Space Stamps
Space Stamps
Coming in to a post office near you: new “Views of Our Planets: Forever stamps featuring iconic images of the planets in our solar system, including the well-known “Blue Marble” photo of Earth.

New “Pluto Explored” Forever stamps commemorating the July 2015 flyby of Pluto by our New Horizons spacecraft are also being issued for online purchase.

The May 31 first-day-of-issue dedication ceremony for the Pluto and planetary stamps will be in New York City at the World Stamp Show. This international gathering of stamp collectors occurs only once each decade in the United States, and – with more than 250,000 visitors expected to attend – is the largest stamp show in the world.

The Pluto stamps are of special significance to the New Horizons team, which placed a 20-cent 1991 “Pluto: Not Yet Explored” stamp on board the spacecraft. On July 14, 2015, New Horizons carried the stamp on its history-making journey to Pluto and beyond, as jubilant members of the mission team celebrated with a large print, striking the words “not yet.”

The above pane of 16 Forever stamps, the Postal Service showcases some of the more visually compelling historic, full-disk images of the planets obtained during the last half-centruy of our space exploration. Eight new colorful Forever stamps – each shown twice – feature Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
This isn’t the first time that space has been featured on postal stamps. In the past, many different space images and missions have been highlighted on the tiny pieces of paper you stick on the corner of your mail.
Here’s a look at a few space stamps of the past:
Nebulae

Stamps depicting multiple nebulae seen by the Hubble Space Telescope were released in 2000.
Pioneer 10

Launched in 1972, Pioneer 10 was the first spacecraft to travel through the asteroid belt and obtain close-ups of Jupiter
U.S. Launches Satellites

This stamp, released in 1999, depicts the post World War II race in space exploration.
Alan Shepard: First American in Space

This stamp, released in 2011, featured Alan Shepard, the first American in space. Flying on the Mercury spacecraft, Shepard launched, flew 116 miles high and came back to Earth. His flight lasted about 15 and a half minutes.
MESSENGER Mission

MESSENGER, launching in 2004, was the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury. This stamp, released in 2011, highlighted this mission and its importance. Understanding Mercury and how it formed is critical to better understanding the conditions on and evolution of the inner planets.
The new “Views of our Planets” stamps will be widely available across the U.S. at post offices and for online purchase beginning May 31. The Pluto – Explored Forever stamps will only be sold online or by calling 800-782-6724.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
How Well Do You Know Mercury?
Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system and is only slightly larger than Earth’s moon. To give you some perspective, if the sun were as tall as a typical front door, Earth would be the size of a nickel and Mercury would be about as big as a green pea.

Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. Daytime temperatures can reach 430 degrees Celsius (800 degrees Fahrenheit) and drop to –180 degrees Celsius (-290 degrees Fahrenheit) at night.
Here are a few fun facts about Mercury:
Mercury takes only 88 Earth days to orbit the sun
If we could stand on Mercury’s surface when it is at its closest point to the sun, the sun would appear more than three times larger than it does here on Earth
Mercury is home to one of the largest impact basins in the solar system: the Caloris Basin. The diameter of this impact basin is the length of 16,404 football fields (minus the end zones) placed end to end!
Mercury is one of only two planets in our solar system that do not have moons (Venus is the other one)
Mercury completes three rotations for every two orbits around the sun. That means that if you wanted to stay up from sunrise to sunrise on Mercury, you’d be up for 176 Earth days…you’d need a LOT of coffee!

Two missions have visited Mercury:
Mariner 10 was the first mission to Mercury, and 30 years later, our MESSENGER mission was the second to visit the planet. Mariner 10 was also the first spacecraft to reach one planet by using the gravity of another planet (in this case, Venus) to alter its speed and trajectory.

MESSENGER was the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury, The spacecraft had its own shades to protect it from the light of the sun. This is important since sunlight on Mercury can be as much as 11 times brighter than it is here on Earth. The spacecraft was originally planned to orbit Mercury for one year, but exceeded expectations and worked for over four years capturing extensive data. On April 30, 2015, the spacecraft succumbed to the pull of solar gravity and impacted Mercury’s surface.
Water Ice?
The MESSENGER spacecraft observed compelling support for the long-held hypothesis that Mercury harbors abundant water ice and other frozen volatile materials in its permanently shadowed polar craters.

This radar image of Mercury’s north polar region. The areas shown in red were captured by MESSENGER, compared to the yellow deposits imaged by Earth-based radar. These areas are believed to consist of water ice.
Mercury Transit of the Sun
For more than seven hours on Monday, May 9, Mercury will be visible as a tiny black dot crossing the face of the sun. This rare event – which happens only slightly more than once a decade – is called a transit.

Where: Skywatchers in Western Europe, South America and eastern North America will be able to see the entirety of the transit. The entire 7.5-hour path across the sun will be visible across the Eastern U.S. – with magnification and proper solar filters – while those in the West can observe the transit in progress at sunrise.

Watch: We will stream a live program on NASA TV and the agency’s Facebook page from 10:30 to 11:30 a.m. – an informal roundtable during which experts representing planetary, heliophysics and astrophysics will discuss the science behind the Mercury transit. Viewers can ask questions via Facebook and Twitter using #AskNASA. Unlike the 2012 Venus transit of the sun, Mercury is too small to be visible without magnification from a telescope or high-powered binoculars. Both must have safe solar filters made of specially-coated glass or Mylar; you can never look directly at the sun.
To learn more about our solar system and the planets, visit: http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Getting to Mars: A New Rocket for the Journey
Do you know what the structural backbone is of our new rocket, the Space Launch System? If you answered the core stage, give yourself a double thumbs up! Or better yet, have astronaut Scott Kelly do it!

We’re on a journey to Mars. For bolder missions to deep space, we need a big, powerful rocket like SLS to take astronauts in the Orion spacecraft to places we've never gone before. The core stage is a major part of that story, as it will house the fuel and avionics systems that will power and guide the rocket to those new destinations beyond Earth’s orbit. Here's how:
It's Big, and It's Fast.
The core stage will be the largest rocket stage ever built and is under construction right now at our Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. It will stand at 212 feet tall and weigh more than 2.3 million pounds with propellant. That propellant is cryogenic liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen that will feed the vehicle’s RS-25 engines. In just 8.5 minutes, the core stage will reach Mach 23, which is faster than 17,000 mph!
It's Smart.

Similar to a car, the rocket needs all the equipment necessary for the "drive" to deep space. The core stage will house the vehicle’s avionics, including flight computers, instrumentation, batteries, power handling, sensors and other electronics. That's a lot of brain power behind those orange-clad aluminum walls. *Fun fact: Orange is the color of the rocket's insulation.
It's a Five-Parter.

The core stage is made up of five parts. Starting from the bottom is the engine section, which will deliver the propellants to the four RS-25 engines. It also will house avionics to steer the engines, and be an attachment point for the two, five-segment solid rocket boosters. The engine section for the first SLS flight has completed welding and is in the final phases of manufacturing at Michoud.

Next up is the liquid hydrogen tank. It will hold 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to -423 degrees Fahrenheit. Right now, engineers are building the tank for the first SLS mission. It will look very similar to the qualification test article that just finished welding at Michoud. That's an impressive piece of rocket hardware!

The next part of the core stage is the intertank, which will join the propellant tanks. It has to be super strong because it is the attachment point for the boosters and absorbs most of the force when they fire 3.6 million pounds of thrust each. It's also a "think tank" of sorts, as it holds the SLS avionics and electronics. The intertank is even getting its own test structure at our Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.

And then there's the liquid oxygen tank. It will store 196,000 gallons of liquid oxygen cooled to -297 degrees. If you haven't done the math, that's 733,000 gallons of propellant for both tanks, which is enough to fill 63 large tanker trucks. Toot, toot. Beep, beep! A confidence version of the tank has finished welding at Michoud, and it's impressive. Just ask this guy.

The topper of the core stage is the forward skirt. Funny name, but serious hardware. It's home to the flight computers, cameras and avionics. The avionics system is being tested right now in a half-ring structure at the Marshall Center.

You can click here for more SLS core stage facts. We'll continue building, and see you at the launch pad for the first flight of SLS with Orion in 2018!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


Whilst practicing solar distancing, Parker Solar Probe caught this rare glimpse of the twin tails on comet NEOWISE.☄
The twin tails are seen more clearly in this WISPR instrument processed image, which increased contrast and removed excess brightness from scattered sunlight, revealing more de-"tails". C/2020 F3 NEOWISE was discovered by our Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE), on March 27. Since it's discovery the comet has been spotted by several NASA spacecraft, including Parker Solar Probe, NASA’s Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory, the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, and astronauts aboard the International Space Station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for May 2016?

What's Up for May? Two huge solar system highlights: Mercury transits the sun and Mars is closer to Earth than it has been in 11 years.

On May 9, wake up early on the west coast or step out for coffee on the east coast to see our smallest planet cross the face of the sun. The transit will also be visible from most of South America, western Africa and western Europe.

A transit occurs when one astronomical body appears to move across the face of another as seen from Earth or from a spacecraft. But be safe! You'll need to view the sun and Mercury through a solar filter when looking through a telescope or when projecting the image of the solar disk onto a safe surface. Look a little south of the sun's Equator. It will take about 7 1/2 hours for the tiny planet's disk to cross the sun completely. Since Mercury is so tiny it will appear as a very small round speck, whether it's seen through a telescope or projected through a solar filter. The next Mercury transit will be Nov. 11, 2019.

Two other May highlights involve Mars. On May 22 Mars opposition occurs. That's when Mars, Earth and the sun all line up, with Earth directly in the middle.

Eight days later on May 30, Mars and Earth are nearest to each other in their orbits around the sun. Mars is over half a million miles closer to Earth at closest approach than at opposition. But you won't see much change in the diameter and brightness between these two dates. As Mars comes closer to Earth in its orbit, it appears larger and larger and brighter and brighter.

During this time Mars rises after the sun sets. The best time to see Mars at its brightest is when it is highest in the sky, around midnight in May and a little earlier in June.

Through a telescope you can make out some of the dark features on the planet, some of the lighter features and sometimes polar ice and dust storm-obscured areas showing very little detail.

After close approach, Earth sweeps past Mars quickly. So the planet appears large and bright for only a couple weeks.

But don't worry if you miss 2016's close approach. 2018's will be even better, as Mars' close approach will be, well, even closer.
You can find out about our #JourneytoMars missions at mars.nasa.gov, and you can learn about all of our missions at http://www.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Going the Distance... In Space
On April 17, NASA's New Horizons crossed a rare deep-space milestone – 50 astronomical units from the Sun, or 50 times farther from the Sun than Earth is. New Horizons is just the fifth spacecraft to reach this great distance, following the legendary Voyagers 1 and 2 and Pioneers 10 and 11. It’s almost 5 billion miles (7.5 billion kilometers) away; a remote region where a signal radioed from NASA's largest antennas on Earth, even traveling at the speed of light, needs seven hours to reach the far-flung spacecraft.
To celebrate reaching 50 AU, the New Horizons team compiled a list of 50 facts about the mission. Here are just a few of them; you'll find the full collection at: http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/Fifty-Facts.php.

New Horizons is the first – and so far, only – spacecraft to visit Pluto. New Horizons sped through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015, providing a history-making close-up view of the dwarf planet and its family of five moons.
New Horizons is carrying some of the ashes of Pluto’s discoverer, Clyde Tombaugh. In 1930, the amateur astronomer spotted Pluto in a series of telescope images at Lowell Observatory in Arizona, making him the first American to discover a planet.

The “Pluto Not Yet Explored” U.S. stamp that New Horizons carries holds the Guinness World Record for the farthest traveled postage stamp. The stamp was part of a series created in 1991, when Pluto was the last unexplored planet in the solar system.

Dispatched at 36,400 miles per hour (58, 500 kilometers per hour) on January 19, 2006, New Horizons is still the fastest human-made object ever launched from Earth.
As the spacecraft flew by Jupiter’s moon Io, in February 2007, New Horizons captured the first detailed movie of a volcano erupting anywhere in the solar system except Earth.

New Horizons’ radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) – its nuclear battery – will provide enough power to keep the spacecraft operating until the late-2030s.

Measurements of the universe’s darkness using New Horizons data found that the universe is twice as bright as predicted – a major extragalactic astronomy discovery!

New Horizons’ Venetia Burney Student Dust Counter is the first student-built instrument on any NASA planetary mission – and is providing unprecedented insight into the dust environment in the outer solar system.

New Horizons is so far away, that even the positons of the stars look different than what we see from Earth. This view of an "alien sky" allowed scientists to make stereo images of the nearest stars against the background of the galaxy.

Arrokoth – the official name the mission team proposed for the Kuiper Belt object New Horizons explored in January 2019 – is a Native American term that means “sky” in the Powhatan/Algonquin language.

Stay tuned in to the latest New Horizons updates on the mission website and follow NASA Solar System on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Hubble Space Telescope: Exploring the Cosmos and Making Life Better on Earth
In the 35 years since its launch aboard space shuttle Discovery, the Hubble Space Telescope has provided stunning views of galaxies millions of light years away. But the leaps in technology needed for its look into space has also provided benefits on the ground. Here are some of the technologies developed for Hubble that have improved life on Earth.

Image Sensors Find Cancer
Charge-coupled device (CCD) sensors have been used in digital photography for decades, but Hubble’s Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph required a far more sensitive CCD. This development resulted in improved image sensors for mammogram machines, helping doctors find and treat breast cancer.
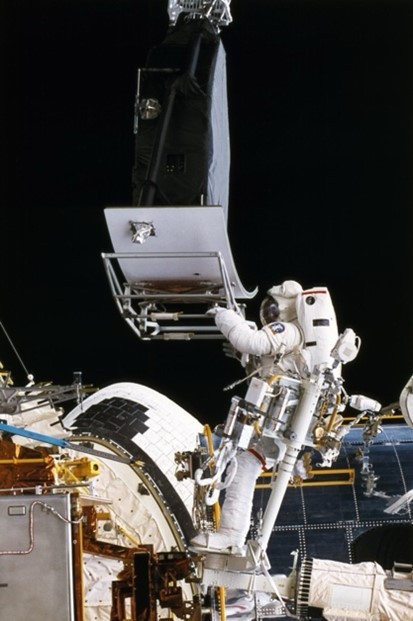

Laser Vision Gives Insights
In preparation for a repair mission to fix Hubble’s misshapen mirror, Goddard Space Flight Center required a way to accurately measure replacement parts. This resulted in a tool to detect mirror defects, which has since been used to develop a commercial 3D imaging system and a package detection device now used by all major shipping companies.
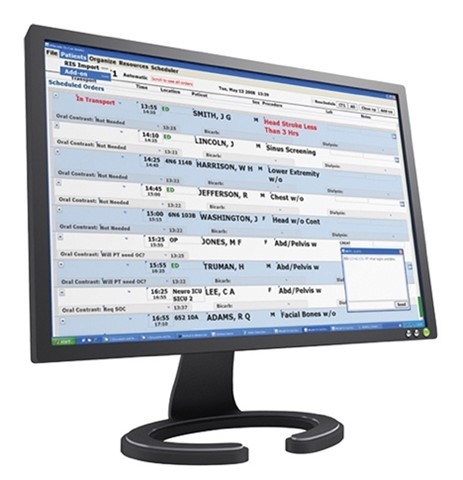
Optimized Hospital Scheduling
A computer scientist who helped design software for scheduling Hubble’s observations adapted it to assist with scheduling medical procedures. This software helps hospitals optimize constantly changing schedules for medical imaging and keep the high pace of emergency rooms going.

Optical Filters Match Wavelengths and Paint Swatches
For Hubble’s main cameras to capture high-quality images of stars and galaxies, each of its filters had to block all but a specific range of wavelengths of light. The filters needed to capture the best data possible but also fit on one optical element. A company contracted to construct these filters used its experience on this project to create filters used in paint-matching devices for hardware stores, with multiple wavelengths evaluated by a single lens.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Apollo 12: The Next Step after the Giant Leap
Launched less than four months after Apollo 11 put the first astronauts on the Moon, Apollo 12 was more than a simple encore. After being struck by lightning on launch -- to no lasting damage, fortunately -- Apollo 12 headed for a rendezvous with a spacecraft that was already on the Moon. The mission would expand the techniques used to explore the Moon and show the coordination between robotic and human exploration, both of which continue today as we get return to return astronauts to the Moon by 2024.
Launch Day

Apollo 12 lifted off at 11:22 a.m. EST, Nov. 14, 1969, from our Kennedy Space Center. Aboard the Apollo 12 spacecraft were astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot; and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot.
Barely 40 seconds after liftoff, lightning struck the spacecraft. Conrad alerted Houston that the crew had lost telemetry and other data from the mission computers. As the Saturn V engines continued to push the capsule to orbit, ground controllers worked out a solution, restarting some electrical systems, and Apollo 12 headed toward the Moon.

Cameras at the Kennedy Space Center captured this image of the same lightning bolt that struck Apollo 12 striking the mobile platform used for the launch.
On the Moon
Apollo 12 landed on the Moon on Nov. 19, and on the second moonwalk Conrad and Bean walked approximately 200 yards to the Surveyor 3 spacecraft. One of seven Surveyor spacecraft sent to land on the Moon and to gather data on the best way to land humans there, Surveyor 3 had been on the Moon for more than two years, exposed to cosmic radiation and the vacuum of space. Scientists on the ground wanted to recover parts of the spacecraft to see what effects the environment had had on it.

Apollo 12 commander Pete Conrad examines the Surveyor 3 spacecraft before removing its camera and other pieces for return to Earth. In the background is the lunar module that landed Conrad and lunar module pilot Alan Bean on the Moon.
Splashdown

Apollo 12 splashed down on Nov. 24. When Artemis returns astronauts to the Moon in 2024, it will be building on Apollo 12 as much as any of the other missions. Just as Apollo 12 had to maneuver off the standard “free return” trajectory to reach its landing site near Surveyor, Artemis missions will take advantage of the Gateway to visit a variety of lunar locations. The complementary work of Surveyor and Apollo -- a robotic mission preparing the way for a crewed mission; that crewed mission going back to the robotic mission to learn more from it -- prefigures how Artemis will take advantage of commercial lunar landers and other programs to make lunar exploration sustainable over the long term.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How hard is it to become an austronaut? I want to start to studie astrophysics and I don't know if I'll ever get any kind of job. Do you have any tips for people like me?
Astrophysics is a perfect field for pursuing any work at NASA! A degree in a STEM field is a requirement of becoming an astronaut, but other than that there are many possibilities. One of the best things about the astronaut office is its diversity. We are scientists, engineers, military pilots, flight test engineers, medical doctors, etc. etc. My biggest tip is to ensure you are pursuing what it is you are passionate about as that’s the only way to truly become exceptional at what you are doing, and most importantly, to be happy doing it. Passion, hard work, and dedication will get you there. Good luck!

