Everyone’s Favourite Crane Master Cristian Marianciuc’s Latest Works Are Just As Stunning.
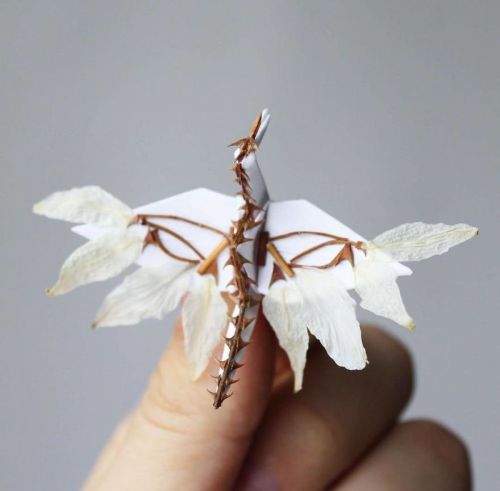
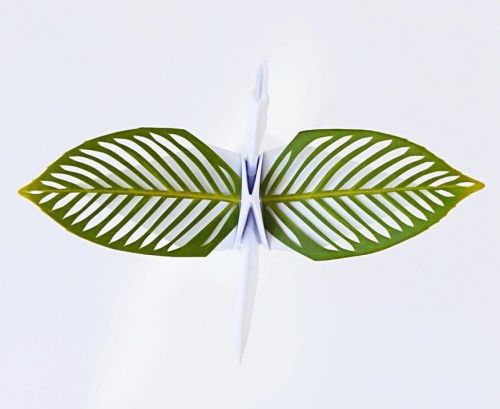
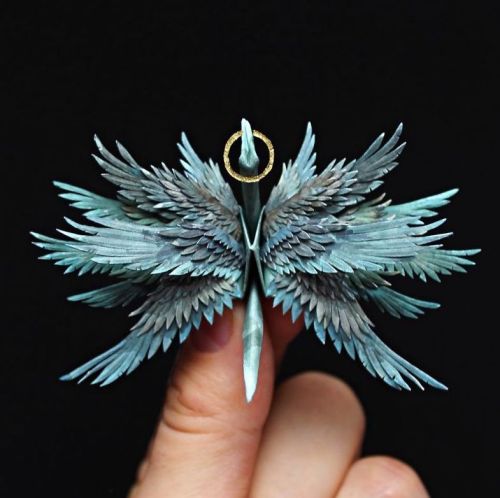
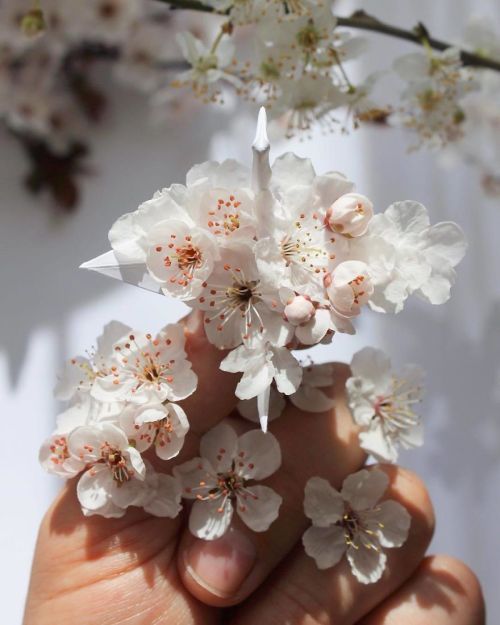
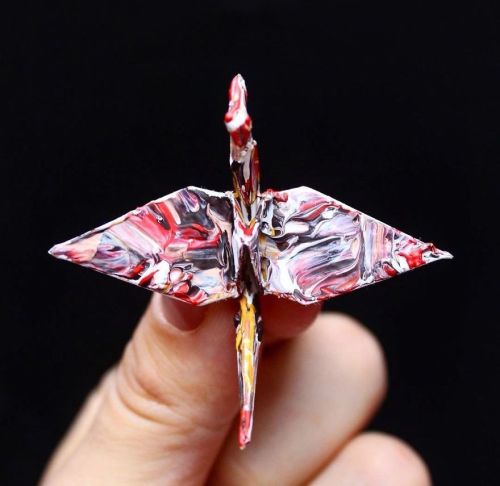
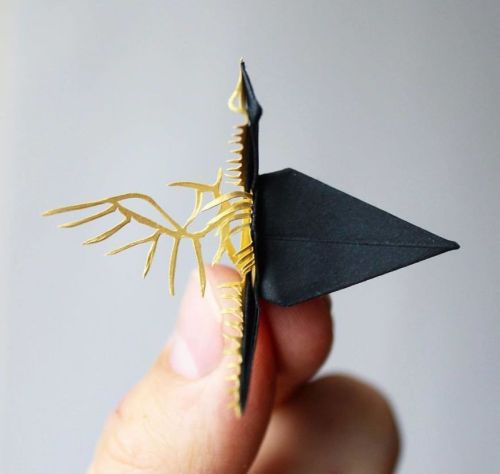
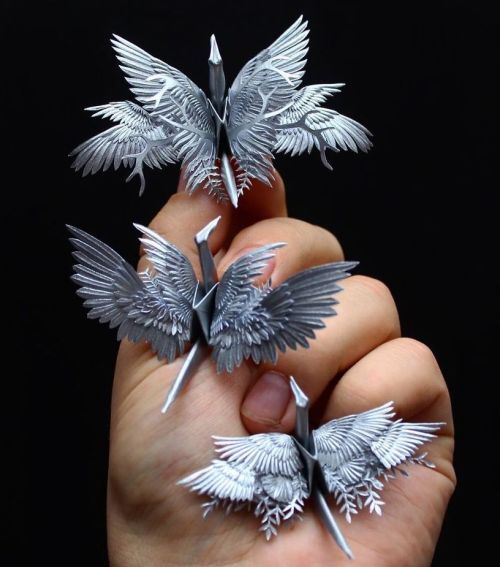










Everyone’s favourite crane master Cristian Marianciuc’s latest works are just as stunning.
More Posts from Thecaffiend and Others

Researchers have used Easter Island Moai replicas to show how they might have been “walked” to where they are displayed.
VIDEO
“When we set children against one another in contests - from spelling bees to awards assemblies to science “fairs” (that are really contests), from dodge ball to honour rolls to prizes for the best painting or the most books read - we teach them to confuse excellence with winning, as if the only way to do something well is to outdo others. We encourage them to measure their own value in terms of how many people they’ve beaten, which is not exactly a path to mental health. We invite them to see their peers not as potential friends or collaborators but as obstacles to their own success… Finally, we lead children to regard whatever they’re doing as a means to an end: The point isn’t to paint or read or design a science experiment, but to win. The act of painting, reading, or designing is thereby devalued in the child’s mind.”
— Alfie Kohn, The Myth Of The Spoiled Child
if you refuse to get the vaccine the government should sneak into your room after you go to sleep and take out the little chip in your neck that makes the supermarket doors open when you go near them
Whenever I take a long car ride I end up exhausted afterwards, and I'm always like "why am I so tired? I was just sitting around doing nothing all day."
But the answer, it turns out, is I was doing something. Riding in a car jars your body in many directions and requires constant microadjustments of your muscles just to stay in place and hold your normal posture. Because you're inside the car, inside the situation, it's easy not to notice all the extra work you're doing just to maintain the status quo.
There's all sorts of work that we think of as "free" that require spending energy: concentrating, making decisions, managing anxiety, maintaining hypervigilance in an unfriendly environment, dealing with stereotype threat, processing a lot of sensory input, repairing skin cells damaged by sun exposure, trying to stay warm in a cold room.
The next time you think you're tired from "nothing", consider instead that you're probably in situation where you're doing a lot of unnoticed extra work just to stay in place.
made a uquiz
things that made me stop wanting to die that require no effort whatsoever
change the color used to highlight text on your laptop
move the pictures on your wall
stack whatever clutter is in your room into piles even if you don’t have time to clean it all
slightly vary your commute, even just by one street
change where you sit and scroll aimlessly on your phone even if it’s only to the chair in your room instead of your bed
drink water or juice out of a wine glass in the morning because nothing is real
shower with the lights off, without music
buy $3 flowers at trader joe’s—they look bad next to the more expensive ones but they look so good in your room
start typing things you don’t post into your notes. your thoughts can be worth documenting even if you don’t deem them worth sharing
wake up super early just once. you don’t have to make it a habit it’s just extra satisfying to go to bed that night
listen to the entirety of your favorite album from 2015

Magic Mushrooms for Depression: Brain Scans Show What’s Happening
A new study has shed light on what’s going on in the brain as psilocybin treats depression
Imagine a house share of several people. The house, technically, functions fine. One housemate sorts out the food. One earns the money. One cleans. One does laundry. Except they don’t help each other, don’t collaborate, and don’t listen to each other. They don’t even talk to each other.
Sounds pretty miserable in there, right? In a very simplified way, that’s what a new study has found is going on in the mind of depressed people, with different parts of the mind working isolated from the others.
Psilocybin, the substance responsible for the magic in magic mushrooms, has been under study for some time now and showing very promising results to help with depression. But on a physical level, no one, until now, knew why. Now, scientists have had a glimpse with the help of brain scan machines.
Let’s go back to that miserable house share. Now, the housemate in charge of the food has prepared a new soup for the housemates, and it contains magic mushrooms. What happens next? They all start talking to each other. And suddenly, overnight, the place gets happier. The even better news is that the next day, after the mushrooms have worn off, the walls have stopped moving and the pattern on the sofa has stopped being so incredibly funny, the housemates are still talking to each other. The living experience in the house has been transformed. It’s no longer a miserable place to be. No longer so… depressing.
So it is, according to the new brain scan study, with psilocybin and the depressed brain. Parts of the brain that struggled to interact and remained entrenched in their neural patterns became more fluid and communicated more with other parts of the brain.
One important element of these findings is they show how psilocybin works differently to antidepressants. As study author David Nutt says;
“These findings are important because for the first time we find that psilocybin works differently from conventional antidepressants — making the brain more flexible and fluid, and less entrenched in the negative thinking patterns associated with depression. This confirms psilocybin could be a real alternative approach to depression treatments.” — Nutt
For sufferers of depression who haven’t been responsive to antidepressants, this is very promising indeed. Especially when compared with a traditional antidepressant, psilocybin appears to work faster and with longer-lasting effects.
How effective was the psilocybin in this study?
Participants in the study had taken psilocybin twice over three weeks, as part of previous studies on psilocybin therapy. The results can be compared to people who take an antidepressant pill daily:
Psilocybin: After three weeks and two psilocybin experiences, participants averaged a drop in depression scores of 64%. Low depression scores were maintained for at least six months.
Antidepressant pills (Lexapro): After six weeks of daily pills, the depression score dropped by 37%, with the improvements not expected to continue after stopping the course.
So, on paper, that’s a win for the mushrooms.
While the pills target serotonin levels to help with the feelings of depression, the psilocybin gets parts of the brain talking, so the negative feelings are less entrenched. The brain can find new ways of doing things by talking to itself in a way a depressed brain can’t.
So, magic mushrooms are better than antidepressants then?
That’s not necessarily the case, though it’s easy and tempting to jump to that conclusion. It’s complicated and what works for one won’t work for another.
There’s a very common fallacy that you can spot in the thoughts of the psychedelic community, especially in users of mushrooms and Ayahuasca. That common thought is this: ‘Of course mushrooms are better than antidepressants… pills are synthetic chemicals, mushrooms are natural.’
This is called the appeal to nature fallacy, where our minds like to simplify things to nature is good, unnatural is bad. This is not good thinking. If you pick the wrong mushroom, you will die horribly, however natural it was. Deadly nightshade berries are called that for a reason. We can’t let our brains fall for the ‘nature is better’ trick.
This is why we rely on science. If we’re making personal decisions on how to treat ourselves, even if self-medicating, we need to be able to think clearly to make our decisions and not fall for common thinking errors.
Internal communication for mental health has a precedent
There’s a fascinating branch of therapy called Internal Family Systems (IFS), where the idea is to get parts of the mind to talk to each other and come to agreements and work together. The system uses talk and imagination.
In early research, the method has been showing positive results for treating depression, even in cases where medication and the more common cognitive behavioural therapy haven’t helped.
In the houseshare analogy, IFS would be like having a therapist show up, sit the housemates down, and get them talking and coming to agreements.
The two methods of creating in-brain communication both seem to be very effective. But we can’t assume they’re doing the same thing.
Psilocybin is shown through scans to improve communication in different parts of the brain. IFS encourages communication in different parts of the mind. These parts of the mind don’t necessarily live in different parts of the physical brain.
The two methods support each other in certain important aspects though: depression can be helped by getting whatever is in our heads to communicate better with itself. They do that in using very different ways.
In a nutshell, the study says psilocybin may work like this;
“…psilocybin’s antidepressant action may depend on a global increase in brain network integration.” — study authors
Internal Family Systems, like this;
“Just as our bodies are made of many parts that form a dynamic, interwoven system that works together, so it is with our psyches.” — Ralph de la Rosa
There’s one more little bit of psychology that we can possibly infer that our wellbeing is related to internal communication of different parts, be that of the mind or the brain: how we refer to ourselves in our inner voice affects our wellbeing.
People who talk to themselves as “You” generally have better wellbeing than those using “I”. There’s no inter-mind communication using I. The part of us that I refers to is itself. When you comes into it, that’s a part of us separate from the bit that uses I. People who use “We” also tend to feel better than those who use I. This again could be related to in-mind communication. This is all inferred and would need proper study.
But what if this inter-mind/brain communication could be done with extra love and compassion for the parts that communicate? Could that help?
Enter MDMA.
MDMA therapy and in-brain communication
MDMA, also under much study to help with various psychological disorders, works, in a super-simplified explanation, by adding compassion to proceedings. In the case of PTSD, for example, it’s by adding compassion to the memories that underly the trauma.
So would adding MDMA to IFS therapy add compassion to how we view and communicate with ourselves, and aid our mental health? The link is in early stages, but it seems so. That’s like entering our miserable houseshare and passing around ecstasy pills — and getting the housemates to talk to and feel very fond of each other in a way the compassion will last even after the drug has worn off. That’s a healthy state for a brain to live in.
Back to the psilocybin study, and brain communication. Would adding MDMA to mushrooms be useful in the same way? Possibly. Research into such an idea has begun, though first with LSD rather than psilocybin. Underground, adding MDMA to mushroom therapy has been used to aid the experience, and to take the edge off a bad psychedelic experience. If inter-brain communication really is the key to aiding depression with psychedelics, adding some extra compassion to the mix may be an effective idea.
Talk to yourself
It seems that one possibility is that helping depression may come down to good, old-fashioned communication. It may just mean doing it on the level of neural pathways with the assistance of psychedelics such as psilocybin.
Don’t rush out and buy or pick yourself a bag of mushrooms though. The study authors stress not to self-medicate based on these results, and psychedelics can have dangers for some people. Taking psychedelics for any reason is a big decision and should be considered thoroughly, with risks in mind as well as benefits.
The new study is another in the growing list in support of using psychedelics to help with mental health, and one of the first to give a clue of how they work physically in our brains. Plenty more research is to come.
By Alexander M. Combstrong (Medium). Image: Pixabay at Pexels.









Okay I’m currently furious that migraines are often so blindly easy to treat and I had to find this out myself at the age of 26 when I’ve been to a neurologist since I was 11 lol so I’m about to teach you two neat and fast little tricks to deal with pain!
The first is the sternocleidomastoid muscle, or the SCM muscle.
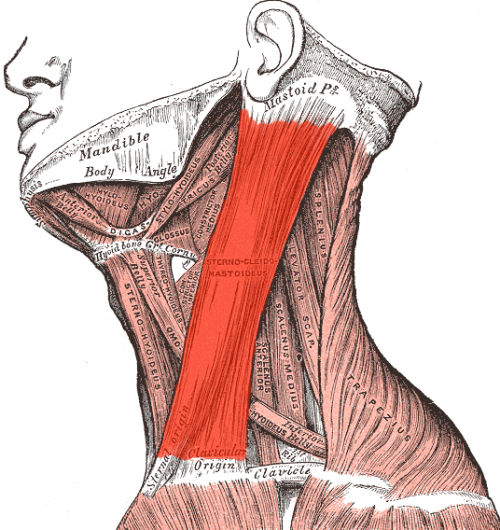
This big red section is responsible for pain around the eye, cheekbone, and jaw, as well as some temple pain. Literally all you have to do is angle your head down a little, angle it away from the side that hurts, and then you can gently pinch and rub that muscle. I find it best to start at the bottom and travel upwards. The relief is so immediate! You can increase pressure as you feel comfortable doing so.
Here is a short and easy video showing this in action
The second is a fast and easy stretch that soothes your vagus nerve, which is the nerve responsible for calming you down. The vagus nerve, for those unfamiliar, is stimulated by deep breathing such as yawning, sighing, singing, or taking a deep breath to calm your anger in a tense situation.
You can stretch this out by sitting up as straight as possible (this does not have to be perfect to work) and interlacing your fingers. Put your hands on the back of your head with your thumbs going down the sides of your neck and, while keeping your face forward, look all the way to one side with just your eyes. Hold that until you feel the urge to breathe deeply or yawn, or until you can tell there’s a change. Then do the same thing on the other side. When you put your arms down, you should clearly be able to turn your head farther in both directions. If the first session doesn’t get rid of your migraine, rest and repeat as many times as necessary. I even get a little fancy with it and roll my eyes up and down along the outer edge sometimes to stretch as much as I can.
If you need a visual here’s a good video on it. I know some of the language they use seems questionable but this is real and simple science and should not be discarded because it’s been adopted by the trendy wellness crowd!
I seriously cannot believe I didn’t hear a word of this from any doctor in my life. Additionally, if you get frequent recurring migraines, you may want to see a dietician. Migraines can be caused by foods containing histamines, lectin, etc. and can also be caused by high blood pressure in specific situations such as exercise, stress, and even sex.
If any of this information helps you I’d love to hear it btw! It’s so so fast and easy to do. Good luck!
like there’s this whole thing in this book about how your brain grows stronger and healthier by practicing responding to stress in healthy ways,
because if a stressor is predictable and you feel a sense of control over it, you habituate and stop reacting to it,
but if it’s random and unpredictable you have the opposite response and become sensitized, so your reaction actually gets more and more extreme.
(if you hear a loud noise at predictable intervals you’ll soon stop noticing or reacting, but if you hear it at random intervals you’ll become sensitive to it and anxious.)
so one way to help people who have adverse reactions to reminders of trauma is to give them control over how they’re reminded of the trauma,
because it helps the brain practice responding to stress in a safe way so you can habituate to the stress response.
which is why if someone tags something for a trigger and you still choose to look,
it’s actually an act of healthy resistance against your reaction to that trigger (because it teaches your brain to habituate),
but encountering something triggering in a random and unpredictable way actually increases your stress response and makes you more sensitive to the trigger.
so people who are against trigger warnings because “you have to learn to cope” are actually taking away your tools for learning to cope,
because encountering stressors in a way that further strips you of control over your trauma is never, ever helpful.
it’s a lot of stuff i kind of knew but integrated and explained with more context and science
-
 kaitlyngilmore6 liked this · 3 months ago
kaitlyngilmore6 liked this · 3 months ago -
 eclectichellmouth reblogged this · 3 months ago
eclectichellmouth reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 finalgirlart liked this · 3 months ago
finalgirlart liked this · 3 months ago -
 ninomeira liked this · 4 months ago
ninomeira liked this · 4 months ago -
 megpo1d liked this · 5 months ago
megpo1d liked this · 5 months ago -
 donkeykongclassifiedsecrets reblogged this · 5 months ago
donkeykongclassifiedsecrets reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 notkendra reblogged this · 6 months ago
notkendra reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 lemongrass-eyelids reblogged this · 6 months ago
lemongrass-eyelids reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 oarfishoriole liked this · 6 months ago
oarfishoriole liked this · 6 months ago -
 marco-gamboa liked this · 6 months ago
marco-gamboa liked this · 6 months ago -
 rayne-showers reblogged this · 6 months ago
rayne-showers reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 donna--c reblogged this · 6 months ago
donna--c reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 d3k3b3 reblogged this · 6 months ago
d3k3b3 reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 d3k3b3 liked this · 6 months ago
d3k3b3 liked this · 6 months ago -
 anna3svkb liked this · 6 months ago
anna3svkb liked this · 6 months ago -
 annakzexo liked this · 6 months ago
annakzexo liked this · 6 months ago -
 lah-reina reblogged this · 7 months ago
lah-reina reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 meruys liked this · 7 months ago
meruys liked this · 7 months ago -
 annaul82f liked this · 7 months ago
annaul82f liked this · 7 months ago -
 darnedanddarted reblogged this · 7 months ago
darnedanddarted reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 books-and-birds liked this · 7 months ago
books-and-birds liked this · 7 months ago -
 latte-cucumber reblogged this · 7 months ago
latte-cucumber reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 rattle-em-bones reblogged this · 7 months ago
rattle-em-bones reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 rattle-em-bones liked this · 7 months ago
rattle-em-bones liked this · 7 months ago -
 otaku-girl-ao3 reblogged this · 7 months ago
otaku-girl-ao3 reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 otaku-girl-ao3 liked this · 7 months ago
otaku-girl-ao3 liked this · 7 months ago -
 aly-cat-universe reblogged this · 8 months ago
aly-cat-universe reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 multifandom-fanfic-writer reblogged this · 8 months ago
multifandom-fanfic-writer reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 metaldragonqueen reblogged this · 8 months ago
metaldragonqueen reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 toads-in-my-pockets reblogged this · 8 months ago
toads-in-my-pockets reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 feragon-dingbat reblogged this · 8 months ago
feragon-dingbat reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 feragon-dingbat liked this · 8 months ago
feragon-dingbat liked this · 8 months ago -
 serrantsaloto reblogged this · 8 months ago
serrantsaloto reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 serrantsaloto liked this · 8 months ago
serrantsaloto liked this · 8 months ago -
 thewick3dyouknow reblogged this · 8 months ago
thewick3dyouknow reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 snowdrop143 liked this · 8 months ago
snowdrop143 liked this · 8 months ago -
 bloodyvalentine93 liked this · 8 months ago
bloodyvalentine93 liked this · 8 months ago -
 thecheshirecat liked this · 8 months ago
thecheshirecat liked this · 8 months ago -
 crumerita reblogged this · 8 months ago
crumerita reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 crumerita liked this · 8 months ago
crumerita liked this · 8 months ago -
 that-art-thou reblogged this · 8 months ago
that-art-thou reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 graytitan96 liked this · 8 months ago
graytitan96 liked this · 8 months ago -
 mrsarnasdelicious reblogged this · 8 months ago
mrsarnasdelicious reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 vaguelyno reblogged this · 9 months ago
vaguelyno reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 arnim liked this · 9 months ago
arnim liked this · 9 months ago -
 versias reblogged this · 9 months ago
versias reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 subbiemech liked this · 9 months ago
subbiemech liked this · 9 months ago