Human Expansion Across Solar System
Human Expansion Across Solar System
On this day in 1972, two NASA astronauts landed on the Moon. Now, 45 years later, we have been instructed to return to the lunar surface.
Today at the White House, President Trump signed the Space Policy Directive 1, a change in national space policy that provides for a U.S.-led program with private sector partners for a human return to the Moon, followed by missions to Mars and beyond.

Among other dignitaries on hand for the signing, were NASA astronauts Sen. Harrison “Jack” Schmitt, Buzz Aldrin, Peggy Whitson and Christina Koch.
Schmitt landed on the moon 45 years to the minute that the policy directive was signed as part of our Apollo 17 mission, and is the most recent living person to have set foot on our lunar neighbor.

Above, at the signing ceremony instructing us to send humans back to the lunar surface, Schmitt shows First Daughter Ivanka Trump the Moon sample he collected in 1972.
The effort signed today will more effectively organize government, private industry and international efforts toward returning humans on the Moon, and will lay the foundation that will eventually enable human exploration of Mars.
To learn more, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/press-release/new-space-policy-directive-calls-for-human-expansion-across-solar-system
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others

Thanks everyone for your fantastic questions! Sorry I couldn’t answer all of them. I hope you have fun on Monday, Aug. 21st and share your photos and experiences with us! https://www.flickr.com/groups/nasa-eclipse2017/
Safe viewing and talk to you later! https://eclipse2017.nasa.gov/safety
Find Out Why We’re Blasting this Rocket with Wind
The world’s most powerful rocket – our Space Launch System (SLS) – may experience ground wind gusts of up to 70 mph as it sits on the launch pad before and during lift off for future missions. Understanding how environmental factors affect the rocket will help us maintain a safe and reliable distance away from the launch tower during launch.

How do we even test this? Great question! Our Langley Research Center’s 14x22-Foot Subsonic Wind Tunnel in Hampton, Virginia, is designed to simulate wind conditions. Rather than having to test a full scale rocket, we’re able to use a smaller, to-scale model of the spacecraft.

Wind tunnel tests are a cost effective and efficient way to simulate situations where cross winds and ground winds affect different parts of the rocket. The guidance, navigation, and control team uses the test data as part of their simulations to identify the safety distance between the rocket and the launch tower.

SLS is designed to evolve as we move crew and cargo farther into the solar system than we have ever been before. The Langley team tested the second more powerful version of the SLS rocket, known as the Block 1B, in both the crew and cargo configuration.
Take a behind-the-scenes look at the hard work being done to support safe explorations to deep-space...
Below, an engineer simulates ground winds on the rocket during liftoff by using what’s called smoke flow visualization. This technique allows engineers to see how the wind flow behaves as it hits the surface of the launch tower model.

The 6-foot model of the SLS rocket undergoes 140 mph wind speeds in Langley’s 14x22-Foot Subsonic Wind Tunnel. Engineers are simulating ground winds impacting the rocket as it leaves the launch pad.

The cargo version of the rocket is positioned at a 0-degree angle to simulate the transition from liftoff to ascent as the rocket begins accelerating through the atmosphere.

Here, engineers create a scenario where the rocket has lifted off 100 feet in the air past the top of the launch tower. At this point in the mission, SLS is moving at speeds of about 100 mph!

Engineers at Langley collect data throughout the test which is used by the rocket developers at our Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to analyze and incorporate into the rocket’s design.

Learn more about our Space Launch System rocket HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com/

The Space Shuttle Challenger landed #OTD in 1983.
Here are astronauts Richard Truly & Guion Bluford of Space Transport System 8 (STS-8) grabbing some shut-eye before the wrap up of their mission. This mission had:
The first African American, Guion Bluford, to fly in space
The first night launch and landing during the Space Shuttle Program
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, let us break it down for you. Here are a few things to know this week:
1. Up at Jupiter, It’s Down to Business

Ever since our Juno mission entered Jupiter's orbit on July 4, engineers and scientists have been busy getting their newly arrived spacecraft ready for operations. Juno's science instruments had been turned off in the days leading up to Jupiter orbit insertion. As planned, the spacecraft powered up five instruments on July 6, and the remaining instruments should follow before the end of the month. The Juno team has also scheduled a short trajectory correction maneuver on July 13 to refine the orbit.
2. The Shadows Know

Scientists with our Dawn mission have identified permanently shadowed regions on the dwarf planet Ceres. Most of these areas likely have been cold enough to trap water ice for a billion years, suggesting that ice deposits could exist there now (as they do on the planet Mercury). Dawn is looking into it.
3. Frosts of Summer

Some dusty parts of Mars get as cold at night year-round as the planet's poles do in winter, even in regions near the equator in summer, according to new findings based on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter observations. The culprit may be Mars' ever-present dust.
4. Can You Hear Me Now?

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is designed to sample an asteroid and return that sample to Earth. After launch in Sept., the mission's success will depend greatly on its communications systems with Earth to relay everything from its health and status to scientific findings from the asteroid Bennu. That's why engineers from our Deep Space Network recently spent a couple of weeks performing detailed tests of the various communications systems aboard OSIRIS-REx.
5. Cometary Close-ups

The Rosetta spacecraft has taken thousands of photographs of Comet 67/P. The European Space Agency (ESA) is now regularly releasing the highest-resolution images. The word "stunning" is used a lot when referring to pictures from space—and these ones truly are. See the latest HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for October 2016?
What’s Up for October? Moon phases, Astronomy Day, meteors and Saturn!

The new moon phase starts the month on October 1. Of course, the new moon isn't visible, because it's between Earth and the sun, and the unlit side is facing Earth.

Night by night the slender crescent gets bigger and higher in the sky and easier to see just after sunset. On the 3rd and 4th, the moon will pass just above Venus!

A week later on the 9th the moon has traveled through one quarter of its 29-day orbit around Earth, and we see the first quarter phase. Also look for Mars just below the moon.

Join us in celebrating International Observe the Moon Night Saturday, October 8th, with your local astronomy club or science center. Conveniently, the 8th is also Fall Astronomy Day, celebrated internationally by astronomy clubs since 1973.

One week later on the 16th the moon reaches opposition, or the full moon phase, when the moon and the sun are on opposite sides of Earth. And the sun completely illuminates the moon as seen from Earth.

During this phase, the moon rises in the east just as the sun is setting in the west. Overnight, the moon crosses the sky and sets at dawn.

A week later, on the 22nd of October, the last quarter moon rises at midnight. Later, the pretty and bright Beehive Cluster will be visible near the moon until dawn.

To wrap up the month, 29 days after the last new moon we start the lunar cycle all over again with another new moon phase on October 30th. Will you be able to spot the one-day old moon on Halloween? It will be a challenge!

There are three meteor showers in October--the Draconids, the Taurids and the Orionids. Try for the Draconids on October 8th.

See the Taurids on October 10th.

The Orionids will be marred by the full moon on the 21st, but all three meteor showers will offer some possible bright meteors.

Finally, you’ll have an especially pretty view of Saturn, when it forms a straight line with Venus and the red star Antares on the 27th.
You can catch up on NASA's lunar mission, the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, the Cassini Mission to Saturn and all of our missions at www.nasa.gov.
Watch the full October “What’s Up" video for more:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What are the moments when you think to yourself "yes. THIS is why I love my job"..? ✨
Solar System: Top 5 Things to Know This Week
Here are five things you need to know about our amazing solar system this week:
1. Perpetual Pluto-palooza

The New Horizons spacecraft continues its ongoing download of data and images from the July 14 flyby of the Pluto system. In the latest weekly release, the new images don’t disappoint, showing fine details in an exotic landscape. The New Horizons team has also described a wide range of findings about the dwarf planet’s system in its first science paper. Learn more HERE.
2. Encounter at Enceladus

The Cassini spacecraft has returned the closest images ever showing the north polar region of Saturn’s intriguing ice moon Enceladus. Scientists expected the area to be heavily cratered, but the new high-resolution Cassini images also show a landscape of stark contrasts, crisscrossed by a spidery network of gossamer-thin cracks that slice through the craters. The robotic spacecraft buzzed by the moon during the first of what will be three close encounters this year -- the last of the long mission. Next up: on Oct. 28 Cassini will deep dive right through Enceladus’ famous ice geyser plume! Learn more HERE.
3. We’re Giving You the Whole World, Every Day
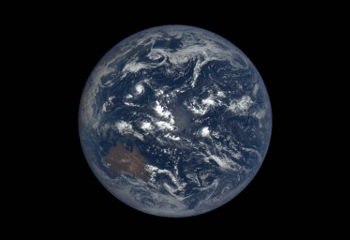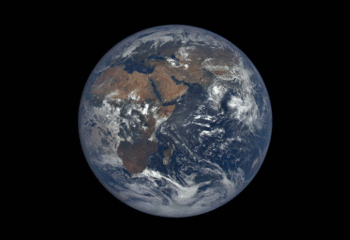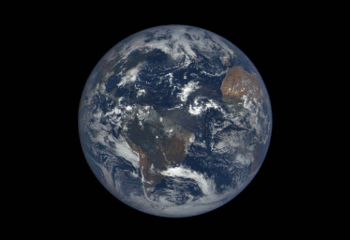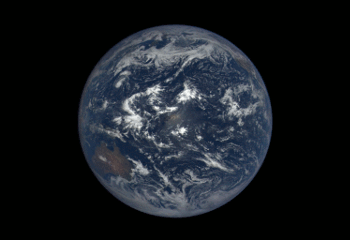
We have worked with NOAA to launch a new website that shows the full, sunlit side of the Earth on a daily basis. The images come from our camera a million miles away aboard the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR). Each daily sequence of images shows the Earth as it rotates, revealing the entire planet over the course of a day. Take a look HERE.
4. Going Big at Jupiter

We have large, new maps of Jupiter, thanks to data from the Wide Field Camera 3 on our Hubble Space Telescope. The big images provide a detailed look at how the giant planet’s features change over time. In fact, the maps are just the first in a planned series of yearly portraits of the solar system’s four outer planets. The views come as we prepare for the Juno mission to arrive at Jupiter in little less than a year.
5. Catch a Falling Star

Meteors aren’t really falling stars, just dust and rock from deep space meeting a fiery end in Earth’s atmosphere -- but they’re a sight to behold if you can catch a glimpse. The Orionid meteors appear every year around this time, when Earth travels through an area of space littered with debris from Halley’s Comet. This year the peak will occur on the night of Wednesday, Oct. 21, into the morning of Thursday, Oct. 22. Find out how to watch HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
From Microscopic to Multicellular: Six Stories of Life that We See from Space
Life. It's the one thing that, so far, makes Earth unique among the thousands of other planets we've discovered. Since the fall of 1997, NASA satellites have continuously and globally observed all plant life at the surface of the land and ocean. During the week of Nov. 13-17, we are sharing stories and videos about how this view of life from space is furthering knowledge of our home planet and the search for life on other worlds.

Earth is the only planet with life, as far as we know. From bacteria in the crevices of the deepest oceans to monkeys swinging between trees, Earth hosts life in all different sizes, shapes and colors. Scientists often study Earth from the ground, but some also look to our satellites to understand how life waxes and wanes on our planet.
Over the years, scientists have used this aerial view to study changes in animal habitats, track disease outbreaks, monitor forests and even help discover a new species. While this list is far from comprehensive, these visual stories of bacteria, plants, land animals, sea creatures and birds show what a view from space can reveal.
1. Monitoring the single-celled powerhouses of the sea

Known as the grass of the ocean, phytoplankton are one of the most abundant types of life in the ocean. Usually single-celled, these plant-like organisms are the base of the marine food chain. They are also responsible for the only long-term transfer of carbon dioxide from Earth’s atmosphere to the ocean.
Even small changes in phytoplankton populations can affect carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere, which could ultimately affect Earth’s global surface temperatures. Scientists have been observing global phytoplankton populations continuously since 1997 starting with the Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of View Sensor (SeaWiFS). They continue to study the small life-forms by satellite, ships and aircrafts.
2. Predicting cholera bacteria outbreaks
Found on the surface of zooplankton and in contaminated water, the bacteria that cause the infectious disease cholera — Vibrio cholerae — affect millions of people every year with severe diarrhea, sometimes leading to death. While our satellite sensors can’t detect the actual bacteria, scientists use various satellite data to look for the environmental conditions that the bacteria thrive in.
Specifically, microbiologist Rita Colwell at the University of Maryland, College Park, and West Virginia University hydrologist Antar Jutla studied data showing air and ocean temperature, salinity, precipitation, and chlorophyllconcentrations, the latter a marker for zooplankton. Anticipating where the bacteria will bloom helps researchers to mitigate outbreaks.

Recently, Colwell and Jutla have been able to estimate cholera risk after major events, such as severe storms, by looking at satellite precipitation data, air temperature, and population maps. The two maps above show the team's predicted cholera risk in Haiti two weeks after Hurricane Matthew hit over October 1-2, 2016 and the actual reported cholera cases in October 2016.
3. Viewing life on land
From helping preserve forests for chimpanzees to predicting deer population patterns, scientists use our satellites to study wildlife across the world. Satellites can also see the impacts of perhaps the most relatable animal to us: humans. Every day, we impact our planet in many ways including driving cars, constructing buildings and farming – all of which we can see with satellites.

Our Black Marble image provides a unique view of human activity. Looking at trends in our lights at night, scientists can study how cities develop over time, how lighting and activity changes during certain seasons and holidays, and even aid emergency responders during power outages caused by natural disasters.
4. Tracking bird populations
Scientists use our satellite data to study birds in a variety of ways, from understanding their migratory patterns, to spotting potential nests, to tracking populations. In a rather creative application, scientists used satellite imagery to track Antarctica’s emperor penguin populations by looking for their guano – or excrement.

Counting emperor penguins from the ground perspective is challenging because they breed in some of the most remote and cold places in the world, and in colonies too large to easily count manually. With their black and white coats, emperor penguins are also difficult to count from an aerial view as they sometimes blend in with shadows on the ice. Instead, Phil Trathan and his colleagues at the British Antarctic Survey looked through Landsat imagery for brown stains on the sea ice. By looking for penguin droppings, Trathan said his team identified 54 emperor penguin colonies along the Antarctic coast.
5. Parsing out plant life
Just as we see plants grow and wilt on the ground, satellites observe the changes from space. Flourishing vegetation can indicate a lively ecosystem while changes in greenery can sometimes reveal natural disasters, droughts or even agricultural practices. While satellites can observe plant life in our backyards, scientists can also use them to provide a global picture.

Using data from satellites including SeaWiFS, and instruments including the NASA/NOAA Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, scientists have the most complete view of global biology to date, covering all of the plant life on land and at the surface of the ocean.
6. Studying life under the sea
Our satellites have helped scientists study creatures living in the oceans whether it’s finding suitable waters for oysters or protecting the endangered blue whale. Scientists also use the data to learn more about one of the most vulnerable ecosystems on the planet – coral reefs.

They may look like rocks or plants on the seafloor, but corals are very much living animals. Receiving sustenance from photosynthetic plankton living within their calcium carbonate structures, coral reefs provide food and shelter for many kinds of marine life, protect shorelines from storms and waves, serve as a source for potential medicines, and operate as some of the most diverse ecosystems on the planet.

However, coral reefs are vulnerable to the warming of the ocean and human activity. Our satellites measure the surface temperature of ocean waters. These measurements have revealed rising water temperatures surrounding coral reef systems around the world, which causes a phenomenon known as “coral bleaching.” To add to the satellite data, scientists use measurements gathered by scuba divers as well as instruments flown on planes.
During the week of Nov. 13-17, check out our stories and videos about how this view of life from space is furthering knowledge of our home planet and the search for life on other worlds. Follow at www.nasa.gov/Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How Well Do You Know Your Space Photos?
Can you guess the subject of each of these pictures? How many will you get right? Test your friends and family to see who knows their space photos the best.
1. Ice on Earth or a Picture of Mars?

2. Dry Land on Earth or a Close-Up of Jupiter?

3. Mercury or Our Moon?

4. Do You Think This is Mars or Our Home Planet?

5. Waves on Jupiter or Saturn?

6. Is this a picture of Mars or Earth?

7. Can You Tell Which is Europa and Which is the Bottom of a Frying Pan?

8. Close-Up of Our Moon or Dwarf Planet Ceres?

9. A Weird World or Our Own World?

10. The Red Planet or a Red Desert?

Answers
1. Mars. You might be surprised, but this image taken by our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is of a light-toned deposit on the Martian surface. Some shapes in the terrain suggest erosion by a fluid moving north to south.
2. Earth. This image taken by our Earth Observing-1 satellite shows Lake Frome in central Australia. In this image, the salt lake appears bone-dry, filled with off-white sediment. This area of Australia receives 149 to 216 millimeters of rainfall a year on average, and the basins pass most of their time as saltpans.
3. Mercury. Our MESSENGER spacecraft captured this image of Mercury during a fly by in October 2008. It shows previously uncharted regions of the planet that have large craters with an internal smoothness similar to Earth’s own moon. It is thought that these craters were to have been flooded by lava flows that are old but not as old as the surrounding more highly cratered surface.
4. Earth. Surprisingly, this image take from the International Space Station shows the western half of the Arabian peninsula in Saudi Arabia. It not only contains large expanses of sand and gravel, but extensive lava fields known as haraat.
5. Saturn. Although this pattern of waves is similar to those seen on Jupiter, this is actually a picture of Saturn. The pattern of an iconic surfer’s wave, has been observed in many places all over the universe, including at the edges of Earth’s magnetic environment.
6. Mars. This image was taken by our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and shows dunes of sand-sized materials that have been trapped on the floors of many Martian craters. The dunes are linear, thought to be due to shifting wind directions.
7. Left: Europa. Right: Frying Pan. Europa is one of Jupiter’s moons, and is about the same size as Earth’s moon.
8. Ceres. This image taken by our Dawn spacecraft shows an intriguing mountain on dwarf planet Ceres protruding from a relatively smooth area.
9. Earth. This image of the Bazman volcano is located in a remote region of souther Iran. While the volcano has the classic cone shape of a stratovolcano, it is also heavily dissected by channels that extend downwards from the summit.
10. Earth. This image of the Great Sandy Desert in northwest Australia shows a variety of dune forms across the region. The photo was taken by the Expedition 35 crew from the International Space Station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space:http://nasa.tumblr.com
So Close, So Far: See Juno’s first orbit of Jupiter in this amateur-created JunoCam “marble movie.”
Credit: NASA/JPL/SwRI/MSSS/Gerald Eichstädt
-
 beyondafinecupofcoffee liked this · 5 months ago
beyondafinecupofcoffee liked this · 5 months ago -
 ercharpuzzsealste liked this · 1 year ago
ercharpuzzsealste liked this · 1 year ago -
 themoi liked this · 5 years ago
themoi liked this · 5 years ago -
 screwyoutunglr liked this · 6 years ago
screwyoutunglr liked this · 6 years ago -
 mylifestylehere-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
mylifestylehere-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 danielrobz-blog liked this · 6 years ago
danielrobz-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 wildsupply liked this · 7 years ago
wildsupply liked this · 7 years ago -
 fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 7 years ago
fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 m4rs-alpha-blog liked this · 7 years ago
m4rs-alpha-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 nasanaut reblogged this · 7 years ago
nasanaut reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 the-empirical-rationalist liked this · 7 years ago
the-empirical-rationalist liked this · 7 years ago -
 thesefaults liked this · 7 years ago
thesefaults liked this · 7 years ago -
 the-nicest-duwang reblogged this · 7 years ago
the-nicest-duwang reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 terrylhills liked this · 7 years ago
terrylhills liked this · 7 years ago -
 shirekat reblogged this · 7 years ago
shirekat reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 iwtv1976 reblogged this · 7 years ago
iwtv1976 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 elegants-men-bauer-blog liked this · 7 years ago
elegants-men-bauer-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 lunargosh reblogged this · 7 years ago
lunargosh reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thisaccountdeactivated reblogged this · 7 years ago
thisaccountdeactivated reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thisaccountdeactivated liked this · 7 years ago
thisaccountdeactivated liked this · 7 years ago -
 bootthegreat liked this · 7 years ago
bootthegreat liked this · 7 years ago -
 dhiromi liked this · 7 years ago
dhiromi liked this · 7 years ago -
 shadowbagelbird reblogged this · 7 years ago
shadowbagelbird reblogged this · 7 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts