Apollo 11 Launch



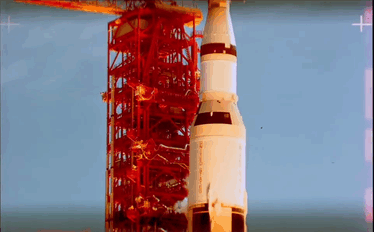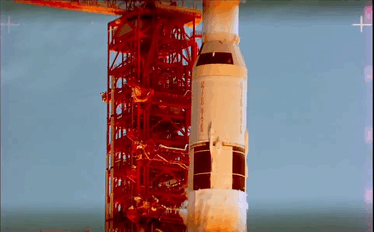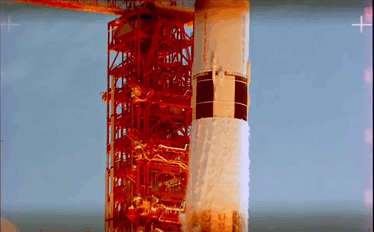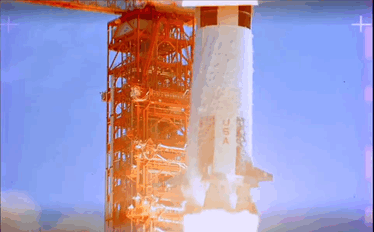

Apollo 11 Launch
More Posts from Xyhor-astronomy and Others

Black Holes are not so Black (Part 3) - Gravitational Waves
The existence of Gravitational Waves have been confirmed. But you probably have heard that. In this post, we will break down this profound discovery into comprehend-able chunks.
This is going to be a amazing journey. Ready ?
Redefining Gravity
When we usually talk of Gravitation we are bound to think like Newton, where objects are assumed to exerting a force upon each other.
Like imaginary arrows of force in space. But this picture, although good for high school crumbled, with the advent of Einstein’s theory of Relativity.
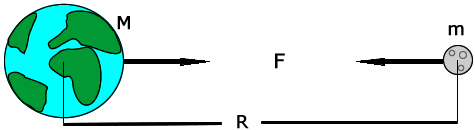
What is the Space-Time Fabric?
Think of space-time fabric as an actual cloth of fabric. ( An analogy )

When you place an object on the fabric, the cloth curves. This is exactly what happens in the solar system as well.

The sun with such a huge mass bends the space-time fabric. And the earth and all the planets are kept in orbit by following this curvature that has been made by the sun.
Attributing to the various masses of objects, the way they bend this fabric also varies.
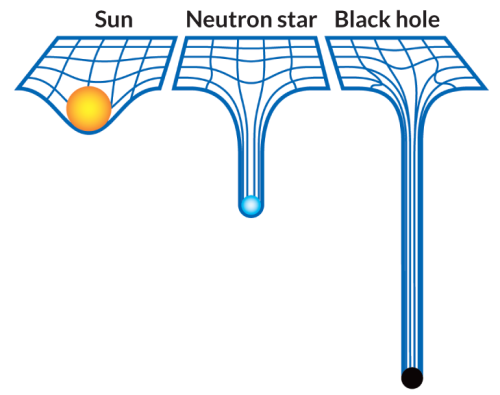
What are Gravitational Waves?
If you drop an object in a medium such as water, they produce ripples that propagate as waves through the medium.

Similarly, Gravitational waves are ripples in space-time fabric produced when you drag heavy objects through space time.
And the nature of these waves is that they don’t require a medium to propagate.
How do you make one?
Everything with mass/energy can create these waves.

Source
Two persons dancing around each other in space too can create gravitational waves. But the waves would be extremely faint.
You need something big and massive accelerating through space-time in order to even detect them.

And orbiting binary stars/black holes are valuable in this retrospect.
How can you detect them?
Let’s turn to the problem to detecting them assuming you do find binary stars/black-holes in the wondrous space to suite your needs.
Well, for starters you cannot use rocks/ rulers to measure them because as the space expands and contracts, so do the rocks. ( the distances will remain same in both the cases )

Here’s where the high school fact that the speed of Light is a constant no matter what plays an important and pivotal role.
If the space expands, the time taken for light to reach from A to B would be longer. And if it contracts, the time taken for it to reach from A to B would be smaller.

PC: PHDComics
By allowing the light waves from the contraction and expansion to interfere with each other, such as done in any interferometry experiment we can detect the expansion or contraction. Voila!
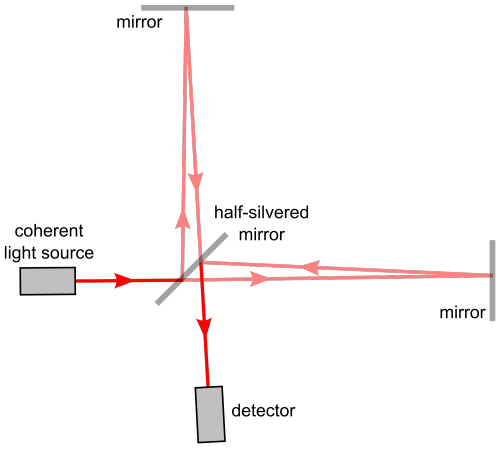
And this is exactly what they did! ( on a macroscopic level ) at LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory)
14 September 2015

Two Black Holes with masses of 29 and 36 solar masses merged together some 1.3 Billion light years away.
Two Black Holes colliding is the header animation of the ‘Black Holes are not so Black Series’, in case if you haven’t noticed.

The merger of these two black holes results in the emission of energy equivalent to 3 solar masses as Gravitational Waves.
This signal was seen by both LIGO detectors, in Livingston and Hanford, with a time difference of 7 milliseconds.
And with the measurement of this time difference, physicists have pronounced the existence of Gravitational Waves.

Source
All this is most certainly easily said than done and requires meticulous and extensive research, not to mention highly sensitive instruments.
Had they not have measured this time difference, we might have had to wait for the merger for more massive black holes to collide and maybe even build more sensitive instruments to detect these waves.
And Einstein predicted this a 100 years back!

Mind Blown!
Note: Hope you are able to understand and appreciate the profundity of the discovery done by mankind.
** All animations used here are merely for Educational purposes. If you have any issues, please write to us at : 153armstrong@gmail.com

Oct. 4, 1957 - Sputnik, the Dawn of the Space Age via NASA http://ift.tt/2hNf1Yq
Curiosity Rover: Five Years on Mars
The evening of August 5, 2012…five years ago…our Mars Curiosity rover landed on the Red Planet.

Arriving at Mars at 10:32 p.m. PDT (morning of Aug 6 EDT), this rover would prove to be the most technologically advanced rover ever built.

Curiosity used a series of complicated landing maneuvers never before attempted.

The specialized landing sequence, which employed a giant parachute, a jet-controlled descent vehicle and a daring “sky crane” maneuver similar to rappelling was devised because testing and landing techniques used during previous rover missions could not safely accommodate the much larger and heavier rover.
Curiosity’s mission: To determine whether the Red Planet ever was, or is, habitable to microbial life.

The car-size rover is equipped with 17 cameras, a robotic arm, specialized instruments and an on-board laboratory.

Let’s explore Curiosity’s top 5 discoveries since she landed on Mars five years ago…
1. Gale Crater had conditions suitable for life about 3.5 billion years ago

In 2013, Curiosity’s analysis of a rock sample showed that ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Scientists identified sulfur, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and carbon – some of the key chemical ingredients for life – in the powder Curiosity drilled out of a sedimentary rock near an ancient stream bed in Gale Crater.

Later, in 2014, Curiosity discovered that these conditions lasted for millions of years, perhaps much longer. This interpretation of Curiosity’s findings in Gale Crater suggests ancient Mars maintained a climate that could have produced long-lasting lakes at many locations on the Red Planet.
2. Organic molecules detected at several locations

In 2014, our Curiosity rover drilled into the Martian surface and detected different organic chemicals in the rock powder. This was the first definitive detection of organics in surface materials of Mars. These Martian organics could either have formed on Mars or been delivered to Mars by meteorites.

Curiosity’s findings from analyzing samples of atmosphere and rock powder do not reveal whether Mars has ever harbored living microbes, but the findings do shed light on a chemically active modern Mars and on favorable conditions for life on ancient Mars.
3. Present and active methane in Mars’ atmosphere

Also in 2014, our Curiosity rover measured a tenfold spike in methane, an organic chemical, in the atmosphere around the planet. This temporary increase in methane tells us there must be some relatively localized source.

Researchers used Curiosity’s onboard Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) laboratory a dozen times in a 20-month period to sniff methane in the atmosphere. During two of those months, in late 2013 and early 2014, four measurements averaged seven parts per billion.
4. Radiation could pose health risks for humans

Measurements taken by our Curiosity rover since launch have provided us with the information needed to design systems to protect human explorers from radiation exposure on deep-space expeditions in the future. Curiosity’s Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD) was the first instrument to measure the radiation environment during a Mars cruise mission from inside a spacecraft that is similar to potential human exploration spacecraft.

The findings indicate radiation exposure for human explorers could exceed our career limit for astronauts if current propulsion systems are used. These measurements are being used to better understand how radiation travels through deep space and how it is affected and changed by the spacecraft structure itself. This, along with research on the International Space Station are helping us develop countermeasures to the impacts of radiation on the human body.
5. A thicker atmosphere and more water in Mars past

In 2015, Curiosity discovered evidence that has led scientists to conclude that ancient Mars was once a warmer, wetter place than it is today.
To produce this more temperate climate, several researchers have suggested that the planet was once shrouded in a much thicker carbon dioxide atmosphere. You may be asking…Where did all the carbon go?

The solar wind stripped away much of Mars’ ancient atmosphere and is still removing tons of it every day. That said, 3.8 billion years ago, Mars might have had a moderately dense atmosphere, with a surface pressure equal to or less than that found on Earth.
Our Curiosity rover continues to explore the Red Planet today. On average, the rover travels about 30 meters per hour and is currently on the lower slope of Mount Sharp.

Get regular updates on the Curiosity mission by following @MarsCuriosity on Twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


Hubble peeks inside a stellar cloud
These bright stars shining through what looks like a haze in the night sky are part of a young stellar grouping in one of the largest known star formation regions of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a dwarf satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. The image was captured by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s Wide Field Planetary Camera 2.
The stellar grouping is known to stargazers as NGC 2040 or LH 88. It is essentially a very loose star cluster whose stars have a common origin and are drifting together through space. There are three different types of stellar associations defined by their stellar properties. NGC 2040 is an OB association, a grouping that usually contains 10–100 stars of type O and B — these are high-mass stars that have short but brilliant lives. It is thought that most of the stars in the Milky Way were born in OB associations.
There are several such groupings of stars in the LMC, including one previously featured as a Hubble Picture of the Week. Just like the others, LH 88 consists of several high-mass young stars in a large nebula of partially ionised hydrogen gas, and lies in what is known to be a supergiant shell of gas called LMC 4.
Over a period of several million years, thousands of stars may form in these supergiant shells, which are the largest interstellar structures in galaxies. The shells themselves are believed to have been created by strong stellar winds and clustered supernova explosions of massive stars that blow away surrounding dust and gas, and in turn trigger further episodes of star formation.
The LMC is the third closest galaxy to our Milky Way. It is located some 160 000 light-years away, and is about 100 times smaller than our own.
This image, which shows ultraviolet, visible and infrared light, covers a field of view of approximately 1.8 by 1.8 arcminutes.
A version of this image was entered into the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures Image Processing Competition by contestant Eedresha Sturdivant. Hidden Treasures is an initiative to invite astronomy enthusiasts to search the Hubble archive for stunning images that have never been seen by the general public.
These bright stars shining through what looks like a haze in the night sky are part of a young stellar grouping in one of the largest known star formation regions of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a dwarf satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. The image was captured by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s Wide Field Planetary Camera 2.
The stellar grouping is known to stargazers as NGC 2040 or LH 88. It is essentially a very loose star cluster whose stars have a common origin and are drifting together through space. There are three different types of stellar associations defined by their stellar properties. NGC 2040 is an OB association, a grouping that usually contains 10–100 stars of type O and B — these are high-mass stars that have short but brilliant lives. It is thought that most of the stars in the Milky Way were born in OB associations.
There are several such groupings of stars in the LMC, including one previously featured as a Hubble Picture of the Week. Just like the others, LH 88 consists of several high-mass young stars in a large nebula of partially ionised hydrogen gas, and lies in what is known to be a supergiant shell of gas called LMC 4.
Over a period of several million years, thousands of stars may form in these supergiant shells, which are the largest interstellar structures in galaxies. The shells themselves are believed to have been created by strong stellar winds and clustered supernova explosions of massive stars that blow away surrounding dust and gas, and in turn trigger further episodes of star formation.
The LMC is the third closest galaxy to our Milky Way. It is located some 160 000 light-years away, and is about 100 times smaller than our own.
This image, which shows ultraviolet, visible and infrared light, covers a field of view of approximately 1.8 by 1.8 arcminutes.
A version of this image was entered into the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures Image Processing Competition by contestant Eedresha Sturdivant. Hidden Treasures is an initiative to invite astronomy enthusiasts to search the Hubble archive for stunning images that have never been seen by the general public.
ESA/Hubble, NASA and D. A Gouliermis. Acknowledgement: Flickr user Eedresha Sturdivant
https://www.spacetelescope.org/images/potw
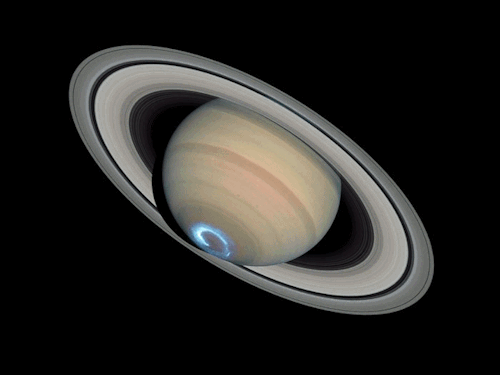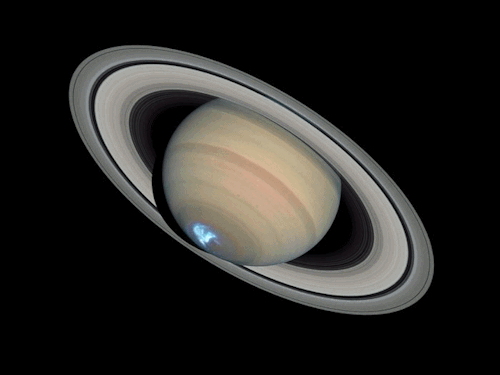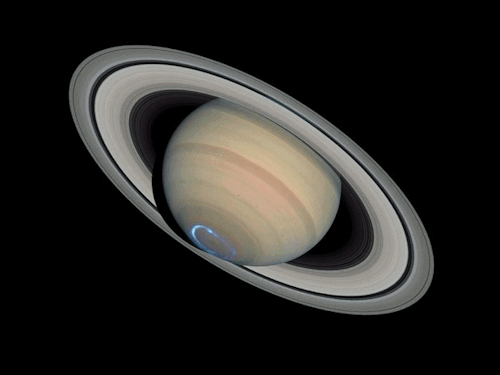
Sequence of images of auroras seen at the south pole of Saturn. Images combine visible and ultraviolet light.
Credit: NASA, ESA, J. Clarke (Boston University, USA), and Z. Levay (STScI)

Curiosity drill site reveals that under its red surface, Mars is grey-blue
via reddit
Observing the Ozone Hole from Space: A Science Success Story
Using our unique ability to view Earth from space, we are working together with NOAA to monitor an emerging success story – the shrinking ozone hole over Antarctica.

Thirty years ago, the nations of the world agreed to the landmark ‘Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.’ The Protocol limited the release of ozone-depleting chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) into the atmosphere.

Since the 1960s our scientists have worked with NOAA researchers to study the ozone layer.

We use a combination of satellite, aircraft and balloon measurements of the atmosphere.

The ozone layer acts like a sunscreen for Earth, blocking harmful ultraviolet, or UV, rays emitted by the Sun.

In 1985, scientists first reported a hole forming in the ozone layer over Antarctica. It formed over Antarctica because the Earth’s atmospheric circulation traps air over Antarctica. This air contains chlorine released from the CFCs and thus it rapidly depletes the ozone.

Because colder temperatures speed up the process of CFCs breaking up and releasing chlorine more quickly, the ozone hole fluctuates with temperature. The hole shrinks during the warmer summer months and grows larger during the southern winter. In September 2006, the ozone hole reached a record large extent.

But things have been improving in the 30 years since the Montreal Protocol. Thanks to the agreement, the concentration of CFCs in the atmosphere has been decreasing, and the ozone hole maximum has been smaller since 2006’s record.

That being said, the ozone hole still exists and fluctuates depending on temperature because CFCs have very long lifetimes. So, they still exist in our atmosphere and continue to deplete the ozone layer.
To get a view of what the ozone hole would have looked like if the world had not come to the agreement to limit CFCs, our scientists developed computer models. These show that by 2065, much of Earth would have had almost no ozone layer at all.

Luckily, the Montreal Protocol exists, and we’ve managed to save our protective ozone layer. Looking into the future, our scientists project that by 2065, the ozone hole will have returned to the same size it was thirty years ago.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
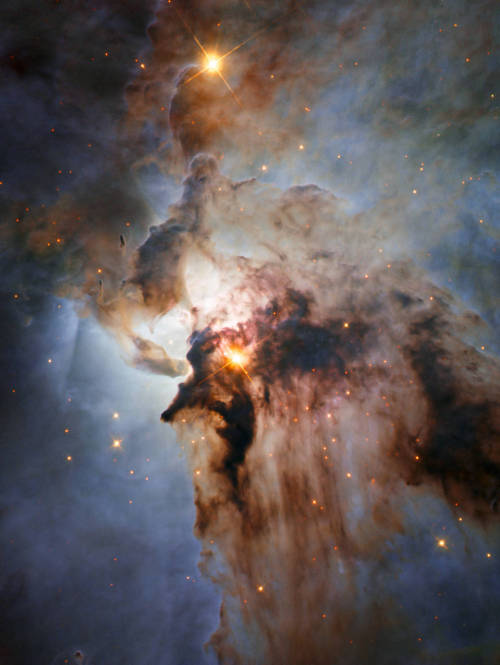

Stormy Seas in Sagittarius
This new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows the center of the Lagoon Nebula, an object with a deceptively tranquil name, in the constellation of Sagittarius. The region is filled with intense winds from hot stars, churning funnels of gas, and energetic star formation, all embedded within an intricate haze of gas and pitch-dark dust.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL/ESA/J. Trauger

Massive Stars in Open Cluster Pismis 24
How massive can a normal star be? Estimates made from distance, brightness and standard solar models had given one star in the open cluster Pismis 24 over 200 times the mass of our Sun, making it a record holder. This star is the brightest object located just above the gas front in the above image. Close inspection of images taken recently with the Hubble Space Telescope, however, have shown that Pismis 24-1 derives its brilliant luminosity not from a single star but from three at least. Component stars would still remain near 100 solar masses, making them among the more massive stars currently on record. Toward the bottom of the image, stars are still forming in the associated emission nebula NGC 6357, including several that appear to be breaking out and illuminating a spectacular cocoon.
Credit: NASA, ESA and J. M. Apellániz (IAA, Spain)
-
 kabrox18 reblogged this · 8 months ago
kabrox18 reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 edminh reblogged this · 8 months ago
edminh reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 edminh liked this · 8 months ago
edminh liked this · 8 months ago -
 mrpalms liked this · 8 months ago
mrpalms liked this · 8 months ago -
 wonderingwhatsnext liked this · 8 months ago
wonderingwhatsnext liked this · 8 months ago -
 wonderingwhatsnext reblogged this · 8 months ago
wonderingwhatsnext reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 krustyspacepimpadventurediary reblogged this · 8 months ago
krustyspacepimpadventurediary reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 visionautiks liked this · 8 months ago
visionautiks liked this · 8 months ago -
 powlor liked this · 8 months ago
powlor liked this · 8 months ago -
 roundabouttotheedge reblogged this · 8 months ago
roundabouttotheedge reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 xploseof reblogged this · 8 months ago
xploseof reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 edweenie liked this · 9 months ago
edweenie liked this · 9 months ago -
 cemeterys reblogged this · 9 months ago
cemeterys reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 mifawarts reblogged this · 9 months ago
mifawarts reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 mortuusflores reblogged this · 9 months ago
mortuusflores reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 saint-laika reblogged this · 9 months ago
saint-laika reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 botryoidal reblogged this · 9 months ago
botryoidal reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 sweetannie66 liked this · 9 months ago
sweetannie66 liked this · 9 months ago -
 nostalgiaispeace liked this · 9 months ago
nostalgiaispeace liked this · 9 months ago -
 a-god-in-ruins-rises reblogged this · 9 months ago
a-god-in-ruins-rises reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 acerimmeradel liked this · 9 months ago
acerimmeradel liked this · 9 months ago -
 cfnmmakesmehard liked this · 9 months ago
cfnmmakesmehard liked this · 9 months ago -
 prettybeatup liked this · 9 months ago
prettybeatup liked this · 9 months ago -
 rauhbutz liked this · 9 months ago
rauhbutz liked this · 9 months ago -
 joespinell reblogged this · 9 months ago
joespinell reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 joespinell liked this · 9 months ago
joespinell liked this · 9 months ago -
 lilo15 reblogged this · 9 months ago
lilo15 reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 jonovos liked this · 9 months ago
jonovos liked this · 9 months ago -
 divaani liked this · 9 months ago
divaani liked this · 9 months ago -
 journeythroughtherain reblogged this · 9 months ago
journeythroughtherain reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 weareallinthegutter liked this · 9 months ago
weareallinthegutter liked this · 9 months ago -
 dagwud reblogged this · 9 months ago
dagwud reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 dagwud liked this · 9 months ago
dagwud liked this · 9 months ago -
 faxe72 liked this · 9 months ago
faxe72 liked this · 9 months ago -
 thunderapache-blog reblogged this · 9 months ago
thunderapache-blog reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 thunderapache-blog liked this · 9 months ago
thunderapache-blog liked this · 9 months ago -
 fusehund reblogged this · 9 months ago
fusehund reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 mikeawood reblogged this · 9 months ago
mikeawood reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 mikeawood liked this · 9 months ago
mikeawood liked this · 9 months ago -
 martinm liked this · 9 months ago
martinm liked this · 9 months ago -
 mdall8 liked this · 9 months ago
mdall8 liked this · 9 months ago -
 allergic-to-chocolate reblogged this · 9 months ago
allergic-to-chocolate reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 allergic-to-chocolate liked this · 9 months ago
allergic-to-chocolate liked this · 9 months ago -
 shallow-www reblogged this · 9 months ago
shallow-www reblogged this · 9 months ago
For more content, Click Here and experience this XYHor in its entirety!Space...the Final Frontier. Let's boldly go where few have gone before with XYHor: Space: Astronomy & Spacefaring: the collection of the latest finds and science behind exploring our solar system, how we'll get there and what we need to be prepared for!
128 posts