This Is Cinema Actually
This is cinema actually
More Posts from Kitunes-02 and Others
The crowns are parasites
okay okay this whole thing comes from the fact that the purple crown is clearly rooted in Shamura's brain and it got me thinking a lil bit :3

as I said, the crowns are parasite, they look for the ideal bearer, to stick onto them for awhile until they can finaly start the process of draining the bearer's life for what you might ask, it's to be more powerful, it's to be more effecient, it's to be more influencial they are dependent on a host to survive they can telepathically comunicate to their bearer for whatever they, either to convince or encourage something as well as discourage honestly, why do you the gods limbs blacken the longer they wear their crown?
I'm still thinking about so like, it could change in the future but I like where it's going :3









“small thread on drawing plus sized characters!”
Source: Ullaiin on Twitter





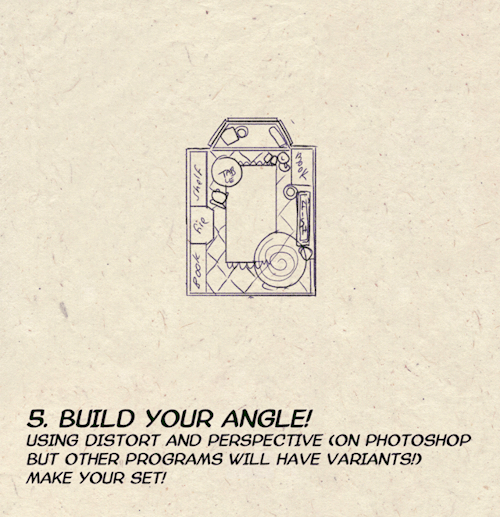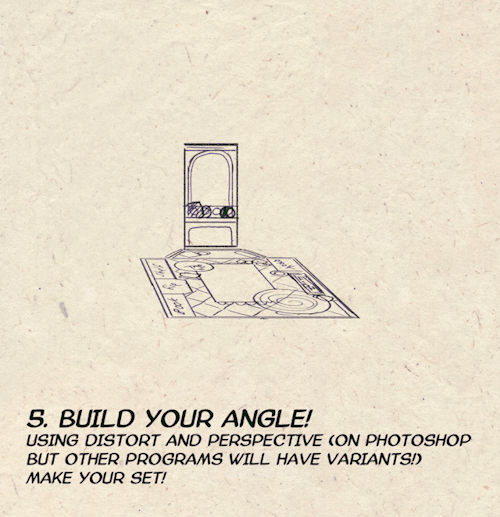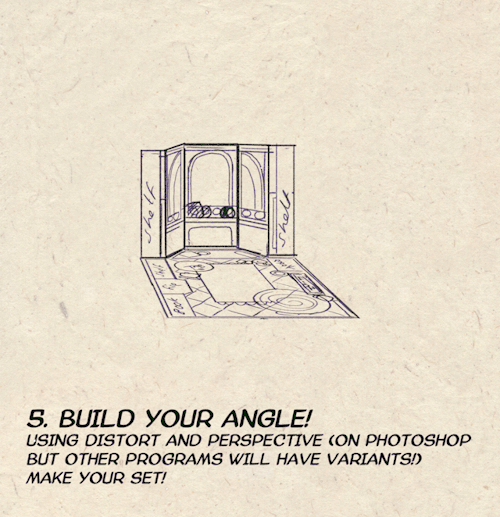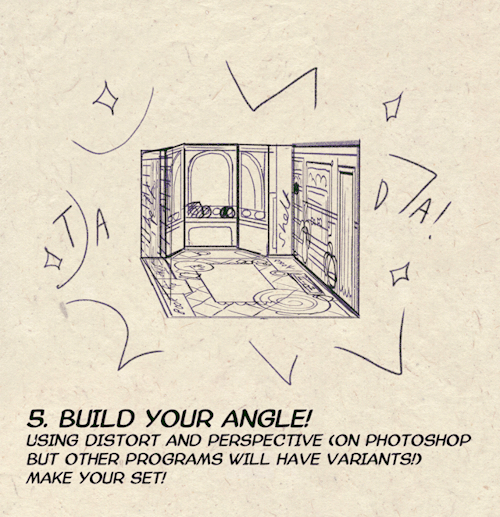



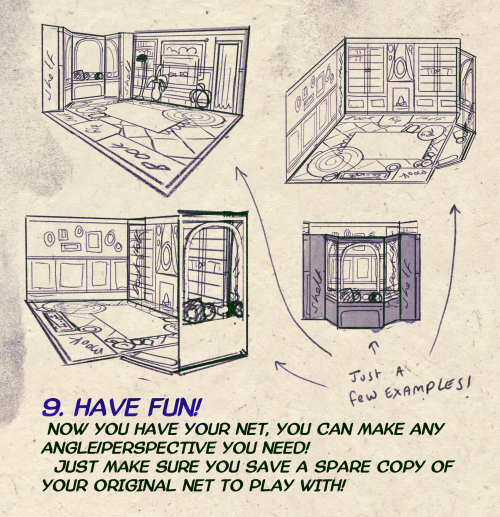
I made a Room Building tutorial! Lemme know if it helps! 🧡
Tip me here| Commission info here!






I took my second ADHD pill a little too late I guess because it was suddenly 4 am and I made this thing about why parasitic organisms are shaped like ways and how to consider that for your fiction settings. Raw text version below the cut for people with busted seeing:
Keep reading
![[Image Source]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/9f3c8930ae15acbb6e0e3956bcbd02ef/f26bba50329d71b2-05/s500x750/88bf47543e6199d4478197d28332a025e8b87f16.jpg)
[Image Source]
Gene Behind Orange Fur in Cats Found at Last
Shared from Science.org.
It would be pretty easy to guess that Garfield was a tomcat even if you didn’t know his name—or didn’t want to peek under his tail. Most orange cats are boys, a quirk of feline genetics that also explains why almost all calicos and tortoiseshells are girls.
Scientists curious about those sex differences—or perhaps just cat lovers—have spent more than 60 years unsuccessfully seeking the gene that causes orange fur and the striking patchwork of colors in calicos and tortoiseshells. Now, two teams have independently found the long-awaited mutation and discovered a protein that influences hair color in a way never seen before in any animal.
“I am fully convinced this is the gene and am happy,” says Carolyn Brown, a University of British Columbia geneticist who was not involved in either study. “It’s a question I’ve always wanted the answer to.”
Scientists have long been fascinated by tortoiseshell and calico cats: the offspring of a black cat and an orange cat. Multicolored cats from such a cross are almost always female, suggesting the gene variant that makes fur orange or black is located on the X chromosome. The male offspring of such a cross are typically unicolor because they inherit just one parent’s X chromosome: We can guess, for instance, that Garfield’s mother is orange because he inherited his only X chromosome from her.**
But female cats inherit an X chromosome from each parent. Cells don’t generally need both, so during embryonic development each cell randomly chooses one X to express genes from. The other chromosome rolls up into a mostly inert ball—a phenomenon called X inactivation. As a result, tortoiseshell cats end up with separate patches of black and orange fur depending on which chromosome was inactivated in that part of their skin. Calico cats add white fur into the mix because they have a second, unrelated genetic mechanism that shuts down pigment production in some cells.
In most mammals, including humans, red hair is caused by mutations in one cell surface protein, Mc1r, that determines whether skin cells called melanocytes produce a dark pigment or a lighter red-yellow pigment in skin or hair. Mutations that make Mc1r less active cause melanocytes to get “stuck” producing the light pigment.
But the gene encoding Mc1r didn’t seem explain where cats’ orange fur came from. It isn’t located on the X chromosome in cats or any other species—and most orange cats don’t have Mc1r mutations. “It’s been a genetic mystery, a conundrum,” says Greg Barsh, a geneticist at Stanford University.
To solve it, Barsh’s team collected skin samples from four orange and four nonorange fetuses from cats at spay-neuter clinics. As a proxy to determine how individual skin cells express genes, the researchers measured the amount of RNA that each melanocyte was producing and determined the gene it encoded. Melanocytes from orange cats, they found, made 13 times as much RNA from a gene called Arhgap36. The gene is located on the X chromosome, which led the team to think they had the key to orange color.
