My Friend Is Studying For The Mcat And Was Just Trying To Explain To Me About Heat Transfer And She Said
my friend is studying for the mcat and was just trying to explain to me about heat transfer and she said ‘you know, like the reason you get cold when you go outside on a freezing day is that your tiny human body is trying to warm up the entire universe’ and i think that’s the best thing i have ever heard
More Posts from We-are-all-paranoid and Others
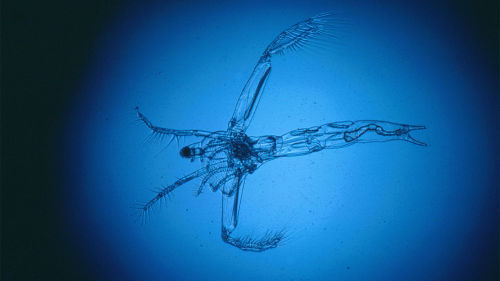
‘Ghost fleas’ bring toxic mercury up from the depths of prairie lakes
How toxic mercury moves through the environment—and accumulates in the fish that people eat—has been known for decades. Now, scientists have discovered an unexpected way that the neurotoxin circulates in lakes, hitching a late-night ride inside small predatory crustaceans dubbed “ghost fleas.” The finding helps explain why some lake fish contain surprising amounts of mercury. It also suggests researchers who sample lakes only during the day might be missing important clues to how those ecosystems work.
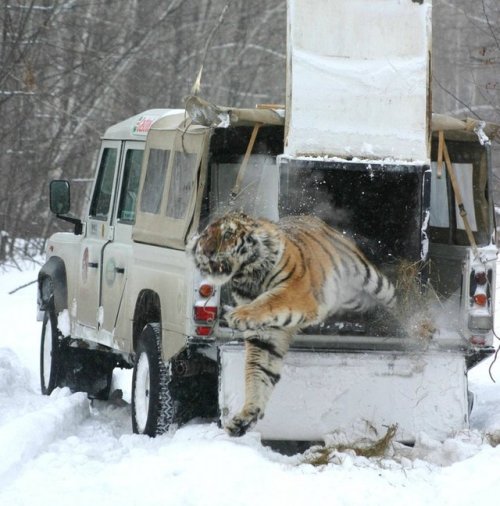

A tiger bursting to freedom after being rescued from a poacher’s snare in the Russian Far East.
Fun fact: my dad, after being a surgeon for 25 years, no longer has fingerprints. The sponge he uses to wash his hands several times a day is so harsh that it’s rubbed off his fingerprints throughout the years. Sometimes he can’t get into our building because the biometric uses a fingerprint scanner 😭


fruitie punches

A door full of opportunities

Stop the ban on blood donation of gay men

The bacteria wars are coming. Researchers at Tel Aviv University have pitted “good” bacteria against “bad” bacteria and the good guys, it appears, are winning.
If the system can be scaled, this new approach could potentially replace antibiotics, which are increasingly struggling against antibiotic-resistant “superbugs.” For the TAU study, the researchers used a toxin injection system known as a “Type 6 Secretion System.” It’s usually deployed by pathogenic (“bad”) bacteria. They introduced the system into a “friendly” bacterium, Vibrio natriegens, which is not harmful to humans. The researchers described their technology as similar to a microscopic poison arrow shot from a good bacterium to eliminate a bad bacterium under specific conditions. “The system that we built allows us to engineer ‘good’ bacteria that can recognize pathogenic bacteria, attack them with toxins, and neutralize them,” explains Dr. Dor Salomon, who co-led the study. “We know how to change and control every component in the system and create a bacterium that neutralizes different strains of bacteria. This is proof of feasibility, showing that we have the knowledge and ability to create bacteria that take advantage of this killing system and may serve as antibiotic treatments. ”The current bacteria prototype is best suited for bugs that occur naturally in saltwater. This is a growing concern, as fish and seafood constitute a major food source in many regions of the world. “Their productivity is severely impaired as a result of bacteria-borne diseases,” Solomon notes, “and since we want to avoid pouring antibiotics into aquaculture farms, a biological solution such as the one we have developed is an effective alternative.” The system will eventually be adapted to treat pathogenic bacteria in humans, farm animals and plants. Tel Aviv University has filed a patent application through Ramot, the university’s technology-transfer company. In addition to Solomon, Dr. Biswanath Jana and Kinga Kappel of the department of clinical microbiology and immunology at TAU’s Sackler Faculty of Medicine participated in the research. The results were published this month in the scientific journal EMBO Reports.

-
 labelleizzy liked this · 1 week ago
labelleizzy liked this · 1 week ago -
 manorinthewoods liked this · 2 months ago
manorinthewoods liked this · 2 months ago -
 lexielove103188 liked this · 2 months ago
lexielove103188 liked this · 2 months ago -
 doveandcrow reblogged this · 3 months ago
doveandcrow reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 pearly-everlasting reblogged this · 3 months ago
pearly-everlasting reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 bearhowls liked this · 3 months ago
bearhowls liked this · 3 months ago -
 solixir reblogged this · 4 months ago
solixir reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 solixir liked this · 4 months ago
solixir liked this · 4 months ago -
 mrhoardingartist reblogged this · 5 months ago
mrhoardingartist reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 huskyheroine liked this · 6 months ago
huskyheroine liked this · 6 months ago -
 fleetgay-super-sonic reblogged this · 6 months ago
fleetgay-super-sonic reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 infinitelysilvr reblogged this · 6 months ago
infinitelysilvr reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 annita899gkdkizqh liked this · 6 months ago
annita899gkdkizqh liked this · 6 months ago -
 pyckionion liked this · 6 months ago
pyckionion liked this · 6 months ago -
 doilooktired liked this · 7 months ago
doilooktired liked this · 7 months ago -
 nostalgic-gay reblogged this · 7 months ago
nostalgic-gay reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 nostalgic-gay liked this · 7 months ago
nostalgic-gay liked this · 7 months ago -
 sintwice liked this · 7 months ago
sintwice liked this · 7 months ago -
 agreymatter liked this · 7 months ago
agreymatter liked this · 7 months ago -
 omegavers reblogged this · 7 months ago
omegavers reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 lady-lucy13 reblogged this · 7 months ago
lady-lucy13 reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 pastacake127 liked this · 7 months ago
pastacake127 liked this · 7 months ago -
 apatheticamateur liked this · 7 months ago
apatheticamateur liked this · 7 months ago -
 lowcalcalzones liked this · 7 months ago
lowcalcalzones liked this · 7 months ago -
 baasthasthezoomies liked this · 7 months ago
baasthasthezoomies liked this · 7 months ago -
 ginniebaker reblogged this · 7 months ago
ginniebaker reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 stuckinsquahamish liked this · 7 months ago
stuckinsquahamish liked this · 7 months ago -
 femslashhistorian liked this · 8 months ago
femslashhistorian liked this · 8 months ago -
 mfdebry liked this · 8 months ago
mfdebry liked this · 8 months ago -
 softcarabiner liked this · 8 months ago
softcarabiner liked this · 8 months ago -
 waytooinvested-main reblogged this · 8 months ago
waytooinvested-main reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 littlelemonkey reblogged this · 8 months ago
littlelemonkey reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 error-core-animations liked this · 8 months ago
error-core-animations liked this · 8 months ago -
 sarue liked this · 8 months ago
sarue liked this · 8 months ago -
 dj-crack reblogged this · 8 months ago
dj-crack reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 legendarypeanutchild liked this · 8 months ago
legendarypeanutchild liked this · 8 months ago -
 mrljester reblogged this · 8 months ago
mrljester reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 willowedhepatica reblogged this · 8 months ago
willowedhepatica reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 willowedhepatica liked this · 8 months ago
willowedhepatica liked this · 8 months ago -
 bratthewurst reblogged this · 8 months ago
bratthewurst reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 geekg1rl3 reblogged this · 8 months ago
geekg1rl3 reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 geekg1rl3 liked this · 8 months ago
geekg1rl3 liked this · 8 months ago -
 0ramge liked this · 8 months ago
0ramge liked this · 8 months ago -
 pevko liked this · 8 months ago
pevko liked this · 8 months ago -
 technatic-k liked this · 8 months ago
technatic-k liked this · 8 months ago -
 proppane reblogged this · 8 months ago
proppane reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 caillte-sa-spas reblogged this · 8 months ago
caillte-sa-spas reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 beeingfulloflove liked this · 8 months ago
beeingfulloflove liked this · 8 months ago


