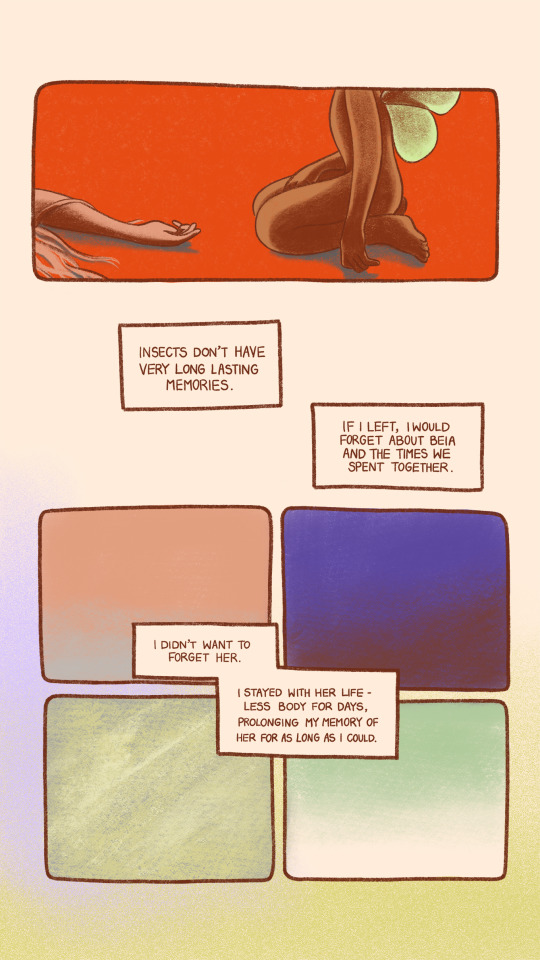
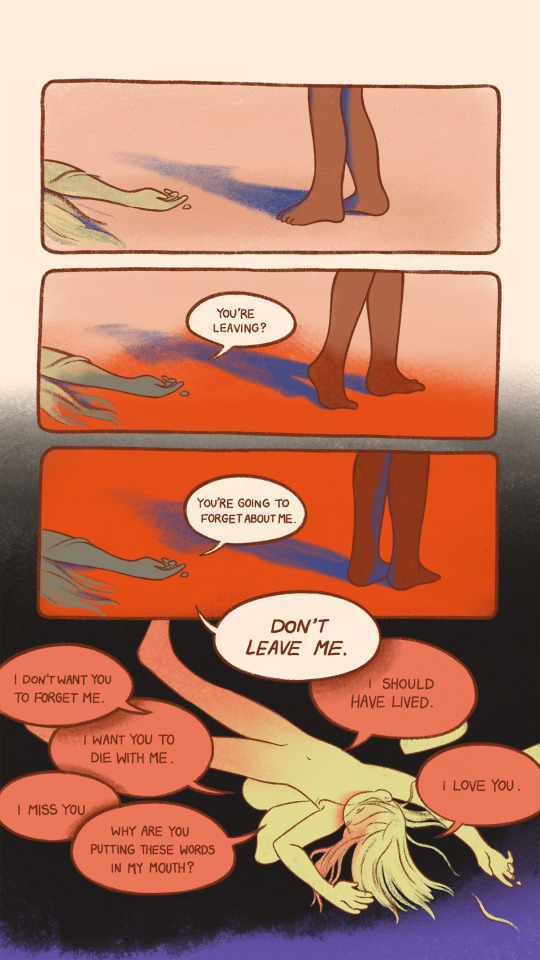
Hello Ashley! Returned To An Old Story Of Mine And Trying To Rebuild Large Parts Of The Plot That Didn't
Hello Ashley! Returned to an old story of mine and trying to rebuild large parts of the plot that didn't satisfy me. I figure it's best to detail all the major story beats before I fill in all the icing around them. From chapter 1 to chapter 15 (so we're not considering spoilers!), what major story beats would you say you finalized first? Was it hard deciding which little bits needed to come up and when, even after you had scripted the major steps?
–You’re definitely on the right track, I also used that method. I had a beginning and an end point for the first book, then looked backwards from there, mapping the major beats in each chapter. It’s also personally important for me to know the WHY of everything. I need a Why for everything I write and do, I find it motivating.
So it’s been a while and my memory is foggy, but I believe the broad outline was like:> Duane & Sette have misadventures that help them understand each other. Why do they need to understand each other? Because they are lonely, broken people and the goal is to better them.> They make it to her cousin’s along with the macguffin, which results in a climax, but macguffin escapes. What is the why of the macguffin? The macguffin isn’t just an antagonist; it’s all antagonism. It is the ultimate macguffin, and is motivated by the misery and misdeeds in the story itself.> They chase the macguffin and wind up isolated in a situation that forces out the best of Sette and the worst of Duane, with disastrous consequences. Why is the worst of Duane important to see? Because if there’s hope for the worst of us, despair is only an excuse. Why is the best of Sette important to see? Because it’s not so very Best, and she needs to see all the room she has to get better.> They reunite with the macguffin for another battle.
Easy-peasy. But now let’s flesh out that first step and mark out the milestones:
engage and fight the wand’ring root, introducing their respective characters in very broad strokes
encounter the RBB, enter the crypt, still in-character, but each gradually starts to crack. Duane goes super violent, Sette shows fear
fight each other at the waystation, Duane’s veneer of civility is fully shattered by admitting he’s a closet cannibal with control issues, Sette’s veneer of roguishness is shattered by admitting she’s scared of failing her da
True selves semi-revealed, Sette has an adventure in town, starts trouble, leads to…
Duane battling Quigley, coming face to face with Alderode
Sette sneaks Duane over the border, enters his memories
By seeing who Duane truly was, Sette fully understands who he is now
During their fight the next day in the toyshop, Duane fully understands what Sette needs of him (he doesn’t fully understand who she is, he’s not as insightful as she is)
And bam, that’s how I outline. It’s a pretty simple structure when you lay it out like that, but then you start adding in B and C plots, two dozen secondary characters, and it becomes deceptively complex!
Otherwise yeah, figuring out where to move the plot forward, where to cut away to other storylines (and how much to devote to them), where to pause and meander for character building - that’s all the most difficult stuff. Most of us can sit around and write cute dialog or character studies all day - fanfiction is FULL of amateur writers who can do this marvellously - but the BEST and most successful writers are able to tell an engaging narrative with lots of moving parts and suspenseful story turns. Maybe they get panned because their prose isn’t elegant or maybe their characters are hackneyed - but they still sell mountains of books because they know how to keep readers turning pages by structuring a suspenseful story.
Good luck with that, ‘cause it’s the hardest part! And personally, I have particular considerations I have to make that you probably don’t have to in prose, particularly prose meant to be read all at once. I need to try and make each page at least mildly engaging and end on a hook wherever I can, since there’s no guarantee the reader is going to come back to progress the story in two days :D
More Posts from Rainwvalker and Others
How do you feel about the fact that Book 1 of Unsounded written in prose would be like one or maybe two books/volumes and take much less time? I often think about stuff like that as a comic artist :o
It’s true, but it would be a different beast. Stories are so dependent on the medium. Think about how they change between books and film, between film and tv, between comics and novels! Watchmen the comic and Watchmen the film are related, but they’re third cousins at best. Are the ATLA comics really a seamless transition from the show? Does FFVII the OG game really feel like it came before Advent Children? I am sorry I only have Boomer examples
Unsounded in prose would lose all the sight gags; the moments of surprise or awe when you load a new page to see a new creature or location or sudden story turn. Reactions that are told with a heart-wrenching facial expression would instead have to be limned in words.
And words are great, words are super powerful, but words do their own thing and have their own strengths. You can paint scenes far more powerfully with words than you can with comic art, because with them, you’re painting on the infinite canvas of the reader’s imagination. But at the same time, you’re losing specificity and some potential impact. Well-done art affects us deeply. We’re drawn to it. We want to see faces.
Anyway, this has actually really been on my mind the last few nights because I’ve been listening to The Neverending Story, which I’d never read before, but I’ve always really enjoyed the movie. And though the plots are basically the same, they are SO different to me! I dislike Bastian so much in the book, and like Atreyu so much more. It was totally opposite for me in the movie. And it’s all to do with the actors.
So I don’t know, Anon, it doesn’t bug me that yes, the plot of the Unsounded could be told faster in prose, in books. Because a work is more than its plot. Webcomics in particular are this crazy modern format that let us communicate like this in-between every page. We have memes and in-jokes and can speculate on mysteries and dream and hope about upcoming pages. It’s cool!
Novels can do this too, of course, and serial fiction has been a thing for centuries. Webcomics are a pretty neat evolution of that.
Anyway, I forgot my point.
hey netizens! i'm not sure how many people are aware, but youtube's been slowly rolling out a new anti-adblock policy that can't be bypassed with the usual software like uBlock Origin and Pi-Hole out of the gate
BUT, if you're a uBlock Origin user (or use an adblocker with a similar cosmetics modifier), you can add these commands in the uBlock dashboard (under My Filters) to get rid of it!
youtube.com##+js(set, yt.config_.openPopupConfig.supportedPopups.adBlockMessageViewModel, false) youtube.com##+js(set, Object.prototype.adBlocksFound, 0) youtube.com##+js(set, ytplayer.config.args.raw_player_response.adPlacements, []) youtube.com##+js(set, Object.prototype.hasAllowedInstreamAd, true)
reblog to help keep the internet less annoying and to tell corporations that try shit like this to go fuck themselves <3
Well now you and Anon have me rereading Ch14 and I've noticed that... Lemuel is much kinder than Duane! Sometimes it feels like Duane is mostly kind when it's convenient, whereas Lemuel looks out for others even outside of his immediate sphere. Heck, just one example: Duane heard how Lem had to strangle someone to death and... didn't even blink twice! I know they're at war, but that seemed so cold. I don't know! tl;dr They're great characters that make me think :)
It’s an interesting observation! I think that Lemuel and Duane are both very kind, but they are also pretty masculine. And at the risk of perpetuating stereotypes, it doesn’t seem that masculinity generally allows a man to easily give voice to his concerns and emotions. So Duane wouldn’t hear that Lemuel had to strangle a foeman to desperately save himself, and then turn around to Lem and ask if he was doing okay. He wouldn’t even do it in private. Likewise Lemuel wouldn’t ask Duane how he was doing after his travails at the Academy and his scary stint in Fachlyne. They just weren’t raised to talk to each other that way. Blame it on them mostly not having a mother, or on their grandpa being a hardass or on Alderode generally expecting men to be so emotionally opaque - but it’s not how these boys communicate with each other
But it doesn’t mean they don’t love each other or don’t do kindnesses for one another. Duane worked very hard to get himself transferred to the same Order as Lemuel. Duane’s very presence is in fact a great show of concern for his brother’s welfare. Seeking him out to fight alongside him in that first battle in ch14 was an act of kindness and concern. After the vliegeng falls from the sky, Lemuel goes into the chapel with Duane to be with him because he knew how nervous the whole thing had made him. The Adeliers may not *say* the right things to each other, but they are *there* for each other.
There were some other more subtle relationship dynamics at play in that chapter as well. In a sense, Lemuel’s ability to show concern for others was a privilege he could afford because he wasn’t an officer. Duane was, and didn’t feel he could show too much compassion because that’s a vulnerability. His charges would respect him less and have less confidence in their own roles if he wasn’t always a paragon of authority and strength to them. So he was always very concerned with their physical welfare, but showing concern for their emotional welfare was off the table.
(you see this learned pattern perfectly repeat fifteen years later with him and Sette)
You also see the brick wall between them in chapter 7 after their stickfight. Duane nudges a brick out of it and invites Lemuel to tell him why he’s been acting weird, but Lemuel does not budge. And Duane does not insist. Just like he never followed up with him in the army. Lemuel breaks down and bawls in his arms one night and Duane looks totally lost, defaulting back to how he would comfort him when he was a little boy. Lemuel holds on to his asploded comrade’s tooth and Duane just yells at him to burn it. Lemuel hacks up a giant boar in the wake of another comrade’s death and Duane continues on with his duties. Lemuel sets a cart of war prisoners on fire and Duane decides not to ever think about it again for fifteen years.
No, I don’t think the issue is one of a lack of kindness. It’s not knowing how to express his (frankly quite severe) concern for his brother in a socially acceptable way. Duane would have done anything for Lemuel, would have died for him happily, but he didn’t have the emotional tools to do what Lemuel really, truly needed.
What's the difference in pronunciations between the Ss in Ssael and the S in Soud? Are they, perhaps, pronounced the same, but spelled so as an artefact from Old Tainish? What about the Mm in Mmatont- how's that pronounced?
Double S is a z. Double m is an m with a stop after, treat the mm like its own syllable. So it’s mm-atont. Like, yum, delicious traitors. Mm-atont.
Double n works the same. ssh- is the same. Double L I borrowed from Spanish, and is an english y, with the interesting New Tainish tweak of becoming a separate syllable if it’s at the end of a word. So sshupall (friend) is pronounced probably nothing like you’d imagine! It’s four syllables. ssh-oo-pah-yeh.
Originally I considered using more apostrophes and diacritics in Tainish but fantasy languages are always tattooed up with marks like eighty year old bikers. If French can have utterly unintuitive orthography, so can Tainish, by gum.
Those who approach the New Testament solely through English translations face a serious linguistic obstacle to apprehending what these writings say about justice. In most English translations, the word ‘justice’ occurs relatively infrequently. It is no surprise, then, that most English-speaking people think the New Testament does not say much about justice; the Bibles they read do not say much about justice. English translations are in this way different from translations into Latin, French, Spanish, German, Dutch — and for all I know, most languages. The basic issue is well known among translators and commentators. Plato’s Republic, as we all know, is about justice. The Greek noun in Plato’s text that is standardly translated as 'justice’ is 'dikaiosune;’ the adjective standardly translated as 'just’ is 'dikaios.’ This same dik-stem occurs around three hundred times in the New Testament, in a wide variety of grammatical variants. To the person who comes to English translations of the New Testament fresh from reading and translating classical Greek, it comes as a surprise to discover that though some of those occurrences are translated with grammatical variants on our word 'just,’ the great bulk of dik-stem words are translated with grammatical variants on our word 'right.’ The noun, for example, is usually translated as 'righteousness,’ not as 'justice.’ In English, we have the word 'just’ and its grammatical variants coming from the Latin iustitia, and the word 'right’ and its grammatical variants coming from the Old English recht. Almost all our translators have decided to translate the great bulk of dik-stem words in the New Testament with grammatical variants on the latter — just the opposite of the decision made by most translators of classical Greek. I will give just two examples of the point. The fourth of the beatitudes of Jesus, as recorded in the fifth chapter of Matthew, reads, in the New Revised Standard Version, 'Blessed are those who hunger and thirst for righteousness, for they will be filled.’ The word translated as 'righteousness’ is 'dikaiosune.’ And the eighth beatitude, in the same translation, reads 'Blessed are those who are persecuted for righteousness’ sake, for theirs is the kingdom of heaven.’ The Greek word translated as 'righteousness’ is 'dikaiosune.’ Apparently, the translators were not struck by the oddity of someone being persecuted because he is righteous. My own reading of human affairs is that righteous people are either admired or ignored, not persecuted; people who pursue justice are the ones who get in trouble. It goes almost without saying that the meaning and connotations of 'righteousness’ are very different in present-day idiomatic English from those of 'justice.’ 'Righteousness’ names primarily if not exclusively a certain trait of personal character. … The word in present-day idiomatic English carries a negative connotation. In everyday speech one seldom any more describes someone as righteous; if one does, the suggestion is that he is self-righteous. 'Justice,’ by contrast, refers to an interpersonal situation; justice is present when persons are related to each other in a certain way. … When one takes in hand a list of all the occurrences of dik-stem words in the Greek New Testament, and then opens up almost any English translation of the New Testament and reads in one sitting all the translations of these words, a certain pattern emerges: unless the notion of legal judgment is so prominent in the context as virtually to force a translation in terms of justice, the translators will prefer to speak of righteousness. Why are they so reluctant to have the New Testament writers speak of primary justice? Why do they prefer that the gospel of Jesus Christ be the good news of the righteousness of God rather than the good news of the justice of God? Why do they prefer that Jesus call his followers to righteousness rather than to justice?
Nicholas Wolsterstorff (via chamerionwrites)
-
 schniggles liked this · 7 months ago
schniggles liked this · 7 months ago -
 deuswyvern liked this · 2 years ago
deuswyvern liked this · 2 years ago -
 kusuiel reblogged this · 2 years ago
kusuiel reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 electricpyre reblogged this · 3 years ago
electricpyre reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 nerdywyrds reblogged this · 4 years ago
nerdywyrds reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 ephemera8 liked this · 4 years ago
ephemera8 liked this · 4 years ago -
 hermdoggydog reblogged this · 4 years ago
hermdoggydog reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 charyeurydice liked this · 4 years ago
charyeurydice liked this · 4 years ago -
 slowpoke-art liked this · 4 years ago
slowpoke-art liked this · 4 years ago -
 khyrberos liked this · 4 years ago
khyrberos liked this · 4 years ago -
 black-solitaire liked this · 4 years ago
black-solitaire liked this · 4 years ago -
 duskmonk liked this · 4 years ago
duskmonk liked this · 4 years ago -
 smuggysnake liked this · 4 years ago
smuggysnake liked this · 4 years ago -
 frostmoths liked this · 4 years ago
frostmoths liked this · 4 years ago -
 dialectrician reblogged this · 4 years ago
dialectrician reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 jasjabberwocky liked this · 4 years ago
jasjabberwocky liked this · 4 years ago -
 dialectrician liked this · 4 years ago
dialectrician liked this · 4 years ago -
 harblkun liked this · 4 years ago
harblkun liked this · 4 years ago -
 awlwren liked this · 4 years ago
awlwren liked this · 4 years ago -
 2woodroses liked this · 4 years ago
2woodroses liked this · 4 years ago -
 ottercopter liked this · 4 years ago
ottercopter liked this · 4 years ago -
 storylinecaroline reblogged this · 4 years ago
storylinecaroline reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 zlukaka liked this · 4 years ago
zlukaka liked this · 4 years ago -
 rainwvalker reblogged this · 4 years ago
rainwvalker reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 feelingkindawoozy reblogged this · 4 years ago
feelingkindawoozy reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 rainwvalker liked this · 4 years ago
rainwvalker liked this · 4 years ago -
 vamonkea reblogged this · 4 years ago
vamonkea reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 rhiarebel liked this · 4 years ago
rhiarebel liked this · 4 years ago -
 magmahurricane liked this · 4 years ago
magmahurricane liked this · 4 years ago -
 breadpartyeighthundred liked this · 4 years ago
breadpartyeighthundred liked this · 4 years ago -
 asynchronouscommunication liked this · 4 years ago
asynchronouscommunication liked this · 4 years ago -
 antialiasis liked this · 4 years ago
antialiasis liked this · 4 years ago -
 griffinnorth reblogged this · 4 years ago
griffinnorth reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 soulbreather liked this · 4 years ago
soulbreather liked this · 4 years ago -
 carnotaur liked this · 4 years ago
carnotaur liked this · 4 years ago -
 gunpowderguillotine liked this · 4 years ago
gunpowderguillotine liked this · 4 years ago -
 afriendlyirin liked this · 4 years ago
afriendlyirin liked this · 4 years ago -
 chainsmithloser liked this · 4 years ago
chainsmithloser liked this · 4 years ago -
 frightninbolt reblogged this · 4 years ago
frightninbolt reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 cean-untitled liked this · 4 years ago
cean-untitled liked this · 4 years ago -
 businesstiramisu liked this · 4 years ago
businesstiramisu liked this · 4 years ago -
 businesstiramisu reblogged this · 4 years ago
businesstiramisu reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 ketamage liked this · 4 years ago
ketamage liked this · 4 years ago -
 leidensygdom liked this · 4 years ago
leidensygdom liked this · 4 years ago -
 pleasespellchimerical liked this · 4 years ago
pleasespellchimerical liked this · 4 years ago -
 flyflystuff liked this · 4 years ago
flyflystuff liked this · 4 years ago -
 moonwhing liked this · 4 years ago
moonwhing liked this · 4 years ago -
 chickensauras liked this · 4 years ago
chickensauras liked this · 4 years ago
Hello! This is a tumblr blog. I do stuff. Actually I don't really do stuff, I just reblog things. Yup. That's about it. Banner art is by @painter-marx, icon is by @rifuye
157 posts