Questions Coming Up From….
Questions coming up from….
@maybeinanotherworld: JWST IS HAPPENING! How are all of you feeling about this?
@Anonymous: How powerful is this telescope, exactly?
@Anonymous: Why are the mirrors on it yellow?
@foeofcolor: How long is this estimated to last for? Like how long will it be able to function in space by estimates?
More Posts from Nasa and Others
What ways were used to determine all of the inner workings under our planet Earth’s surface?
Leap Day…Why Does It Exist?
Once every four years, an extra calendar day is added: a leap day. But why?
The reason for adding leap days to the calendar is to align the calendar year with the actual year – which is defined by the time it takes Earth to circle the sun. It is equal to 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes and 46 seconds, or 365.24219 days.

If all calendar years contained exactly 365 days, they would drift from the actual year by about 1 day every 4 years. Eventually, July would occur during the northern hemisphere winter! Wouldn’t that be weird?
To correct (approximately), we add 1 day every 4 years...resulting in a leap year.
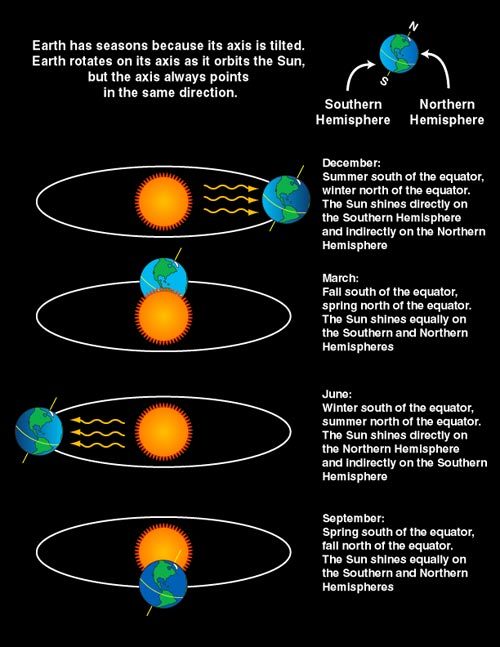
By making most years 365 days but every fourth year 366 days, the calendar year and the actual year remain more nearly in step.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Mercury In the Spotlight
For more than seven hours on Monday, May 9, Mercury will be visible as a tiny black dot crossing the face of the sun. This rare event – which happens only slightly more than once a decade – is called a transit.

Although Mercury whips around the sun every 88 days – over four times faster than Earth – the three bodies rarely align. Because Mercury orbits in a plane 7 degrees tilted from Earth’s orbit, it usually darts above or below our line of sight to the sun. As a result, a Mercury transit happens only about 13 times a century. The last one was in 2006, and the next one isn’t until 2019.

When: On May 9, shortly after 7:00 a.m. EDT, Mercury will appear as a tiny black dot against a blazing backdrop, traversing the sun’s disk over seven and a half hours. Mercury will cross the edge of the sun (ingress) after 7:00 a.m. EDT. The mid-transit point will occur a little after 10:45 a.m. EDT, with egress around 2:30 p.m. EDT.
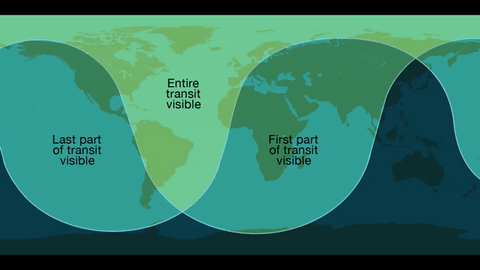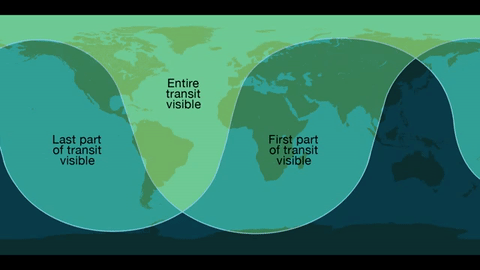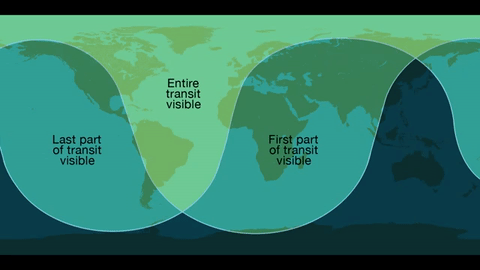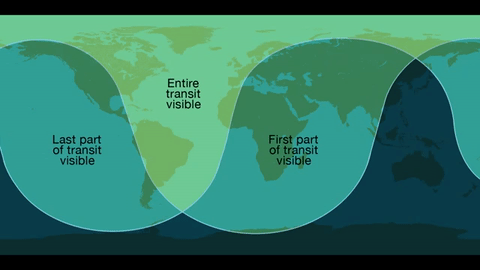
Where: Skywatchers in Western Europe, South America and eastern North America will be able to see the entirety of the transit. The entire 7.5-hour path across the sun will be visible across the Eastern U.S. – with magnification and proper solar filters – while those in the West can observe the transit in progress at sunrise.

Safety!
Unlike the 2012 Venus transit of the sun, Mercury is too small to be visible without magnification from a telescope or high-powered binoculars. Both must have safe solar filters made of specially-coated glass or Mylar; you can never look directly at the sun. We’re offering several avenues for the public to view the event without specialized and costly equipment, including images on NASA.gov, a one-hour NASA Television special, and social media coverage.

The Science…Why are Planetary Transits Important?
Transits like this allowed scientists in the 17th century to make the first estimates of Earth’s distance from the sun. Transit observations over the past few centuries have also helped scientists study everything from the atmosphere of Venus to the slight shifts in Mercury’s orbit that could only be explained by the theory of general relativity. Because we know Mercury’s size and location precisely, this transit will help scientists calibrate telescopes on solar observatories SDO, SOHO, and Hinode.

Transits can also teach us more about planets – both in and out of our solar system. The Venus transit in 2012 provided observations of the planet's atmosphere. Transits are also the main way we find planets outside the solar system, called exoplanets.

The transit method looks for a drop in the brightness of a star when a planet passes in front of it. This method will not find every planet – only those that happen to cross our line of sight from Earth to the star. But with enough sensitivity, the transit method through continuous monitoring is a great way to detect small, Earth-size planets, and has the advantage of giving us both the planet’s size (from the fraction of starlight blocked), as well as its orbit (from the period between transits). Our Kepler/K2 mission uses this method to find exoplanets, as will the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellites, or TESS, following its launch in 2017/2018.
We will stream a live program on NASA TV and the agency’s Facebook page from 10:30 to 11:30 a.m. -- an informal roundtable during which experts representing planetary, heliophysics and astrophysics will discuss the science behind the Mercury transit. Viewers can ask questions via Facebook and Twitter using #AskNASA.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Scott Kelly Was the First To…

Astronaut Scott Kelly returned home from his year in space mission on March 1. Spending that much time in space allowed him to rack up some pretty cool milestones. Here are some of his awesome “firsts”:
Firsts on Social Media

While in space, Scott Kelly had the opportunity to host the first NASA TweetChat from space.

The first ever Tumblr AnswerTime from space was hosted by Scott Kelly during his One Year Mission.

Scott Kelly hosted the first NASA Reddit AMA from space.

Before leaving for his year in space, President Obama asked him to Instagram his time on orbit…a Presidential request to Instagram is a first!
Firsts for Scott

During his year in space, Scott conducted his first spacewalk. He hadn’t spacewalked on any of his previous missions, but did so three times during the One Year Mission.
Firsts for an American Astronaut

Most notably, Scott Kelly is the first U.S. astronaut to spend a year in space. His time on orbit also allowed us to conduct the first ever Twins Study on the space station. While Scott was in space, his twin brother Mark Kelly was on Earth. Since their genetic makeup is as close to identical as we can get, this allows a unique research perspective. We can now compare all of the results from Scott in space to his brother Mark on Earth.

During his year in space, Scott had the opportunity to be one of the first astronauts to harvest and eat lettuce grown in the space station’s VEGGIE facility.

Space flowers! Scott was also one of the firsts to help grow and harvest zinnia flowers in the VEGGIE facility. Growing flowering plants in space will help scientists learn more about growing crops for deep-space missions and our journey to Mars.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What can you see from the space station? Can you see stars, the moon and sun, and Earth weather like lightening storms?
Black Holes Dine on Stellar Treats!

See that tiny blob of light, circled in red? Doesn’t look like much, does it? But that blob represents a feast big enough to feed a black hole around 30 million times the mass of our Sun! Scientists call these kinds of stellar meals tidal disruption events, and they’re some of the most dramatic happenings in the cosmos.

Sometimes, an unlucky star strays too close to a black hole. The black hole’s gravity pulls on the star, causing it to stretch in one direction and squeeze in another. Then the star pulls apart into a stream of gas. This is a tidal disruption event. (If you’re worried about this happening to our Sun – don’t. The nearest black hole we know about is over 1,000 light-years away. And black holes aren’t wild space vacuums. They don’t go zipping around sucking up random stars and planets. So we’re pretty safe from tidal disruption events!)

The trailing part of the stream gets flung out of the system. The rest of the gas loops back around the black hole, forming a disk. The material circling in the disk slowly drifts inward toward the black hole’s event horizon, the point at which nothing – not even light – can escape. The black hole consumes the gas and dust in its disk over many years.

Sometimes the black hole only munches on a passing star – we call this a partial tidal disruption event. The star loses some of its gas, but its own gravity pulls it back into shape before it passes the black hole again. Eventually, the black hole will have nibbled away enough material that the star can’t reform and gets destroyed.

We study tidal disruptions, both the full feasts and the partial snacks, using many kinds of telescopes. Usually, these events are spotted by ground-based telescopes like the Zwicky Transient Facility and the All-Sky Automated Survey for Supernovae network.

They alert other ground- and space-based telescopes – like our Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory (illustrated above) and the European Space Agency’s XMM-Newton – to follow up and collect more data using different wavelengths, from visible light to X-rays. Even our planet-hunting Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite has observed a few of these destructive wonders!
We’re also studying disruptions using multimessenger astronomy, where scientists use the information carried by light, particles, and space-time ripples to learn more about cosmic objects and occurrences.

But tidal disruptions are super rare. They only happen once every 10,000 to 100,000 years in a galaxy the size of our own Milky Way. Astronomers have only observed a few dozen events so far. By comparison, supernovae – the explosive deaths of stars – happen every 100 years or so in a galaxy like ours.
That’s why scientists make their own tidal disruptions using supercomputers, like the ones shown in the video here. Supercomputers allow researchers to build realistic models of stars. They can also include all of the physical effects they’d experience whipping ‘round a black hole, even those from Einstein’s theory of general relativity. They can alter features like how close the stars get and how massive the black holes are to see how it affects what happens to the stars. These simulations will help astronomers build better pictures of the events they observe in the night sky.
Keep up with what’s happening in the universe and how we study it by following NASA Universe on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Getting to Mars: 4 Things We’re Doing Now
We’re working hard to send humans to Mars in the 2030s. Here are just a few of the things we’re doing now that are helping us prepare for the journey:
1. Research on the International Space Station

The International Space Station is the only microgravity platform for the long-term testing of new life support and crew health systems, advanced habitat modules and other technologies needed to decrease reliance on Earth.

When future explorers travel to the Red Planet, they will need to be able to grow plants for food, atmosphere recycling and physiological benefits. The Veggie experiment on space station is validating this technology right now! Astronauts have grown lettuce and Zinnia flowers in space so far.

The space station is also a perfect place to study the impacts of microgravity on the human body. One of the biggest hurdles of getting to Mars in ensuring that humans are “go” for a long-duration mission. Making sure that crew members will maintain their health and full capabilities for the duration of a Mars mission and after their return to Earth is extremely important.

Scientists have solid data about how bodies respond to living in microgravity for six months, but significant data beyond that timeframe had not been collected…until now! Former astronaut Scott Kelly recently completed his Year in Space mission, where he spent a year aboard the space station to learn the impacts of microgravity on the human body.
A mission to Mars will likely last about three years, about half the time coming and going to Mars and about half the time on the Red Planet. We need to understand how human systems like vision and bone health are affected and what countermeasures can be taken to reduce or mitigate risks to crew members.
2. Utilizing Rovers & Tech to Gather Data

Through our robotic missions, we have already been on and around Mars for 40 years! Before we send humans to the Red Planet, it’s important that we have a thorough understanding of the Martian environment. Our landers and rovers are paving the way for human exploration. For example, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has helped us map the surface of Mars, which will be critical in selecting a future human landing site on the planet.

Our Mars 2020 rover will look for signs of past life, collect samples for possible future return to Earth and demonstrate technology for future human exploration of the Red Planet. These include testing a method for producing oxygen from the Martian atmosphere, identifying other resources (such as subsurface water), improving landing techniques and characterizing weather, dust and other potential environmental conditions that could affect future astronauts living and working on Mars.

We’re also developing a first-ever robotic mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid, collect a multi-ton boulder from its surface and redirect it into a stable orbit around the moon. Once it’s there, astronauts will explore it and return with samples in the 2020s. This Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) is part of our plan to advance new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
3. Building the Ride
Okay, so we’ve talked about how we’re preparing for a journey to Mars…but what about the ride? Our Space Launch System, or SLS, is an advanced launch vehicle that will help us explore beyond Earth’s orbit into deep space. SLS will be the world’s most powerful rocket and will launch astronauts in our Orion spacecraft on missions to an asteroid and eventually to Mars.

In the rocket's initial configuration it will be able to take 154,000 pounds of payload to space, which is equivalent to 12 fully grown elephants! It will be taller than the Statue of Liberty and it’s liftoff weight will be comparable to 8 fully-loaded 747 jets. At liftoff, it will have 8.8 million pounds of thrust, which is more than 31 times the total thrust of a 747 jet. One more fun fact for you…it will produce horsepower equivalent to 160,000 Corvette engines!

Sitting atop the SLS rocket will be our Orion spacecraft. Orion will be the safest most advanced spacecraft ever built, and will be flexible and capable enough to carry humans to a variety of destinations. Orion will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
4. Making it Sustainable
When humans get to Mars, where will they live? Where will they work? These are questions we’ve already thought about and are working toward solving. Six partners were recently selected to develop ground prototypes and/or conduct concept studies for deep space habitats.

These NextSTEP habitats will focus on creating prototypes of deep space habitats where humans can live and work independently for months or years at a time, without cargo supply deliveries from Earth.

Another way that we are studying habitats for space is on the space station. In June, the first human-rated expandable module deployed in space was used. The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is a technology demonstration to investigate the potential challenges and benefits of expandable habitats for deep space exploration and commercial low-Earth orbit applications.
Our journey to Mars requires preparation and research in many areas. The powerful new Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft will travel into deep space, building on our decades of robotic Mars explorations, lessons learned on the International Space Station and groundbreaking new technologies.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Will the robot be able to send vedio footage?
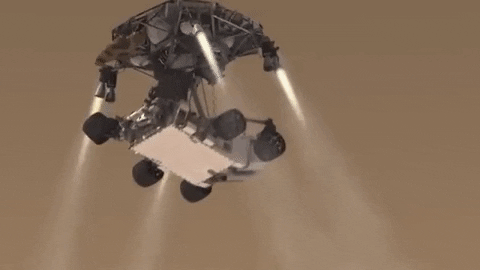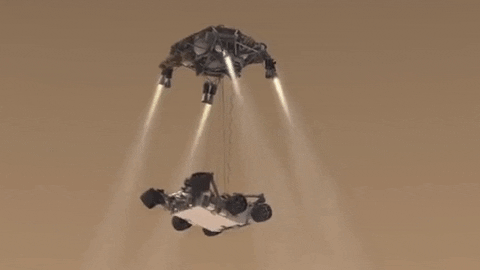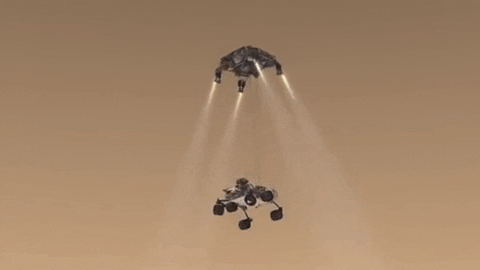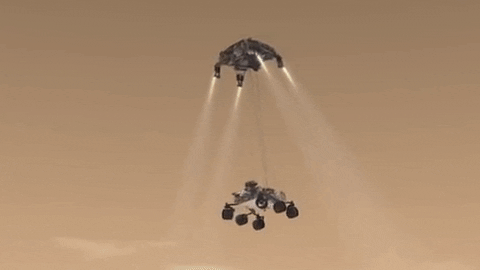
INCOMING! Roving scientist to arrive on Mars.
Save the date! One year from today, Feb. 18, 2021, our next rover is set to land on Mars. Get to know #Mars2020 now! Click here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Five Orion Technologies That Will Help Us Get Home From Mars
Orion is a key piece of NASA’s journey to Mars. The spacecraft, which was first tested in space last year, will enable crew to travel to deep space on the journey to the Red Planet and bring astronauts home safely. It’s a critical technology we’ll use to help NASA test, demonstrate and hone the skills and capabilities we need to operate farther and farther away from Earth.

Environmental Control and Life Support Systems
Water. Air. A temperate environment. A bathroom. These are some of the things astronauts need to survive the long journey back to Earth from Mars. NASA has developed an environmental control and life support system on the International Space Station and is designing such a system for Orion. The system can recycle carbon dioxide and make it back into useable air and process urine to make it into potable water, for example. Right now on the space station, engineers and astronauts are testing a filtering system for efficiency and reliability on long-duration missions. The investigation uses an amine-based chemical compound combined with the vacuum of space to filter and renew cabin air for breathing. When astronauts travel home from Mars, they won’t be able to count on the arrival of spare parts or extra supplies if something breaks or gets depleted, so engineers are hard at work developing reliable and robust technologies to keep crews alive and healthy in space.

Radiation protection
Astronauts traveling to and from Mars will be far away from the protective shield of Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field, and their spacecraft and its systems will need to be able to protect against the full spectrum of space radiation. NASA is working now to develop protective methods.
Orion will use items already on board to protect the crew and create a temporary shelter in the aft bay of the spacecraft, which is the inside portion closest to the heat shield. This location minimizes the amount of equipment to move around while maximizing the amount of material that can be placed between the crew and the outside environment. The items that will be used include supplies, equipment and launch and re-entry seats as well as water and food. By using the items already on board, the astronauts benefit from additional shielding without adding to Orion’s mass.

Power and Propulsion
A spacecraft needs power and propulsion in space to refine its trajectory during the trip back to Earth. Orion will include a service module capable of helping the spacecraft make any necessary mid-course corrections. A service module provides power, heat rejection, in-space propulsion and water and air for crews, and NASA is working with ESA (European Space Agency) to provide Orion’s service module for its next mission in a partnership that will also bring international cooperation on the journey to Mars. The service module will provide propulsion, batteries and solar arrays to generate power and contain all the air, nitrogen and water for crews.
The ESA-provided element brings together new technology and lightweight materials while also taking advantage of spaceflight-proven hardware. For example, ESA is modeling several key components – like the solar arrays – from technology developed for its Automated Transfer Vehicle-series of cargo vessels, which delivered thousands of pounds of supplies to the space station during five missions between 2008 and 2015. NASA is providing ESA one of the Orbital Maneuvering System pods that allowed space shuttles to move in space to be upgraded and integrated into the service module.

Heat shield
When an uncrewed Orion was tested in space in 2014, the heat shield withstood temperatures of about 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit, or about twice as hot as molten lava. That heat was generated when the spacecraft, traveling at about 20,000 mph back toward our planet, made its way through Earth’s atmosphere, which acts as a braking mechanism to cause friction and slow down a returning spacecraft. Its speed was about 80 percent of what Orion will experience when it comes back from missions near the moon and will need to be even more robust for missions where return speeds, and therefore reentry temperatures, are higher.
Orion’s heat shield is built around a titanium skeleton and carbon fiber skin that provide structural support. A honeycomb structure fits over the skin with thousands of cells that are filled with a material called Avcoat. That layer is 1.6 inches at its thickest and erodes as Orion travels through Earth’s atmosphere.

Parachutes
A spacecraft bringing crews back to Earth after a long trip to Mars will need a parachute system to help it slow down from its high-speed reentry through the atmosphere to a relatively slow speed for splashdown in the ocean. While Earth’s atmosphere will initially slow Orion down from thousands of miles per hour to about 325 mph, its 11 parachutes will deploy in precise sequence to further slow the capsule’s descent. There are three forward bay cover parachutes that pull a protective cover off the top of the capsule, two drogue parachutes that deploy to stabilize the spacecraft, and three pilot parachutes that are used to pull out Orion’s three orange and white main parachutes that are charged with slowing the spacecraft to its final landing speed. The main parachutes are so big that the three of them together nearly cover an entire football field.
Engineers are currently building the Orion spacecraft that will launch on the world’s most powerful rocket, the Space Launch System, and will enable astronauts to travel farther into space than ever before on the journey to Mars.
Visit NASA on the Web for more information about Orion and NASA’s journey to Mars. http://www.nasa.gov/orion
-
 tea-withnofixinsplease liked this · 2 years ago
tea-withnofixinsplease liked this · 2 years ago -
 foeofcolor-redux liked this · 2 years ago
foeofcolor-redux liked this · 2 years ago -
 ava1enzue1a reblogged this · 2 years ago
ava1enzue1a reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 ava1enzue1a liked this · 2 years ago
ava1enzue1a liked this · 2 years ago -
 carolina-star liked this · 2 years ago
carolina-star liked this · 2 years ago -
 big-monavse liked this · 3 years ago
big-monavse liked this · 3 years ago -
 rubyredfortncarnivorousplants liked this · 3 years ago
rubyredfortncarnivorousplants liked this · 3 years ago -
 shan2o liked this · 3 years ago
shan2o liked this · 3 years ago -
 hereforthefanart liked this · 3 years ago
hereforthefanart liked this · 3 years ago -
 lekaisernoir liked this · 3 years ago
lekaisernoir liked this · 3 years ago -
 antrimundo liked this · 3 years ago
antrimundo liked this · 3 years ago -
 cloversposts liked this · 3 years ago
cloversposts liked this · 3 years ago -
 angelayasmim liked this · 3 years ago
angelayasmim liked this · 3 years ago -
 mrbdngl liked this · 3 years ago
mrbdngl liked this · 3 years ago -
 murfpersonalblog reblogged this · 3 years ago
murfpersonalblog reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 wolfofromania liked this · 3 years ago
wolfofromania liked this · 3 years ago -
 thequeerish liked this · 3 years ago
thequeerish liked this · 3 years ago -
 cr3ntist liked this · 3 years ago
cr3ntist liked this · 3 years ago -
 stengheli2 liked this · 3 years ago
stengheli2 liked this · 3 years ago -
 universerover liked this · 3 years ago
universerover liked this · 3 years ago -
 pregnantstallion liked this · 3 years ago
pregnantstallion liked this · 3 years ago -
 cobracommanderofficial reblogged this · 3 years ago
cobracommanderofficial reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 cobracommanderofficial liked this · 3 years ago
cobracommanderofficial liked this · 3 years ago -
 egyptnews2021-blog liked this · 3 years ago
egyptnews2021-blog liked this · 3 years ago -
 kozume57 liked this · 3 years ago
kozume57 liked this · 3 years ago -
 just-evil liked this · 3 years ago
just-evil liked this · 3 years ago -
 temporaryurlbecauseimindecisive reblogged this · 3 years ago
temporaryurlbecauseimindecisive reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 specificallyparamain liked this · 3 years ago
specificallyparamain liked this · 3 years ago -
 casualtalefestival liked this · 3 years ago
casualtalefestival liked this · 3 years ago -
 sidelinevictorian liked this · 3 years ago
sidelinevictorian liked this · 3 years ago -
 kryptokraptokroop liked this · 3 years ago
kryptokraptokroop liked this · 3 years ago -
 mentalidrainedfangirl liked this · 3 years ago
mentalidrainedfangirl liked this · 3 years ago -
 mayjor-lochardt liked this · 3 years ago
mayjor-lochardt liked this · 3 years ago -
 keylimon liked this · 3 years ago
keylimon liked this · 3 years ago -
 aduckable reblogged this · 3 years ago
aduckable reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 froggyan liked this · 3 years ago
froggyan liked this · 3 years ago -
 the-supreme-g0ddess liked this · 3 years ago
the-supreme-g0ddess liked this · 3 years ago -
 sirneb liked this · 3 years ago
sirneb liked this · 3 years ago -
 akiinai-alt liked this · 3 years ago
akiinai-alt liked this · 3 years ago -
 dragons-barb liked this · 3 years ago
dragons-barb liked this · 3 years ago -
 karmen-fourie liked this · 3 years ago
karmen-fourie liked this · 3 years ago -
 oneul-bam liked this · 3 years ago
oneul-bam liked this · 3 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts