IT'S TIME AGAIN TO TAKE A CENSUS OF THE U.S. POPULATION.
IT'S TIME AGAIN TO TAKE A CENSUS OF THE U.S. POPULATION.
MAKE SURE THAT YOU'RE COUNTED!
2020 Census: Everyone Counts
It’s that time again. Census time! Once every ten years the federal government counts every single person living in the U.S. of A. in order to effectively allocate representation and resources across the country. It’s an ambitious endeavor, for sure, but one designed to benefit everyone by making sure each community can adequately fund crucial public goods and services, like roads, hospitals, and schools. It determines how many seats each state gets in the U.S. House of Representatives. Also, congressional and state legislative boundaries are drawn and redrawn based on the data collected. Political representation at the state and federal level hinges on census participation. That’s a big deal!
The census count kicked off in March, with its biggest push for people to respond on their own in April, a.k.a. tax month. Although people in the U.S. pay federal income taxes every year, only once every decade do we have the power to influence how those dollars come back to us
The census is a nine-part questionnaire that takes just 10 minutes to complete. To combat all the misinformation flying around about what the census is and how the collected data is used, we’re gonna bust some of the myths and answer a few of the frequently asked questions:
Is there a citizenship question?
No. The courts have permanently blocked asking respondent their citizenship status and the courts have permanently blocked the Trump administration from adding one. Furthermore, federal law prohibits the Census Bureau from sharing individual census information with any person, organization or government body, including law enforcement. Your responses can only be used for statistical purposes (individual records are released only after 72 years!).
What will you be asked?
The questionnaire asks for basic demographic information such as age, race, type of housing, etc. It will not ask for compromising or sensitive information like social security numbers, bank account numbers, or immigration status.
Who should be counted on the Census?
Every person living in the United States, regardless of citizenship status, including kids and babies!
How can I take the Census?
Great news! Completing the census questionnaire is literally the easiest it’s ever been. For the first time ever, you can complete the census online at 2020Census.gov or by phone at 844-330-2020. Also, by April 1st, every home will receive a mailed notice to participate in the 2020 Census.
When is the deadline?
Ideally, Uncle Sam would like to receive your data by April 30th. But as of right now, you can respond on your own all the way until mid-August. If you don’t respond on your own by the end of May, a Census worker may come to your home and ask to record your answers in person. And while it was funny on screen, please do not behave like Christopher Walken in this classic SNL Census sketch.
Is it safe?
Yes. The census is safe, your information is handled with the utmost confidentiality meaning that no one can take your data and use it against you. Your individual data will not be shared with any person, organization or government body, including other federal agencies or any law enforcement or housing authorities. It’s to your benefit to participate.
Sure, filling out a form sounds boring, but it helps to think of it as an opportunity to make your voices heard in a way that really matters. That sounds exciting, no? Plus, you only have to spend 10 minutes doing it once every 10 years.
Make sure to pass this information to your friends and family in order to stop the spread of misinformation. If you have any questions, please check out the United States Census Bureau Fact Sheet.
Please visit 2020census.gov for more information.
More Posts from Aspergers1044 and Others
The Science of Photosynthetic Lifeforms on Habitable Zone Worlds in other solar_systems.
Nearby Exoplanet is 'excellent' target in The Search for Life.
It's not quite Warp Drive, but Researchers are hot on the trail of building Nuclear Fusion Impulse Engines, to complete with Real-Life Dilithium Crystals.
Different Types of Supernovae are the Primary Origins of Different Classes of Chemical_Elements.
You Are Made of Stardust
Though the billions of people on Earth may come from different areas, we share a common heritage: we are all made of stardust! From the carbon in our DNA to the calcium in our bones, nearly all of the elements in our bodies were forged in the fiery hearts and death throes of stars.

The building blocks for humans, and even our planet, wouldn’t exist if it weren’t for stars. If we could rewind the universe back almost to the very beginning, we would just see a sea of hydrogen, helium, and a tiny bit of lithium.
The first generation of stars formed from this material. There’s so much heat and pressure in a star’s core that they can fuse atoms together, forming new elements. Our DNA is made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. All those elements (except hydrogen, which has existed since shortly after the big bang) are made by stars and released into the cosmos when the stars die.

Each star comes with a limited fuel supply. When a medium-mass star runs out of fuel, it will swell up and shrug off its outer layers. Only a small, hot core called a white dwarf is left behind. The star’s cast-off debris includes elements like carbon and nitrogen. It expands out into the cosmos, possibly destined to be recycled into later generations of stars and planets. New life may be born from the ashes of stars.

Massive stars are doomed to a more violent fate. For most of their lives, stars are balanced between the outward pressure created by nuclear fusion and the inward pull of gravity. When a massive star runs out of fuel and its nuclear processes die down, it completely throws the star out of balance. The result? An explosion!
Supernova explosions create such intense conditions that even more elements can form. The oxygen we breathe and essential minerals like magnesium and potassium are flung into space by these supernovas.
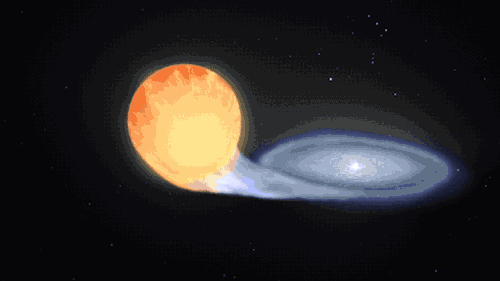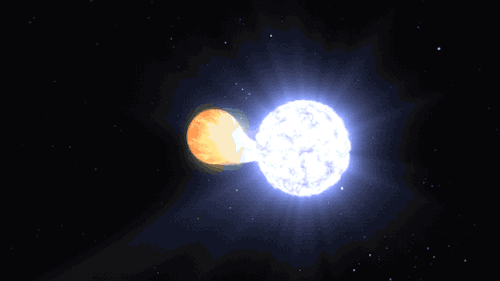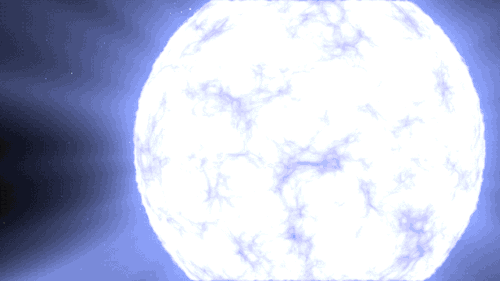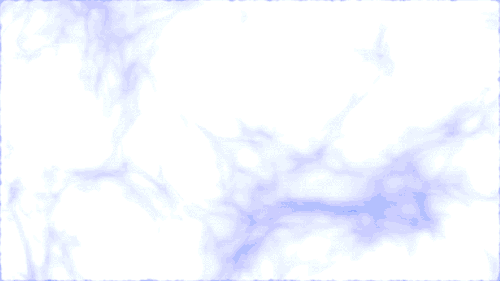
Supernovas can also occur another way in binary, or double-star, systems. When a white dwarf steals material from its companion, it can throw everything off balance too and lead to another kind of cataclysmic supernova. Our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will study these stellar explosions to figure out what’s speeding up the universe’s expansion.
This kind of explosion creates calcium – the mineral we need most in our bodies – and trace minerals that we only need a little of, like zinc and manganese. It also produces iron, which is found in our blood and also makes up the bulk of our planet’s mass!

A supernova will either leave behind a black hole or a neutron star – the superdense core of an exploded star. When two neutron stars collide, it showers the cosmos in elements like silver, gold, iodine, uranium, and plutonium.

Some elements only come from stars indirectly. Cosmic rays are nuclei (the central parts of atoms) that have been boosted to high speed by the most energetic events in the universe. When they collide with atoms, the impact can break them apart, forming simpler elements. That’s how we get boron and beryllium – from breaking star-made atoms into smaller ones.
Half a dozen other elements are created by radioactive decay. Some elements are radioactive, which means their nuclei are unstable. They naturally break down to form simpler elements by emitting radiation and particles. That’s how we get elements like radium. The rest are made by humans in labs by slamming atoms of lighter elements together at super high speeds to form heavier ones. We can fuse together elements made by stars to create exotic, short-lived elements like seaborgium and einsteinium.
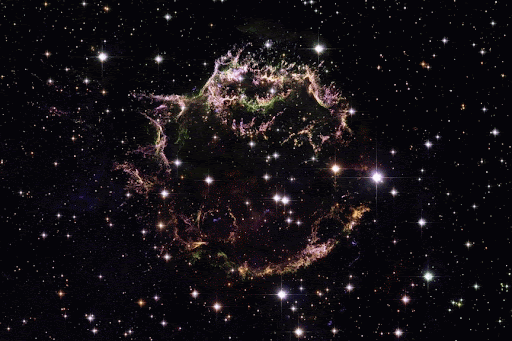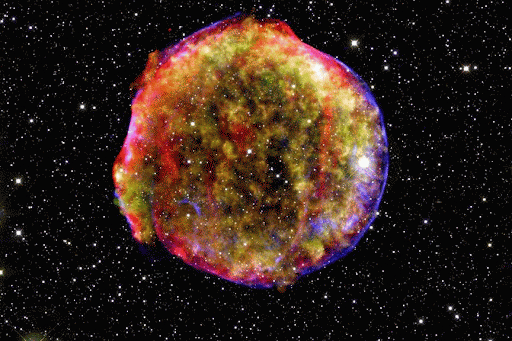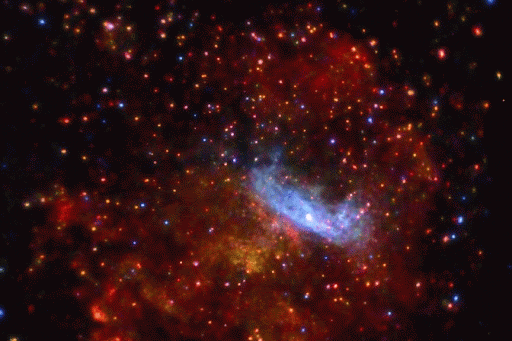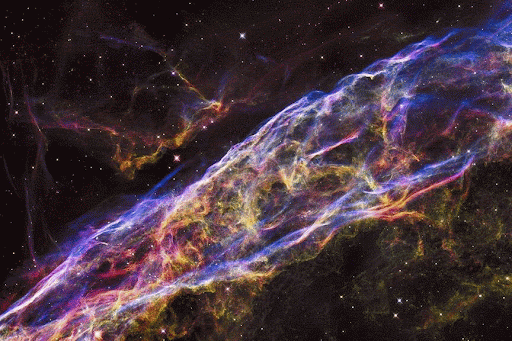
From some of the most cataclysmic events in the cosmos comes all of the beauty we see here on Earth. Life, and even our planet, wouldn’t have formed without them! But we still have lots of questions about these stellar factories.
In 2006, our Stardust spacecraft returned to Earth containing tiny particles of interstellar dust that originated in distant stars, light-years away – the first star dust to ever be collected from space and returned for study. You can help us identify and study the composition of these tiny, elusive particles through our Stardust@Home Citizen Science project.
Our upcoming Roman Space Telescope will help us learn more about how elements were created and distributed throughout galaxies, all while exploring many other cosmic questions. Learn more about the exciting science this mission will investigate on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
NASA’s TESS Mission to Search for Lots More EXOPLANETS is now about to be Launched someday really soon!
The Hunt for New Worlds Continues with TESS
We’re getting ready to start our next mission to find new worlds! The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will find thousands of planets beyond our solar system for us to study in more detail. It’s preparing to launch from our Kennedy Space Center at Cape Canaveral in Florida.

Once it launches, TESS will look for new planets that orbit bright stars relatively close to Earth. We’re expecting to find giant planets, like Jupiter, but we’re also predicting we’ll find Earth-sized planets. Most of those planets will be within 300 light-years of Earth, which will make follow-up studies easier for other observatories.

TESS will find these new exoplanets by looking for their transits. A transit is a temporary dip in a star’s brightness that happens with predictable timing when a planet crosses between us and the star. The information we get from transits can tell us about the size of the planet relative to the size of its star. We’ve found nearly 3,000 planets using the transit method, many with our Kepler space telescope. That’s over 75% of all the exoplanets we’ve found so far!

TESS will look at nearly the entire sky (about 85%) over two years. The mission divides the sky into 26 sectors. TESS will look at 13 of them in the southern sky during its first year before scanning the northern sky the year after.

What makes TESS different from the other planet-hunting missions that have come before it? The Kepler mission (yellow) looked continually at one small patch of sky, spotting dim stars and their planets that are between 300 and 3,000 light-years away. TESS (blue) will look at almost the whole sky in sections, finding bright stars and their planets that are between 30 and 300 light-years away.

TESS will also have a brand new kind of orbit (visualized below). Once it reaches its final trajectory, TESS will finish one pass around Earth every 13.7 days (blue), which is half the time it takes for the Moon (gray) to orbit. This position maximizes the amount of time TESS can stare at each sector, and the satellite will transmit its data back to us each time its orbit takes it closest to Earth (orange).

Kepler’s goal was to figure out how common Earth-size planets might be. TESS’s mission is to find exoplanets around bright, nearby stars so future missions, like our James Webb Space Telescope, and ground-based observatories can learn what they’re made of and potentially even study their atmospheres. TESS will provide a catalog of thousands of new subjects for us to learn about and explore.

The TESS mission is led by MIT and came together with the help of many different partners. Learn more about TESS and how it will further our knowledge of exoplanets, or check out some more awesome images and videos of the spacecraft. And stay tuned for more exciting TESS news as the spacecraft launches!
Watch the Launch + More!

Sunday, April 15 11 a.m. EDT - NASA Social Mission Overview
Join mission experts to learn more about TESS, how it will search for worlds beyond our solar system and what scientists hope to find! Have questions? Use #askNASA to have them answered live during the broadcast.
Watch HERE.
1 p.m. EDT - Prelaunch News Conference
Get an update on the spacecraft, the rocket and the liftoff operations ahead of the April 16 launch! Have questions? Use #askNASA to have them answered live during the broadcast.
Watch HERE.
3 p.m. EDT - Science News Conference
Hear from mission scientists and experts about the science behind the TESS mission. Have questions? Use #askNASA to have them answered live during the broadcast.
Watch HERE.
4 p.m. EDT - TESS Facebook Live
This live show will dive into the science behind the TESS spacecraft, explain how we search for planets outside our solar system and will allow you to ask your questions to members of the TESS team.
Watch HERE.
Monday, April 16 10 a.m. EDT - NASA EDGE: TESS Facebook Live
This half-hour live show will discuss the TESS spacecraft, the science of searching for planets outside our solar system, and the launch from Cape Canaveral.
Watch HERE.
1 p.m. EDT - Reddit AMA
Join us live on Reddit for a Science AMA to discuss the hunt for exoplanets and the upcoming launch of TESS!
Join in HERE.
6 p.m. EDT - Launch Coverage!
TESS is slated to launch at 6:32 p.m. EDT on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from our Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Watch HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Project Blue for Alpha Centauri.
One Search for Planets in The Alpha_Centauri System is: Project Blue. https://techcrunch.com/2016/10/10/project-blue-aims-to-snap-the-first-picture-of-an-exoplanet-in-alpha-centauri/
Here's some advice from off of Wrong_Planet about how to thrive as a Special_Needs Family.

Snow covered House in Winter
Could the demand for a cure to autism be coming exclusively from neurotypical parents given the existence of advocates against a cure who...
It could be that most of The Demand for a Cure for Autism comes from Neurotypicals. Answer by Zem Jones:
To "cure" me would be to change the person I am into someone I don't recognise. To "cure" some of the issues caused by my autism, such as my heightened anxiety, or hyperacusis, or my bowel problems, would be a blessed relief. People who want a cure for autism do not understand what needs curing and generally they must be people who don't know autism from the inside, or people who have been taught that it is autism that is the whole problem when it is probably a sensory difference or comorbid condition or combination of them that causes the discomfort and distress they see on the outside. I have a friend who has a child with Kanner's autism. He also has epilepsy. She tells me that when his epilepsy is under control he thrives as if his presentation was more like Asperger's rather than Kanner's but she always knows when a big fit is coming because he regresses into classic autistic behaviours for days beforehand. To me this says the autism is not the problem for him and I suspect the same is true for most children diagnosed with classic autism - if they could tell us what the problem really is and we could cure that then how much better would their lives be? I think people who want to cure the autism itself don't even know what autism really is.
Could the demand for a cure to autism be coming exclusively from neurotypical parents given the existence of advocates against a cure who...
Here’s Some_Thing really interesting to Look at.
A Soviet Arctic Exploration Vehicle with Tracks on it.
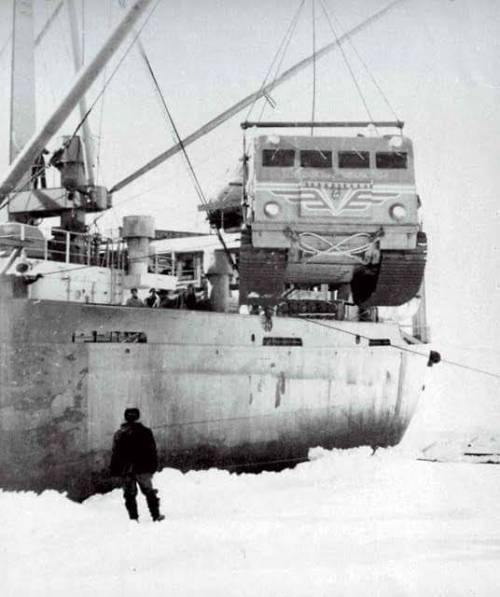




Arctic exploration vehicle Harkovchnka.
-
 sweettrashparadise liked this · 1 year ago
sweettrashparadise liked this · 1 year ago -
 travishowellw liked this · 1 year ago
travishowellw liked this · 1 year ago -
 winfwassalu liked this · 1 year ago
winfwassalu liked this · 1 year ago -
 moor-mother liked this · 2 years ago
moor-mother liked this · 2 years ago -
 purplelawyerartisanbasketball liked this · 2 years ago
purplelawyerartisanbasketball liked this · 2 years ago -
 pinkwobblerstatesmanpasta liked this · 3 years ago
pinkwobblerstatesmanpasta liked this · 3 years ago -
 neptunes-mooons liked this · 3 years ago
neptunes-mooons liked this · 3 years ago
