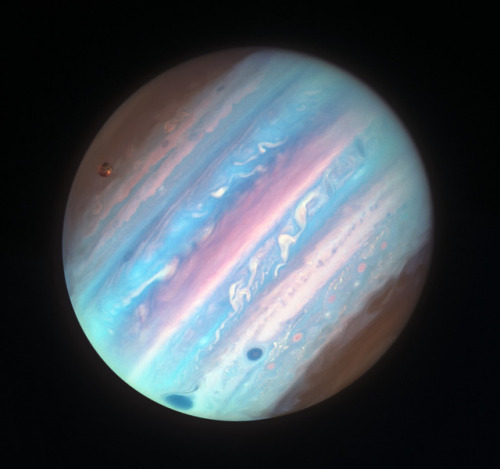


Jupiter in Near-Infrared Jupiter and Ganymede in Near-UV and Blue
by Judy Schmidt

Io transiting Jupiter, photographed by Voyager 1, 31 January 1979. South is up, which is why the Great Red Spot’s in the upper hemisphere.
(As with yesterday’s gif, I’m not fully certain I’ve identified the moon correctly: it looks like Io to me, and the orbital speed seems about right, but for the life of me I can’t get HORIZONS to agree with the pictures: at the time of the first frame (C1541036), my spreadsheet tells me that none of the Galilean moons should even be in the frame. The problem’s fixed if I pretend that the z-coordinate of every position is zero, but that’s cheating….)





CGI renderings of Jupiter, ‘King of the Planets’
The largest planet in the Solar System, likely the first planet to form after the Sun did, continues to dominate over the System with its almost 80 moons and immensely steep and influential gravity well.
Keep reading




Jupiter ✨ gifs made by me :)