Apparently One Whale Years Ago Was Observed Doing This For Hours And Now More And More Whales In The

apparently one whale years ago was observed doing this for hours and now more and more whales in the area are seen copying it so we think it’s a whole new behavior and it seems to be a response to shrinking food sources.
Instead of expending any energy actively hunting, the whale just holds its mouth open wherever fish are being hunted by birds. To escape the birds, the fish try to hide in the whale’s mouth because it’s a darker area that looks like shelter. …They’re turning into giant, sea-mammal pitcher plants.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/mms.12557?referrer_access_token=bXLTS5BeSw_vlIKHkM0bYIta6bR2k8jH0KrdpFOxC654HjreJ8D19K86UreR5JPsSRb0CuGhiJSV1L1ht-N1Gf_K_1a9MREFzQGU9oJDNctsKDin_HXcYEdsLg3EbcTl
More Posts from T-sci-eng and Others


A portal to another universe ?
That my dear friends is a CT scan machine. Stripped off all the body parts, you can see clearly see what goes on inside.
A computerized tomography (CT) or computerized axial tomography (CAT) scan combines data from several X-rays to produce a detailed image of structures inside the body.

CT scan of Brain
Pretty cool, don’t you think ?
Extras
Difference between MRI and CT scan
Why dont you spin the patient instead ? - Awesome reddit thread
Better quality gifs : here
Source Video: Micheal Jonnson
10 “Spinoffs of Tomorrow” You Can License for Your Business
The job of the our Technology Transfer Program is pretty straight-forward – bring NASA technology down to Earth. But, what does that actually mean? We’re glad you asked! We transfer the cool inventions NASA scientists develop for missions and license them to American businesses and entrepreneurs. And that is where the magic happens: those business-savvy licensees then create goods and products using our NASA tech. Once it hits the market, it becomes a “NASA Spinoff.”
If you’re imagining that sounds like a nightmare of paperwork and bureaucracy, think again. Our new automated “ATLAS” system helps you license your tech in no time — online and without any confusing forms or jargon.
So, sit back and browse this list of NASA tech ripe for the picking (well, licensing.) When you find something you like, follow the links below to apply for a license today! You can also browse the rest of our patent portfolio - full of hundreds of available technologies – by visiting technology.nasa.gov.

1. Soil Remediation with Plant-Fungal Combinations
Ahh, fungus. It’s fun to say and fun to eat—if you are a mushroom fan. But, did you know it can play a crucial role in helping trees grow in contaminated soil? Scientists at our Ames Research Center discovered that a special type of the fungus among us called “Ectomycorrhizal” (or EM for short) can help enhance the growth of trees in areas that have been damaged, such as those from oil spills.

2. Preliminary Research Aerodynamic Design to Lower Drag
When it comes to aircraft, drag can be, well…a drag. Luckily, innovators at our Armstrong Flight Research Center are experimenting with a new wing design that removes adverse yaw (or unwanted twisting) and dramatically increases aircraft efficiency by reducing drag. Known as the “Preliminary Research Aerodynamic Design to Lower Drag (PRANDTL-D)” wing, this design addresses integrated bending moments and lift to achieve drag reduction.

3. Advancements in Nanomaterials
What do aircraft, batteries, and furniture have in common? They can ALL be improved with our nanomaterials. Nanomaterials are very tiny materials that often have unique optical, electrical and mechanical properties. Innovators at NASA’s Glenn Research Center have developed a suite of materials and methods to optimize the performance of nanomaterials by making them tougher and easier to process. This useful stuff can also help electronics, fuel cells and textiles.

4. Green Precision Cleaning
Industrial cleaning is hard work. It can also be expensive when you have to bring in chemicals to get things squeaky. Enter “Green Precision Cleaning,” which uses the nitrogen bubbles in water instead. The bubbles act as a scrubbing agent to clean equipment. Goddard Space Flight Center scientists developed this system for cleaning tubing and piping that significantly reduces cost and carbon consumption. Deionized water (or water that has been treated to remove most of its mineral ions) takes the place of costlier isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and also leaves no waste, which cuts out the pricey process of disposal. The cleaning system quickly and precisely removes all foreign matter from tubing and piping.

5. Self-Contained Device to Isolate Biological Samples
When it comes to working in space, smaller is always better. Innovators at our Johnson Space Center have developed a self-contained device for isolating microscopic materials like DNA, RNA, proteins, and cells without using pipettes or centrifuges. Think of this technology like a small briefcase full of what you need to isolate genetic material from organisms and microorganisms for analysis away from the lab. The device is also leak-proof, so users are protected from chemical hazards—which is good news for astronauts and Earth-bound scientists alike.

6. Portable, Rapid, Quiet Drill
When it comes to “bringing the boom,” NASA does it better than anyone. But sometimes, we know it’s better to keep the decibels low. That’s why innovators at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory have developed a new handheld drilling device, suitable for a variety of operations, that is portable, rapid and quiet. Noise from drilling operations often becomes problematic because of the location or time of operations. Nighttime drilling can be particularly bothersome and the use of hearing protection in the high-noise areas may be difficult in some instances due to space restrictions or local hazards. This drill also weighs less than five pounds – talk about portable power.

7. Damage Detection System for Flat Surfaces
The ability to detect damage to surfaces can be crucial, especially on a sealed environment that sustains human life or critical equipment. Enter Kennedy Space Center’s damage detection system for flat composite surfaces. The system is made up of layered composite material, with some of those layers containing the detection system imbedded right in. Besides one day potentially keeping humans safe on Mars, this tech can also be used on aircrafts, military shelters, inflatable structures and more.

8. Sucrose-Treated Carbon Nanotube and Graphene Yarns and Sheets
We all know what a spoonful of sugar is capable of. But, who knew it could help make some materials stronger? Innovators at NASA’s Langley Research Center did! They use dehydrated sucrose to create yarns and woven sheets of carbon nanotubes and graphene.
The resulting materials are lightweight and strong. Sucrose is inexpensive and readily available, making the process cost-effective. Makes you look at the sweet substance a little differently, doesn’t it?

9. Ultrasonic Stir Welding
NASA scientists needed to find a way to friction weld that would be gentler on their welding equipment. Meet our next tech, ultrasonic stir welding.
NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center engineers developed ultrasonic stir welding to join large pieces of very high-strength, high-melting-temperature metals such as titanium and Inconel. The addition of ultrasonic energy reduces damaging forces to the stir rod (or the piece of the unit that vibrates so fast, it joins the welding material together), extending its life. The technology also leaves behind a smoother, higher-quality weld.

10. A Field Deployable PiezoElectric Gravimeter (PEG)
It’s important to know that the fuel pumping into rockets has remained fully liquid or if a harmful chemical is leaking out of its container. But each of those things, and the many other places sensors are routinely used, tends to require a specially designed, one-use device.
That can result in time-consuming and costly cycles of design, test and build, since there is no real standardized sensor that can be adapted and used more widely.
To meet this need, the PiezoElectric Gravimeter (PEG) was developed to provide a sensing system and method that can serve as the foundation for a wide variety of sensing applications.

See anything your business could use? Did anything inspire you to start your own company? If so, head to our website at technology.nasa.gov to check them out.
When you’ve found what you need, click, “Apply Now!” Our licensing system, ATLAS, will guide you through the rest.
If the items on this round-up didn’t grab you, that’s ok, too. We have hundreds of other technologies available and ready to license on our website.
And if you want to learn more about the technologies already being used all around you, visit spinoff.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

The ocean is where the aliens live.
Transcript under the cut.
Patreon | Instagram | Facebook | Twitter | deviantArt
Keep reading





Google’s Wireless ‘Pixel Buds’ Headphones Can Translate 40 Languages in Real Time

The simple physics behind a Fidget Spinner
When you want something to spin for a really long time you need to make sure that the friction does not slow it down.

And we can do this by adopting ball bearings. This is so because friction offered due to rolling is much smaller than due to sliding.

And many Fidget spinners indeed use ceramic ball bearings to keep them spinning for a long time. **
Mass Distribution
The next most crucial component is the Angular Momentum. Angular momentum is equal to the product of rotational velocity and the moment of inertia.

And by distributing more mass towards the edge, the fidget spinner gains high moment of inertia keeping it spinning longer.
That’s why the spinners have that weird peculiar shape.
But, Why do they feel alive ?

The angular momentum of a fidget spinner happens to point outwards from the spinner’s center.
And so to change the direction of the momentum — rotating the spinner with your fingers — you must apply a force. You push on the spinner, and the spinner pushes back on you.
That’s why a fidget spinner feels like it fights you, like it’s alive.
- Nerdist
A very fascinating toy nevertheless!
** Spin Test : Ceramic Vs Steel ball bearings
*** Fidget spinner trick shots

This room starts charging your phone as soon as you walk in. Inspired by Tesla’s vision of global wireless power, scientists at Disney Research company explored how wireless charging works in large spaces. The copper pole at the room’s center sends currents through the walls and floor that charge phones and laptops without harming humans. Source Source 2

Devices can be charged regardless of their orientation in the room thanks to a new receiver design

The setup outside the room

The setup inside the room
If I could catch a rainbow
If i could catch a rainbow,
I would just do it for you
And share with you it’s beauty,
On the days you are feeling Blue.
Rainbows are nature’s optical illusion.

It’s not possible unfortunately to catch a rainbow. They are not objects and are not located at specific distance from the observer that one can physically approach.
Rainbows stems from an optical illusion caused by any water droplets viewed from a certain angle relative to a light source.

They are user-specific and everyone sees a different rainbow.
The monochrome rainbow
Not all rainbows that occur in nature are multicolored. Under specific atmospheric conditions, one can spot the Mono-chrome rainbow i.e It has only one color.

PC : rodjonesphotography
Moonbows
A Moonbow / Lunar rainbow /White rainbow is a rainbow produced by light reflected off the surface of the moon (as opposed to direct sunlight) refracting off of moisture-laden clouds in the atmosphere / from waterfalls.

PC: GanMed64
Each of your eyes sees a different rainbow.
Just as no two people see exactly the same rainbow, even if they’re standing next to each other, the few inches between your eyes make a difference in what you are viewing.

There is no color- indigo ( sort of )
One can distinguish almost all colors in a rainbow but Indigo.
Legend has it that Newton included indigo because he felt that there should be seven rather than six colors in a rainbow due to his strong religious beliefs.

Origins of ‘Iris’
The Greeks and Romans thought a rainbow was the path made by Iris, the goddess of the rainbow, between heaven and earth, linking gods with humans. “Rainbow” in Latin is arcus iris or arcus pluvius, a “rainy arch”.

The iris of the eye is named after her, because of its colour.
The Greeks used the word “iris” to describe any coloured circle, such as the “eye” of a peacock’s tail. The flower called iris gets its name from the Greek, as does the chemical iridium (Ir), compounds of which are highly coloured. Iris is also the root of “iridescent”.
Pulsating Rainbows
Place a linear polarizer over the camera whilst capturing a rainbow and you get pulsating rainbows.

Source
Double Rainbows/ Multiple Rainbows
A double rainbow is a phenomenon in which two rainbows appear. They are caused by a double reflection of sunlight inside the raindrops. Similarly multiple rainbows are a possibility as well.
Observe that the colors in the second rainbow are inverted because the light is reflected twice inside the water droplet

PC: Janbazian
Viral Double Rainbow Video
This video of a man witnessing a double rainbow for the first time went viral, featuring on numerous popular talk shows. Pure ecstasy!
The full rainbow
Whilst standing on earth, we see rainbows as magical arcs across the sky, but rainbows are full circles. The bottom part of the full circle is usually blocked by the horizon.
Pilots however do not face this difficulty. Under the right sky conditions, pilots are spectators to one of nature’s most beautiful spectacles - The full rainbow.

PC : Steve Kaufman
Everything has beauty, but not everyone sees it.
Have a great day!
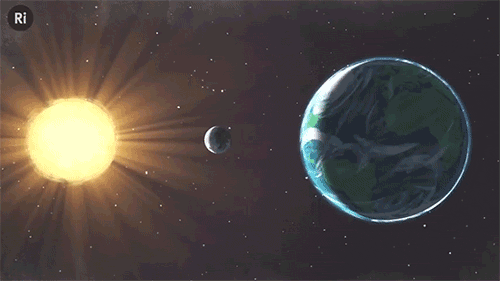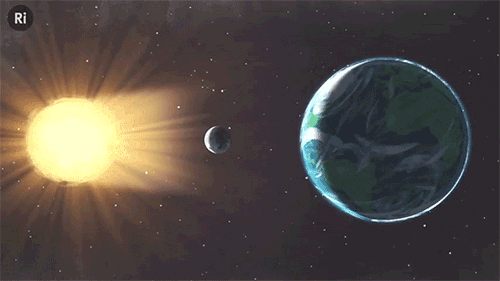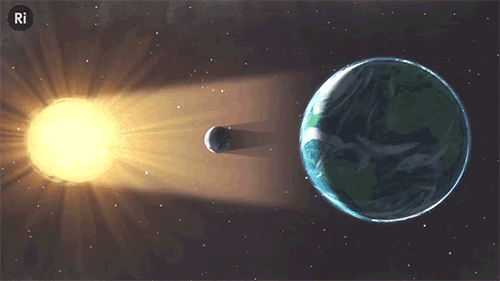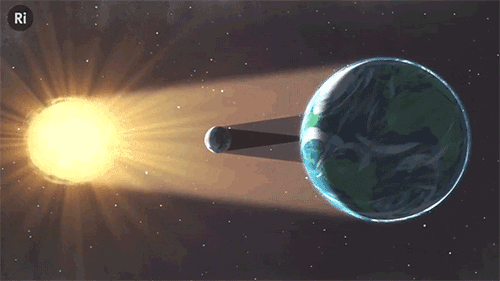
What have eclipses ever done for science? Quite a lot, actually!
The first measurement of the width of the Atlantic ocean in the 16th Century



When British settlers arrived in Virginia in the US, they weren’t sure how far across the globe they’d gone. They recorded the local time of a total eclipse of the moon - which is seen all across the night-time side of the planet. Their colleagues in London did the same, and when the travellers returned they could figure out the five hour time difference.
Edmond Halley discovered that the moon is moving away from the Earth


Halley realised you could back-calculate when previous eclipses would have occurred. But he noticed a mismatch between his predictions and the history books. The reason, he discovered, what that he was assuming the moon stayed the same distance from the Earth. It is actually getting further at about the rate your fingernails grow. And that means that one day (in a few million years, that is), the moon will be too far away to create any more total solar eclipses.
In 1919 a solar eclipse proved Einstein’s theory of relativity

Einstein’s theory predicted that the sun’s gravity should bend the light of nearby stars, meaning that in theory we should be able to see stars that are hidden just behind the sun. However, sunlight always blocks our view of these stars, and it was only during a solar eclipse that there was a short window to see if hidden stars were visible, as predicted. Astronomer Arthur Eddington travelled to West Africa and took photos that proved Einstein right.
Scientists still use solar eclipses today
It’s very hard to study the sun’s corona - a tenuous hot gas, which just one millionth of the light intensity of the sun. The shapes and lines of the corona show the nature of the sun’s magnetic field, and are only visible to study during an eclipse. NASA are also using this opportunity to help create the first thermal map of Mercury!
Want to know more? Watch our full video.
-
 maybeillstoplurking-blog liked this · 4 days ago
maybeillstoplurking-blog liked this · 4 days ago -
 sercharllee reblogged this · 5 days ago
sercharllee reblogged this · 5 days ago -
 xbubbledumbbx liked this · 5 days ago
xbubbledumbbx liked this · 5 days ago -
 autism-crime reblogged this · 5 days ago
autism-crime reblogged this · 5 days ago -
 autism-crime liked this · 5 days ago
autism-crime liked this · 5 days ago -
 feste-the-mad reblogged this · 5 days ago
feste-the-mad reblogged this · 5 days ago -
 poorunfortunatesolanin liked this · 5 days ago
poorunfortunatesolanin liked this · 5 days ago -
 freedom-of-speech333 liked this · 5 days ago
freedom-of-speech333 liked this · 5 days ago -
 bat-snake reblogged this · 5 days ago
bat-snake reblogged this · 5 days ago -
 calciferous-kelpie reblogged this · 5 days ago
calciferous-kelpie reblogged this · 5 days ago -
 puppetmaster13u liked this · 1 month ago
puppetmaster13u liked this · 1 month ago -
 thebaronneverlies reblogged this · 1 month ago
thebaronneverlies reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 fishareneutraltowardsme reblogged this · 2 months ago
fishareneutraltowardsme reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 a-voltage reblogged this · 2 months ago
a-voltage reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 mrspitshark reblogged this · 2 months ago
mrspitshark reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 mo-betta reblogged this · 2 months ago
mo-betta reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 hatonpat reblogged this · 2 months ago
hatonpat reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 soggy-bread liked this · 2 months ago
soggy-bread liked this · 2 months ago -
 ryujivinated liked this · 2 months ago
ryujivinated liked this · 2 months ago -
 lemonandhoneytea reblogged this · 2 months ago
lemonandhoneytea reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 leanmeancritmachine reblogged this · 2 months ago
leanmeancritmachine reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 kalotyper reblogged this · 2 months ago
kalotyper reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 fibbonaccisequins reblogged this · 2 months ago
fibbonaccisequins reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 rampoogie reblogged this · 2 months ago
rampoogie reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 cowarddragon reblogged this · 2 months ago
cowarddragon reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 cowarddragon liked this · 2 months ago
cowarddragon liked this · 2 months ago -
 nbbaern reblogged this · 3 months ago
nbbaern reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 fogandfireflies liked this · 3 months ago
fogandfireflies liked this · 3 months ago -
 1712117121 reblogged this · 3 months ago
1712117121 reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 dullkrad reblogged this · 3 months ago
dullkrad reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 dullkrad liked this · 3 months ago
dullkrad liked this · 3 months ago -
 uququ liked this · 3 months ago
uququ liked this · 3 months ago -
 john-cherry-the-6th liked this · 3 months ago
john-cherry-the-6th liked this · 3 months ago -
 fluxion-fluent reblogged this · 3 months ago
fluxion-fluent reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 fluxion-fluent liked this · 3 months ago
fluxion-fluent liked this · 3 months ago -
 ofbloodandshadow liked this · 3 months ago
ofbloodandshadow liked this · 3 months ago -
 allia-silvs reblogged this · 3 months ago
allia-silvs reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 allia-silvs liked this · 3 months ago
allia-silvs liked this · 3 months ago -
 miniar reblogged this · 3 months ago
miniar reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 solarsleepless reblogged this · 3 months ago
solarsleepless reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 tableundkrzeslo reblogged this · 3 months ago
tableundkrzeslo reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 soltosia liked this · 3 months ago
soltosia liked this · 3 months ago -
 alchemistdoctor reblogged this · 3 months ago
alchemistdoctor reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 alchemistdoctor liked this · 3 months ago
alchemistdoctor liked this · 3 months ago -
 acidgrime reblogged this · 3 months ago
acidgrime reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 kitsuneluvuh reblogged this · 3 months ago
kitsuneluvuh reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 kitsuneluvuh liked this · 3 months ago
kitsuneluvuh liked this · 3 months ago -
 theresponseblog liked this · 3 months ago
theresponseblog liked this · 3 months ago -
 the42ndcynicalreader liked this · 3 months ago
the42ndcynicalreader liked this · 3 months ago









