If We Ever Want A Long-distance Relationship With Aliens, They Have To Be Able To Find Us.
If we ever want a long-distance relationship with aliens, they have to be able to find us.
More Posts from Xyhor-astronomy and Others

A wispy and filamentary cloud of gas and dust, the Crab nebula is the remnant of a supernova explosion that was observed by Chinese astronomers in the year 1054.
The image combines Hubble’s view of the nebula at visible wavelengths, obtained using three different filters sensitive to the emission from oxygen and sulphur ions and is shown here in blue. Herschel’s far-infrared image reveals the emission from dust in the nebula and is shown here in red.
Credit: NASA/ESA/Hubble
Oldest recorded solar eclipse helps date the Egyptian pharaohs

UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE—Researchers have pinpointed the date of what could be the oldest solar eclipse yet recorded. The event, which occurred on 30 October 1207 BC, is mentioned in the Bible, and could have consequences for the chronology of the ancient world.
Using a combination of the biblical text and an ancient Egyptian text, the researchers were then able to refine the dates of the Egyptian pharaohs, in particular the dates of the reign of Ramesses the Great. The results are published in the Royal Astronomical Society journal Astronomy & Geophysics.
The biblical text in question comes from the Old Testament book of Joshua and has puzzled biblical scholars for centuries. It records that after Joshua led the people of Israel into Canaan - a region of the ancient Near East that covered modern-day Israel and Palestine - he prayed: “Sun, stand still at Gibeon, and Moon, in the Valley of Aijalon. And the Sun stood still, and the Moon stopped, until the nation took vengeance on their enemies.” Read more.
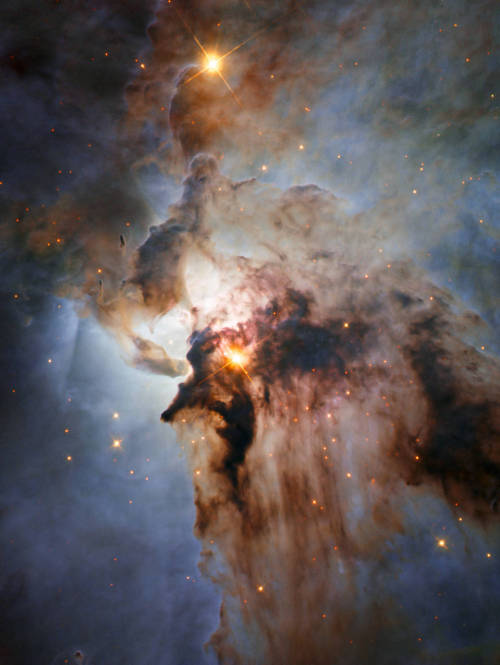

Stormy Seas in Sagittarius
This new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows the center of the Lagoon Nebula, an object with a deceptively tranquil name, in the constellation of Sagittarius. The region is filled with intense winds from hot stars, churning funnels of gas, and energetic star formation, all embedded within an intricate haze of gas and pitch-dark dust.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL/ESA/J. Trauger
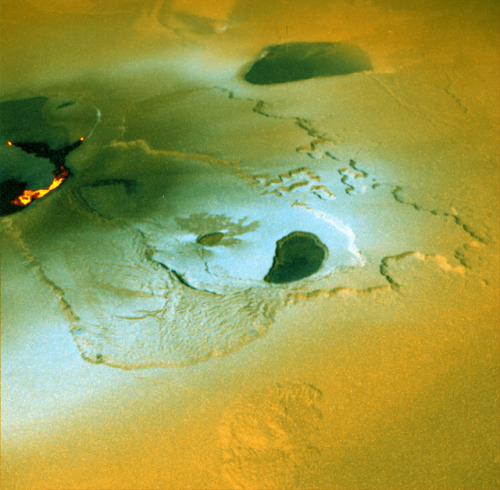
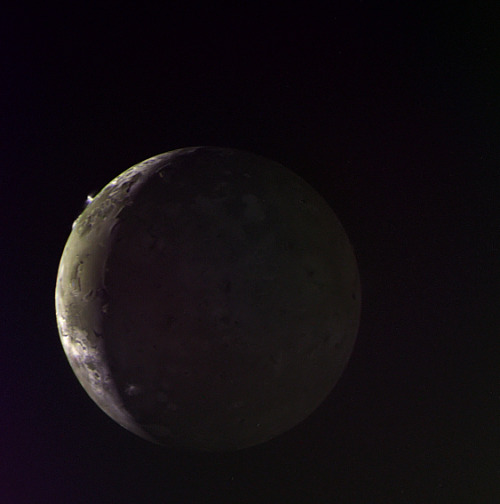
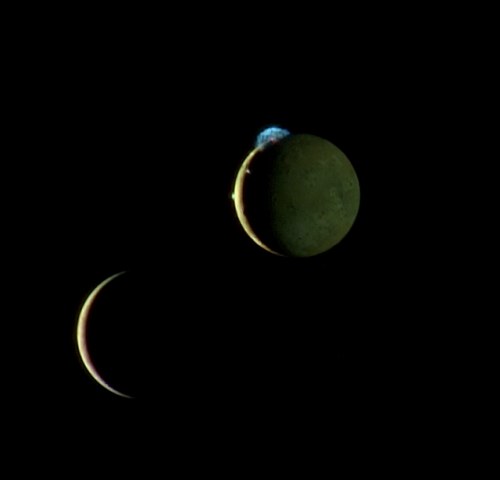
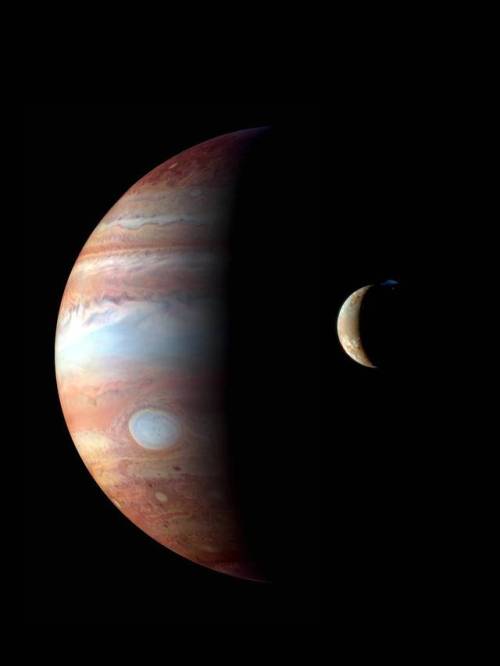
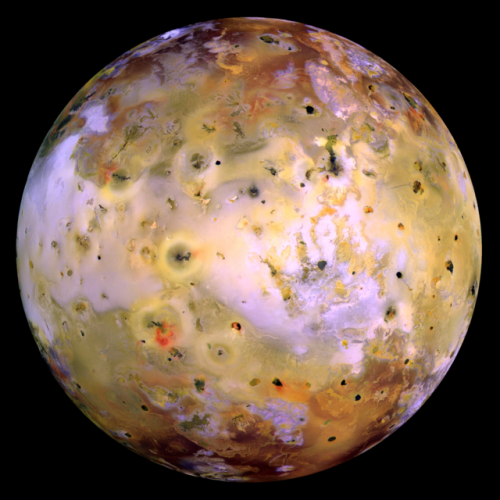
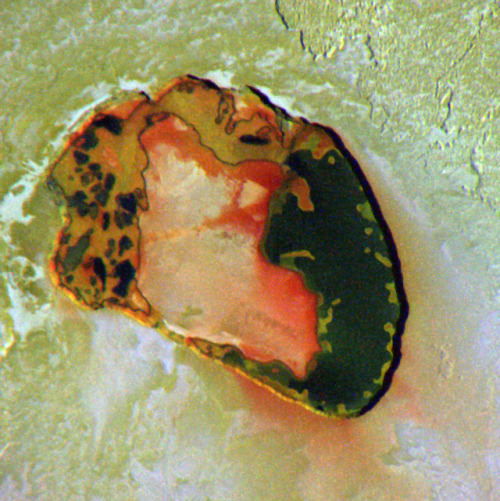


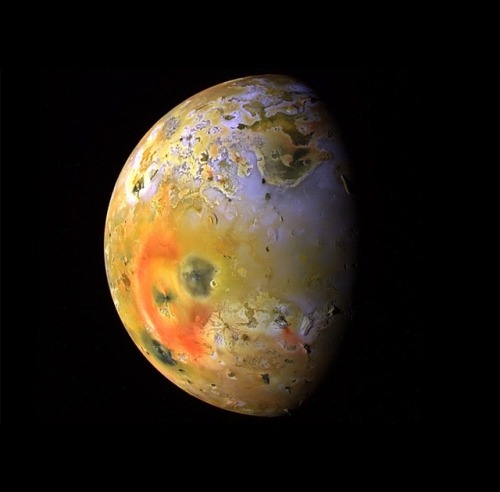





Io - The Volcanic Moon
Looking like a giant pizza covered with melted cheese and splotches of tomato and ripe olives, Io is the most volcanically active body in the solar system. Volcanic plumes rise 300 km (190 miles) above the surface, with material spewing out at nearly half the required escape velocity.
A bit larger than Earth’s Moon, Io is the third largest of Jupiter’s moons, and the fifth one in distance from the planet.
Although Io always points the same side toward Jupiter in its orbit around the giant planet, the large moons Europa and Ganymede perturb Io’s orbit into an irregularly elliptical one. Thus, in its widely varying distances from Jupiter, Io is subjected to tremendous tidal forces. These forces cause Io’s surface to bulge up and down (or in and out) by as much as 100 m (330 feet)! Compare these tides on Io’s solid surface to the tides on Earth’s oceans. On Earth, in the place where tides are highest, the difference between low and high tides is only 18 m (60 feet), and this is for water, not solid ground!
This tidal pumping generates a tremendous amount of heat within Io, keeping much of its subsurface crust in liquid form seeking any available escape route to the surface to relieve the pressure. Thus, the surface of Io is constantly renewing itself, filling in any impact craters with molten lava lakes and spreading smooth new floodplains of liquid rock. The composition of this material is not yet entirely clear, but theories suggest that it is largely molten sulfur and its compounds (which would account for the varigated coloring) or silicate rock (which would better account for the apparent temperatures, which may be too hot to be sulfur). Sulfur dioxide is the primary constituent of a thin atmosphere on Io. It has no water to speak of, unlike the other, colder Galilean moons. Data from the Galileo spacecraft indicates that an iron core may form Io’s center, thus giving Io its own magnetic field.
Io was discovered on 8 January 1610 by Galileo Galilei. The discovery, along with three other Jovian moons, was the first time a moon was discovered orbiting a planet other than Earth.

Eruption of the Tvashtar volcano on Jupiter’s moon Io, photographed by New Horizons.
Image credit: NASA/JPL/Galileo/New Horizons ( Stuart Rankin | Kevin Gill)
Source: NASA







10 Spacetime Mysteries That Quantum Gravity Could Solve
“4.) In most approaches to quantum gravity, space-time is not fundamental but made of something else. That might be strings, loops, qbits, or some variant of space-time “atoms” which appear in condensed-matter based approaches. The individual constituents, however, can only be resolved when probed with extremely high energies, far beyond what we can achieve on Earth.”
What is the fundamental nature of the Universe? When it comes to General Relativity, our answer is matter and energy on one hand, and spacetime on the other. But there’s another side to that story: a quantum one. While matter and energy can be discretized into quanta, our notion of spacetime is purely classical. But depending on what our true, fundamental theory of quantum gravity actually is, it could have incredible implications for our Universe. Perhaps we have tiny little black holes popping in and out of existence on a continuous basis; perhaps the vacuum of space isn’t entirely transparent to light; perhaps time turns into space at some level; perhaps wormholes and baby Universes are real. These are mysteries that are currently unresolved, but quantum gravity could provide the answer.
What are the mysteries, and what does it all mean? Sabine Hossenfelder explores, with a fantastic video!
Drilling Through Ice in the Hunt of Celestial Life




North Cascades National Park, Washington
A night in the Cascade Mountains
What’s Up November 2017
What’s Up For November?
Dawn pairing of Jupiter and Venus, Moon shines near star clusters, meteor activity all month long!

This month binoculars will come in handy–to view the moon, star clusters, and a close pairing of Venus and Jupiter.

You can’t miss bright Venus in the predawn sky. This month Venus pairs up with Jupiter on the morning of November 13th.

The Leonids peak on a moonless November 17th. Expect no more than 10 meteors an hour around 3:00 a.m., the height of the shower.

The Northern and Southern sub-branches of the Taurid meteor shower offer sparse counts of about 5 meteors per hour, but slow, bright meteors are common.

The nearby November Orionids peak on the 28th. In contrast to the Taurids, the Orionids are swift. But don’t expect more than 3 meteors per hour.

The moon glides by three beautiful star clusters in the morning sky this month, and a pair of binoculars will allow you to see the individual stars in the clusters. Aim your binoculars at the Pleiades and the moon on the 5th.

Then aim at the Messier or M-35 cluster and the moon on the 7th and the Beehive cluster and the moon on the 10th.

Meanwhile, at dusk, catch Saturn as it dips closer to the western horizon and pairs up with Mercury on the 24th through the 28th.

Also, Comet C/2017 O1 should still be a binocular-friendly magnitude 7 or 8 greenish object in November. Use Polaris, the North Star as a guide. Look in the East to Northeast sky in the late evening.
Watch the full What’s Up for November Video:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Image of Titan taken by the Cassini spacecraft
NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI/Kevin M. Gill










Dunes, peaks and craters on Mars obtained by HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment), a camera on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Image credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona
-
 cabult liked this · 7 years ago
cabult liked this · 7 years ago -
 braininnajar liked this · 7 years ago
braininnajar liked this · 7 years ago -
 tblindszy-blog liked this · 7 years ago
tblindszy-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 duclocksm-blog liked this · 7 years ago
duclocksm-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 jorecitat-blog liked this · 7 years ago
jorecitat-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 myparalla-blog liked this · 7 years ago
myparalla-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 luciselenyx liked this · 7 years ago
luciselenyx liked this · 7 years ago -
 vboilingr-blog liked this · 7 years ago
vboilingr-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 gagradien-blog liked this · 7 years ago
gagradien-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 tunusable-blog liked this · 7 years ago
tunusable-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 jurearran-blog liked this · 7 years ago
jurearran-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 tribeofawakeningsovereignty-blog liked this · 7 years ago
tribeofawakeningsovereignty-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 vuatmosph-blog liked this · 7 years ago
vuatmosph-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 kujmous liked this · 7 years ago
kujmous liked this · 7 years ago -
 f1zzybutt liked this · 7 years ago
f1zzybutt liked this · 7 years ago -
 stephaneraymond-blog liked this · 7 years ago
stephaneraymond-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 gbohrcyxe-blog liked this · 7 years ago
gbohrcyxe-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 srefuelin-blog liked this · 7 years ago
srefuelin-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 mrcheese1996 liked this · 7 years ago
mrcheese1996 liked this · 7 years ago -
 kabretoss reblogged this · 7 years ago
kabretoss reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 kbrechtel liked this · 7 years ago
kbrechtel liked this · 7 years ago -
 joar80 liked this · 7 years ago
joar80 liked this · 7 years ago -
 blackcatgodess liked this · 7 years ago
blackcatgodess liked this · 7 years ago -
 rain-in-the-slums liked this · 7 years ago
rain-in-the-slums liked this · 7 years ago -
 shiberet reblogged this · 7 years ago
shiberet reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 polishguy1-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago
polishguy1-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago -
 leda-timeandspace liked this · 7 years ago
leda-timeandspace liked this · 7 years ago -
 mikeyperes liked this · 7 years ago
mikeyperes liked this · 7 years ago -
 kaospersona liked this · 7 years ago
kaospersona liked this · 7 years ago -
 xyhor-astronomy reblogged this · 7 years ago
xyhor-astronomy reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 cinturon-cadena liked this · 7 years ago
cinturon-cadena liked this · 7 years ago -
 originalwoods liked this · 7 years ago
originalwoods liked this · 7 years ago -
 lucarimmie reblogged this · 7 years ago
lucarimmie reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 lucarimmie liked this · 7 years ago
lucarimmie liked this · 7 years ago -
 whichhomonym reblogged this · 7 years ago
whichhomonym reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ashtreenomy liked this · 7 years ago
ashtreenomy liked this · 7 years ago -
 utterlyinconspicuous liked this · 7 years ago
utterlyinconspicuous liked this · 7 years ago -
 mrschmaltz reblogged this · 7 years ago
mrschmaltz reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 lordtableshark reblogged this · 7 years ago
lordtableshark reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 lordtableshark liked this · 7 years ago
lordtableshark liked this · 7 years ago -
 reynaderoma liked this · 7 years ago
reynaderoma liked this · 7 years ago -
 lexxi-bird liked this · 7 years ago
lexxi-bird liked this · 7 years ago
For more content, Click Here and experience this XYHor in its entirety!Space...the Final Frontier. Let's boldly go where few have gone before with XYHor: Space: Astronomy & Spacefaring: the collection of the latest finds and science behind exploring our solar system, how we'll get there and what we need to be prepared for!
128 posts