How To Help Your Anxious Partner — And Yourself
How To Help Your Anxious Partner — And Yourself
Living with anxiety can be tough — your thoughts might race, you might dread tasks others find simple (like driving to work) and your worries might feel inescapable. But loving someone with anxiety can be hard too. You might feel powerless to help or overwhelmed by how your partner’s feelings affect your daily life.
If so, you’re not alone: Multiple studies have shown that anxiety disorders may contribute to marital dissatisfaction.
“We often find that our patients’ … partners are somehow intertwined in their anxiety,” says Sandy Capaldi, associate director at the Center for the Treatment and Study of Anxiety at the University of Pennsylvania.
Anxiety is experienced at many different levels and in different forms — from moderate to debilitating, from generalized anxiety to phobias — and its impacts can vary. But psychiatrists and therapists say there are ways to help your partner navigate challenges while you also take care of yourself.
Read the full story here
More Posts from Study-astronomy-biology-ref and Others




I’ve been receiving tonnes of questions on Note - Taking recently, so I’d thought I make a post. Plus, I had fun making these graphics.
There are three different methods that I prefer when it comes to note taking:
Notes written During the Lecture
I highly recommend taking notes during the lecture.
I also use abbreviations for quicker and more efficient note taking. Some examples of abbreviation that I use are:
w/ - With
w/o - Without
e.g. - For example
Notes written After the Lecture
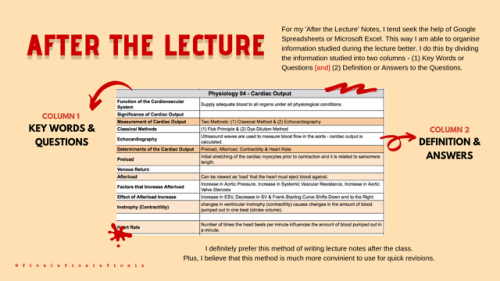
As for notes written after the lecture, I tend to seek the help of Google Spreadsheets or Microsoft Excel. This way I am able to organise information learnt. I do this by dividing the information provided into two columns, one for keywords or questions and the other for definitions and answers.
*Note: This method was adapted from the note taking method I’ve used during college.
Rewritten Notes
I also rewrite my notes. My rewritten notes are arranged based on the order they appear in the syllabus unless there are pieces of information that are related to more than one topic.
I use a black pen or pencil for my written notes, as well as coloured pens and highlighters to highlight the key words and terminologies for emphasise.
Before writing them down, I tend to visualise the layout - alternating between words and pictures/diagram. This definitely helps me with remembering for exams. All I have to do is imagine that I’m looking at that page and I can remember where everything is.
______________________________________________________________________
Please click on the images for a much clearer view.
Well, that’s all from me! I hope that you found this information helpful. And, don’t hesitate to ask me questions if you’re confused about this method of note-taking, or any other problems you might have. For more information of how to survive university, follow this page. And, for more medical school chronicles, follow me on IG. Follow my studygram/medgram for more content.

Underwater explosions are incredibly dangerous and destructive, and this animation shows you why. What you see here are three balloons, each half-filled with water and half with air. A small explosive has been set off next to them in a pool. In air, the immense energy of an explosion actually doesn’t propagate all that far because much of it gets expended in compressing the air. Water, on the other hand, is incompressible, so that explosive energy just keeps propagating. For squishy, partially air-filled things like us humans or these balloons, that explosion’s force transmits into us with nearly its full effect, causing expansion and contraction of anything compressible inside us as our interior and exterior pressures try to equalize. The results can be devastating. To see the equivalent experiment in air, check out Mark Rober’s full video on how to survive a grenade blast. (Image credit: M. Rober, source)

A section of Hubble’s sharpest view of the Andromeda galaxy to date, taken last year.
source

Three galaxies at once
Rising majestically above the telescopes of ESO’s La Silla Observatory in Chile we see the Milky Way accompanied by its two dwarf neighbour galaxies, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
Credit: ESO/A. Santerne
Science When the Sun Don’t Shine
About once a year, somewhere on Earth, the sun is blocked by the moon. This phenomenon – called a total solar eclipse – is one of the most beautiful natural events.

Blocking the light of the sun during a total solar eclipse reveals the sun’s relatively faint, feathery atmosphere, called the corona. The corona is one of the most interesting parts of the sun. We usually study it using an instrument called a coronagraph, which uses a solid disk to make an artificial eclipse by blocking the sun’s face.

To successfully block all of the sun’s bright light – which can bend around the sharp edges of a coronagraph disk – coronagraphs must block much more than just the face of the sun. So total solar eclipses are a rare chance to study the lower part of the corona, close to the surface of the sun.

We have sent a team of scientists to Indonesia, where they’re preparing for an experiment during the March 8, 2016, eclipse, visible from Southeast Asia.

The scientists are measuring a certain kind of light – called polarized light – scattered by electrons in the lower corona, which will help us understand the temperature and speed of these electrons.

The March 8 eclipse is a preview of the total solar eclipse that will be visible across the US in August 2017.

Remember, you should never look directly at the sun – even if the sun is partly obscured. This also applies during a total eclipse up until the time when the sun is completely and totally blocked. More on safety: http://go.nasa.gov/1L6xpnI
For more eclipse information, check out nasa.gov/eclipse
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com









Cosmic Web
The concept of the cosmic web—viewing the universe as a set of discrete galaxies held together by gravity—is deeply ingrained in cosmology. Yet, little is known about architecture of this network or its characteristics. Our research used data from 24,000 galaxies to construct multiple models of the cosmic web, offering complex blueprints for how galaxies fit together. These three interactive visualizations help us imagine the cosmic web, show us differences between the models, and give us insight into the fundamental structure of the universe.
An awesome work of the Center for Complex Network Research


MARTIAN STORMS - Seen in 1977 by the Viking 2 Orbiter
“Like its predecessor, the Viking 2 mission consisted of a lander and an orbiter designed to take high-resolution images, and study the Martian surface and atmosphere. Both the Viking 1 and 2 landers benefited greatly from their orbiting counterparts, which snapped images that helped mission controllers navigate the landers to safe landing sites.”
This particular image was taken by the Viking 2 Orbiter and shows a massive dust storm on the red planet. This spectacular storm can be seen on a global scale. The Viking 2 mission would end 3 years later on April 11, 1980.
Credit: NASA/JPL

I saw this a long time ago and finally got it to convert to GIF format on tumblr. It shows how it’s the Earth that’s moving, space is standing still. I love this perspective.
-
 mini--thoughts liked this · 4 years ago
mini--thoughts liked this · 4 years ago -
 foodformili liked this · 4 years ago
foodformili liked this · 4 years ago -
 communiquokka reblogged this · 4 years ago
communiquokka reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 communiquokka liked this · 4 years ago
communiquokka liked this · 4 years ago -
 shhiwillspeakforyou liked this · 4 years ago
shhiwillspeakforyou liked this · 4 years ago -
 ghostlybutterfly liked this · 4 years ago
ghostlybutterfly liked this · 4 years ago -
 passionsthoughts reblogged this · 4 years ago
passionsthoughts reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 tortoise2win reblogged this · 4 years ago
tortoise2win reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 thirdsy liked this · 4 years ago
thirdsy liked this · 4 years ago -
 tremble-in-the-hips liked this · 4 years ago
tremble-in-the-hips liked this · 4 years ago -
 anth3na liked this · 4 years ago
anth3na liked this · 4 years ago -
 lemongrass5-blog liked this · 4 years ago
lemongrass5-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 wasp9000 liked this · 4 years ago
wasp9000 liked this · 4 years ago -
 raincloudsandsunbeams liked this · 4 years ago
raincloudsandsunbeams liked this · 4 years ago -
 twigs-n-twine liked this · 4 years ago
twigs-n-twine liked this · 4 years ago -
 penguinworlds liked this · 5 years ago
penguinworlds liked this · 5 years ago -
 brrbrrbrrbrr liked this · 5 years ago
brrbrrbrrbrr liked this · 5 years ago -
 intomytinyworld liked this · 5 years ago
intomytinyworld liked this · 5 years ago -
 ourvisiontouchedthesky liked this · 5 years ago
ourvisiontouchedthesky liked this · 5 years ago -
 languagedemon liked this · 5 years ago
languagedemon liked this · 5 years ago -
 ucielavadonia reblogged this · 5 years ago
ucielavadonia reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ucielavadonia liked this · 5 years ago
ucielavadonia liked this · 5 years ago -
 thelittlestprincess7 reblogged this · 5 years ago
thelittlestprincess7 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 shy-magpie reblogged this · 5 years ago
shy-magpie reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 1mac00k13 liked this · 5 years ago
1mac00k13 liked this · 5 years ago -
 shy-magpie liked this · 5 years ago
shy-magpie liked this · 5 years ago -
 remy-labelle-purple reblogged this · 5 years ago
remy-labelle-purple reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 nekaaaaa liked this · 5 years ago
nekaaaaa liked this · 5 years ago -
 sukoshi-mumin liked this · 5 years ago
sukoshi-mumin liked this · 5 years ago -
 mervb liked this · 5 years ago
mervb liked this · 5 years ago -
 borrowed-black liked this · 5 years ago
borrowed-black liked this · 5 years ago -
 waffleofmine liked this · 5 years ago
waffleofmine liked this · 5 years ago -
 faustprouvaire reblogged this · 5 years ago
faustprouvaire reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sassymoneybearpie-blog liked this · 5 years ago
sassymoneybearpie-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 phantomblack05 liked this · 5 years ago
phantomblack05 liked this · 5 years ago -
 merpsderps7 liked this · 5 years ago
merpsderps7 liked this · 5 years ago -
 solvingpuzzles-savingtheday liked this · 5 years ago
solvingpuzzles-savingtheday liked this · 5 years ago -
 fakesmilesandhonesty reblogged this · 5 years ago
fakesmilesandhonesty reblogged this · 5 years ago

This is a studyblr for everyone have some passion for science, especially astronomy and biology
129 posts

