Mars Helicopter: 6 Things To Know About Ingenuity
Mars Helicopter: 6 Things to Know About Ingenuity

When our Perseverance Mars rover lands on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021, it will bring along the Ingenuity helicopter.
This small-but-mighty craft is a technology demonstration that will attempt the first powered, controlled flight on another planet. Its fuselage is about the size of a tissue box, and it weighs about 4 pounds (1.8 kg) on Earth. It started out six years ago as an implausible prospect and has now passed its Earthbound tests.
Here are six things to know about Ingenuity as it nears Mars:
1. Ingenuity is an experimental flight test.

This Mars helicopter is known as a technology demonstration, which is a project that aims to test a new capability for the first time with a limited scope. Previous technology demonstrations include Sojourner, the first Mars rover, and the Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeStats that flew by Mars.
Ingenuity does not carry any science instruments and is not part of Perseverance’s science mission. The only objective for this helicopter is an engineering one – to demonstrate rotorcraft flight in the thin and challenging Martian atmosphere.
2. Mars won’t make it easy for Ingenuity.

Mars’ atmosphere is around 1% the density of Earth’s. Because of that lack of density, Ingenuity has rotor blades that are much larger and spin faster than a helicopter of Ingenuity’s mass here on our planet. It also must be extremely light to travel to Mars.
The Red Planet also has incredibly cold temperatures, with nights reaching minus 130 degrees Fahrenheit (-90 degrees Celsius) in Jezero Crater, where our rover and helicopter will land. Tests on Earth at the predicted temperatures indicate Ingenuity’s parts should work as designed, but the real test will be on Mars.
3. Ingenuity relies on Perseverance for safe passage to Mars and operations on the Martian surface.

Ingenuity is nestled sideways under Perseverance’s belly with a cover to protect the helicopter from debris during landing. The power system on the Mars 2020 spacecraft periodically charges Ingenuity’s batteries during the journey to the Red Planet.
In the first few months after landing, Perseverance will find a safe place for Ingenuity. Our rover will shed the landing cover, rotate the helicopter so its legs face the ground and gently drop it on the Martian surface.
4. Ingenuity is smart for a small robot.

NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory will not be able to control the helicopter with a joystick due to delays communicating with spacecraft across interplanetary distances. That means Ingenuity will make some of its own decisions based on parameters set by its engineering team on Earth.
During flight, Ingenuity will analyze sensor data and images of the terrain to ensure it stays on a flight path designed by project engineers.
5. The Ingenuity team counts success one step at a time.

Ingenuity’s team has a long list of milestones the helicopter must pass before it can take off and land in the Martian atmosphere.
Surviving the journey to and landing on Mars
Safely deploying onto the Martian surface from Perseverance’s belly
Autonomously keeping warm through those intensely cold Martian nights
Autonomously charging itself with its solar panel
Successfully communicating to and from the helicopter via the Mars Helicopter Base Station on Perseverance
6. If Ingenuity succeeds, future Mars exploration could include an ambitious aerial dimension.

The Mars helicopter intends to demonstrate technologies and first-of-its-kind operations needed for flying on Mars. If successful, these technologies and flight experience on another planet could pave the way for other advanced robotic flying vehicles.
Possible uses of a future helicopter on Mars include:
A unique viewpoint not provided by current orbiters, rovers or landers
High-definition images and reconnaissance for robots or humans
Access to terrain that is difficult for rovers to reach
Could even carry light but vital payloads from one site to another
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Earth: Our Oasis in Space

Earth: It’s our oasis in space, the one place we know that harbors life. That makes it a weird place -- so far, we haven’t found life anywhere else in the solar system...or beyond. We study our home planet and its delicate balance of water, atmosphere and comfortable temperatures from space, the air, the ocean and the ground.

To celebrate our home, we want to see what you love about our planet. Share a picture, or several, of Earth with #PictureEarth on social media. In return, we’ll share some of our best views of our home, like this one taken from a million miles away by the Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (yes, it’s EPIC).

From a DC-8 research plane flying just 1500 feet above Antarctic sea ice, we saw a massive iceberg newly calved off Pine Island Glacier. This is one in a series of large icebergs Pine Island has lost in the last few years – the glacier is one of the fastest melting in Antarctica.

It’s not just planes. We also saw the giant iceberg, known as B-46, from space. Landsat 8 tracked B-46’s progress after it broke off from Pine Island Glacier and began the journey northward, where it began to break apart and melt into the ocean.

Speaking of change, we’ve been launching Earth-observing satellites since 1958. In that time, we’ve seen some major changes. Cutting through soft, sandy soil on its journey to the Bay of Bengal, the Padma River in Bangladesh dances across the landscape in this time-lapse of 30 years’ worth of Landsat images.

Our space-based view of Earth helps us track other natural activities, too. With both a daytime and nighttime view, the Aqua satellite and the Suomi NPP satellite helped us see where wildfires were burning in California, while also tracking burn scars and smoke plumes..

Astronauts have an out-of-this-world view of Earth, literally. A camera mounted on the International Space Station captured this image of Hurricane Florence after it intensified to Category 4.

It’s not just missions studying Earth that capture views of our home planet. Parker Solar Probe turned back and looked at our home planet while en route to the Sun. Earth is the bright, round object.
Want to learn more about our home planet? Check out our third episode of NASA Science Live where we talked about Earth and what makes it so weird.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
That’s a Wrap - September
Each month, the International Space Station focuses on an area of research. In September, the research focus was biology, encompassing cells, plants, animals, genetics, biochemistry, human physiology and more.
Benefits from this research are vast and include: combating diseases, reducing our environmental footprint, feeding the world’s population and developing cleaner energy.
Here’s a recap of some topics we studied this month:
Cells

Scientists studied T-cells in orbit to better understand how human immune systems change as they age. For an immune cell, the microgravity environment mimics the aging process. Because spaceflight-induced and aging-related immune suppression share key characteristics, researchers expect the results from this study will be relevant for the general population.
NASA to Napa

We raised a glass to the space station to toast how the study of plants in space led to air purification technology that keeps the air clean in wine cellars and is also used in homes and medical facilities to help prevent mold.
One-Year Mission

This month also marked the halfway point of the One-Year Mission. NASA Astronaut Scott Kelly and Roscosmos Cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko reached the midpoint on Sept. 15. This mission will result in valuable data about human health and the effects of microgravity on the body.
Microbes

Since microbes can threaten crew health and jeopardize equipment, scientists study them on astronauts’ skin and aboard the space station. Samples like saliva, blood, perspiration and swaps of equipment are collected to determine how microgravity, environment, diet and stress affect the microorganisms.
Model Organisms

Model organisms have characteristics that allow them to easily be maintained, reproduced and studied in a laboratory. Scientists investigate roundworms, medaka fish and rodents on the station because of this reason. They can also provide insight into the basic cellular and molecular mechanisms of the human body.
For more information about research on the International Space Station, go HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Thank you for joining! It’s time to find out how YOU can get involved with NASA as a student or send your experiments to the International Space Station.
One of our experts today is Hannah Johnson, the team lead of a student group sending their experiment to the space station! She is joined by Becky Kamas, our lead for STEM on Station activities for students.
Between 12-1 p.m. EDT today, our experts will talk about about designing an experiment for microgravity, working with NASA to launch it to space, how you can join this initiative, and more!
View all answers HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Studying Circadian Rhythms and Sleep in Space
Do you remember the last time you stayed awake all night? Maybe you had a major exam, or flew across the ocean. How did you feel the following day? The time at which you would normally feel sleepy was probably different from usual. Your eyes “told” you that it was day, time for work or school. Your brain or muscles disagreed. They “told” you that it was middle of the night, and that you should sleep.

Changing when you sleep, or being in areas where daytime and nighttime are “off-schedule”, affects your circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm exists in humans as a roughly 24-hour clock that prompts us to sleep or wake.

The European Space Agency’s experiment, Circadian Rhythms, investigates the role of this “biological clock” and its changes during spaceflight. Researchers hypothesize that a non-24-hour cycle of light and dark affects crew members’ circadian rhythms. Understanding the effects of life in space on astronauts’ circadian rhythms may help improve performance and health for future crew members.
Researchers collect data on astronaut’s circadian rhythms by using a “double-sensor,” which measures the temperature at the core of the body. The crew attaches one sensor to their head, and the other to their chest.

Based on results from this research, future crew members could more accurately adjust their sleep, work and physical activity scheduled to accommodate natural circadian cycles, which could improve productivity and health.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Going the Distance... In Space
On April 17, NASA's New Horizons crossed a rare deep-space milestone – 50 astronomical units from the Sun, or 50 times farther from the Sun than Earth is. New Horizons is just the fifth spacecraft to reach this great distance, following the legendary Voyagers 1 and 2 and Pioneers 10 and 11. It’s almost 5 billion miles (7.5 billion kilometers) away; a remote region where a signal radioed from NASA's largest antennas on Earth, even traveling at the speed of light, needs seven hours to reach the far-flung spacecraft.
To celebrate reaching 50 AU, the New Horizons team compiled a list of 50 facts about the mission. Here are just a few of them; you'll find the full collection at: http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/Fifty-Facts.php.

New Horizons is the first – and so far, only – spacecraft to visit Pluto. New Horizons sped through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015, providing a history-making close-up view of the dwarf planet and its family of five moons.
New Horizons is carrying some of the ashes of Pluto’s discoverer, Clyde Tombaugh. In 1930, the amateur astronomer spotted Pluto in a series of telescope images at Lowell Observatory in Arizona, making him the first American to discover a planet.

The “Pluto Not Yet Explored” U.S. stamp that New Horizons carries holds the Guinness World Record for the farthest traveled postage stamp. The stamp was part of a series created in 1991, when Pluto was the last unexplored planet in the solar system.

Dispatched at 36,400 miles per hour (58, 500 kilometers per hour) on January 19, 2006, New Horizons is still the fastest human-made object ever launched from Earth.
As the spacecraft flew by Jupiter’s moon Io, in February 2007, New Horizons captured the first detailed movie of a volcano erupting anywhere in the solar system except Earth.

New Horizons’ radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) – its nuclear battery – will provide enough power to keep the spacecraft operating until the late-2030s.

Measurements of the universe’s darkness using New Horizons data found that the universe is twice as bright as predicted – a major extragalactic astronomy discovery!

New Horizons’ Venetia Burney Student Dust Counter is the first student-built instrument on any NASA planetary mission – and is providing unprecedented insight into the dust environment in the outer solar system.

New Horizons is so far away, that even the positons of the stars look different than what we see from Earth. This view of an "alien sky" allowed scientists to make stereo images of the nearest stars against the background of the galaxy.

Arrokoth – the official name the mission team proposed for the Kuiper Belt object New Horizons explored in January 2019 – is a Native American term that means “sky” in the Powhatan/Algonquin language.

Stay tuned in to the latest New Horizons updates on the mission website and follow NASA Solar System on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
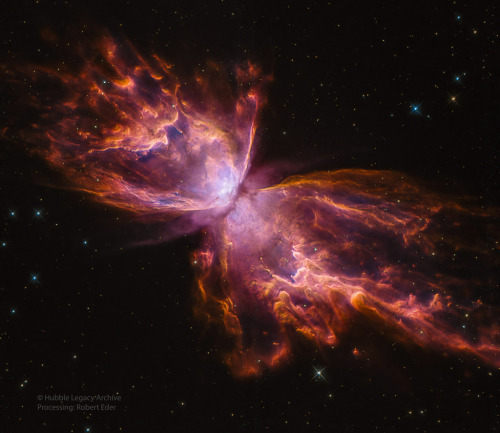

DYK the bright clusters and nebulae of planet Earth's night sky are often named for flowers or insects?
Though its wingspan covers over 3 light-years, NGC 6302: The Butterfly Nebula is no exception! With an estimated surface temperature of about 250,000 degrees C, the dying central star of this particular planetary nebula has become exceptionally hot, shining brightly in ultraviolet light but hidden from direct view by a dense torus of dust. This sharp close-up was recorded by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2009. The Hubble image data is reprocessed here, showing off the remarkable details of the complex planetary nebula.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble, HLA; Reprocessing & Copyright: Robert Eder
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Exploring the Invisible: Magnetic Reconnection
People always say that space is a vacuum. That’s true – space is about a thousand times emptier than even the best laboratory vacuums on Earth. Even so, space contains lots of stuff we can’t see. We study this invisible space stuff because we need to understand it to safely send technology and astronauts into space.
The stuff that fills space is mostly plasma, which is gas where particles have separated into positive ions and negative electrons, creating a sea of electrically-charged particles. This plasma also contains something else – magnetic fields.

The particles in space can reach very high speeds, creating radiation. One of the main engines that drives that acceleration to high speeds is called magnetic reconnection. But what is magnetic reconnection?
Magnetic reconnection happens when two oppositely-aligned magnetic fields pinch together and explosively realign. As the lines snap into their new configuration – as in the animation below – the sudden change sends electrons and ions flying at incredible speeds.

Magnetic reconnection releases energy. We can't see the energy itself, but we can see the results: It can set off solar explosions – such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections – or disturbances near Earth that cause auroras.
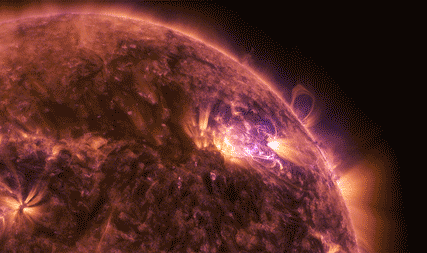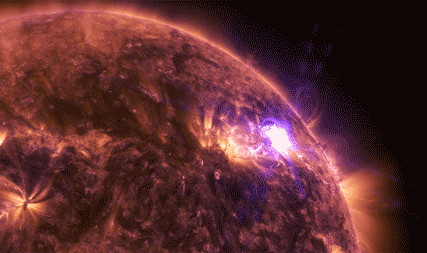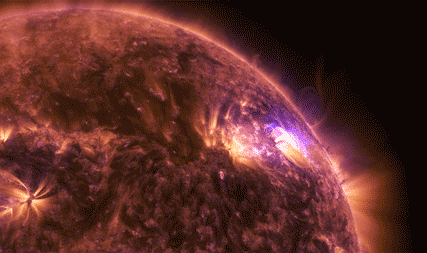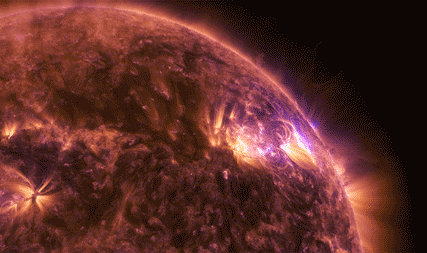
In March 2015, we launched the four Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft on a mission to study magnetic reconnection. Magnetic reconnection only happens in a vacuum with ionized gas. These conditions are vanishingly rare on Earth, so we went to space to study this explosive process.
Because MMS has four separate – but essentially identical – spacecraft, it can watch magnetic reconnection in three dimensions.

The below animation shows what MMS sees – the magnetic fields are magenta, positive ions are purple, and electrons are yellow. The arrows show which the direction the fields and particles are moving.

Like how a research plane flies through a hurricane, MMS flew directly through a magnetic reconnection event in October 2015.
In the data visualization below, you can see the magnetic reconnection happening as the yellow arrows (which represent electrons) explode in all directions. You’ll notice that the magnetic field (represented by magenta arrows) changes direction after the magnetic reconnection, showing that the magnetic field has reconfigured.

Magnetic reconnection transfers energy into Earth’s atmosphere – but it’s not inherently dangerous. Sometimes, the changes in Earth’s magnetic field caused by magnetic reconnection can create electric currents that put a strain on power systems. However, the energy released is more often channeled into auroras, the multicolored lights that most often appear near the North and South Poles.

As the MMS mission continues the four spacecraft can be moved closer together or farther apart, letting us measure magnetic reconnection on all different scales. Each set of observations contributes to explaining different aspects of this invisible phenomenon of magnetic reconnection. Together, the information will help scientists better map out our space environment — crucial information as we journey ever farther beyond our home planet.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Five Orion Technologies That Will Help Us Get Home From Mars
Orion is a key piece of NASA’s journey to Mars. The spacecraft, which was first tested in space last year, will enable crew to travel to deep space on the journey to the Red Planet and bring astronauts home safely. It’s a critical technology we’ll use to help NASA test, demonstrate and hone the skills and capabilities we need to operate farther and farther away from Earth.

Environmental Control and Life Support Systems
Water. Air. A temperate environment. A bathroom. These are some of the things astronauts need to survive the long journey back to Earth from Mars. NASA has developed an environmental control and life support system on the International Space Station and is designing such a system for Orion. The system can recycle carbon dioxide and make it back into useable air and process urine to make it into potable water, for example. Right now on the space station, engineers and astronauts are testing a filtering system for efficiency and reliability on long-duration missions. The investigation uses an amine-based chemical compound combined with the vacuum of space to filter and renew cabin air for breathing. When astronauts travel home from Mars, they won’t be able to count on the arrival of spare parts or extra supplies if something breaks or gets depleted, so engineers are hard at work developing reliable and robust technologies to keep crews alive and healthy in space.

Radiation protection
Astronauts traveling to and from Mars will be far away from the protective shield of Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field, and their spacecraft and its systems will need to be able to protect against the full spectrum of space radiation. NASA is working now to develop protective methods.
Orion will use items already on board to protect the crew and create a temporary shelter in the aft bay of the spacecraft, which is the inside portion closest to the heat shield. This location minimizes the amount of equipment to move around while maximizing the amount of material that can be placed between the crew and the outside environment. The items that will be used include supplies, equipment and launch and re-entry seats as well as water and food. By using the items already on board, the astronauts benefit from additional shielding without adding to Orion’s mass.

Power and Propulsion
A spacecraft needs power and propulsion in space to refine its trajectory during the trip back to Earth. Orion will include a service module capable of helping the spacecraft make any necessary mid-course corrections. A service module provides power, heat rejection, in-space propulsion and water and air for crews, and NASA is working with ESA (European Space Agency) to provide Orion’s service module for its next mission in a partnership that will also bring international cooperation on the journey to Mars. The service module will provide propulsion, batteries and solar arrays to generate power and contain all the air, nitrogen and water for crews.
The ESA-provided element brings together new technology and lightweight materials while also taking advantage of spaceflight-proven hardware. For example, ESA is modeling several key components – like the solar arrays – from technology developed for its Automated Transfer Vehicle-series of cargo vessels, which delivered thousands of pounds of supplies to the space station during five missions between 2008 and 2015. NASA is providing ESA one of the Orbital Maneuvering System pods that allowed space shuttles to move in space to be upgraded and integrated into the service module.

Heat shield
When an uncrewed Orion was tested in space in 2014, the heat shield withstood temperatures of about 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit, or about twice as hot as molten lava. That heat was generated when the spacecraft, traveling at about 20,000 mph back toward our planet, made its way through Earth’s atmosphere, which acts as a braking mechanism to cause friction and slow down a returning spacecraft. Its speed was about 80 percent of what Orion will experience when it comes back from missions near the moon and will need to be even more robust for missions where return speeds, and therefore reentry temperatures, are higher.
Orion’s heat shield is built around a titanium skeleton and carbon fiber skin that provide structural support. A honeycomb structure fits over the skin with thousands of cells that are filled with a material called Avcoat. That layer is 1.6 inches at its thickest and erodes as Orion travels through Earth’s atmosphere.

Parachutes
A spacecraft bringing crews back to Earth after a long trip to Mars will need a parachute system to help it slow down from its high-speed reentry through the atmosphere to a relatively slow speed for splashdown in the ocean. While Earth’s atmosphere will initially slow Orion down from thousands of miles per hour to about 325 mph, its 11 parachutes will deploy in precise sequence to further slow the capsule’s descent. There are three forward bay cover parachutes that pull a protective cover off the top of the capsule, two drogue parachutes that deploy to stabilize the spacecraft, and three pilot parachutes that are used to pull out Orion’s three orange and white main parachutes that are charged with slowing the spacecraft to its final landing speed. The main parachutes are so big that the three of them together nearly cover an entire football field.
Engineers are currently building the Orion spacecraft that will launch on the world’s most powerful rocket, the Space Launch System, and will enable astronauts to travel farther into space than ever before on the journey to Mars.
Visit NASA on the Web for more information about Orion and NASA’s journey to Mars. http://www.nasa.gov/orion
What You Need to Know About Our Space Launch System (SLS) Rocket’s Green Run Test

The comprehensive test series called Green Run for our Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is underway at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi.
During Green Run, the rocket’s massive, 212-foot-tall core stage — the same flight hardware that will help launch Artemis I to the Moon – will operate together for the first time.
Here’s what you need to know about this top-to-bottom test series of our megarocket’s huge core:
The Meaning Behind the Name

Why is it called Green Run? “Green” refers to the new, untested hardware (AKA the core stage), and “run” represents the succession of tests the core stage paces through. One by one, this series will bring together several “firsts” for the rocket stage as the flight hardware undergoes eight different tests. Each test is designed to gradually bring our rocket’s core stage and all its systems to life for the first time.
So far, engineers have completed three of the series: the modal test, the avionics power-on, and the safety systems checkout. The safety systems are designed to end the test and shutdown systems automatically under undesirable conditions.
You can follow the progress of Green Run with this Green Run checklist infographic. Our team will be updating in real time as each Green Run test is completed.
Setting the Stage

The world’s tallest rocket stage is tested in an equally giant test stand. We upgraded the B-2 Test Stand used for the Saturn V rocket stages during the Apollo Program and, later, for the Space Shuttle Program. Now, the B-2 Test Stand is customized for testing our SLS core stage. When all four core stage engines fire up, they can generate some serious heat. So, the B-2 Test Stand will use roughly 100,000 gallons of water every 18 seconds to protect the stand and the hardware.
Hot fire in 3, 2, 1…

Speaking of engines firing up, the core stage will really show what it is capable of during the grand finale of Green Run. The goal is for the entire core stage to operate as one for up to 8.5 minutes — and that includes an impressive firing of all four RS-25 engines simultaneously. Just like at launch, more than 733,000 gallons of liquid propellant will flow from the two propellant tanks through the fuel lines to feed the RS-25 engines. When operating at sea level on the test stand, the cluster of four RS-25 engines will produce just over 1.6 million pounds of thrust – the same amount it will produce during the early phase of launch. During ascent, the core stage will produce a maximum thrust of over 2 million pounds.
Data, data, data

All the Green Run tests, check outs and the 100 terabytes of collected data certify the core stage design and help verify the stage is ready for launch. To put the sheer amount of data collected during Green Run into perspective, just one terabyte is the equivalent of roughly 500 hours of movies. Even the Library of Congress’s collection only amounts to a total of 15 terabytes!
Next stop: Kennedy

The next time our SLS rocket’s core stage fires up will be on the launch pad at Kennedy Space Center for the debut of the Artemis program. This inaugural SLS flight will be just the beginning of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Are You Ready to #BeTheSpark?
Students - want to modify a NASA Spinoff technology and solve a real word problem?

Our Optimus Prime Spinoff Promotion and Research Challenge, known as OPSPARC for short, is a student challenge that guides teams through various NASA Spinoff technologies that are in their everyday world. The teams use their imagination, creativity, and engineering skills to develop their own ideas for NASA spinoff technology.

Spinoffs are technologies originally created for space and modified into everyday products used here on Earth.

Perhaps the most widely recognized NASA spinoff, memory foam was invented by NASA-funded researchers looking for ways to keep test pilots cushioned during flights. Today, memory foam makes for more comfortable beds, couches and chairs, not to mention better shoes, movie theater seats and even football helmets.
There are more than two-thousand NASA Spinoffs They include memory foam, invisible braces, firefighting equipment, programmable pace makers, artificial limbs, scratch-resistant lenses, aircraft anti-icing systems, endangered species tracking software, cochlear implants, satellite television, long-distance telecommunications, and many, many more.

The deadline has been extended to February 26th for our Mission 3 student challenge. Sign up NOW here: https://opsparc.gsfc.nasa.gov/
Fans of the Hasbro TRANSFORMERS brand will pick up on the play on words between the challenge name, OPSPARC, and the "AllSpark" from the TRANSFORMERS universe. The AllSpark is what gave the TRANSFORMERS robots life and knowledge, which they use to help mankind — just like NASA spinoffs. Students from around the globe will have the opportunity to Be The Spark!
OPTIMUS PRIME and TRANSFORMERS are trademarks of Hasbro and are used with permission. © 2018 Hasbro, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
-
 iknowaladygoodandevil liked this · 9 months ago
iknowaladygoodandevil liked this · 9 months ago -
 brotherjaybird liked this · 1 year ago
brotherjaybird liked this · 1 year ago -
 bronzecelestial liked this · 2 years ago
bronzecelestial liked this · 2 years ago -
 princesspink48484 reblogged this · 2 years ago
princesspink48484 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 princesspink48484 liked this · 2 years ago
princesspink48484 liked this · 2 years ago -
 beomseokchae liked this · 2 years ago
beomseokchae liked this · 2 years ago -
 idee-montijo liked this · 2 years ago
idee-montijo liked this · 2 years ago -
 artistlearningsstuff liked this · 3 years ago
artistlearningsstuff liked this · 3 years ago -
 wachsurfer2018 liked this · 3 years ago
wachsurfer2018 liked this · 3 years ago -
 drewcifer4 liked this · 3 years ago
drewcifer4 liked this · 3 years ago -
 the-queer-spanish-inquisition liked this · 3 years ago
the-queer-spanish-inquisition liked this · 3 years ago -
 mrclaw61 liked this · 3 years ago
mrclaw61 liked this · 3 years ago -
 classygreenwarlock liked this · 3 years ago
classygreenwarlock liked this · 3 years ago -
 metalzoic liked this · 3 years ago
metalzoic liked this · 3 years ago -
 mythbookworm18 liked this · 3 years ago
mythbookworm18 liked this · 3 years ago -
 k-crimson liked this · 3 years ago
k-crimson liked this · 3 years ago -
 wakayume liked this · 3 years ago
wakayume liked this · 3 years ago -
 bridge-to-knowhere liked this · 3 years ago
bridge-to-knowhere liked this · 3 years ago -
 gerrytwin reblogged this · 3 years ago
gerrytwin reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 gerrytwin liked this · 3 years ago
gerrytwin liked this · 3 years ago -
 quamatoc reblogged this · 3 years ago
quamatoc reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 lyydt liked this · 4 years ago
lyydt liked this · 4 years ago -
 cliffsteele reblogged this · 4 years ago
cliffsteele reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 irishwhiskeyneatplease liked this · 4 years ago
irishwhiskeyneatplease liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts