Best Star Wars Movie Can’t Deny It
Best Star Wars movie can’t deny it
Prequels and sequels eat your heart out
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!
The Empire Strikes Back opened in theaters on this day in 1980.
More Posts from Acosmicgeek and Others
That’s a great explanation of particle physics xD
But really, this stuff is so interesting! I love reading about stuff like this - so good work NASA!
If you liked the four forces governing the universe, you might like this book I just finished reading for the seventh time (Neil DeGrasse Tyson’s “Astrophysics for People in a Hurry”). It talks about these forces and a lot of other really cool concepts, like dark energy and chemistry-related-to-space.
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!
May the Four Forces Be With You!
May the force be with you? Much to learn you still have, padawan. In our universe it would be more appropriate to say, “May the four forces be with you.”
There are four fundamental forces that bind our universe and its building blocks together. Two of them are easy to spot — gravity keeps your feet on the ground while electromagnetism keeps your devices running. The other two are a little harder to see directly in everyday life, but without them, our universe would look a lot different!
Let’s explore these forces in a little more detail.
Gravity: Bringing the universe together

If you jump up, gravity brings you back down to Earth. It also keeps the solar system together … and our galaxy, and our local group of galaxies and our supercluster of galaxies.
Gravity pulls everything together. Everything, from the bright centers of the universe to the planets farthest from them. In fact, you (yes, you!) even exert a gravitational force on a galaxy far, far away. A tiny gravitational force, but a force nonetheless.

Credit: NASA and the Advanced Visualization Laboratory at the National Center for Supercomputing and B. O'Shea, M. Norman
Despite its well-known reputation, gravity is actually the weakest of the four forces. Its strength increases with the mass of the two objects involved. And its range is infinite, but the strength drops off as the square of the distance. If you and a friend measured your gravitational tug on each other and then doubled the distance between you, your new gravitational attraction would just be a quarter of what it was. So, you have to be really close together, or really big, or both, to exert a lot of gravity.
Even so, because its range is infinite, gravity is responsible for the formation of the largest structures in our universe! Planetary systems, galaxies and clusters of galaxies all formed because gravity brought them together.
Gravity truly surrounds us and binds us together.
Electromagnetism: Lighting the way
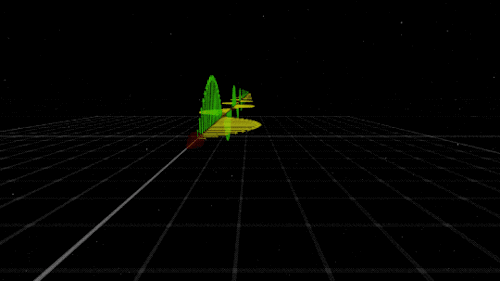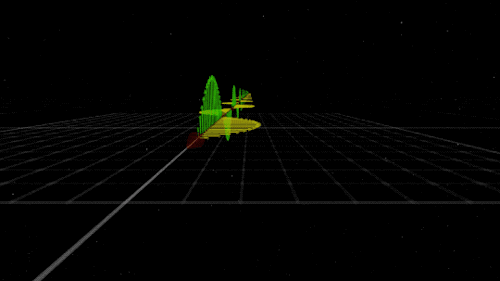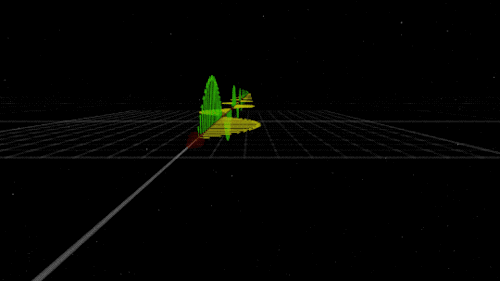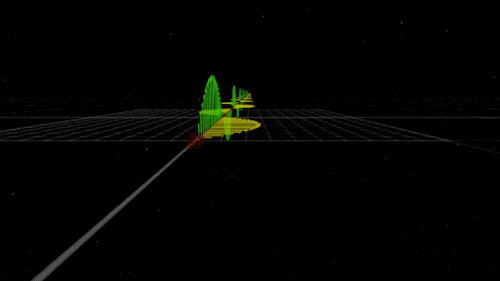
You know that shock you get on a dry day after shuffling across the carpet? The electricity that powers your television? The light that illuminates your room on a dark night? Those are all the work of electromagnetism. As the name implies, electromagnetism is the force that includes both electricity and magnetism.
Electromagnetism keeps electrons orbiting the nucleus at the center of atoms and allows chemical compounds to form (you know, the stuff that makes up us and everything around us). Electromagnetic waves are also known as light. Once started, an electromagnetic wave will travel at the speed of light until it interacts with something (like your eye) — so it will be there to light up the dark places.

