Latest Posts by startdoost - Page 2

quick reminder that my own gay ass genuinely supports the hell outta each and every one of you. regardless if i know you or not, im happy to be living in this shithole of a life in the same world with you.
and im proud of you, i know in my heart just how beautiful, amazing, talented, smart, and worthy you are and i hope you can see that too🏳️🌈🌈

NEXT UP ON THE SEPTEMBER UPDATE
Glass animals!
These real animals have transluscent properties, where their skin is see through and you're able to see their skeleton and insides... of course I tried my best to cutify them for you all!
This is a series of charms that utilises the transparency of the acrylic to make these creatures pop out, and with the addition of double sided epoxy it gives the effect of holding a real animal (pretty weird to experience!)
With 8 designs I'm sure there's some which catch your eye 👀


アオミノウミウシ-神奈川、東京、埼玉、千葉から伊豆の海への玄関口 小田原ダイビングスクール


どれが本物だ♡
🪼Daily Cnidarian Fact:🪼
Upside-Down Jellyfish: Down is up for this jelly — it rests its bell on the seafloor and waves its lacy underparts up toward the sun. Why? This jelly is a farmer. Its brownish color is caused by symbiotic dinoflagellates living inside the jelly’s tissues. By lying upside-down, the jelly exposes its algae to the sun, allowing it to photosynthesize. The jelly can sustain itself off just the byproducts of the algae, and capture zooplankton for additional energy to grow.



A new study sheds light on the unexplored diversity of galeommatoidean bivalves, a little-known group of marine mollusks, from the western coast of South Africa. The research, led by Paul Valentich-Scott from the Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History, along with collaborators from the University of Cape Town, Sea Change Trust, Stellenbosch University, and the University of Colorado Boulder, offers a curious glimpse into the habitats, symbiotic relationships, and taxonomy of these interesting creatures.
Continue Reading.


A team of researchers including scientists from the University of Oxford have made an astonishing discovery of a new species of mollusk that lived 500 million years ago. The new fossil, called Shishania aculeata, reveals that the most primitive mollusks were flat, shell-less slugs covered in a protective spiny armor. The findings have been published in the journal Science. The new species was found in exceptionally well-preserved fossils from eastern Yunnan Province in southern China dating from a geological period called the early Cambrian, approximately 514 million years ago. The specimens of Shishania are all only a few centimeters long and are covered in small spikey cones (sclerites) made of chitin, a material also found in the shells of modern crabs, insects, and some mushrooms.
Continue Reading.
What is senescence?

Deep Sea Brotula
During a dive to the Galapagos Rift Zone in 1988, scientists in Alvin saw this strange purple fish hanging out in the super-hot water gushing from hydrothermal vents at about 8,200 feet (2500 meters) depth. Pilot Ralph Hollis quickly netted the fish and brought it back to the surface for further examination. Scientists determined that it was in the genus Bythites, of which there are three Atlantic species, and promptly named it after Hollis: Bythites hollisi. They also found that it produces live young (as opposed to eggs) and is a relative of the better-known cusk eel. By 2002, more of these fish had been caught, and scientists decided that this Equatorial Eastern Pacific specimen was so different from the three Atlantic species that it warranted a new genus, Gerhardia. But a few years later, scientists wishing to avoid confusion with a beetle with the same moniker proposed another name, Thermichthys hollisi, referring to the fish’s preferred hangout, the hydrothermal vents of the Galapagos Rift Zone. So far, no other fish of this genus have been found.
via: Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI)

When viruses pay us a visit, they sometimes leave parts of themselves behind. Silently tucked away in our genomes, some of these bits of foreign DNA can get passed down through the generations. They were long thought inactive, but we've since learned these stowaway sequences can be turned back on to wreak all sorts of havoc. Now researchers led by University of Colorado bioinformatician Atma Ivancevic, have found cancers can make use of some of these zombie virus parts for their own benefit.
Continue Reading.

I have TWO classes this fall! Both of them cover the biology of delightful ocean weirdos, and neither will add stress to your life because there's no grades/homework.
Deep sea Sept 17- Oct 8

Squid Class Oct 15-Nov 12

Uncharismatic Fact of the Day
It's not every day you see a fish walking on land! However, when the streams and ponds of the airbreathing catfish dry up, this species will readily wriggle across the jungle floor in search of a new home. Thanks to a special organ called a labyrinth organ, they are able to breathe air and can remain outside of water for several hours provided they stay moist.

(Image: A Java walking catfish, Clarias batrachus, by sdickman via iNaturalist)
If you like what I do, consider buying me a ko-fi!
Byzantine history be like:
In 874 Emperor Kostalogous IV ascended to the throne after blinding sixteen nephews, and married his wife, Theodora.
However, he soon ran afoul of the Patriarch of Constantinople, Theopelagionikus, and his wife Theodora.
In 895 he was deposed by his general, Justiniapelomaxorianous II, and his wife Theodora.
This created nine new church schisms.
Uncharismatic Fact of the Day
Humans have been consuming alcohol for thousands of years, but we're not the only ones with a taste for it! The pen-tailed treeshrew's diet consists almost entirely of naturally fermented nectar, which can have an alcohol content as high as 3.8%. Given their small size, that's the human equivalent of consuming 10-12 glasses of wine. However, this species is able to fully metabolize the alcohol and avoid the intoxicating side-effects.

(Image: A pen-tailed treeshrew (Ptilocercus lowii) by Annette Zitzmann)
If you like what I do, consider buying me a ko-fi!
Anomalocaris? Isn't that the vice president


A rescued pelican in the backseat.



Weighing up the pros and cons of different sanitary products requires sound knowledge of what risks and benefits each poses. For the first time, researchers have measured concentrations of various metals in tampons, finding worrying levels of several toxic types, including lead, for which there is no safe level of exposure. The walls of the human vagina are lined with a highly absorptive tissue that has the potential to soak up stray pollutants – like metals – that would circulate in the bloodstream without being filtered by the liver first.
Continue Reading.

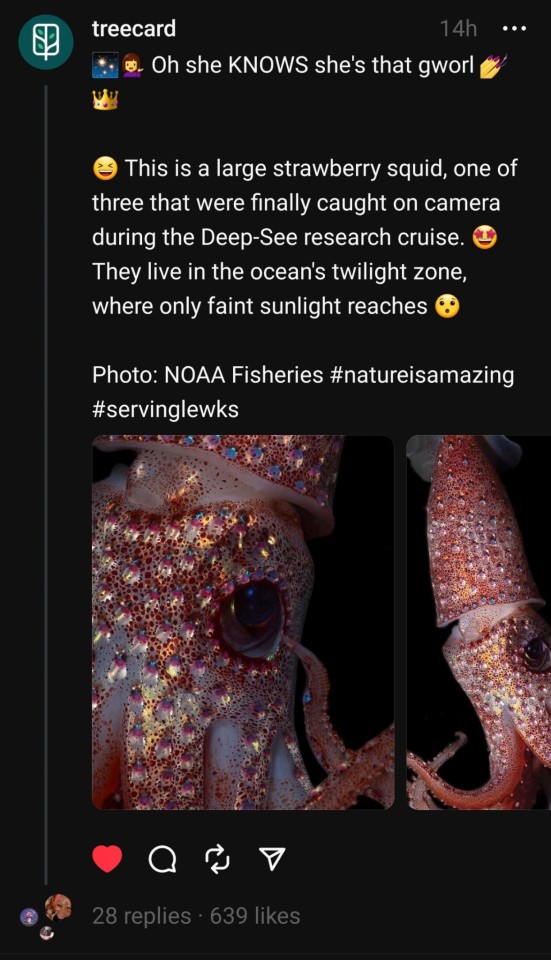



Wake up babe new fish dropped
ITS THIS THING TUESDAY

my fish delivered a hot new reaction image

literally me
DRAG CRAB DRAG CRAB DRAG CRAB
look at the shape range of crabs. yeti crab vs atlantic mole crab vs japanese spider crab



i am in awe!!!!
Sea stars and friends by Alycia Uyeoka (mostlymarine on Instagram)
Daily fish fact #786
Peacock flounder!

It only takes a peacock flounder two to eight seconds to change its colour and blend into its surroundings! They study their environment and then with the use of pigment-containing cells, chromatophores, alter the patterns on their skin. When not camouflaged, these fish have striking blue rings.

As bones encased in rock rotted away, water-borne silica seeped into the crevices, solidifying into opal and preserving precious details for 100 million years. The resulting fossils now provide evidence that there really may have been an Age of Monotremes, before other mammals came to dominate. "It's like discovering a whole new civilization," says Australian Museum paleontologist Tim Flannery. "Today, Australia is known as a land of marsupials, but discovering these new fossils is the first indication that Australia was previously home to a diversity of monotremes." Only five of these rare mammals still cling to existence: one platypus and four echidna species, shared between Australia and Papua New Guinea. But due to their reptilian-like egg-laying feature, it has long been thought these animals evolved before placental mammals like us and marsupials.
Continue Reading.

Elephants call out to each other using individual names that they invent for their fellow pachyderms, a study said on Monday. While dolphins and parrots have been observed addressing each other by mimicking the sound of others from their species, elephants are the first non-human animals known to use names that do not involve imitation, the researchers suggested. For the new study, a team of international researchers used an artificial intelligence algorithm to analyse the calls of two wild herds of African savannah elephants in Kenya. The research "not only shows that elephants use specific vocalisations for each individual, but that they recognise and react to a call addressed to them while ignoring those addressed to others," lead study author Michael Pardo said. "This indicates that elephants can determine whether a call was intended for them just by hearing the call, even when out of its original context," the behavioural ecologist at Colorado State University said in a statement.
Continue Reading.
