bigbluenasa
The latest view from my corner at NASA.
36 posts
Latest Posts by bigbluenasa
Small Tissue Chips in Space a Big Leap Forward for Research
Tissue chips, thumb-drive sized devices that contain human cells in a 3D matrix, represent a giant leap in science.
They can test cells’ response to:
•stresses
•drugs
•genetic changes

The Tissue Chips in Space initiative seeks to better understand the role of microgravity on human health and disease and to translate that understanding to improved human health on Earth.
This series of investigations to test tissue chips in microgravity aboard the International Space Station is planned through a collaboration between the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) at the National Institutes for Health (NIH) and the National Laboratory in partnership with NASA.

Many of the changes in the human body caused by microgravity resemble the onset and progression of diseases associated with aging on Earth, but in space, changes occur much faster. Scientists may be able to use tissue chips in space to model changes that take months or years to happen on Earth.
A tissue chip needs three properties, according to Lucie Low, scientific program manager at NCATS. “It has to be 3D,” she explained. “It must have multiple different types of cells, and it must have microfluidic channels. Essentially, you get a functional unit of what human tissues are like, outside of the body,” said Low.

As accurate models of the structure and function of human organs, tissue chips provide a model for predicting whether a drug, vaccine or biologic agent is safe in humans more quickly and effectively than current methods.

This first phase of Tissue Chips in Space includes five investigations. An investigation of immune system aging is planned for launch on the SpaceX CRS-16 flight, scheduled for mid-November. The other four, scheduled to launch on subsequent flights, include lung host defense, the blood-brain barrier, musculoskeletal disease and kidney function. This phase tests the effects of microgravity on the tissue chips and demonstrates the capability of the automated system.
All five investigations make a second flight about 18 months later to confirm use of the model, such as testing potential drugs on the particular organs. Four more projects are scheduled for launch in summer 2020, including two on engineered heart tissue to understand cardiovascular health, one on muscle wasting and another on gut inflammation.
Ultimately, the technology could allow astronauts going into space to take along personalized chips that could be used to monitor changes in their bodies and to test possible countermeasures and therapies. That would be a major leap forward in keeping astronauts healthy on missions to deep space!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
2017 - Johnson Space Center Year in Review

@nasajohnson NBL tour with #nasamei2017 on Monday. (at NASA Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory)

Designing a NASA mission using the engineering design process is just part of a day's work for educators @nasajohnson attending our #nasamei2017 (at NASA - Johnson Space Center in Houston, TX)

NASA BEST engineering design challenges offer a transdisciplinary STEM approach that's fun and engaging! #nasamei2017 (at NASA - Johnson Space Center in Houston, TX)
Incoming! We’ve Got Science from Jupiter!
Our Juno spacecraft has just released some exciting new science from its first close flyby of Jupiter!

In case you don’t know, the Juno spacecraft entered orbit around the gas giant on July 4, 2016…about a year ago. Since then, it has been collecting data and images from this unique vantage point.

Juno is in a polar orbit around Jupiter, which means that the majority of each orbit is spent well away from the gas giant. But once every 53 days its trajectory approaches Jupiter from above its north pole, where it begins a close two-hour transit flying north to south with its eight science instruments collecting data and its JunoCam camera snapping pictures.

Space Fact: The download of six megabytes of data collected during the two-hour transit can take one-and-a-half days!

Juno and her cloud-piercing science instruments are helping us get a better understanding of the processes happening on Jupiter. These new results portray the planet as a complex, gigantic, turbulent world that we still need to study and unravel its mysteries.
So what did this first science flyby tell us? Let’s break it down…
1. Tumultuous Cyclones

Juno’s imager, JunoCam, has showed us that both of Jupiter’s poles are covered in tumultuous cyclones and anticyclone storms, densely clustered and rubbing together. Some of these storms as large as Earth!

These storms are still puzzling. We’re still not exactly sure how they formed or how they interact with each other. Future close flybys will help us better understand these mysterious cyclones.

Seen above, waves of clouds (at 37.8 degrees latitude) dominate this three-dimensional Jovian cloudscape. JunoCam obtained this enhanced-color picture on May 19, 2017, at 5:50 UTC from an altitude of 5,500 miles (8,900 kilometers). Details as small as 4 miles (6 kilometers) across can be identified in this image.

An even closer view of the same image shows small bright high clouds that are about 16 miles (25 kilometers) across and in some areas appear to form “squall lines” (a narrow band of high winds and storms associated with a cold front). On Jupiter, clouds this high are almost certainly comprised of water and/or ammonia ice.
2. Jupiter’s Atmosphere
Juno’s Microwave Radiometer is an instrument that samples the thermal microwave radiation from Jupiter’s atmosphere from the tops of the ammonia clouds to deep within its atmosphere.

Data from this instrument suggest that the ammonia is quite variable and continues to increase as far down as we can see with MWR, which is a few hundred kilometers. In the cut-out image below, orange signifies high ammonia abundance and blue signifies low ammonia abundance. Jupiter appears to have a band around its equator high in ammonia abundance, with a column shown in orange.

Why does this ammonia matter? Well, ammonia is a good tracer of other relatively rare gases and fluids in the atmosphere…like water. Understanding the relative abundances of these materials helps us have a better idea of how and when Jupiter formed in the early solar system.
This instrument has also given us more information about Jupiter’s iconic belts and zones. Data suggest that the belt near Jupiter’s equator penetrates all the way down, while the belts and zones at other latitudes seem to evolve to other structures.
3. Stronger-Than-Expected Magnetic Field

Prior to Juno, it was known that Jupiter had the most intense magnetic field in the solar system…but measurements from Juno’s magnetometer investigation (MAG) indicate that the gas giant’s magnetic field is even stronger than models expected, and more irregular in shape.

At 7.766 Gauss, it is about 10 times stronger than the strongest magnetic field found on Earth! What is Gauss? Magnetic field strengths are measured in units called Gauss or Teslas. A magnetic field with a strength of 10,000 Gauss also has a strength of 1 Tesla.

Juno is giving us a unique view of the magnetic field close to Jupiter that we’ve never had before. For example, data from the spacecraft (displayed in the graphic above) suggests that the planet’s magnetic field is “lumpy”, meaning its stronger in some places and weaker in others. This uneven distribution suggests that the field might be generated by dynamo action (where the motion of electrically conducting fluid creates a self-sustaining magnetic field) closer to the surface, above the layer of metallic hydrogen. Juno’s orbital track is illustrated with the black curve.
4. Sounds of Jupiter
Juno also observed plasma wave signals from Jupiter’s ionosphere. This movie shows results from Juno’s radio wave detector that were recorded while it passed close to Jupiter. Waves in the plasma (the charged gas) in the upper atmosphere of Jupiter have different frequencies that depend on the types of ions present, and their densities.
Mapping out these ions in the jovian system helps us understand how the upper atmosphere works including the aurora. Beyond the visual representation of the data, the data have been made into sounds where the frequencies and playback speed have been shifted to be audible to human ears.
5. Jovian “Southern Lights”

The complexity and richness of Jupiter’s “southern lights” (also known as auroras) are on display in this animation of false-color maps from our Juno spacecraft. Auroras result when energetic electrons from the magnetosphere crash into the molecular hydrogen in the Jovian upper atmosphere. The data for this animation were obtained by Juno’s Ultraviolet Spectrograph.

During Juno’s next flyby on July 11, the spacecraft will fly directly over one of the most iconic features in the entire solar system – one that every school kid knows – Jupiter’s Great Red Spot! If anybody is going to get to the bottom of what is going on below those mammoth swirling crimson cloud tops, it’s Juno.

Stay updated on all things Juno and Jupiter by following along on social media: Twitter | Facebook | YouTube | Tumblr
Learn more about the Juno spacecraft and its mission at Jupiter HERE.
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is a jewel box filled with a glittering variety of beautiful worlds–and not all of them are planets. This week, we present our solar system’s most marvelous moons.

1. Weird Weather: Titan
Saturn’s hazy moon Titan is larger than Mercury, but its size is not the only way it’s like a planet. Titan has a thick atmosphere, complete with its own “water cycle” – except that it’s way too cold on Titan for liquid water. Instead, rains of liquid hydrocarbons like ethane and methane fall onto icy mountains, run into rivers, and gather into great seas. Our Cassini spacecraft mapped the methane seas with radar, and its cameras even caught a glimpse of sunlight reflecting off the seas’ surface. Learn more about Titan: saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/science/titan/

2. Icy Giant: Ganymede
Jupiter’s moon Ganymede is the largest in the solar system. It’s bigger than Mercury and Pluto, and three-quarters the size of Mars. It’s also the only moon known to have its own magnetic field. Details: solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/ganymede/indepth

3. Retrograde Rebel: Triton
Triton is Neptune’s largest moon, and the only one in the solar system to orbit in the opposite direction of its planet’s rotation, a retrograde orbit. It may have been captured from the Kuiper Belt, where Pluto orbits. Despite the frigid temperatures there, Triton has cryovolcanic activity – frozen nitrogen sometimes sublimates directly to gas and erupts from geysers on the surface. More on Triton: solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/triton/indepth