But when the researchers looked at Arhgap36’s genetic sequence in orange cats, they didn’t find any mutations in the DNA that encodes the Arhgap36 protein. Instead, they found the orange cats were missing a nearby stretch of DNA that didn’t affect the protein’s amino acid components but might be involved in regulating how much of it the cell produced. Scanning a database of 188 cat genomes, Barsh’s team found every single orange, calico, and tortoiseshell cat had the exact same mutation. The group reports the discovery this month on the preprint server bioRxiv.
A separate study, also posted to bioRxiv this month, confirms these findings. Similar experiments run by developmental biologist Hiroyuki Sasaki at Kyushu University and his colleagues revealed the same genetic deletion in 24 feral and pet cats from Japan, as well as among 258 cat genomes collected from around the world. They also found that skin from calico cats had more Arghap36 RNA in orange regions than in brown or black regions. Moreover Arhgap36 genes in mice, cats, and humans acquire chemical modifications that silence them on one of the two X chromosomes in females, Sasaki’s team documented, suggesting the gene is subject to X inactivation.
When Barsh and Sasaki learned their respective teams had discovered the same mutation, they decided to post their preprints at the same time. (Because they are preprints, neither study has been peer reviewed.) Both groups further found that increasing the amount of Arhgap36 in melanocytes activates a molecular pathway that switches the cells to producing light red pigment regardless of whether MC1r is active.
No one previously knew Arhgap36 could affect skin or hair coloration—it is involved in many aspects of embryonic development, and major mutations that affect its function throughout the body would probably kill the animal, Barsh says. But because the deletion mutation appears to only affect Arhgap36 function in melanocytes, cats with the mutation are not only healthy, but also cute.
Arhgap36’s inactivation pattern in calicos and tortoiseshells is typical of a gene on the X chromosome, Brown says, but it’s unusual that a deletion mutation would make a gene more active, not less. “There is probably something special about cats.”
Experts are thrilled by the two studies. “It’s a long-awaited gene,” says Leslie Lyons, a feline geneticist at the University of Missouri. The discovery of a new molecular pathway for hair color was unexpected, she says, but she’s not surprised how complex the interactions seem to be. “No gene ever stands by itself.”
Lyons would like to know where and when the mutation first appeared: There is some evidence, she says, that certain mummified Egyptian cats were orange. Research into cat color has revealed all kinds of phenomena, she says, including how the environment influences gene expression. “Everything you need to know about genetics you can learn from your cat.”
A Deletion at the X-linked Arhgap36 Gene Locus is Associated With the Orange Coloration of Tortoiseshell and Calico Cats
Molecular and Genetic Characterization of Sex-linked Orange Coat Color in the Domestic Cat
**Minor correction: Garfield’s mother could also have been a tortoiseshell.

“Pearl painting process by Camilla Cuesta applies to hand-painted gameart texture painting too!”
Source: Twitter at artofjeffp
How to draw: Not white characters
How to draw a Black person
How to colour Black people skin tones
How to draw dreadlocks
How to draw African hair
How to draw curly hair
How to draw braids
How to draw braids part 2
How to draw cornrows
How to draw Bantu knots
How to draw two strand twists
How to draw an East Asian person
How to colour darker skin tones with alcohol markers
How to draw hijabs/traditional Muslim hair coverings (note, he used incorrect terminology, what he called a burqa was actually a niqab! Sorry for the mistake)
How to draw a hijabi girl
All links and art provided by @ itsajart on TikTok
Before you go “mY aRt sTyLe iS dIfFrEnT tHoUgH” you can moderate it and play around with your style to get it to fit.

This is my favorite section of this baking book i recently bought
(1)Learn the rules before you break them + Gather proper references

(2) Understand what you want to break and how


(3) Can't do it? Find someone who can

(4) It's going to look really bad for a while

(5) Have fun with it!

(1) -Yes, I am that kind of artist. Yet, not in the conventional way. I encourage people to go in guns blazing when it comes to drawing something new, then coming out analyzing what they know, and what they need to learn more of right away.
-Here, I broke down the anatomical pieces of Nour and Narinder's face with the same labels so you guys can understand this weird invisible pattern that I follow in my work. Doing this with any animal you're attempting to draw greatly improves your line confidence when drawing different face shapes. Also understanding the biological function for why animals look a certain way helps you keep consistency.
(3) Time to throw any artistic guilt you have for heavily referencing people's art OUT THE WINDOW and start ANALYZING PEOPLE'S WORK YOU WANT TO BE LIKE✨ I've always done this, having a reference of someone else's amazing work right next to my own drawing so I can try and understand how they make their magic work! No shame, no embarrassment, nada. Pure, unadulterated will and spite that I would be just as good as the artist who made me so motivated and happy with their work! I couldn't figure out how to make Nour's face both sheep-like, and humanly expressive, so I looked at a LOT of Zootopia and old Disney art for help!
(2) With how I draw narilamb, I'm still working on it (as you can see) but I wanted to break Narinder's face to be fluffier and slimmer, while Nour's face would be shorter and flatter. If you look at it for too long, it's absolutely going to look weird, in the way that if you look at Anna from Frozen for too long she starts looking really weird. The anatomy isn't meant to be correct or consistent, it's meant to convey the emotion and energy I want out of the characters in that moment. If you're able to properly get that across, then you don't need to think about how broken something looks, as long as your eye is happy enough to trick your brain into thinking what you're seeing is canny.
(4) Yeah, I hate this part too. It's going to look like shit at first. I can't even look at my art from a few months ago when I was figuring out their designs... God, so fucking ugly. If it weren't for the shittiness of those drawings, I would have never gotten here! Wading through the "trust the process" stage always really sucks, but it's absolutely worth the relief of when you finally get something to look right.
(5) Art is work, yes. It's stressful, it's long, it's straining, its draining, it's exclaiming, blah blah blah. But, I try to keep my art FUN. If I find my artwork becoming slow as I depressingly drag my pen over my tablet, I'm failing. You MUST keep spirit and life in your work. The spirit of emptiness or the life of sadness can have a very meaningful place in art, but those can only exist with keeping work light, easy, and fun! If you're stressing how a specific thing looks or how you can't get something to look right no matter what, FUCK IT. Draw something to bring the flavor back in your work! I'm kind of rambling, but just, HAVE FUN!✨️ Be messy, scream, laugh, slash canvases, throw paint, smash sculptures, tear apart books, GO CRAZY

To all my wildlife, ecology, biology, nature enthusiasts: if you haven't already checked it out, PLEASE check out The Wild with Chris Morgan. It's a fantastic podcast that I've been consuming voraciously these last few weeks. It touches on all kinds of animals, biomes and regions, and issues that impact conservation. He talks with experts as well as civilians that have a vested interest in each animal or plant and it's absolutely amazing to listen to. Cannot praise it highly enough.
https://www.thewildpod.org/
-
 secondhandirrelevance reblogged this · 1 week ago
secondhandirrelevance reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 humanoid-desu reblogged this · 1 week ago
humanoid-desu reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 humanoid-desu liked this · 1 week ago
humanoid-desu liked this · 1 week ago -
 francisnyx reblogged this · 1 week ago
francisnyx reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 sapphicbtch liked this · 1 week ago
sapphicbtch liked this · 1 week ago -
 deathkiss-aka-kathrencullen reblogged this · 1 week ago
deathkiss-aka-kathrencullen reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 deathkiss-aka-kathrencullen liked this · 1 week ago
deathkiss-aka-kathrencullen liked this · 1 week ago -
 violetablood reblogged this · 1 week ago
violetablood reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 im-a-jinxed-potato liked this · 1 week ago
im-a-jinxed-potato liked this · 1 week ago -
 namewentbrrrandwaybeyondthat reblogged this · 1 week ago
namewentbrrrandwaybeyondthat reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 halpya reblogged this · 1 week ago
halpya reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 lilmissmutant reblogged this · 1 week ago
lilmissmutant reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 pacmanthepeach reblogged this · 1 week ago
pacmanthepeach reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 fuzzyturtlechild reblogged this · 1 week ago
fuzzyturtlechild reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 fleetofwarships reblogged this · 1 week ago
fleetofwarships reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 fleetofwarships liked this · 1 week ago
fleetofwarships liked this · 1 week ago -
 ya-bumblebee-babe reblogged this · 1 week ago
ya-bumblebee-babe reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 jinxstarfire reblogged this · 1 week ago
jinxstarfire reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 deborahpflover reblogged this · 1 week ago
deborahpflover reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 thedynamicworm reblogged this · 1 week ago
thedynamicworm reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 thedynamicworm liked this · 1 week ago
thedynamicworm liked this · 1 week ago -
 nattyjeans liked this · 1 week ago
nattyjeans liked this · 1 week ago -
 onyxthewriter1041 liked this · 1 week ago
onyxthewriter1041 liked this · 1 week ago -
 one-of-the-them reblogged this · 1 week ago
one-of-the-them reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 frankensteinspenisenvy reblogged this · 1 week ago
frankensteinspenisenvy reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 frankensteinspenisenvy liked this · 1 week ago
frankensteinspenisenvy liked this · 1 week ago -
 huginsmemory reblogged this · 1 week ago
huginsmemory reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 mngwa reblogged this · 1 week ago
mngwa reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 rattoes420 liked this · 1 week ago
rattoes420 liked this · 1 week ago -
 gaycodedvillainy reblogged this · 1 week ago
gaycodedvillainy reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 digitalis-obscura liked this · 1 week ago
digitalis-obscura liked this · 1 week ago -
 vhs-dvd-comboplayer liked this · 1 week ago
vhs-dvd-comboplayer liked this · 1 week ago -
 raindrops-and-bubbles reblogged this · 1 week ago
raindrops-and-bubbles reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 raindrops-and-bubbles liked this · 1 week ago
raindrops-and-bubbles liked this · 1 week ago -
 notshelbie reblogged this · 1 week ago
notshelbie reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 graciereadshannigram liked this · 1 week ago
graciereadshannigram liked this · 1 week ago -
 eggpla reblogged this · 1 week ago
eggpla reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 korasigma reblogged this · 1 week ago
korasigma reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 madmonnette reblogged this · 1 week ago
madmonnette reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 villainouspotential reblogged this · 1 week ago
villainouspotential reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 sevenstevearmy reblogged this · 1 week ago
sevenstevearmy reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 crowleys-hips reblogged this · 1 week ago
crowleys-hips reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 crowleys-hips liked this · 1 week ago
crowleys-hips liked this · 1 week ago -
 starrykn1ght reblogged this · 1 week ago
starrykn1ght reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 brokenchordae liked this · 1 week ago
brokenchordae liked this · 1 week ago -
 thehiccupwhisperer reblogged this · 1 week ago
thehiccupwhisperer reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 memyselfandwifi reblogged this · 1 week ago
memyselfandwifi reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 ech0light reblogged this · 1 week ago
ech0light reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 whatthedamnhelldude reblogged this · 1 week ago
whatthedamnhelldude reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 whatthedamnhelldude liked this · 1 week ago
whatthedamnhelldude liked this · 1 week ago

main/art account @kitunes-0 // Here I repost stuff I want to come back to later!
129 posts