No, this red beam in space isn't a light saber! It's a galaxy, far, far away — 44 million light-years away, to be exact.
We often imagine galaxies as having massive spiral arms or thick disks of dust, but not all galaxies are oriented face-on as viewed from Earth. From our viewpoint, our Spitzer Space Telescope can detect this galaxy's infrared light but can only view the entire galaxy on its side where we can't see its spiral features. We know it has a diameter of roughly 60,000 light-years — a little more than half the diameter of our own Milky Way galaxy.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 numbrsguy liked this · 3 months ago
numbrsguy liked this · 3 months ago -
 tt-squid reblogged this · 3 years ago
tt-squid reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 tt-squid liked this · 3 years ago
tt-squid liked this · 3 years ago -
 meanheans reblogged this · 4 years ago
meanheans reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 bluerainofcomets liked this · 5 years ago
bluerainofcomets liked this · 5 years ago -
 sojoydesign-blog liked this · 6 years ago
sojoydesign-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 i-universeinsaneme-blog liked this · 7 years ago
i-universeinsaneme-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 creepercat reblogged this · 7 years ago
creepercat reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 fals-ehopes liked this · 7 years ago
fals-ehopes liked this · 7 years ago -
 edreyventis liked this · 7 years ago
edreyventis liked this · 7 years ago -
 intergalacticdeliveryboy reblogged this · 8 years ago
intergalacticdeliveryboy reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 theshadowofmysoul7-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
theshadowofmysoul7-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 theshadowofmysoul7-blog liked this · 8 years ago
theshadowofmysoul7-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 thoughtfulkoalacherryblosso-blog liked this · 8 years ago
thoughtfulkoalacherryblosso-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 mifavdiy reblogged this · 8 years ago
mifavdiy reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 captain-boomeraang reblogged this · 8 years ago
captain-boomeraang reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 aninhaelric liked this · 8 years ago
aninhaelric liked this · 8 years ago -
 importantkryptonitemagazine liked this · 8 years ago
importantkryptonitemagazine liked this · 8 years ago -
 an-old-telephone liked this · 8 years ago
an-old-telephone liked this · 8 years ago -
 ohsassohfrass liked this · 8 years ago
ohsassohfrass liked this · 8 years ago -
 fuzzyangrybird reblogged this · 8 years ago
fuzzyangrybird reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 gyrox82 liked this · 8 years ago
gyrox82 liked this · 8 years ago -
 le-mon-light reblogged this · 8 years ago
le-mon-light reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 starsaremymuse reblogged this · 8 years ago
starsaremymuse reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 stamp-a-gram-blog liked this · 8 years ago
stamp-a-gram-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 tspks-blog liked this · 8 years ago
tspks-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 nebulea liked this · 8 years ago
nebulea liked this · 8 years ago -
 agitated-gemini reblogged this · 8 years ago
agitated-gemini reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 cosmic-quark reblogged this · 8 years ago
cosmic-quark reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 cosmic-quark liked this · 8 years ago
cosmic-quark liked this · 8 years ago -
 queenofthemagicbluebox1103 reblogged this · 8 years ago
queenofthemagicbluebox1103 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 queenofthemagicbluebox1103 liked this · 8 years ago
queenofthemagicbluebox1103 liked this · 8 years ago -
 dresserdrawer1278 reblogged this · 8 years ago
dresserdrawer1278 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 dresserdrawer1278 liked this · 8 years ago
dresserdrawer1278 liked this · 8 years ago -
 sleepsunshinesleep reblogged this · 8 years ago
sleepsunshinesleep reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 eynali liked this · 8 years ago
eynali liked this · 8 years ago -
 wholocksarecool reblogged this · 8 years ago
wholocksarecool reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 heroingoldveinz reblogged this · 8 years ago
heroingoldveinz reblogged this · 8 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts