The SLS (Space Launch System) Core Stage By Numbers
ALT: This video shows blades of grass moving in the wind on a beautiful day at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the background, we see the 212-foot-core stage for the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) rocket used for Artemis I. The camera ascends, revealing the core stage next to a shimmering body of water as technicians lead it towards NASA’s Pegasus barge. Credit: NASA
The SLS (Space Launch System) Core Stage by Numbers
Technicians with NASA and SLS core stage lead contractor Boeing, along with RS-25 engines lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, are nearing a major milestone for the Artemis II mission. The SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s core stage for Artemis II is fully assembled and will soon be shipped via barge from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, it will be prepped for stacking and launch activities.
Get to know the core stage – by the numbers.

Standing 212 feet tall and measuring 27.6 feet in diameter, the SLS core stage is the largest rocket stage NASA has ever built. Due to its size, the hardware must be shipped aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge.

900 miles
Once loaded, the barge – which was updated to accommodate the giant core stage -- will travel 900 miles to Florida across inland and ocean waterways. Once at Kennedy, teams with our Exploration Ground Systems team will complete checkouts for the core stage prior to stacking preparations.

18 Miles + 500 Sensors
As impressive as the core stage is on the outside, it’s also incredible on the inside. The “brains” of the rocket consist of three flight computers and special avionics systems that tell the rocket what to do. This is linked to 18 miles of cabling and more than 500 sensors and systems to help feed fuel and steer the four RS-25 engines.

8.8 million
Speaking of engines… Our SLS Moon rocket generates approximately 8.8 million pounds of thrust at launch. Two million pounds come from the four powerful RS-25 engines at the base of the core stage, while each of the two solid rocket boosters produces a maximum thrust of 3.6 million pounds. Together, the engines and boosters will help launch a crew of four Artemis astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft beyond Earth orbit to venture around the Moon.

733,000 Gallons
Achieving the powerful thrust required at launch calls for a large amount of fuel - 733,000 gallons, to be precise. The stage has two huge propellant tanks that hold the super-cooled liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen that make the rocket “go.” A new liquid hydrogen storage sphere has recently been built at Kennedy, which can store 1.25 million gallons of liquid hydrogen.

Four
The number four doesn’t just apply to the RS-25 engines. It’s also the number of astronauts who will fly inside our Orion spacecraft atop our SLS rocket for the first crewed Artemis mission. When NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Christina Koch, and Victor Glover along with CSA astronaut Jeremy Hansen launch, they will be the first astronauts returning to the Moon in more than 50 years.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Here are a few things you should know about our solar system this week:
1. Gearing Up for a Grand Finale

There’s just a year left until the Cassini mission begins its Grand Finale – the final phase of its mission, during which the spacecraft will dive repeatedly between the planet and the rings. To get ready, the Cassini team has launched an enhanced, mobile device-friendly version of the mission website. The site includes information about Cassini, Saturn, the moons and the rings – but it also tells the human stories behind one of the most ambitions expeditions of all time.
2.Caught in Transit

On Monday, May 9, the planet Mercury will cross directly in front of the sun, an event that hasn’t occurred since 2006 and won’t happen again until 2019. Find out how to watch HERE.
3. A Moon for Makemake

Our Hubble Space Telescope has spotted a small, dark moon orbiting Makemake (pronounced “MAH-kay MAH-kay). Make make is the second brightest icy dwarf planet – after Pluto – in the faraway Kuiper Belt.
4. The Age of the Aquarids

The Eta Aquarid meteor shower is the first of two showers that occur each year as a result of Earth passing through dust released by Halley’s Comet. This year, it should peak on the night of May 5/6. Get tips for watching HERE.
5. The Southern Lights of Saturn

On May 4, Cassini will reach periapse, the closest point to Saturn in the spacecraft’s orbit. At about this time, Cassini’s cameras will monitor Saturn’s south polar aurorae, and also image the bright limb of the planet to better understand its upper haze layers.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Whats the coolest thing u have seen or discovered???!!!! Like i mean cool as in something that made u nerd out! I used to want to work for nasa but found a love for teaching art instead so i find myself nersing out over the cool research yall put out! Much love from wise county texas!
What do you hope to find on the mars? / What would be the best possible outcome?
We Like Big Rockets and We Cannot Lie: Saturn V vs. SLS
On this day 50 years ago, human beings embarked on a journey to set foot on another world for the very first time.

At 9:32 a.m. EDT, millions watched as Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins lifted off from Launch Pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, flying high on the most powerful rocket ever built: the mighty Saturn V.

As we prepare to return humans to the lunar surface with our Artemis program, we’re planning to make history again with a similarly unprecedented rocket, the Space Launch System (SLS). The SLS will be our first exploration-class vehicle since the Saturn V took American astronauts to the Moon a decade ago. With its superior lift capability, the SLS will expand our reach into the solar system, allowing astronauts aboard our Orion spacecraft to explore multiple, deep-space destinations including near-Earth asteroids, the Moon and ultimately Mars.

So, how does the Saturn V measure up half a century later? Let’s take a look.
Mission Profiles: From Apollo to Artemis
Saturn V

Every human who has ever stepped foot on the Moon made it there on a Saturn V rocket. The Saturn rockets were the driving force behind our Apollo program that was designed to land humans on the Moon and return them safely back to Earth.

Developed at our Marshall Space Flight Center in the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket (V for the Roman numeral “5”) launched for the first time uncrewed during the Apollo 4 mission on November 9, 1967. One year later, it lifted off for its first crewed mission during Apollo 8. On this mission, astronauts orbited the Moon but did not land. Then, on July 16, 1969, the Apollo 11 mission was the first Saturn V flight to land astronauts on the Moon. In total, this powerful rocket completed 13 successful missions, landing humans on the lunar surface six times before lifting off for the last time in 1973.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Just as the Saturn V was the rocket of the Apollo generation, the Space Launch System will be the driving force behind a new era of spaceflight: the Artemis generation.

During our Artemis missions, SLS will take humanity farther than ever before. It is the vehicle that will return our astronauts to the Moon by 2024, transporting the first woman and the next man to a destination never before explored – the lunar South Pole. Over time, the rocket will evolve into increasingly more powerful configurations to provide the foundation for human exploration beyond Earth’s orbit to deep space destinations, including Mars.
SLS will take flight for the first time during Artemis 1 where it will travel 280,000 miles from Earth – farther into deep space than any spacecraft built for humans has ever ventured.
Size: From Big to BIGGER
Saturn V

The Saturn V was big.
In fact, the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center is one of the largest buildings in the world by volume and was built specifically for assembling the massive rocket. At a height of 363 feet, the Saturn V rocket was about the size of a 36-story building and 60 feet taller than the Statue of Liberty!
Space Launch System (SLS)

Measured at just 41 feet shy of the Saturn V, the initial SLS rocket will stand at a height of 322 feet. Because this rocket will evolve into heavier lift capacities to facilitate crew and cargo missions beyond Earth’s orbit, its size will evolve as well. When the SLS reaches its maximum lift capability, it will stand at a height of 384 feet, making it the tallest rocket in the world.
Power: Turning Up the Heat
Saturn V
For the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket was a beast – to say the least.
Fully fueled for liftoff, the Saturn V weighed 6.2 million pounds and generated 7.6 million pounds of thrust at launch. That is more power than 85 Hoover Dams! This thrust came from five F-1 engines that made up the rocket’s first stage. With this lift capability, the Saturn V had the ability to send 130 tons (about 10 school buses) into low-Earth orbit and about 50 tons (about 4 school buses) to the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Photo of SLS rocket booster test
Unlike the Saturn V, our SLS rocket will evolve over time into increasingly more powerful versions of itself to accommodate missions to the Moon and then beyond to Mars.
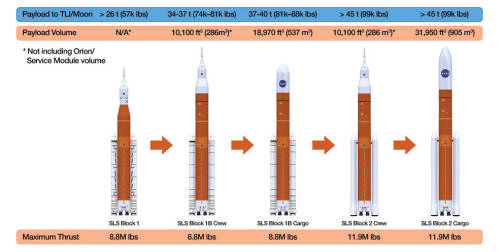
The first SLS vehicle, called Block 1, will weigh 5.75 million pounds and produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust at time of launch. That’s 15 percent more than the Saturn V produced during liftoff! It will also send more than 26 tons beyond the Moon. Powered by a pair of five-segment boosters and four RS-25 engines, the rocket will reach the period of greatest atmospheric force within 90 seconds!

Following Block 1, the SLS will evolve five more times to reach its final stage, Block 2 Cargo. At this stage, the rocket will provide 11.9 million pounds of thrust and will be the workhorse vehicle for sending cargo to the Moon, Mars and other deep space destinations. SLS Block 2 will be designed to lift more than 45 tons to deep space. With its unprecedented power and capabilities, SLS is the only rocket that can send our Orion spacecraft, astronauts and large cargo to the Moon on a single mission.
Build: How the Rockets Stack Up
Saturn V

The Saturn V was designed as a multi-stage system rocket, with three core stages. When one system ran out of fuel, it separated from the spacecraft and the next stage took over. The first stage, which was the most powerful, lifted the rocket off of Earth’s surface to an altitude of 68 kilometers (42 miles). This took only 2 minutes and 47 seconds! The first stage separated, allowing the second stage to fire and carry the rest of the stack almost into orbit. The third stage placed the Apollo spacecraft and service module into Earth orbit and pushed it toward the Moon. After the first two stages separated, they fell into the ocean for recovery. The third stage either stayed in space or crashed into the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)
Much like the Saturn V, our Space Launch System is also a multi-stage rocket. Its three stages (the solid rocket boosters, core stage and upper stage) will each take turns thrusting the spacecraft on its trajectory and separating after each individual stage has exhausted its fuel. In later, more powerful versions of the SLS, the third stage will carry both the Orion crew module and a deep space habitat module.
A New Era of Space Exploration
Just as the Saturn V and Apollo era signified a new age of exploration and technological advancements, the Space Launch System and Artemis missions will bring the United States into a new age of space travel and scientific discovery.
Join us in celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 Moon landing and hear about our future plans to go forward to the Moon and on to Mars by tuning in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Small Tissue Chips in Space a Big Leap Forward for Research
Tissue chips, thumb-drive sized devices that contain human cells in a 3D matrix, represent a giant leap in science.
They can test cells’ response to:
•stresses
•drugs
•genetic changes

The Tissue Chips in Space initiative seeks to better understand the role of microgravity on human health and disease and to translate that understanding to improved human health on Earth.
This series of investigations to test tissue chips in microgravity aboard the International Space Station is planned through a collaboration between the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) at the National Institutes for Health (NIH) and the National Laboratory in partnership with NASA.

Many of the changes in the human body caused by microgravity resemble the onset and progression of diseases associated with aging on Earth, but in space, changes occur much faster. Scientists may be able to use tissue chips in space to model changes that take months or years to happen on Earth.
A tissue chip needs three properties, according to Lucie Low, scientific program manager at NCATS. “It has to be 3D,” she explained. “It must have multiple different types of cells, and it must have microfluidic channels. Essentially, you get a functional unit of what human tissues are like, outside of the body,” said Low.

As accurate models of the structure and function of human organs, tissue chips provide a model for predicting whether a drug, vaccine or biologic agent is safe in humans more quickly and effectively than current methods.

This first phase of Tissue Chips in Space includes five investigations. An investigation of immune system aging is planned for launch on the SpaceX CRS-16 flight, scheduled for mid-November. The other four, scheduled to launch on subsequent flights, include lung host defense, the blood-brain barrier, musculoskeletal disease and kidney function. This phase tests the effects of microgravity on the tissue chips and demonstrates the capability of the automated system.
All five investigations make a second flight about 18 months later to confirm use of the model, such as testing potential drugs on the particular organs. Four more projects are scheduled for launch in summer 2020, including two on engineered heart tissue to understand cardiovascular health, one on muscle wasting and another on gut inflammation.
Ultimately, the technology could allow astronauts going into space to take along personalized chips that could be used to monitor changes in their bodies and to test possible countermeasures and therapies. That would be a major leap forward in keeping astronauts healthy on missions to deep space!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s your favorite black hole fact that you like to share with people?
What's a SPOC? Isn't that a star trek character?

Not all galaxies are lonely. Some have galaxy squads.
NGC 1706, captured in this image by our Hubble Space Telescope, belongs to something known as a galaxy group, which is just as the name suggests — a group of up to 50 galaxies which are gravitationally bound and relatively close to each other.
Our home galaxy, the Milky Way, has its own squad — known as the Local Group, which also contains the Andromeda galaxy, the Large and Small Magellanic clouds and the Triangulum galaxy.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What’s a Space Headache?
Headaches can be a common complaint during spaceflight. The Space Headaches experiment improves our understanding of such conditions, which helps in the development of methods to alleviate associated symptoms, and improve the well-being and performance of crew members in orbit. This can also improve our knowledge of similar conditions on Earth.

10 Ways to Celebrate Pi Day with Us on March 14
On March 14, we will join people across the U.S. as they celebrate an icon of nerd culture: the number pi.
So well known and beloved is pi, also written π or 3.14, that it has a national holiday named in its honor. And it’s not just for mathematicians and rocket scientists. National Pi Day is widely celebrated among students, teachers and science fans, too. Read on to find out what makes pi so special, how it’s used to explore space and how you can join the celebration with resources from our collection.

1—Remind me, what is pi?
Pi, also written π, is the Swiss Army knife of numbers. No matter how big or small a circle – from the size of our universe all the way down to an atom or smaller – the ratio of a circle’s circumference (the distance around it) to its diameter (the distance across it) is always equal to pi. Most commonly, pi is used to answer questions about anything circular or spherical, so it comes in handy especially when you’re dealing with space exploration.

2—How much pi do you need?
For simplicity, pi is often rounded to 3.14, but its digits go on forever and don’t appear to have any repeating patterns. While people have made it a challenge to memorize record-breaking digits of pi or create computer programs to calculate them, you really don’t need that many digits for most calculations – even at NASA. Here’s one of our engineers on how many decimals of pi you need.

3—Officially official.
Pi pops up in everything from rocket-science-level math to the stuff you learn in elementary school, so it’s gained a sort of cult following. On March 14 (or 3/14 in U.S. date format) in 1988, a physicist at the San Francisco Exploratorium held what is thought to be the first official Pi Day celebration, which smartly included the consumption of fruit pies. Math teachers quickly realized the potential benefits of teaching students about pi while they ate pie, and it all caught on so much that in 2009, the U.S. Congress officially declared March 14 National Pi Day. Here’s how to turn your celebration into a teachable moment.

4—Pi helps us explore space!
Space is full of circular and spherical features, and to explore them, engineers at NASA build spacecraft that make elliptical orbits and guzzle fuel from cylindrical fuel tanks, and measure distances on circular wheels. Beyond measurements and space travel, pi is used to find out what planets are made of and how deep alien oceans are, and to study newly discovered worlds. In other words, pi goes a long way at NASA.

5—Not just for rocket scientists.
No Pi Day is complete without a little problem solving. Even the math-averse will find something to love about this illustrated math challenge that features real questions scientists and engineers must answer to explore and study space – like how to determine the size of a distant planet you can’t actually see. Four new problems are added to the challenge each year and answers are released the day after Pi Day.

6—Teachers rejoice.
For teachers, the question is not whether to celebrate Pi Day, but how to celebrate it. (And how much pie is too much? Answer: The limit does not exist.) Luckily, our Education Office has an online catalog for teachers with all 20 of its “Pi in the Sky” math challenge questions for grades 4-12. Each lesson includes a description of the real-world science and engineering behind the problem, an illustrated handout and answer key, and a list of applicable Common Core Math and Next Generation Science Standards.

7—How Do We celebrate?
In a way, we celebrate Pi Day every day by using pi to explore space. But in our free time, we’ve been known to make and eat space-themed pies, too! Share your own nerdy celebrations with us here.

8—A pop-culture icon.
The fascination with pi, as well its popularity and accessibility have made it a go-to math reference in books, movies and television. Ellie, the protagonist in Carl Sagan’s book “Contact,” finds a hidden message from aliens in the digits of pi. In the original “Star Trek” series, Spock commanded an alien entity that had taken over the computer to compute pi to the last digit – an impossible task given that the digits of pi are infinite. And writers of “The Simpsons,” a show known for referencing math, created an episode in which Apu claims to know pi to 40,000 digits and proves it by stating that the 40,000th digit is 1.

9—A numbers game.
Calculating record digits of pi has been a pastime of mathematicians for millennia. Until the 1900s, these calculations were done by hand and reached records in the 500s. Once computers came onto the scene, that number jumped into the thousands, millions and now trillions. Scientist and pi enthusiast Peter Trueb holds the current record – 22,459,157,718,361 digits – which took his homemade computer 105 days of around-the-clock number crunching to achieve. The record for the other favorite pastime of pi enthusiasts, memorizing digits of pi, stands at 70,030.

10—Time to throw in the tau?
As passionate as people are about pi, there are some who believe things would be a whole lot better if we replaced pi with a number called tau, which is equal to 2π or 6.28. Because many formulas call for 2π, tau-enthusiasts say tau would provide a more elegant and efficient way to express those formulas. Every year on Pi Day, a small debate ensues. While we won’t take sides, we will say that pi is more widely used at NASA because it has applications far beyond geometry, where 2π is found most often. Perhaps most important, though, for pi- and pie-lovers alike is there’s no delicious homonym for tau.
Enjoy the full version of this article HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 shadow-king-club liked this · 2 weeks ago
shadow-king-club liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 emily19869 liked this · 1 month ago
emily19869 liked this · 1 month ago -
 andy202405 liked this · 1 month ago
andy202405 liked this · 1 month ago -
 ascuteasbellah liked this · 1 month ago
ascuteasbellah liked this · 1 month ago -
 constelacao-andromeda liked this · 1 month ago
constelacao-andromeda liked this · 1 month ago -
 kelemengabi liked this · 1 month ago
kelemengabi liked this · 1 month ago -
 astrodezign liked this · 2 months ago
astrodezign liked this · 2 months ago -
 the-cerulean-seal liked this · 3 months ago
the-cerulean-seal liked this · 3 months ago -
 lillyorlyracat liked this · 3 months ago
lillyorlyracat liked this · 3 months ago -
 the-cerulean-seal reblogged this · 3 months ago
the-cerulean-seal reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 katoani liked this · 4 months ago
katoani liked this · 4 months ago -
 papawolf1969 liked this · 4 months ago
papawolf1969 liked this · 4 months ago -
 little-black-rain-cloud reblogged this · 4 months ago
little-black-rain-cloud reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 little-black-rain-cloud liked this · 4 months ago
little-black-rain-cloud liked this · 4 months ago -
 onodakun reblogged this · 4 months ago
onodakun reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 onodakun liked this · 4 months ago
onodakun liked this · 4 months ago -
 starhasarrived reblogged this · 5 months ago
starhasarrived reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 starhasarrived liked this · 5 months ago
starhasarrived liked this · 5 months ago -
 a1-1976 liked this · 5 months ago
a1-1976 liked this · 5 months ago -
 doc183-blog liked this · 5 months ago
doc183-blog liked this · 5 months ago -
 dopeycruiser liked this · 5 months ago
dopeycruiser liked this · 5 months ago -
 tmesis2022 liked this · 5 months ago
tmesis2022 liked this · 5 months ago -
 finder-of-things liked this · 5 months ago
finder-of-things liked this · 5 months ago -
 claiminghigh liked this · 5 months ago
claiminghigh liked this · 5 months ago -
 flyboy1917 reblogged this · 5 months ago
flyboy1917 reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 flyboy1917 liked this · 5 months ago
flyboy1917 liked this · 5 months ago -
 the-inquisition-scmh reblogged this · 5 months ago
the-inquisition-scmh reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 the-inquisition-scmh liked this · 5 months ago
the-inquisition-scmh liked this · 5 months ago -
 lportesani-blog liked this · 5 months ago
lportesani-blog liked this · 5 months ago -
 lonestarflight reblogged this · 5 months ago
lonestarflight reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 steamfitter75 liked this · 6 months ago
steamfitter75 liked this · 6 months ago -
 paintermagazine liked this · 6 months ago
paintermagazine liked this · 6 months ago -
 tina-aumont reblogged this · 6 months ago
tina-aumont reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 tina-aumont liked this · 6 months ago
tina-aumont liked this · 6 months ago -
 comicshistory liked this · 6 months ago
comicshistory liked this · 6 months ago -
 unknownnazy90 liked this · 7 months ago
unknownnazy90 liked this · 7 months ago -
 sakuraswordly reblogged this · 7 months ago
sakuraswordly reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 anamariaurrutia reblogged this · 7 months ago
anamariaurrutia reblogged this · 7 months ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts