Solar System: Top 5 Things To Know This Week
Solar System: Top 5 Things to Know This Week
1. A Ceres of Fortunate Events

Our Dawn mission continues its exploration at Ceres, and the team is working with the data coming back to Earth, looking for explanations for the tiny world’s strange features. Follow Dawn’s expedition HERE.
2. Icy Moon Rendezvous

One of the most interesting places in the entire solar system is Saturn’s moon Enceladus, with its underground ocean and spectacular geyser plume. This month, the Cassini spacecraft will be buzzing close by Enceladus several times, the last such encounters of the mission. On October 14, Cassini will perform a targeted flyby at a distance of just 1,142 miles (1,838 kilometers) over the moon’s northern latitudes. Ride along with Cassini HERE.
3. Make Your Own Mars Walkabout
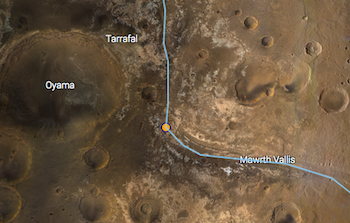
You can retrace Opportunity’s journey, see where the Curiosity rover is now, or even follow along with fictional astronaut Mark Watney from The Martian movie using the free online app MarsTrek. The app lets you zoom in on almost any part of the planet and see images obtained by our spacecraft, so you can plan your on Red Planet excursion. Take a hike HERE.
4. Elusive Features on Jupiter

New imagery from our Hubble Space Telescope is capturing details never before seen on Jupiter. High-resolution maps and spinning globes, rendered in the 4K Ultra HD format, reveal an elusive wave and changes to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. Explore Jupiter HERE.
5. Mr. Blue Sky

Another week, another amazing picture from Pluto. The first color images of Pluto’s atmospheric hazes, returned by our New Horizons spacecraft last week, reveal that the hazes are blue. Who would have expected a blue sky in the Kuiper Belt? Most of the data collected during July’s Pluto flyby remains aboard the spacecraft, but the team publishes new batches of pictures and other findings on a weekly basis. Keep up with the latest HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Water on Mars!

Did you hear? New findings from our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) provide the strongest evidence yet that liquid water flows intermittently on present-day Mars.
Using an imaging spectrometer on MRO, we found hydrated minerals on slopes where mysterious streaks are seen on Mars. One thing that researchers noticed was that the darkish streaks appear to ebb and flow over time. During warm seasons, they darken and then fade in cooler seasons.

When discovered in 2010, these downhill flows known as recurring slope lineae (RSL) were thought to be related to liquid water. With the recent spectral detection of molecular water, we’re able to say it’s likely a shallow subsurface flow explains the darkening.
Mars is so cold, how could liquid water flow there? Great question! Since this liquid water is briny, the freezing point would be lower than that of pure water. Also, these saline slopes appear on Mars when temperatures are above minus 10 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 23 Celsius).
The dark, narrow streaks flowing downhill in the below image are roughly the length of a football field.

So there’s water, but how much? Currently we think this area has a very small amount of water, probably just enough to wet the top layer of the surface of Mars. The streaks are around four to five meters wide and 200 to 300 meters long.
Could humans drink this water? The salts in the water appear to be perchlorates, so you probably wouldn’t want to drink the water. It would most likely be very salty and would need to be purified before human consumption.
Perchlorate...What is that? A perchlorate is a salt that absorbs water from the air. Learn more about how it’s helping us unlock the mysteries of Mars in this video:
What’s next? We want to look for more locations where brine flows may occur. We have only covered 3% of Mars at resolutions high enough to see these features.
For more information on the Mars announcement, visit our Journey to Mars landing page. There is also a full recap of the press conference HERE, and a short recap below.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
5 Unpredictable Things Swift Has Studied (and 1 It’s Still Looking For)
Our Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory — Swift for short — is celebrating its 20th anniversary! The satellite studies cosmic objects and events using visible, ultraviolet, X-ray, and gamma-ray light. Swift plays a key role in our efforts to observe our ever-changing universe. Here are a few cosmic surprises Swift has caught over the years — plus one scientists hope to see.

#BOAT
Swift was designed to detect and study gamma-ray bursts, the most powerful explosions in the universe. These bursts occur all over the sky without warning, with about one a day detected on average. They also usually last less than a minute – sometimes less than a few seconds – so you need a telescope like Swift that can quickly spot and precisely locate these new events.
In the fall of 2022, for example, Swift helped study a gamma-ray burst nicknamed the BOAT, or brightest of all time. The image above depicts X-rays Swift detected for 12 days after the initial flash. Dust in our galaxy scattered the X-ray light back to us, creating an extraordinary set of expanding rings.

Star meets black hole
Tidal disruptions happen when an unlucky star strays too close to a black hole. Gravitational forces break the star apart into a stream of gas, as seen above. Some of the gas escapes, but some swings back around the black hole and creates a disk of debris that orbits around it.
These events are rare. They only occur once every 10,000 to 100,000 years in a galaxy the size of our Milky Way. Astronomers can’t predict when or where they’ll pop up, but Swift’s quick reflexes have helped it observe several tidal disruption events in other galaxies over its 20-year career.

Active galaxies
Usually, we think of galaxies – and most other things in the universe – as changing so slowly that we can’t see the changes. But about 10% of the universe’s galaxies are active, which means their black hole-powered centers are very bright and have a lot going on. They can produce high-speed particle jets or flares of light. Sometimes scientists can catch and watch these real-time changes.
For example, for several years starting in 2018, Swift and other telescopes observed changes in a galaxy’s X-ray and ultraviolet light that led them to think the galaxy’s magnetic field had flipped 180 degrees.

Magnetic star remnants
Magnetars are a type of neutron star, a very dense leftover of a massive star that exploded in a supernova. Magnetars have the strongest magnetic fields we know of — up to 10 trillion times more intense than a refrigerator magnet and a thousand times stronger than a typical neutron star’s.
Occasionally, magnetars experience outbursts related to sudden changes in their magnetic fields that can last for months or even years. Swift detected such an outburst from a magnetar in 2020. The satellite’s X-ray observations helped scientists determine that the city-sized object was rotating once every 10.4 seconds.

Comets
Swift has also studied comets in our own solar system. Comets are town-sized snowballs of frozen gases, rock, and dust. When one gets close to our Sun, it heats up and spews dust and gases into a giant glowing halo.
In 2019, Swift watched a comet called 2I/Borisov. Using ultraviolet light, scientists calculated that Borisov lost enough water to fill 92 Olympic-size swimming pools! (Another interesting fact about Borisov: Astronomers think it came from outside our solar system.)

What's next for Swift?
Swift has studied a lot of cool events and objects over its two decades, but there are still a few events scientists are hoping it’ll see.
Swift is an important part of a new era of astrophysics called multimessenger astronomy, which is where scientists use light, particles, and space-time ripples called gravitational waves to study different aspects of cosmic events.

In 2017, Swift and other observatories detected light and gravitational waves from the same event, a gamma-ray burst, for the first time. But what astronomers really want is to detect all three messengers from the same event.
As Swift enters its 20th year, it’ll keep watching the ever-changing sky.
Keep up with Swift through NASA Universe on X, Facebook, and Instagram. And make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
It’s a U.S. Record! Cumulative Days in Space: 383

Today, Astronaut Scott Kelly has broken the record for longest time spent in space by a U.S. astronaut! Over the course of his four missions, Kelly has spent 383 cumulative days in space. This record was previously held by Astronaut Mike Fincke, with 382 days in space over three flights. Here are some more fun facts about this milestone:
4: The number of humans that have spent a year or more in orbit on a single mission
215 Days: The record currently held by Mike Lopez-Alegria for most time on a single spaceflight by U.S. astronaut. On Oct. 29, Kelly will break this record
377 Days: The current record for most days in space by a U.S. female astronaut, held by Peggy Whitson
879 Days: The record for most cumulative days in space by a human, currently held by Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka

Why Spend a Year in Space?
Kelly’s One-Year Mission is an important stepping stone on our journey to Mars and other deep space destinations. These investigations are expected to yield beneficial knowledge on the medical, psychological and biomedical challenges faced by astronauts during long-duration spaceflight.
Kelly is also involved in the Twins Study, which consists of ten separate investigations that are being conducted with his twin brother, who is on Earth. Since we are able to study two individuals who have the same genetics, but are in different environments for one year, we can gain a broader insight into the subtle effects and changes that may occur in spaceflight.
For regular updates on Kelly’s one-year mission aboard the space station, follow him on social media: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Astronaut Journal Entry - Alarms
Currently, six humans are living and working on the International Space Station, which orbits 250 miles above our planet at 17,500mph. Below you will find a real journal entry, written in space, by NASA astronaut Scott Tingle.
To read more entires from this series, visit our Space Blogs on Tumblr.

The smoke detectors have been setting off alarms. This happens routinely due to dust circulating in the modules, but every alarm is taken seriously. This is the third time that the alarm has sounded while I was using the Waste & Hygiene Compartment (toilet). I am starting to think that my actions are causing the alarms…. maybe I should change my diet?
Find more ‘Captain’s Log’ entries HERE.
Follow NASA astronaut Scott Tingle on Instagram and Twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
do you have a favourite planet etc?
Hubble Space Telescope
You’ve probably heard of our Hubble Space Telescope, but have you had the chance to actually take a look at the amazing images it has captured for us over the years? Since Hubble launched in April 1990, it has made more than 1.2 million observations, some to locations more than 13.4 billion light years from Earth!
Hubble can see astronomical objects with an angular size of 0.05 arc seconds, which is like seeing a pair of fireflies in Tokyo from your home in Maryland…yea, that’s pretty far! This accuracy allows us to see images like this one of Little Gem Nebula, roughly 6,000 light-years away from us.

Images from Hubble are regularly released to the public, and are some of the most breathtaking views in the Universe. Images like this one of Lagoon Nebula, in the constellation of Sagittarius, not only make for amazing desktop screen-savers, but provide us with valuable scientific information about distant stars and galaxies, as well as the planets in our solar system.

We recently celebrated Hubble’s 25th Anniversary, and look forward to many more years of discovery and captivating images.
Reinventing the Wheel
Planning a trip to the Moon? Mars? You’re going to need good tires…

Exploration requires mobility. And whether you’re on Earth or as far away as the Moon or Mars, you need good tires to get your vehicle from one place to another. Our decades-long work developing tires for space exploration has led to new game-changing designs and materials. Yes, we’re reinventing the wheel—here’s why.
Wheels on the Moon

Early tire designs were focused on moving hardware and astronauts across the lunar surface. The last NASA vehicle to visit the Moon was the Lunar Roving Vehicle during our Apollo missions. The vehicle used four large flexible wire mesh wheels with stiff inner frames. We used these Apollo era tires as the inspiration for new designs using newer materials and technology to better function on a lunar surface.
Up springs a new idea

During the mid-2000s, we worked with industry partner Goodyear to develop the Spring Tire, an airless compliant tire that consists of several hundred coiled steel wires woven into a flexible mesh, giving the tires the ability to support high loads while also conforming to the terrain. The Spring Tire has been proven to generate very good traction and durability in soft sand and on rocks.
Spring Tires for Mars

A little over a year after the Mars Curiosity Rover landed on Mars, engineers began to notice significant wheel damage in 2013 due to the unexpectedly harsh terrain. That’s when engineers began developing new Spring Tire prototypes to determine if they would be a new and better solution for exploration rovers on Mars.

In order for Spring Tires to go the distance on Martian terrain, new materials were required. Enter nickel titanium, a shape memory alloy with amazing capabilities that allow the tire to deform down to the axle and return to its original shape.
These tires can take a lickin’

After building the shape memory alloy tire, Glenn engineers sent it to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory’s Mars Life Test Facility. It performed impressively on the punishing track.
Why reinvent the wheel? It’s worth it.

New, high performing tires would allow lunar and Mars rovers to explore greater regions of the surface than currently possible. They conform to the terrain and do not sink as much as rigid wheels, allowing them to carry heavier payloads for the same given mass and volume. Also, because they absorb energy from impacts at moderate to high speeds, there is potential for use on crewed exploration vehicles which are expected to move at speeds significantly higher than the current Mars rovers.
Airless tires on Earth

Maybe. Recently, engineers and materials scientists have been testing a spinoff tire version that would work on cars and trucks on Earth. Stay tuned as we continue to push the boundaries on traditional concepts for exploring our world and beyond.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
From the unique vantage point of about 25,000 feet above Earth, our Associate Administrator of Science at NASA, Dr. Thomas Zurbuchen, witnessed the 2017 eclipse. He posted this video to his social media accounts saying, “At the speed of darkness...watch as #SolarEclipse2017 shadow moves across our beautiful planet at <1 mile/second; as seen from GIII aircraft”.
Zurbuchen, along with NASA Acting Administrator Robert Lightfoot, Associate Administrator Lesa Roe traveled on a specially modified Gulfstream III aircraft flying north over the skies of Oregon.
In order to capture images of the event, the standard windows of the Gulfstream III were replaced with optical glass providing a clear view of the eclipse. This special glass limits glare and distortion of common acrylic aircraft windows. Heaters are aimed at the windows where the imagery equipment will be used to prevent icing that could obscure a clear view of the eclipse.
Learn more about the observations of the eclipse made from this aircraft HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Astronaut Journal Entry - The Last Week
Currently, six humans are living and working on the International Space Station, which orbits 250 miles above our planet at 17,500mph. Below you will find a real journal entry, written in space, by NASA astronaut Scott Tingle.
To read more entires from this series, visit our Space Blogs on Tumblr.

I can’t believe that Expedition 55 is already over. Today is Sunday, and we will depart the International Space Station (ISS) next Sunday morning (June 3).
168 days in space.
There have been many challenging moments, but even more positive highlights of our time on ISS. The new crew from the Soyuz MS-08 spacecraft (Oleg Artymyev, Drew Feustel and Ricky Arnold) joined Norishige Kanai (Nemo), Anton Shkaplerov and I last March. Since then, we have completed two spacewalks, captured and released the SpaceX Dragon-14 cargo craft, captured the Cygnus OA-9 cargo craft and completed a myriad of maintenance and science activities.

The team on the ground controlling, monitoring, supporting and planning has been amazing. It is always great to work with them, and especially during the moments where the equipment, tools, procedures or crew need help. It is incredible to see how much a good team can accomplish when methodically placing one foot in front of the other.
I have been lucky in that the first crew (Mark Vande Hei, Joe Acaba and Alexander Misurkin (Sasha)) and the second crew (Drew, Ricky and Oleg) were all amazing to work with. I do believe the planets aligned for my mission onboard ISS.

Drew and Ricky have been friends forever, and listening to them nip at each other provided a ton of great humor for the ground and for us. Their one-liners to each other reminded me of several scenes from the movie Space Cowboys.
This a great example that happened as I was writing this log entry:
Ricky: Hey Maker, is this your smoothie?
Maker: No.
Ricky: It must be Drew’s.
Drew: Hey Ricky, don’t drink my smoothie.
Ricky: What smoothie? This one has my name on it (as he writes his name on it).
Drew: Okay, Grandpa Underpants, hands off my smoothie.
Ricky: Okay, Feustelnaut – we have rules around here, so this is my smoothie now!
All: Much laughing. (To quote my kids: “LOL!”)
One the hardest things to do in space is to maintain positive control of individual items such as tools, spare parts, fasteners, etc. We try very hard not to lose things, but even with all of the attention and positive control, items can still float away and disappear.
We generally hold items in a crew transfer bag (CTB). Inside the CTB are many items for the system that it supports. When the CTB is opened, the items are free floating inside the bag and tend to escape. It is very difficult to maintain control of the items – especially if they are small, do not have Velcro, or when the daily schedule is so tight that we are rushing to stay on time. We always try to close the CTB’s and Ziploc bags after removing or replacing each item to maintain positive control, but this takes much more time to do for individual items, and if the timeline is tight, we absorb more risk by rushing.

The same applies for tools, which we usually keep in a Ziploc bag while working on individual systems and tasks. Last month, I was installing a new low temperature cooling loop pump that had failed a month or two earlier. I gathered the needed tools into my modified (with Velcro) Ziploc bag as I always do and floated over to the work area. When I got there, one of the tools that I had gathered was missing. I looked for 30 minutes, and could not find it. Lost items are very hard to find because the items that escape are usually barely moving and blend in with the environment very quickly. A lost item could be right in front of us and we would never see it.

Our crew, after learning these lessons, decided that when anyone loses something, we would tell the other crew members what we had lost with a general location. This has had a huge impact on finding items. If a different crew member can help within the first minutes of losing an item, the new crew member has an excellent chance of finding the item. We have proven this technique several times during the expedition – and Nemo was the very best at quickly finding lost items. But, in my case, we still could not find the missing tool. Our amazing ground team understood and vectored me to a replacement tool and I finished the job. I spent the next 3 weeks watching, looking and never forgetting about the lost tool. Then, one day last week, Oleg came to the lab and handed us a tool he had found in his Soyuz spacecraft, way on the aft side of the ISS. Amazing. We finally found the tool and I was happy again. This was a lucky ending. ISS has many corners, crevices and hard-to-see areas where missing items could hide and never be found.

We captured a Cygnus cargo craft last Thursday. I was very impressed with the entire team. Our specialists and training professionals in Mission Control did a great job preparing the necessary procedures and making sure we were proficient and ready to conduct operations. The robotic arm is a wonderful system that we could not operate ISS without. Being in space, however, it has some very unique handling qualities. If you think about a spring-mass-damper system just as you did during physics or control theory class, and then remove the damper, you will see a system that is very subject to slow rate oscillations.
In test pilot terms, damping ratio is very low and the latency is well over a half of a second. Also in test pilot terms – this is a pilot-induced oscillations (PIO) generator. These characteristics require crew to “fly” the robotic arm using open-loop techniques, which requires a huge amount of patience. Test pilots are sometimes not very patient, but understanding the system and practicing with the incredible simulators that our ground team built and maintain help keep our proficiency as high as possible. The capture went flawlessly, and I was very impressed with the professionalism across the board – crew, flight controllers and training professionals – what a great job!

Drew, Ricky and I got to play guitar a few times while on ISS. This was fun! Drew connected pickups to the acoustic guitars and then connected the pickups to our tablets for amplification. I’ve never heard an acoustic guitar sound like an electric guitar amped up for heavy metal before. We had a great jam on the song “Gloria”, and a couple others. Rock on!
Last night we had our last movie night. The entire crew gathered in Node 2 and watched Avengers Infinity Wars on the big screen. We enjoy each other’s company, as we did during Expedition 54, and this was a welcome break from the daily grind of trying to complete the required stowage, maintenance and science activities while preparing for departure.
Our last full weekend here on ISS. I gave myself a haircut. We usually clean our spaces each weekend to make sure we can maintain a decent level of organization, efficiency and morale. This weekend is no different, and it is time for me to vacuum out all of our filters and vents. You’d be amazed at what we find!
The top 5 things I will miss when I am no longer in space:
The incredible team that supports ISS operations from our control centers
The camaraderie onboard ISS
The breathtaking view of the Earth, Moon, Sun and Stars
Floating/flying from location to location with very little effort
Operations in the extreme environment of space
Find more ‘Captain’s Log’ entries HERE.
Follow NASA astronaut Scott Tingle on Instagram and Twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Which is scarier? Launch VS re-entry?
-
 deathicus-sling reblogged this · 2 years ago
deathicus-sling reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 softeningandripening liked this · 5 years ago
softeningandripening liked this · 5 years ago -
 fredrick-smith liked this · 7 years ago
fredrick-smith liked this · 7 years ago -
 impala-moose liked this · 7 years ago
impala-moose liked this · 7 years ago -
 madokakaname1 reblogged this · 7 years ago
madokakaname1 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ageorgebir liked this · 8 years ago
ageorgebir liked this · 8 years ago -
 juliejuno reblogged this · 8 years ago
juliejuno reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 weeabooslut liked this · 8 years ago
weeabooslut liked this · 8 years ago -
 amigo155 liked this · 8 years ago
amigo155 liked this · 8 years ago -
 jaihind2110 liked this · 8 years ago
jaihind2110 liked this · 8 years ago -
 juliejuno reblogged this · 8 years ago
juliejuno reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 shippingtech-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
shippingtech-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 four-leaf-charm reblogged this · 9 years ago
four-leaf-charm reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 yeezynation8-blog liked this · 9 years ago
yeezynation8-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 aegisoracle liked this · 9 years ago
aegisoracle liked this · 9 years ago -
 happy420borderline liked this · 9 years ago
happy420borderline liked this · 9 years ago -
 seemply-d-best reblogged this · 9 years ago
seemply-d-best reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 annesully liked this · 9 years ago
annesully liked this · 9 years ago -
 megaradcollectionwolfthings-blog liked this · 9 years ago
megaradcollectionwolfthings-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 manicuredforwar reblogged this · 9 years ago
manicuredforwar reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 manicuredforwar liked this · 9 years ago
manicuredforwar liked this · 9 years ago -
 stormy-child reblogged this · 9 years ago
stormy-child reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tommie-james liked this · 9 years ago
tommie-james liked this · 9 years ago -
 theedsagroup-blog liked this · 9 years ago
theedsagroup-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 mobdividual liked this · 9 years ago
mobdividual liked this · 9 years ago -
 proffesionaldreamer reblogged this · 9 years ago
proffesionaldreamer reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 alpacachigga reblogged this · 9 years ago
alpacachigga reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 khaled-taleb-blog liked this · 9 years ago
khaled-taleb-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 anadeansky liked this · 9 years ago
anadeansky liked this · 9 years ago -
 faradayscandle liked this · 9 years ago
faradayscandle liked this · 9 years ago -
 iymerc01 liked this · 9 years ago
iymerc01 liked this · 9 years ago -
 grelse reblogged this · 9 years ago
grelse reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 fiamontague reblogged this · 9 years ago
fiamontague reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 thatgirlrobyn97 liked this · 9 years ago
thatgirlrobyn97 liked this · 9 years ago -
 melonssoup reblogged this · 9 years ago
melonssoup reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 fuyunoakegata reblogged this · 9 years ago
fuyunoakegata reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 prwtiapototelos liked this · 9 years ago
prwtiapototelos liked this · 9 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts