Solar System: Things To Know This Week
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn more about our Deep Space Network, where to watch the Ursid meteor shower, Cassini’s ring-grazing at Saturn and more.

1. A Deep Space Anniversary
On Dec. 24, 1963, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Deep Space Information Facility was renamed the Deep Space Network. And, it’s been humanity's ear to the skies ever since.
+ History of the Deep Space Network
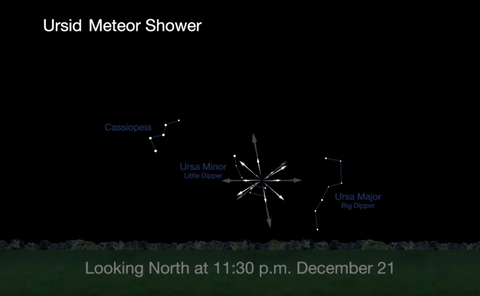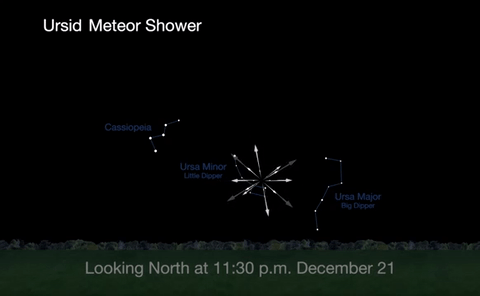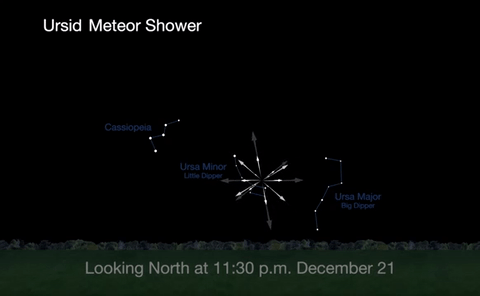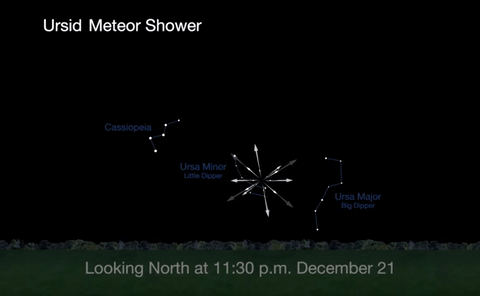
2. Ursid Meteor Shower
The best time to view the Ursids, radiating from Ursa Minor, or the little Dipper, will be from midnight on December 21 until about 1a.m. on December 22, before the moon rises.

3. At Saturn, the Ring-Grazing Continues
Our Cassini spacecraft has completed several orbits that take it just outside Saturn’s famous rings. The first ring-grazing orbit began on November 30. The spacecraft will repeat this feat 20 times, with only about a week between each ring-plane crossing.
+ Learn more

4. Preparing for the 2017 Total Solar Eclipse
Next year North America will see one of the most rare and spectacular of all sky events. Learn how to prepare.
+ 2017 Solar Eclipse Toolkit

5. Searching for Rare Asteroids
Our first mission to return an asteroid sample to Earth will be multitasking during its two-year outbound cruise to the asteroid Bennu. On February 9-20, OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security-Regolith Explorer) will activate its onboard camera suite and begin its search for elusive “Trojan,” asteroids, constant companions to planets in our solar system as they orbit the sun, remaining near a stable point 60 degrees in front of or behind the planet. Because they constantly lead or follow in the same orbit, they will never collide with their companion planet.
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others