Like gravity, electromagnetism works at infinite distances. And, also like gravity, the electromagnetic force between two objects falls as the square of their distance. However, unlike gravity, electromagnetism doesn’t just attract. Whether it attracts or repels depends on the electric charge of the objects involved. Two negative charges or two positive charges repel each other; one of each, and they attract each other. Plus. Minus. A balance.
This is what happens with common household magnets. If you hold them with the same “poles” together, they resist each other. On the other hand, if you hold a magnet with opposite poles together — snap! — they’ll attract each other.
Electromagnetism might just explain the relationship between a certain scruffy-looking nerf-herder and a princess.
Strong Force: Building the building blocks

Credit: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
The strong force is where things get really small. So small, that you can’t see it at work directly. But don’t let your eyes deceive you. Despite acting only on short distances, the strong force holds together the building blocks of the atoms, which are, in turn, the building blocks of everything we see around us.
Like gravity, the strong force always attracts, but that’s really where their similarities end. As the name implies, the force is strong with the strong force. It is the strongest of the four forces. It brings together protons and neutrons to form the nucleus of atoms — it has to be stronger than electromagnetism to do it, since all those protons are positively charged. But not only that, the strong force holds together the quarks — even tinier particles — to form those very protons and neutrons.
However, the strong force only works on very, very, very small distances. How small? About the scale of a medium-sized atom’s nucleus. For those of you who like the numbers, that’s about 10-15 meters, or 0.000000000000001 meters. That’s about a hundred billion times smaller than the width of a human hair! Whew.
Its tiny scale is why you don’t directly see the strong force in your day-to-day life. Judge a force by its physical size, do you?
Weak Force: Keeping us in sunshine

If you thought it was hard to see the strong force, the weak force works on even smaller scales — 1,000 times smaller. But it, too, is extremely important for life as we know it. In fact, the weak force plays a key role in keeping our Sun shining.
But what does the weak force do? Well … that requires getting a little into the weeds of particle physics. Here goes nothing! We mentioned quarks earlier — these are tiny particles that, among other things, make up protons and neutrons. There are six types of quarks, but the two that make up protons and neutrons are called up and down quarks. The weak force changes one quark type into another. This causes neutrons to decay into protons (or the other way around) while releasing electrons and ghostly particles called neutrinos.
So for example, the weak force can turn a down quark in a neutron into an up quark, which will turn that neutron into a proton. If that neutron is in an atom’s nucleus, the electric charge of the nucleus changes. That tiny change turns the atom into a different element! Such reactions are happening all the time in our Sun, giving it the energy to shine.
The weak force might just help to keep you in the (sun)light.

All four of these forces run strong in the universe. They flow between all things and keep our universe in balance. Without them, we’d be doomed. But these forces will be with you. Always.
You can learn more about gravity from NASA’s Space Place and follow NASAUniverse on Twitter or Facebook to learn about some of the cool cosmic objects we study with light.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
They’re so lonely :(
Wait I guess that means I’m an electron since I’m #foreveralone. I feel like I should be sad about this but electrons are cool so I can’t really be lol.
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!

Poor electrons
How do I constantly forget how beautiful the universe is?
Also, this is true, Jewels DEFINITELY aren’t as bright as stars!
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!

A Stellar Jewel Box: Open Cluster NGC 290 : Jewels don’t shine this bright – only stars do. Like gems in a jewel box, though, the stars of open cluster NGC 290 glitter in a beautiful display of brightness and color. The photogenic cluster, pictured here, was captured in 2006 by the orbiting Hubble Space Telescope. Open clusters of stars are younger, contain few stars, and contain a much higher fraction of blue stars than do globular clusters of stars. NGC 290 lies about 200,000 light-years distant in a neighboring galaxy called the Small Cloud of Magellan (SMC). The open cluster contains hundreds of stars and spans about 65 light years across. NGC 290 and other open clusters are good laboratories for studying how stars of different masses evolve, since all the open cluster’s stars were born at about the same time. via NASA
The rickroll is basically all scientists in a nutshell
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!

Let’s keep asking questions…
This is why I’m so excited for the supernova chapter ehehe
It’s so amazing that this little dot growing a bit but still being little is a supernova!
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!

This is the galaxy Messier 85! 🌌🌌🌌
Just last month, scientists found a supernova taking place! The event is named SN 2020nlb and has been continuously getting brighter. It is classified as a Type Ia supernova, which results from a white dwarf exploding within a binary star system. The brightness of this supernova can be used to calculate the distance to the galaxy! 🤩🤩🤩
Taken by me (Michelle Park) using the Slooh Canary Two telescope.

So I’m taking AP Calc next year and even though I have an A in Pre Calc I’m really nervous so I’m like frantically summer studying xD
I dunno my teacher seems to think I’ll do fine but everyone makes it sound really intimidating and I’m a worry freak, but I love math so I’m hoping I’ll enjoy it.
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!
Neptune!
Mercury will always be my favorite planet (closest to the Sun, underappreciated, proved Einstein’s general relativity, among other things) but I think Neptune’s the most beautiful. Look at that hue!
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!
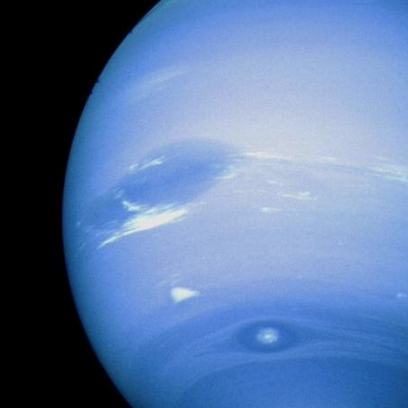


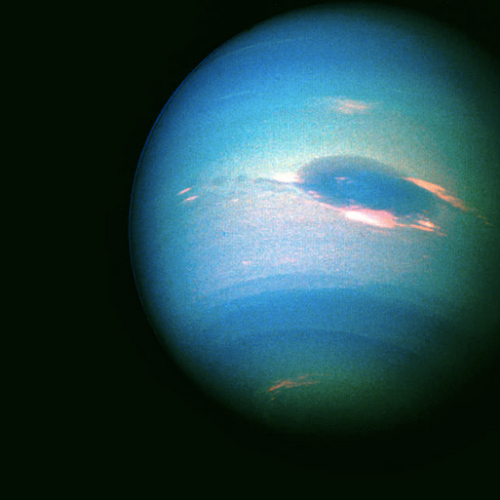


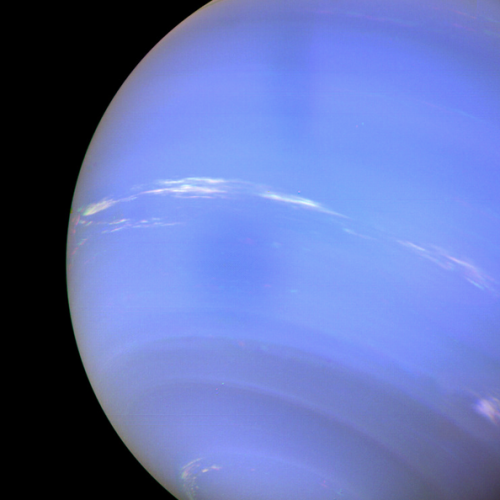
neptune.
Woah :o
So, basically, like the Mission Space ride at Epcot (that one is my favoriteeeee)?
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!

Testing and Training on the Boeing Starliner : NASA astronaut Mike Fincke works through a check list inside a mockup of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner during a simulation at NASA’s Johnson Space Center on Aug. 21, 2019. (via NASA)
You could say that they’re very ... NOBLE!
hehe
WANT MORE? GET YOUR HEAD STUCK IN THE STARS AT MY BLOG!

i hope i translated it correctly
-
 buxtonwhater liked this · 2 years ago
buxtonwhater liked this · 2 years ago -
 lonesome2nite liked this · 4 years ago
lonesome2nite liked this · 4 years ago -
 wagnerrms liked this · 4 years ago
wagnerrms liked this · 4 years ago -
 yesdeliciousinternetstudent liked this · 4 years ago
yesdeliciousinternetstudent liked this · 4 years ago -
 themightyfoo reblogged this · 4 years ago
themightyfoo reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 wachsurfer2018 liked this · 4 years ago
wachsurfer2018 liked this · 4 years ago -
 monster-shindig liked this · 4 years ago
monster-shindig liked this · 4 years ago -
 nymphfae reblogged this · 4 years ago
nymphfae reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 nymphfae liked this · 4 years ago
nymphfae liked this · 4 years ago -
 bengoombs liked this · 4 years ago
bengoombs liked this · 4 years ago -
 miscalculating-entity liked this · 4 years ago
miscalculating-entity liked this · 4 years ago -
 screaming-inthe-void liked this · 4 years ago
screaming-inthe-void liked this · 4 years ago -
 pinkpuppe liked this · 4 years ago
pinkpuppe liked this · 4 years ago -
 experiencecase liked this · 4 years ago
experiencecase liked this · 4 years ago -
 diwite liked this · 4 years ago
diwite liked this · 4 years ago -
 comet-online reblogged this · 4 years ago
comet-online reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 meiolesa reblogged this · 4 years ago
meiolesa reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 psychodollyuniverse liked this · 4 years ago
psychodollyuniverse liked this · 4 years ago -
 children-of-the-neon-god liked this · 4 years ago
children-of-the-neon-god liked this · 4 years ago -
 acosmicgeek reblogged this · 4 years ago
acosmicgeek reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 vegetalovescats liked this · 4 years ago
vegetalovescats liked this · 4 years ago -
 teameplease liked this · 4 years ago
teameplease liked this · 4 years ago -
 dobie56 liked this · 4 years ago
dobie56 liked this · 4 years ago -
 zackman liked this · 4 years ago
zackman liked this · 4 years ago -
 annabellekenobi2005 liked this · 4 years ago
annabellekenobi2005 liked this · 4 years ago -
 humongousbasementnerd liked this · 4 years ago
humongousbasementnerd liked this · 4 years ago -
 ringsideruckus liked this · 4 years ago
ringsideruckus liked this · 4 years ago -
 mikhailsavidad liked this · 4 years ago
mikhailsavidad liked this · 4 years ago -
 curlywhirliness reblogged this · 4 years ago
curlywhirliness reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 batsratsandalleycats reblogged this · 4 years ago
batsratsandalleycats reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 batsratsandalleycats liked this · 4 years ago
batsratsandalleycats liked this · 4 years ago -
 voorhees1138 reblogged this · 4 years ago
voorhees1138 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 voorhees1138 liked this · 4 years ago
voorhees1138 liked this · 4 years ago -
 s4lvo-blog liked this · 4 years ago
s4lvo-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 reclusivesketch liked this · 4 years ago
reclusivesketch liked this · 4 years ago

