Let's Talk For A Moment About Food Prices, Inflation, And The Nitrogen Fertilizer Shortage, And Steps
Let's talk for a moment about food prices, inflation, and the nitrogen fertilizer shortage, and steps you can take. We're going to go from food bank to growing your own, so stick around. This is mostly written for people who do not have much, if any, start up money.
To be brief, food prices are high, and inflation is going to mean more people will be struggling. On top of that, there has been a nitrogen fertilizer shortage, and on top of that, China and Russia said they wouldn't be exporting any until June.
I'm not here to discuss how bad it'll be, I'm here to provide some options.
First off, if you have money, donate money to food banks. If you're in a well-off area and your food banks have lots of support, consider donating money to areas that aren't as well off. Food banks can buy in bulk, so they can get way more food for the same dollar, which is why I'm not saying donate food.
Secondly, if you're struggling or even if it would make life a bit easier, use your food bank. If it's coming down to rent or food, go to the food bank and pay your rent. This might be different where you are, but here they get enough support that they really want and encourage people to come get food. If you're not sure, you can always call and ask.
Consider joining a bulk buying club (this is where a lot of food coops started) - people joining together so they can buy in bulk, get the cheaper prices, and then divide it up. If there's not one where you are, consider starting one. Buying in bulk is so much more cost efficient!
Where to grow:
Next comes growing food. If you don't have space, see if there are community gardens that you can join- or start one by asking the owners of vacant land if you can put in a garden. Join your local gardening groups (they're probably on facebook) and see if there's anyone with space willing to let you garden, or make some kind of arrangement.
If none of those options work, look into guerrilla gardening. Two factors for success here are that your plants be located a) close enough to you that you could feasibly walk by them multiple times per week and b) located where they either won't be noticed or won't bother the type of people who would notice. There has been much written about this, read up on it.
Of course, if you're lucky, you have your own yard, and can just grow in the ground there.
What to grow:
We've got a different mind set than many self-sufficiency folks, because we don't have enough time or space to grow all our own food. So, the focus instead is on growing what we can to reduce our grocery bills as much as possible.
What do you eat a lot of? What costs a lot per square foot and unit of time? It's the plants that you eat a lot of AND are costly AND are productive that we're going to want to focus on. Keep in mind that what might be true for my climate might not be true for yours. I'll give you a few examples:
Onions: If you eat a lot of onions, you might be tempted to grow them- but they are usually less than $1/lb and they take the whole growing season to make one harvest.
Kale: relatively expensive to buy, multiple harvests, and super easy to grow while not taking up a lot of space.
Artichokes: super expensive to buy, easy to grow (once established), but takes up a lot of space.
Personally, I grow the kale, and skip the artichokes & onions.
This person actually looked at yield per squarefoot and cost at the store and made a table for it:

But keep in mind, again, yields depend a lot on climate. In general, fresh herbs, leafy greens, and things like tomatoes are your most cost efficient plants to grow.
Look at what you actually eat and figure out what will be most cost efficient to grow. Don't grow a bunch of cilantro unless you really like to eat it, no matter how cost efficient it is.
Once you know what you want to grow, check out your local extension office/ master gardener program and learn HOW to grow it in your area!
Next: getting and growing food plants
If you're doing this on the cheap, first look to your local free groups, mutual aid groups, seed libraries, and gardening groups. There will be seed and plant swaps where people just want to share and don't particularly want or need a trade in return.
If you get food stamps, those can be used to buy seeds and vegetable starts in some states.
Other than that, I prefer to grow from seed, but I know that can be scary for new gardeners. Give it a try anyway! You'll be amazed.
How to feed your vegetables for free:
The best time to start composting is 6 months ago, but alas. Start composting now. Get coffee grounds, get lawn clippings, get whatever you can, and compost it. Heavy feeders grow well with a mulch of lawn clippings around them. Someone near you has horses or rabbits or something else and would love to give you some manure.
You can also straight up bury kitchen scraps and plant over them and the decomposers will still do their job if you don't have room for a compost pile.
Do you know what the limiting nutrient in most gardens is? Nitrogen. Do you know what you have an unlimited, free supply of?* Just saying, raspberries love it. Look into it and read up on it so you're not just going out there willy-nilly and burning your plants to a crisp.
Also, if you're municipality has yard waste/Organics pick up, there's a good chance they have a very large pile of free compost/mulch some where. Make use of it.
I'm sure there's more, but I gotta get going. Add your thoughts!
P.S. if you really do want to look into growing more of your calories, look into potatoes, corn for corn flour (not the same as sweet corn!), fava beans, and dry beans. What will work for your climate might be different.
*pee
More Posts from Solarpiracy and Others

In a small patch of green space on Andry Street in New Orleans’ lower ninth ward, nine garden beds lie next to one another, each 6 feet by 9 feet, each the size of one standard solitary-confinement cell. Each garden bed grows a mix of herbs and flowers, among them pansies, stinging nettles, onions, mugwort. They are a mix of plants with medicinal properties and some that just bring pleasure to the eyes, and their growth is limited to the parts of the tiny space where a person would be free to move in a solitary cell, with space blocked off for where the furniture—nothing more than a bed and a toilet—would be. The plants in each garden are chosen by someone in solitary confinement and planted by a volunteer gardener on the outside.
The result is both symbolic and produces plants with tangible uses, says jackie sumell (who does not capitalize her name), who conceived the project; plants with healing properties will be redistributed to people who need them through what sumell calls a “prisoner’s apothecary.” The solitary beds are eventually overrun with plant life, a visual representation of a world without prisons, an idea that forms the project’s core mission.
Typically, a volunteer gardener on the outside will send a list of plants to an incarcerated gardener. The list provides plenty of options but is limited to what will thrive in the climate and season. They collaborate on a gardening plan and a calendar, often with a small floor plan filled in by the incarcerated gardener laying out the positioning of plants.
HELL WORLD OH MY GOD

I love how you're completely ignoring the fact that the grand jury pored over every piece of evidence available and still made the right decision. Officer Wilson was protecting himself from a thug that wanted to kill him.
Mike Brown was shot six times, including twice in the head which breaks standard protocol for self defense
Multiple eyewitness accounts of the murder of Mike Brown, all stating that the murder was unprovoked and that Michael was unarmed and had his hands up
Owner from the convenience store that Michael allegedly stole from (which is often used as a justification for his murder) stated that no one from his store called the police on Mike, and nothing was taken
First hand account from a friend of Michael’s who was with him during his murder, as well as more accounts from eyewitnesses all refuting Darren Wilson’s claims
‘Officer Wilson was protecting himself from a thug that wanted to kill him'
i'm begging you guys to start pirating shit from streaming platforms. there are so many websites where you can stream that shit for free, here's a quick HOW TO:
1) Search for: watch TITLE OF WORK free online

2) Scroll to the bottom of results. Click any of the "Complaint" links

3) You will be taken to a long list of links that were removed for copyright infringement. Use the 'find' function to search for the name of the show/movie you were originally searching for. You will get something like this (specifics removed because if you love an illegal streaming site you don't post its url on social media)

4) each of these links is to a website where you can stream shit for free. go to the individual websites and search for your show/movie. you might have to copy-paste a few before you find exactly what you're looking, but the whole process only takes a minute. the speed/quality is usually the same as on netflix/whatever, and they even have subtitles! (make sure to use an adblocker though, these sites are funded by annoying popups)
In conclusion, if you do this often enough you will start recognizing the most dependable websites, and you can just bookmark those instead. (note: this is completely separate from torrenting, which is also a beautiful thing but requires different software and a vpn)
you can also download the media in question (look for a "download" button built into the video window, or use a browser extension such as Video DownloadHelper.)
With all the talk about telling people to start planting and growing crops to feed themselves and their communities during this time of crisis, I’m surprised I haven’t seen much about HOW MUCH to plant to feed people. Here’s a good article to serve as a jumping-off point, to give people an idea of when to plant and how much to plant to keep people fed. Keep in mind that unless you live on a fairly sizeable plot of land that has ideal growing conditions, you probably won’t be able to completely feed a family of four, at least with traditional gardening methods. However, you can still heavily supplement your diet with homegrown food if you plot your garden carefully.

Some things you can do to save space include growing plants in stackable towers rather than flat rows. Not everything can grow this way, but growing herbs or even strawberries or some kinds of tomatoes in them can save a lot of space. Bonus points if you can get some vertical vining plants like beans or tomatoes to grow up the sides of them to maximize the space used.

Hanging planters can also be used for things like tomatoes, herbs, some berries, etc. The people who grew up watching TV in the 2000s may remember ads for the topsy-turvy tomato planter. I can’t vouch for the effectiveness of them, but it may be good inspiration for creative DIY hanging planters.

Many people don’t seem to know this (to be fair, it’s not very intuitive), but small melons and gourds can be grown vertically on a trellis. You will need pantyhose or something else that can act like a sling for when the fruit gets large enough, and you’ll also want to make sure the trellis is very sturdy. Here is an example of a watermelon growing on a trellis, with squash growing in the background:

Other good options that require a bit more DIY are hydroponics towers and walls. It’s basically just a series of pipes with holes for plants to grow out of. The only downside is they will require very regular fertilization and supplementation with other micronutrients that are essential for plant growth, because the plants are typically grown in either a non-nutritious medium like coconut coir or nothing at all.
Planter walls are the next step down, basically just building shelves with pots in them to fill with soil. Put these on a wall that gets good morning sun and some afternoon sunlight for best results. These and hydroponics both also have the advantage of being able to hook up to your gutters so that rainwater will go towards watering your plants rather than just being wasted.
If you want to get really fancy, aquaponics is the next step up. With aquaponics, you create a system that circulates water between plants and a tank full of fish. The fish waste provides fertilizer for the plants, and the plants help filter out the waste so the water stays cleaner. I’ve heard they’re a bit tricky to establish, but once you find the right balance, all you’ll need to do is feed the fish. This has the added bonus of providing a source of fish for people who can’t eat things like nuts and legumes but need protein. Here is a link to an article explaining what aquaponics is, how it works, and how it differs from hydroponics.

I also want to add that if you don’t have the space or ability to maintain a large garden, there are other options. Find or create a group with access to enough food to supplement or completely fulfill your diet, and offer another service. If you have space for a vermicompost bin or tower, that can still help contribute to the garden. Learning other skills like soap making, cooking, sewing/knitting/crocheting, electrical skills like wiring and soldering, welding, woodworking/carpentry, etc. means you will still have valuable skills to contribute towards the group, and this will set up the basis for a larger mutual aid network within your community.
it’s omega!fawnlock in heat. NSFW.
if you want to see it click the picture or link below it

le link


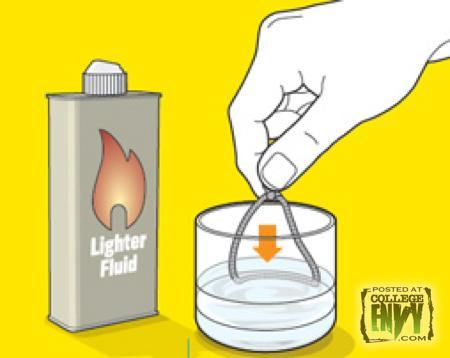




Glassware can get pretty expensive especially if you’re in college and always getting sht faced and breaking your glasses. Start just using your empty beer bottles and turning them into your new glasses. Look dope, easy to make and cheap! Follow these 5 easy steps.
Step 1 – Grab a beer bottle preferably with thick glass such as corona bottles. Tie a string just above the label on the empty bottle
Step 2 – Keep the string tied and soak it in lighter fluid.
Step 3 – Put the string back on the bottle and hold it horizontally. Light the sting rotating the bottle so the flame spreads. You should hear the bottle crack slightly in about 10 seconds.
Step 4 – After you hear the crack, pour cold water on the string and the top of the bottle will fall off.
Step 5 – Now grab sandpaper and sand the edges of the bottle till it is smooth.

Despite their enormous ecological values, new research reveals we don’t understand how most arachnid species are faring right now – or do much to protect them.
Spiders need our help, and we may need to overcome our biases and fears to make that happen.“The feeling that people have towards spiders is not unique,” says Marco Isaia, an arachnologist and associate professor at the University of Turin in Italy. […] A new paper by Isaia and 18 other experts digs into the conservation status of Europe’s 4,154 known spider species and finds that only a few have any protection at the national level. Most have never even been adequately assessed or studied in detail, so we don’t know much about their extinction risk or their ecological needs.
Italy, for example, is home to more than 1,700 spider species, but fewer than 450 have had their conservation status assessed and only two have any legal protection in that country. Greece, meanwhile, has nearly 1,300 spider species within its borders, but scientists have only assessed the conservation needs of 32 of them. None are legally protected. […] “What surprised us most while assembling the data was the extremely poor level of knowledge about the conservation status, extinction risk and factors threatening the survival of European spider species, despite Europe being one of the most studied regions of the world in terms of biodiversity,” says Filippo Milano, the study’s lead author […].
And of course, this is not unique to Europe; other countries and continents fail to protect arachnids, and for similar reasons.
“Spiders are understudied, underappreciated and under attack by both the climate crisis and humans affecting our environment,” says spider expert and science communicator Sebastian Alejandro Echeverri, who was not affiliated with the study. “These are one of the most diverse groups of animals that we don’t really think about on a day-to-day basis. There’s like 48,000-plus species, but my experience is that most people don’t really have a sense of how many are in their area. In the United States, for example, we have just 12 spiders on the endangered species list out of the thousands of species recorded here.” This lack of information or protection at the national level affects international efforts. At the time the research was conducted the IUCN Red List, which includes conservation status assessments for 134,400 species around the world, covered just 301 spider species, eight of which are from Europe. That number has since increased — to all of 318 species from the order Araneae.
As we see with so many other wide-ranging species, a transnational border is often not a spider’s friend. The paper identifies several examples of species protected in one country but not its neighbor, despite being found in both places. According to the paper only 17 spider species are protected by conservation legislation in two or more European countries.
“Animals aren’t limited by our political lines on a map,” notes Echeverri. […]
And maybe, along the way, their work can help inspire people who fear spiders to look at them in a different light — or even to help look for them, like the Map the Spider project that asks citizen scientists to upload locations of the complex webs woven by elusive purse-web spiders. […]
“Focusing on spiders has been a very important choice […],” Isaia says. “You may study their web, their venom, their bizarre behaviors, the interactions between different species, their role as predators, their amazing taxonomical and functional diversity, their key role in the maintaining ecosystem equilibrium. You may also use them as sources of inspiration in architecture and visual arts. Aren’t these good reasons to find them attractive?”
——-
Headline and text published by: John R. Platt. “We Need to Talk About Spider Conservation.” As republished by Salon, 23 May 2021. Originally published by Platt at The Revelator, 10 May 2021.
Yesterday was the circassian day of mourning where we adyghe people remember our ancestors that were killed during a genocide that began in the 1840s, with deportations going on until the 1870s.
Our tribes lost many members during that time, with survivors being forced to leave our homelands, leaving almost no one behind. An estimated 70-90% of our people disappeared from our mountains, either dead or displaced.
I'd like to stress that us being muslim and indigenous was an important factor in all this.
I don't want to go into the details and would like to link to the wikipedia article instead, however it might be important to share at least a single story: since survivors of the first killings were forced across the Black Sea and then died on the way plenty of those that made it to the coast never ate fish again. They feared that those fish may have fed on their loved ones. To this day fish is not common in our cuisine and many still refuse to eat it.
Back then the Ottoman Empire offered us refuge (although to make it clear, circassian warriors and circassian women were popular and thus sometimes made to serve in certain roles), and so today most of us can be found in Turkey, Syria, Jordan, and many former Ottoman territories but also in Germany and even the US. Thankfully we still exist in Kavkazye, but that's a minority.
I took a break from social media a bit, but now that I post this I also want to extend my respects to the communities that still face genocide, the palestinian and the uyghur people in particular.
Finally I'd like to remind everyone of this crucial thing:
Genocides do not start when the killings begin.
Genocides do not stop when the killings end.

You think “oh it would be useful to learn how to identify my thrifted yarn and clothing” and before you know it you’ve been recruited by fiber witches giving out their spells willy nilly, again
-
 angel--fish reblogged this · 1 month ago
angel--fish reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 considerate-void reblogged this · 2 months ago
considerate-void reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 thegemstonejedi reblogged this · 3 months ago
thegemstonejedi reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 jjongs-tae-and-biscuits liked this · 4 months ago
jjongs-tae-and-biscuits liked this · 4 months ago -
 grungepoetica reblogged this · 6 months ago
grungepoetica reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 lessproblematical reblogged this · 6 months ago
lessproblematical reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 greattyphoontimemachine liked this · 7 months ago
greattyphoontimemachine liked this · 7 months ago -
 positiveagressive reblogged this · 8 months ago
positiveagressive reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 georg-prime liked this · 8 months ago
georg-prime liked this · 8 months ago -
 generally-proven reblogged this · 8 months ago
generally-proven reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 generally-proven liked this · 8 months ago
generally-proven liked this · 8 months ago -
 adaptingant reblogged this · 8 months ago
adaptingant reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 happy-quack reblogged this · 8 months ago
happy-quack reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 devotedfire liked this · 10 months ago
devotedfire liked this · 10 months ago -
 waxandwanewitchery reblogged this · 10 months ago
waxandwanewitchery reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 solhaelan liked this · 10 months ago
solhaelan liked this · 10 months ago -
 russianimport reblogged this · 11 months ago
russianimport reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 gloriouspuppet-blog liked this · 1 year ago
gloriouspuppet-blog liked this · 1 year ago -
 so-fucking-gay26 liked this · 1 year ago
so-fucking-gay26 liked this · 1 year ago -
 banukii liked this · 1 year ago
banukii liked this · 1 year ago -
 they-who-wander reblogged this · 1 year ago
they-who-wander reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 kitch-n-sync liked this · 1 year ago
kitch-n-sync liked this · 1 year ago -
 quite-fond-of-geckos liked this · 1 year ago
quite-fond-of-geckos liked this · 1 year ago -
 kris-cross-applesauce reblogged this · 1 year ago
kris-cross-applesauce reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 everything-changes-once-again reblogged this · 1 year ago
everything-changes-once-again reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 strange-wanderings reblogged this · 1 year ago
strange-wanderings reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 thefaminetournaments liked this · 1 year ago
thefaminetournaments liked this · 1 year ago -
 runawayfuture reblogged this · 1 year ago
runawayfuture reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 caffeinebrewingdruid liked this · 1 year ago
caffeinebrewingdruid liked this · 1 year ago -
 harmonysong liked this · 1 year ago
harmonysong liked this · 1 year ago -
 ureverydaymain liked this · 1 year ago
ureverydaymain liked this · 1 year ago -
 softpastelqueer liked this · 1 year ago
softpastelqueer liked this · 1 year ago -
 bheska reblogged this · 1 year ago
bheska reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 justanawesomeowl reblogged this · 1 year ago
justanawesomeowl reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 yumeveggie reblogged this · 1 year ago
yumeveggie reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 bonesandblood-sunandmoon reblogged this · 1 year ago
bonesandblood-sunandmoon reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 bitterness-barbie-x liked this · 1 year ago
bitterness-barbie-x liked this · 1 year ago -
 muymuysugoi liked this · 1 year ago
muymuysugoi liked this · 1 year ago -
 skys-fallin-baby liked this · 1 year ago
skys-fallin-baby liked this · 1 year ago -
 hat-full-of-sky reblogged this · 1 year ago
hat-full-of-sky reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lord-starquaad reblogged this · 1 year ago
lord-starquaad reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 cielosphere liked this · 1 year ago
cielosphere liked this · 1 year ago -
 ebullientpropensity reblogged this · 1 year ago
ebullientpropensity reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 jlzimms reblogged this · 1 year ago
jlzimms reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lunar-lattice reblogged this · 1 year ago
lunar-lattice reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 evidentutensil reblogged this · 1 year ago
evidentutensil reblogged this · 1 year ago

a repository of information, tools, civil disobedience, gardening to feed your neighbors, as well as punk-aesthetics. the revolution is an unending task: joyous, broken, and sublime
211 posts