“I realized, really for the first time, that people who didn’t even know me were wishing for my success — hoping to share in the pride of future accomplishments, but even more important, willing to provide encouragement in the face of disappointments. I hope that by sharing my experiences, others will be inspired to set high goals for themselves.”
- Ellen Ochoa is the first Hispanic director of NASA’s Johnson Space Center and the first Hispanic woman to go to space.
Q: You were the first Hispanic woman to go to space, and you’re the first Hispanic director of the Johnson Space Center. What does the achievement of firsts like these mean to you? What kind of responsibility comes with paving the way?
Becoming an astronaut was a personal goal for me, so I was surprised and overwhelmed to receive such warm support from the entire Hispanic community when I was selected for the astronaut corps. I realized, really for the first time, that people who didn’t even know me were wishing for my success — hoping to share in the pride of future accomplishments, but even more important, willing to provide encouragement in the face of disappointments. In the same way, in addition to working hard to do my best at every position I’ve had, it became an important part of my job to provide encouragement to others, particularly women and minorities underrepresented in STEM [Science Technology Engineering and Math] fields. I hope that by sharing my experiences, others will be inspired to set high goals for themselves.
Q: Have you experienced any particular challenges as a female astronaut? How have you stayed motivated in the face of such challenges?
Actually, the women astronauts who came before me performed their jobs so well that it really wasn’t an issue. There was probably more skepticism due to my research background, given that the job is an operational one, and I didn’t have much experience in that environment. The training we’re provided helped prepare me well, as did veterans astronauts who passed on helpful tips.
Q: As a pioneer of spacecraft technology and a champion of outreach, how do you think we can inspire more women to enter STEM fields?
Use every available communications avenue to let women know about the interesting and rewarding careers in the STEM fields. The website Women@NASA profiles many women around the agency, having them describe in their own words what they do and the path that led them to their careers. And since girls start making choices in middle school that can limit their options later on, there’s a section on the website aimed specifically at middle school girls called Aspire to Inspire featuring women at Johnson Space Center. NASA has also made great use of many social media platforms to spread the word on what we are doing in space exploration, both human and robotics. From the first flyby of Pluto to the completion of a one-year mission onboard the International Space Station, this has been an exciting year for NASA.
Polar Vortex spills Arctic weather into North America

What in the world is a polar vortex? On Earth, it’s a large area of low pressure and extremely cold air that usually swirls over the Arctic, with strong counter-clockwise winds that trap the cold around the Pole. But disturbances in the jet stream and the intrusion of warmer mid-latitude air masses can disturb this polar vortex and make it unstable, sending Arctic air south into middle latitudes.
That has been the case in late January 2019 as frigid weather moves across the Midwest and Northern Plains of the United States, as well as interior Canada. Forecasters are predicting that air temperatures in parts of the continental United States will drop to their lowest levels since at least 1994, with the potential to break all-time record lows for January 30 and 31. With clear skies, steady winds, and snow cover on the ground, as many as 90 million Americans could experience temperatures at or below 0 degrees Fahrenheit (-18° Celsius), according to the National Weather Service (NWS).
The Goddard Earth Observing System Model above shows this air temperature movement at 2 meters (around 6.5 feet above the ground) from January 23-29. You can see some portions of the Arctic are close to the freezing point—significantly warmer than usual for the dark of mid-winter—while masses of cooler air plunge toward the interior of North America.

Science Behind the Polar Vortex / Credit: NOAA
Meteorologists predicted that steady northwest winds (10 to 20 miles per hour) were likely to add to the misery, causing dangerous wind chills below -40°F (-40°C) in portions of 12 states. A wind chill of -20°F can cause frostbite in as little as 30 minutes, according to the weather service.
Not sure how cold that is? Check out the low temperatures on January 30, 2019 in some of the coldest places on Earth—and a planetary neighbor:
-46°F (-43°C) -- Chesterfield, Newfoundland
-36°F (-33°C) -- Yukon Territory, Canada
-33°F (-27°C) -- Fargo, North Dakota (Within the Polar Vortex)
-28°F (-18°C) -- Minneapolis, Minnesota (Within the Polar Vortex)
-27°F (-33°C) -- Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station, Antarctica
-24°F (-31°C) -- Chicago, Illinois (Within the Polar Vortex)
-15°F (5°C) -- Barrow, Alaska
-99°F (-73°C) -- Mars
Learn more about the science behind the polar vortex and how NASA is modeling it here: https://go.nasa.gov/2Wtmb43.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Eight Things to Know About Our Flying Observatory
Our flying observatory, called SOFIA, is the world’s largest airborne observatory. It is a partnership with the German Aerospace Center (DLR). SOFIA studies the life cycle of stars, planets (including Pluto’s atmosphere), how interstellar dust can contribute to planet formation, analyzes the area around black holes, and identifies complex molecules in space.
1. A Telescope in an Airplane

SOFIA stands for the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy. It is a Boeing 747SP aircraft that carries a 100-inch telescope to observe the universe while flying between 38,000 and 45,000 feet – the layer of Earth’s atmosphere called the stratosphere.
2. The Short Aircraft Means Long Flights

SP stands for “special performance.” The plane is 47 feet shorter than a standard 747, so it’s lighter and can fly greater distances. Each observing flight lasts 10-12 hours.
3. It Flies with A Hole in the Side of the Plane…

The telescope is behind a door that opens when SOFIA reaches altitude so astronomers on board can study the universe. The kind of light SOFIA observes, infrared, is blocked by almost all materials, so engineers designed the side of the aircraft to direct air up-and-over the open cavity, ensuring a smooth flight.
4. …But the Cabin is Pressurized!

A wall, called a pressure bulkhead, was added between the telescope and the cabin so the team inside the aircraft stays comfortable and safe. Each flight has pilots, telescope operators, scientists, flight planners and mission crew aboard.
5. This Telescope Has to Fly

Water vapor in Earth’s atmosphere blocks infrared light from reaching the ground. Flying at more than 39,000 feet puts SOFIA above more than 99% of this vapor, allowing astronomers to study infrared light coming from space. The airborne observatory can carry heavier, more powerful instruments than space-based observatories because it is not limited by launch weight restrictions and solar power.
6. Studying the Invisible Universe

Humans cannot see what is beyond the rainbow of visible light. However, many interesting astronomical processes happen in the clouds of dust and gas that often surround the objects SOFIA studies, like newly forming stars. Infrared light can pass through these clouds, allowing astronomers to study what is happening inside these areas.
7. The German Telescope

The telescope was built our partner, the German Aerospace Center, DLR. It is made of a glass-ceramic material called Zerodur that does not change shape when exposed to extremely cold temperatures. The telescope has a honeycomb design, which reduces the weight by 80%, from 8,700 lb to 1,764 lb. (Note that the honeycomb design was only visible before the reflective aluminum coating was applied to the mirror’s surface).
8. ZigZag Flights with a Purpose

The telescope can move up and down, between 20-60 degrees above the horizon. But it can only move significantly left and right by turning the whole aircraft. Each new direction of the flight means astronomers are studying a new celestial object. SOFIA’s flight planners carefully map where the plane needs to fly to best observe each object planned for that night.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Would you smooch an alien?
Depends what he looks like!
History Made: Apollo 11 Splashes Down Today in 1969

The Apollo 11 Command Module “Columbia” is hoisted onto its recovery ship the USS Hornet, following splashdown on July 24, 1969. Credit: NASA
Four days after their historic achievement, Apollo 11 astronauts Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins splashed down in the Pacific Ocean at 12:49 p.m. EDT, about 900 miles from Hawaii. The crew was recovered by the crew of the USS Hornet where President Richard Nixon was waiting to greet them.
Watch a replay of the original live broadcast of the recovery on NASA TV starting at 12:45 p.m. EDT.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Our water-seeking robotic Moon rover just booked a ride to the Moon’s South Pole. Astrobotic of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, has been selected to deliver the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER, to the Moon in 2023. During its 100-Earth-day mission, the approximately 1,000-pound rover will roam several miles and use its four science instruments to sample various soil environments in search of water ice. Its survey will help pave the way for a new era of human missions to the lunar surface and will bring us a step closer to developing a sustainable, long-term robotic and human presence on the Moon as part of the Artemis program.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Watch a Launch From Your Own Backyard
On Monday, Oct. 17, we’re launching cargo to the International Space Station, and if you live on the east coast, there’s a chance you can catch a glimpse!

The above map shows the areas on the east coast where launch may be visible, depending on cloud conditions.
Liftoff is currently scheduled for 7:40 p.m. EDT from our Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
The launch of Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft will carry around 5,100 pounds of supplies and research materials to the crew on the space station.
Not in the launch viewing area? No worries! Full launch coverage will be available starting at 6:45 p.m. EDT HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What do you do to relax in stressing situations?
What’s Up October 2017
What’s Up For October?
Planet Pairs, Stellar Superstars, Observe The Moon Night!!

This month, catch planet pairs, our moon near red stars, an asteroid, meteors and International Observe the Moon Night!

You can't miss bright Venus in the predawn sky. Look for fainter Mars below Venus on the 1st, really close on the 5th, and above Venus after that.

Midmonth, the moon is visible near Regulus, the white starry heart of the constellation Leo.

In the October 8-11 predawn sky watch the moon glide near the Pleiades star cluster and pass near the red stars Aldebaran in the constellation Taurus and Betelgeuse in Orion.

After dusk in the early part of the month look for Saturn in the southwest sky above another red star: Antares in Scorpius. Later in the month, find the moon above Antares October 22 and 23.

Saturn will be above the moon on the 23rd and below it on the 24th.

Uranus reach opposition on October 19th. It's visible all night long and its blue-green color is unmistakeable. It may be bright enough to see with your naked eye--and for sure in binoculars.

The Orionids peak on October 20--a dark, moonless night. Look near Orion's club in the hours before dawn and you may see up to 10 to 15 meteors per hour.

Use binoculars to look for bright asteroid 7 Iris in the constellation Aries. Newbies to astronomy should be able to spot this magnitude 6.9 asteroid - even from the city.

Look later in the month and sketch its positions a day or two apart--to see it move.

Finally, celebrate International Observe the Moon Night on October 28 with your local astronomy club, Solar System Ambassador, museum, or planetarium. The first quarter moon that night will display some great features!
Watch the full What’s Up for October Video:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

O_o When we peer deep into space, we don't expect to find something staring back at us...
This galactic ghoul, captured by our Hubble Space Telescope, is actually a titanic head-on collision between two galaxies. Each "eye" is the bright core of a galaxy, one of which slammed into another. The outline of the face is a ring of young blue stars. Other clumps of new stars form a nose and mouth.
Although galaxy collisions are common most of them are not head-on smashups like this Arp-Madore system. Get spooked & find out what lies inside this ghostly apparition, here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 5lj162yq reblogged this · 3 years ago
5lj162yq reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 rh35211 reblogged this · 6 years ago
rh35211 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 alezandritexndrito reblogged this · 7 years ago
alezandritexndrito reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 sue-isfinalyadult liked this · 7 years ago
sue-isfinalyadult liked this · 7 years ago -
 astrorevival reblogged this · 7 years ago
astrorevival reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 grappleguy-blog liked this · 8 years ago
grappleguy-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 thingsmydadmightlike-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
thingsmydadmightlike-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 childwhodreams reblogged this · 8 years ago
childwhodreams reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ooccultus liked this · 8 years ago
ooccultus liked this · 8 years ago -
 ooccultus reblogged this · 8 years ago
ooccultus reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 g3ntly-blog1 reblogged this · 8 years ago
g3ntly-blog1 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 falenanera liked this · 8 years ago
falenanera liked this · 8 years ago -
 merakikick liked this · 8 years ago
merakikick liked this · 8 years ago -
 skurtusblr liked this · 8 years ago
skurtusblr liked this · 8 years ago -
 haz77zard reblogged this · 8 years ago
haz77zard reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 augusteightnine reblogged this · 8 years ago
augusteightnine reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 8 years ago
fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 ashteroid liked this · 8 years ago
ashteroid liked this · 8 years ago -
 mahdpod01 liked this · 8 years ago
mahdpod01 liked this · 8 years ago -
 mykidshavefeathers reblogged this · 8 years ago
mykidshavefeathers reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 natebegins1 liked this · 8 years ago
natebegins1 liked this · 8 years ago -
 santiagoguzmanr liked this · 8 years ago
santiagoguzmanr liked this · 8 years ago -
 div-grad-curl-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
div-grad-curl-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 temnet liked this · 8 years ago
temnet liked this · 8 years ago -
 nuttydefendordaze-blog liked this · 8 years ago
nuttydefendordaze-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 grandpiratecreator-blog liked this · 8 years ago
grandpiratecreator-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 deliciouspeacedream-blog liked this · 8 years ago
deliciouspeacedream-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 turdlesquared reblogged this · 8 years ago
turdlesquared reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 inuyasha420 reblogged this · 8 years ago
inuyasha420 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 likealimestonecowboy reblogged this · 8 years ago
likealimestonecowboy reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 jess-d-mateos liked this · 8 years ago
jess-d-mateos liked this · 8 years ago -
 jchapa13 liked this · 8 years ago
jchapa13 liked this · 8 years ago -
 kalisyo-blog liked this · 8 years ago
kalisyo-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 ethe-realisms liked this · 8 years ago
ethe-realisms liked this · 8 years ago -
 frankenstabbyseawimp liked this · 8 years ago
frankenstabbyseawimp liked this · 8 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts