The North Face Of Mt St Helens Collapses At 8:32 A.m. On Sunday, May 18, 1980, Creating The Largest Landslide
The north face of Mt St Helens collapses at 8:32 a.m. on Sunday, May 18, 1980, creating the largest landslide ever recorded and signalling the start of a VEI 5 eruption, considered the most disastrous in US history.
More Posts from Sciencebloggin and Others
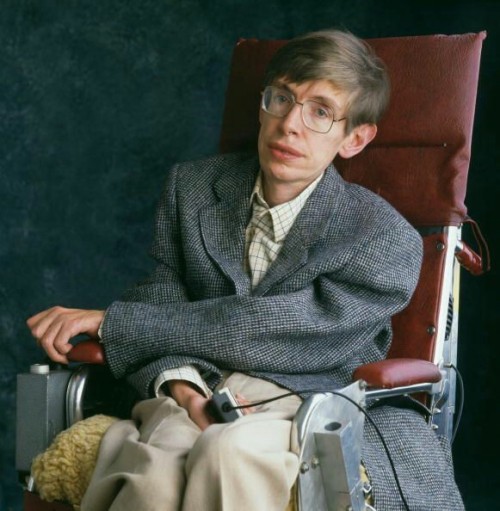



“I’m not afraid of death, but I’m in no hurry to die. I have so much I want to do first.”
And he did so much. He became an evershining star for humankind to look up to. Rest in peace.
Time And Space

When Apollo 11 successfully landed and the images were released, ‘The Sun’ newspaper in Vancouver changed it’s name to ‘The Moon’ to report it.
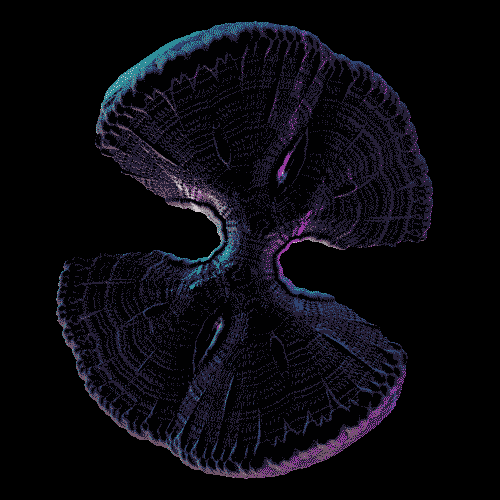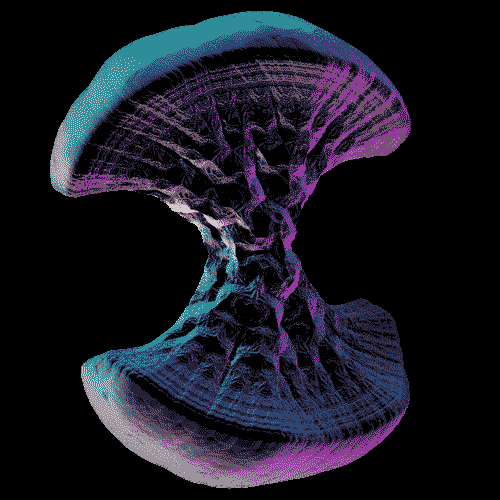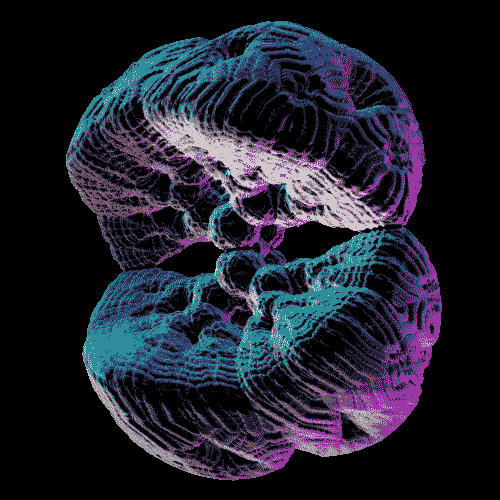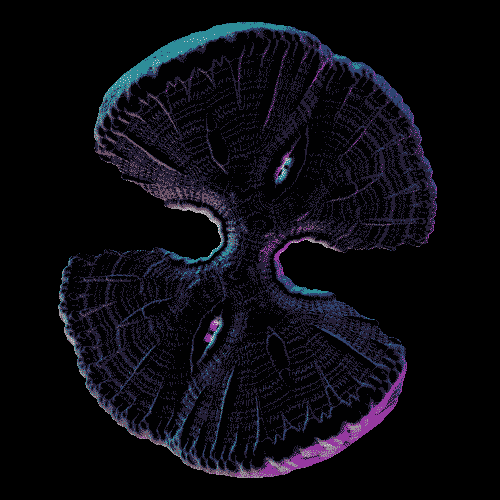

The Infrared Universe - NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope
NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope celebrated its 12th anniversary with the release of a new digital calendar showcasing some of the best pictures taken by the telescope. The images above demonstrate the Spitzer space telescope’s amazing infrared imaging abilities. These images include Nebulae, Galaxies, Super Nova, and much more. Though the calendar is now outdated, it still has a lot of great science information (and cool images). Check the credit for links!
Credit: NASA/JPL








some of my favourite microscope images I’ve taken
please don’t repost without credit
Solar System: 10 Things to Know This Week
Pioneer Days
Someone’s got to be first. In space, the first explorers beyond Mars were Pioneers 10 and 11, twin robots who charted the course to the cosmos.

1-Before Voyager

Voyager, with its outer solar system tour and interstellar observations, is often credited as the greatest robotic space mission. But today we remember the plucky Pioneers, the spacecraft that proved Voyager’s epic mission was possible.
2-Where No One Had Gone Before

Forty-five years ago this week, scientists still weren’t sure how hard it would be to navigate the main asteroid belt, a massive field of rocky debris between Mars and Jupiter. Pioneer 10 helped them work that out, emerging from first the first six-month crossing in February 1973. Pioneer 10 logged a few meteoroid hits (fewer than expected) and taught engineers new tricks for navigating farther and farther beyond Earth.
3-Trailblazer No. 2

Pioneer 11 was a backup spacecraft launched in 1973 after Pioneer 10 cleared the asteroid belt. The new mission provided a second close look at Jupiter, the first close-up views of Saturn and also gave Voyager engineers plotting an epic multi-planet tour of the outer planets a chance to practice the art of interplanetary navigation.
4-First to Jupiter

Three-hundred and sixty-three years after humankind first looked at Jupiter through a telescope, Pioneer 10 became the first human-made visitor to the Jovian system in December 1973. The spacecraft spacecraft snapped about 300 photos during a flyby that brought it within 81,000 miles (about 130,000 kilometers) of the giant planet’s cloud tops.
5-Pioneer Family

Pioneer began as a Moon program in the 1950s and evolved into increasingly more complicated spacecraft, including a Pioneer Venus mission that delivered a series of probes to explore deep into the mysterious toxic clouds of Venus. A family portrait (above) showing (from left to right) Pioneers 6-9, 10 and 11 and the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and Multiprobe series. Image date: March 11, 1982.
6-A Pioneer and a Pioneer

Classic rock has Van Halen, we have Van Allen. With credits from Explorer 1 to Pioneer 11, James Van Allen was a rock star in the emerging world of planetary exploration. Van Allen (1914-2006) is credited with the first scientific discovery in outer space and was a fixture in the Pioneer program. Van Allen was a key part of the team from the early attempts to explore the Moon (he’s pictured here with Pioneer 4) to the more evolved science platforms aboard Pioneers 10 and 11.
7-The Farthest…For a While

For more than 25 years, Pioneer 10 was the most distant human-made object, breaking records by crossing the asteroid belt, the orbit of Jupiter and eventually even the orbit of Pluto. Voyager 1, moving even faster, claimed the most distant title in February 1998 and still holds that crown.
8-Last Contact

We last heard from Pioneer 10 on Jan. 23, 2003. Engineers felt its power source was depleted and no further contact should be expected. We tried again in 2006, but had no luck. The last transmission from Pioneer 11 was received in September 1995. Both missions were planned to last about two years.
9-Galactic Ghost Ships

Pioneers 10 and 11 are two of five spacecraft with sufficient velocity to escape our solar system and travel into interstellar space. The other three—Voyagers 1 and 2 and New Horizons—are still actively talking to Earth. The twin Pioneers are now silent. Pioneer 10 is heading generally for the red star Aldebaran, which forms the eye of Taurus (The Bull). It will take Pioneer over 2 million years to reach it. Pioneer 11 is headed toward the constellation of Aquila (The Eagle) and will pass nearby in about 4 million years.
10-The Original Message to the Cosmos

Years before Voyager’s famed Golden Record, Pioneers 10 and 11 carried the original message from Earth to the cosmos. Like Voyager’s record, the Pioneer plaque was the brainchild of Carl Sagan who wanted any alien civilization who might encounter the craft to know who made it and how to contact them. The plaques give our location in the galaxy and depicts a man and woman drawn in relation to the spacecraft.
Read the full version of this week’s 10 Things article HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Image of Saturn taken by Cassini spacecraft in October 28, 2016.
Credit: NASA/JPL

Quantum tunnelling
Tunneling is a quantum mechanical effect. A tunneling current occurs when electrons move through a barrier that they classically shouldn’t be able to move through. In classical terms, if you don’t have enough energy to move “over” a barrier, you won’t. However, in the quantum mechanical world, electrons have wavelike properties. These waves don’t end abruptly at a wall or barrier, but taper off quickly. If the barrier is thin enough, the probability function may extend into the next region, through the barrier! Because of the small probability of an electron being on the other side of the barrier, given enough electrons, some will indeed move through and appear on the other side. When an electron moves through the barrier in this fashion, it is called tunneling.

Quantum mechanics tells us that electrons have both wave and particle-like properties. Tunneling is an effect of the wavelike nature.

The top image shows us that when an electron (the wave) hits a barrier, the wave doesn’t abruptly end, but tapers off very quickly - exponentially. For a thick barrier, the wave doesn’t get past.
The bottom image shows the scenario if the barrier is quite thin (about a nanometer). Part of the wave does get through and therefore some electrons may appear on the other side of the barrier.
Because of the sharp decay of the probability function through the barrier, the number of electrons that will actually tunnel is very dependent upon the thickness of the barrier. The current through the barrier drops off exponentially with the barrier thickness
Source: nanoscience.com | Images: x | x | x

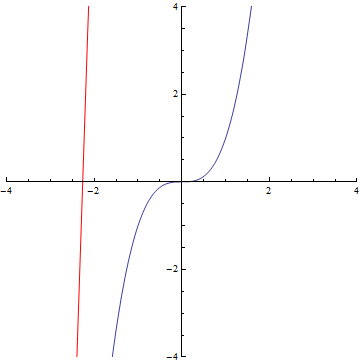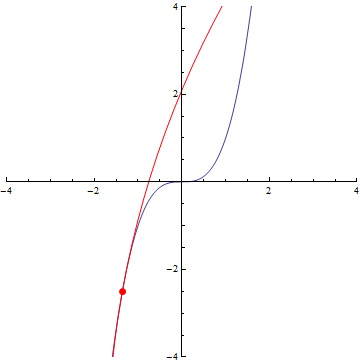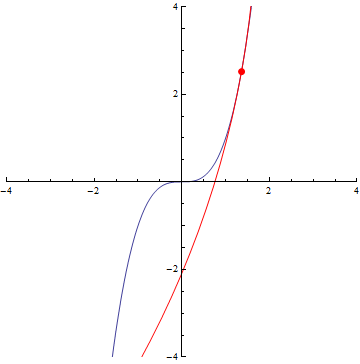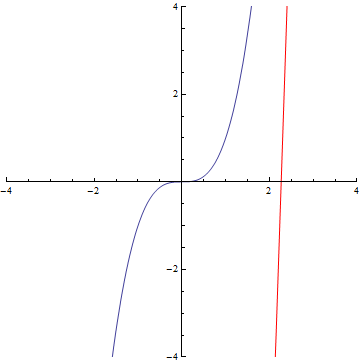

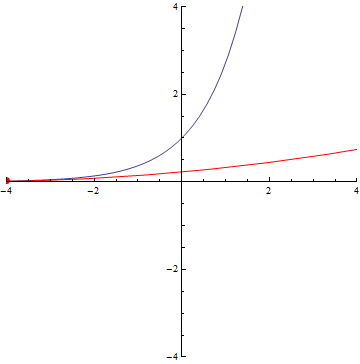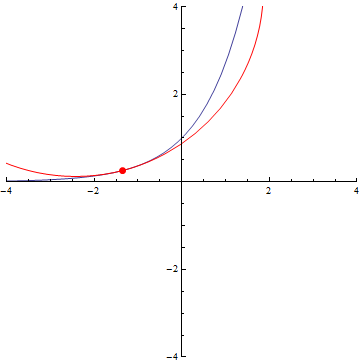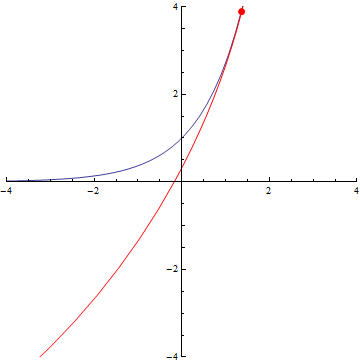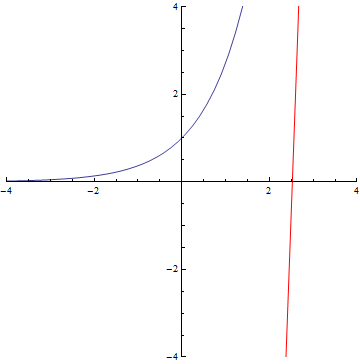


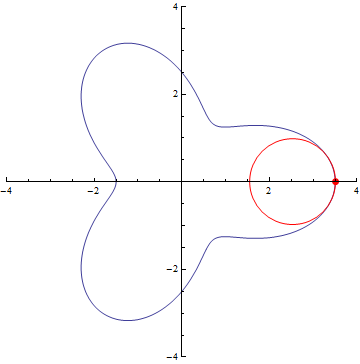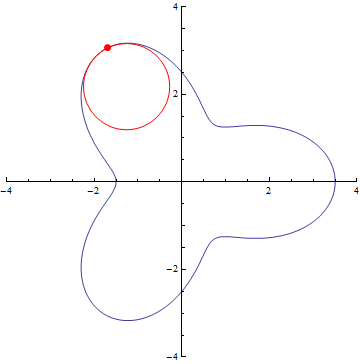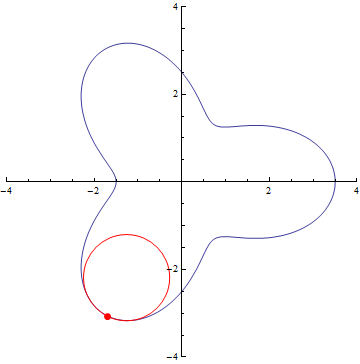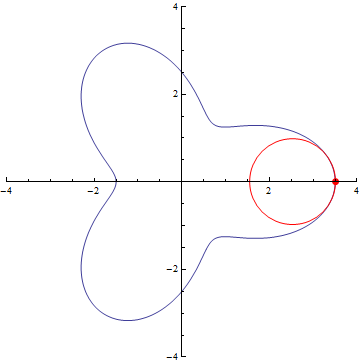



The curvature of curves.
x²
x³
sin(x)
exp(x)
Normal distribution (y=exp(-x²/2))
Ellipse
r=5/2+cos(3τθ)
x=(t-1)(t+1), y=t(t-1)(t+1)
Archimedes’ Spiral
Logarithmic spiral
If you want to try your own curve, try on Desmos graphing calculator!
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/lpm3igzbhy



dude.
-
 sciencebloggin reblogged this · 1 year ago
sciencebloggin reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 theoldbluerockpalaceshow liked this · 1 year ago
theoldbluerockpalaceshow liked this · 1 year ago -
 stigandr111x reblogged this · 3 years ago
stigandr111x reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 stigandr111x liked this · 3 years ago
stigandr111x liked this · 3 years ago -
 ukg reblogged this · 3 years ago
ukg reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 cromamon liked this · 3 years ago
cromamon liked this · 3 years ago -
 rkbob reblogged this · 3 years ago
rkbob reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 mukarose reblogged this · 3 years ago
mukarose reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 just-a-random-guy liked this · 4 years ago
just-a-random-guy liked this · 4 years ago -
 biphonatix reblogged this · 4 years ago
biphonatix reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 biphonatix liked this · 4 years ago
biphonatix liked this · 4 years ago -
 mayflame15 liked this · 4 years ago
mayflame15 liked this · 4 years ago -
 horticulturehomo reblogged this · 4 years ago
horticulturehomo reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 du-rauthr-vrangr reblogged this · 4 years ago
du-rauthr-vrangr reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 du-rauthr-vrangr liked this · 4 years ago
du-rauthr-vrangr liked this · 4 years ago -
 teenblunder reblogged this · 4 years ago
teenblunder reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 inknstars reblogged this · 4 years ago
inknstars reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 inknstars liked this · 4 years ago
inknstars liked this · 4 years ago -
 if-youre-not-a-dog-then-leave liked this · 4 years ago
if-youre-not-a-dog-then-leave liked this · 4 years ago -
 zaethtalk reblogged this · 4 years ago
zaethtalk reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 zaethien liked this · 4 years ago
zaethien liked this · 4 years ago -
 scurvyeunuch reblogged this · 4 years ago
scurvyeunuch reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 erisnyxgrim liked this · 4 years ago
erisnyxgrim liked this · 4 years ago -
 deepestgardentreemuffin liked this · 4 years ago
deepestgardentreemuffin liked this · 4 years ago -
 keymonkey69-3 reblogged this · 4 years ago
keymonkey69-3 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 keymonkey69-3 liked this · 4 years ago
keymonkey69-3 liked this · 4 years ago -
 crabber44 reblogged this · 4 years ago
crabber44 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 uhhhhh-jpg liked this · 4 years ago
uhhhhh-jpg liked this · 4 years ago -
 sphinxnomore liked this · 4 years ago
sphinxnomore liked this · 4 years ago -
 rednecktoreason liked this · 4 years ago
rednecktoreason liked this · 4 years ago -
 marxsound liked this · 4 years ago
marxsound liked this · 4 years ago -
 jansgrace liked this · 4 years ago
jansgrace liked this · 4 years ago -
 stanfave reblogged this · 4 years ago
stanfave reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 ssolson liked this · 4 years ago
ssolson liked this · 4 years ago -
 stupideffinbee reblogged this · 4 years ago
stupideffinbee reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 kitgirl91 liked this · 4 years ago
kitgirl91 liked this · 4 years ago -
 digestionmachine reblogged this · 4 years ago
digestionmachine reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 areyouintothis1 reblogged this · 4 years ago
areyouintothis1 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 az-coyote-nate reblogged this · 4 years ago
az-coyote-nate reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 lovethycar reblogged this · 5 years ago
lovethycar reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 vikingforkliftsafari reblogged this · 5 years ago
vikingforkliftsafari reblogged this · 5 years ago
