Curate, connect, and discover
Hubble - Blog Posts

The Bubble Nebula, also known as NGC 7653, captured by the Hubble Telescope.Photograph: Nasa/ Esa/ Hubble Heritage Team








photos from hubble space telescope

Here is the Cat’s Eye Nebula (aka NGC 6543) taken from Hubble. It is one of the most complex planetary nebulae ever seen. Planetary nebulae form when Sun-like stars gently eject their outer gaseous layers, creating amazing and confounding shapes as seen in the image.
Space Scene

Here is a great shot caught by the Hubble Telescope showing Uranus and its Moons in enhanced colour.
See more Space content at the Telescope Scene!
Should it be worrying if I’ve seen all those tints in water samples from last three months?

Planetary Nebula NGC 2818 from Hubble.
js
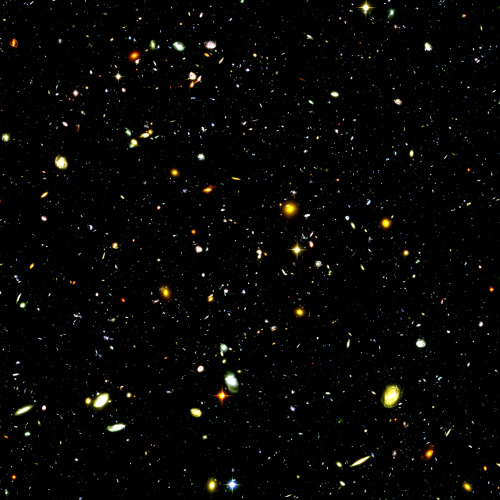

The Hubble Ultra-Deep Field is an image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, containing an estimated 10,000 galaxies.
Image credit: NASA/ESA/Hubble





NASA’s beloved space telescopes: HUBBLE, TESS, WEBB, KEPLER & SPITZER l Exoplanet Travel Bureau

The arrangement of the spiral arms in the galaxy Messier 63, seen here in an image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, recall the pattern at the center of a sunflower. So the nickname for this cosmic object -- the Sunflower Galaxy -- is no coincidence. Discovered by Pierre Mechain in 1779, the galaxy later made it as the 63rd entry into fellow French astronomer Charles Messier's famous catalogue, published in 1781. The two astronomers spotted the Sunflower Galaxy's glow in the small, northern constellation Canes Venatici (the Hunting Dogs). We now know this galaxy is about 27 million light-years away and belongs to the M51 Group -- a group of galaxies, named after its brightest member, Messier 51, another spiral-shaped galaxy dubbed the Whirlpool Galaxy. Galactic arms, sunflowers and whirlpools are only a few examples of nature's apparent preference for spirals. For galaxies like Messier 63 the winding arms shine bright because of the presence of recently formed, blue-white giant stars and clusters, readily seen in this Hubble image. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA Text credit: European Space Agency Hubble Space Telescope
'NASA's Hubble Telescope Detects ‘Sunscreen' Layer on Distant Planet': via #NASA_APP

Make sure you pick the best filter 📸
This photo of a barred spiral galaxy 48 million light-years from Earth, taken by @NASAHubble, is a cosmic wonder. In its original form, though, it wouldn't look nearly as dazzling—raw images from Hubble and other space telescopes come in shades of gray, only showing the amount of light captured across all wavelengths the telescope's camera can measure.
In order to turn those images into colorful sights like this one, we take photos with special filters that block out almost all wavelengths of light. One of the filters used on this image sees only light that would appear green to human eyes: light at wavelengths around 555 nanometers. The final multicolor image you see here uses data from seven different filters, collected with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 and Advanced Camera for Surveys.
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, D. Sand, K. Sheth

"What do you know about spherical aberration?"
"when amateurs build mirrors and do it sloppily they get what's called a downturned edge, and on different radii of the mirror it focuses the light on different parts of the optical axis and it's physically impossible to ever focus a telescope; they're useless."
"Well you launched Hubble Space Telescope with a spherically aberrated mirror."

SNR 0519-69.0
When a massive star exploded in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy to the Milky Way, it left behind an expanding shell of debris called SNR 0519-69.0. Here, multimillion degree gas is seen in X-rays from Chandra (blue). The outer edge of the explosion (red) and stars in the field of view are seen in visible light from Hubble.
Credit: NASA / Hubble & Chandra
happy 127 bday Mr. Hubble 💕🔭







On the occasion of astronomer Edwin Hubble’s birthday, let’s take a look at his stock in trade – galaxies. It was through his observations of these celestial wonders that Hubble changed our perception of the universe. This excerpt from NASA’s bio will give you the gist (and please note that all these galactic images are, of course, captured by the Hubble Space Telescope):
“Most astronomers of Hubble’s day thought that all of the universe — the planets, the stars seen with the naked eye and with powerful telescopes, and fuzzy objects called nebulae — was contained within the Milky Way galaxy. Our galaxy, it was thought, was synonymous with the universe.
In 1923 Hubble trained the Hooker telescope on a hazy patch of sky called the Andromeda Nebula. He found that it contained stars just like the ones in our galaxy, only dimmer. One star he saw was a Cepheid variable, a type of star with a known, varying brightness that can be used to measure distances. From this Hubble deduced that the Andromeda Nebula was not a nearby star cluster but rather an entire other galaxy, now called the Andromeda galaxy.
In the following years he made similar discoveries with other nebulae. By the end of the 1920s, most astronomers were convinced that our Milky Way galaxy was but one of millions in the universe. This was a shift in thought as profound as understanding the world was round and that it revolved around the sun.
Hubble then went one step further. By the end of that decade he had discovered enough galaxies to compare to each other. He created a system for classifying galaxies into ellipticals, spirals and barred spirals — a system called the Hubble tuning fork diagram, used today in an evolved form.
But the most astonishing discovery Hubble made resulted from his study of the spectra of 46 galaxies, and in particular of the Doppler velocities of those galaxies relative to our own Milky Way galaxy. What Hubble found was that the farther apart galaxies are from each other, the faster they move away from each other. Based on this observation, Hubble concluded that the universe expands uniformly. Several scientists had also posed this theory based on Einstein’s General Relativity, but Hubble’s data, published in 1929, helped convince the scientific community.”
You can click photos to identify the galaxies.
(Text: NASA/Images: HubbleSite)

Hubble Space Telescope: Exploring the Cosmos and Making Life Better on Earth
In the 35 years since its launch aboard space shuttle Discovery, the Hubble Space Telescope has provided stunning views of galaxies millions of light years away. But the leaps in technology needed for its look into space has also provided benefits on the ground. Here are some of the technologies developed for Hubble that have improved life on Earth.

Image Sensors Find Cancer
Charge-coupled device (CCD) sensors have been used in digital photography for decades, but Hubble’s Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph required a far more sensitive CCD. This development resulted in improved image sensors for mammogram machines, helping doctors find and treat breast cancer.

Laser Vision Gives Insights
In preparation for a repair mission to fix Hubble’s misshapen mirror, Goddard Space Flight Center required a way to accurately measure replacement parts. This resulted in a tool to detect mirror defects, which has since been used to develop a commercial 3D imaging system and a package detection device now used by all major shipping companies.
Optimized Hospital Scheduling
A computer scientist who helped design software for scheduling Hubble’s observations adapted it to assist with scheduling medical procedures. This software helps hospitals optimize constantly changing schedules for medical imaging and keep the high pace of emergency rooms going.

Optical Filters Match Wavelengths and Paint Swatches
For Hubble’s main cameras to capture high-quality images of stars and galaxies, each of its filters had to block all but a specific range of wavelengths of light. The filters needed to capture the best data possible but also fit on one optical element. A company contracted to construct these filters used its experience on this project to create filters used in paint-matching devices for hardware stores, with multiple wavelengths evaluated by a single lens.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!


Glorious star formation in NGC 1569, a galaxy in our local neighbourhood. Taken by Hubble.
Source

In this new image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, a firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy LEDA 36252 — also known as Kiso 5649.
(via LEDA 36252, a cosmic tadpole | ESA/Hubble)

Hubble Image of NGC 3324
Located in the Southern Hemisphere, NGC 3324 is at the northwest corner of the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372), home of the Keyhole Nebula and the active, outbursting star Eta Carinae. The entire Carina Nebula complex is located at a distance of roughly 7,200 light-years, and lies in the constellation Carina.
Credit: NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

Whirlpool galaxy
Credit : Hubble and chandraxray

Mars
Credit: space hub

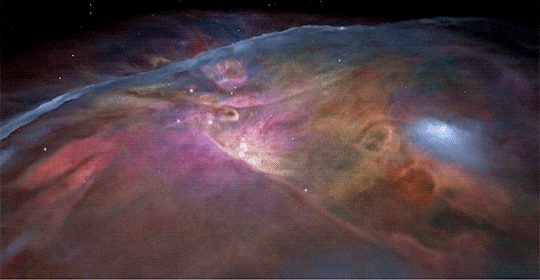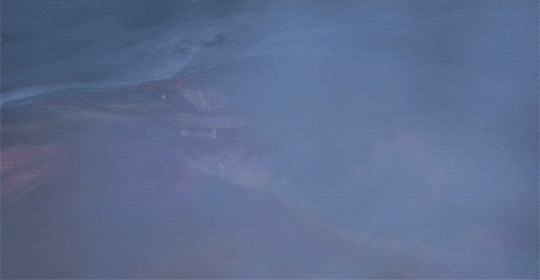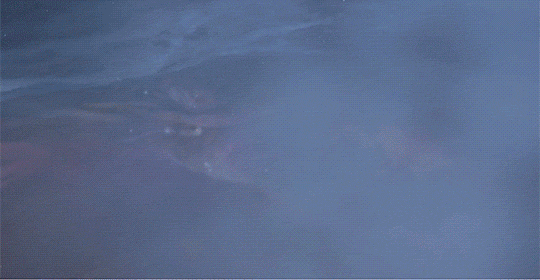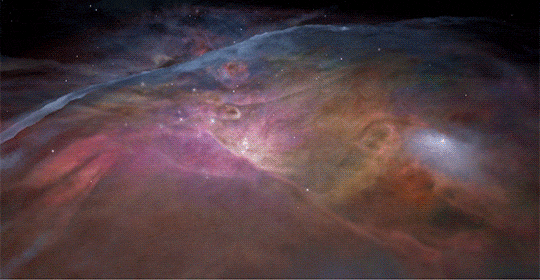
Hubble classic view of Orion nebula🌌