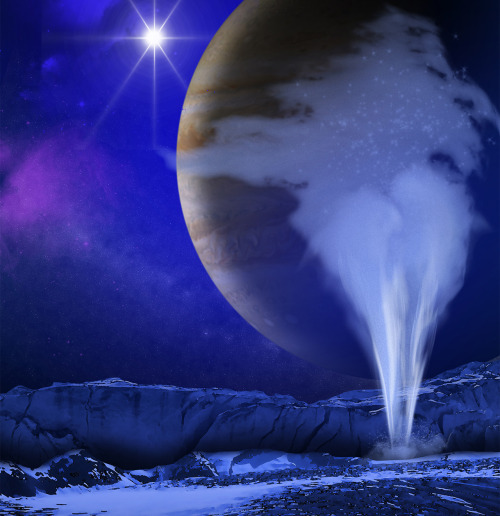
4. Cold Faithful: Enceladus
The most famous geysers in our solar system (outside of those on Earth) belong to Saturn’s moon Enceladus. It’s a small, icy body, but Cassini revealed this world to be one of the solar system’s most scientifically interesting destinations. Geyser-like jets spew water vapor and ice particles from an underground ocean beneath the icy crust of Enceladus. With its global ocean, unique chemistry and internal heat, Enceladus has become a promising lead in our search for worlds where life could exist. Get the details: saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/science/enceladus/

5. Volcano World: Io
Jupiter’s moon Io is subjected to tremendous gravitational forces that cause its surface to bulge up and down by as much as 330 feet (100 m). The result? Io is the most volcanically active body in the Solar System, with hundreds of volcanoes, some erupting lava fountains dozens of miles high. More on Io’s volcanoes: solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/io/indepth

6. Yin and Yang Moon: Iapetus
When Giovanni Cassini discovered Iapetus in 1671, he observed that one side of this moon of Saturn was bright and the other dark. He noted that he could only see Iapetus on the west side of Saturn, and correctly concluded that Iapetus had one side much darker than the other side. Why? Three centuries later, the Cassini spacecraft solved the puzzle. Dark, reddish dust in Iapetus’s orbital path is swept up and lands on the leading face of the moon. The dark areas absorb energy and become warmer, while uncontaminated areas remain cooler. Learn more: saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/news/2892/cassini-10-years-at-saturn-top-10-discoveries/#nine

7. A Double World: Charon and Pluto
At half the size of Pluto, Charon is the largest of Pluto’s moons and the largest known satellite relative to its parent body. The moon is so big compared to Pluto that Pluto and Charon are sometimes referred to as a double planet system. Charon’s orbit around Pluto takes 6.4 Earth days, and one Pluto rotation (a Pluto day) takes 6.4 Earth days. So from Pluto’s point of view Charon neither rises nor sets, but hovers over the same spot on Pluto’s surface, and the same side of Charon always faces Pluto. Get the details: www.nasa.gov/feature/pluto-and-charon-new-horizons-dynamic-duo

8. “Death Star” Moon: Mimas
Saturn’s moon Mimas has one feature that draws more attention than any other: the crater Herschel, which formed in an impact that nearly shattered the little world. Herschel gives Mimas a distinctive look that prompts an oft-repeated joke. But, yes, it’s a moon. More: olarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/mimas

9. Don’t Be Afraid, It’s Just Phobos
In mythology, Mars is a the god of war, so it’s fitting that its two small moons are called Phobos, “fear,” and Deimos, “terror.” Our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter caught this look at Phobos, which is roughly 17 miles (27 km) wide. In recent years, NASA scientists have come to think that Phobos will be torn apart by its host planet’s gravity. Details: www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/phobos-is-falling-apart
Learn more about Phobos: solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/phobos/indepth

10. The Moon We Know Best
Although decades have passed since astronauts last set foot on its surface, Earth’s moon is far from abandoned. Several robotic missions have continued the exploration. For example, this stunning view of the moon’s famous Tycho crater was captured by our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, which continues to map the surface in fine detail today. More: www.lroc.asu.edu/posts/902
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
It’s May the 4th: Are Star Wars Planets Real?
Look at what we’ve found so far.
Is your favorite Star Wars planet a desert world or an ice planet or a jungle moon?
It’s possible that your favorite planet exists right here in our galaxy. Astronomers have found over 3,400 planets around other stars, called “exoplanets.”
Some of these alien worlds could be very similar to arid Tatooine, watery Scarif and even frozen Hoth, according to NASA scientists.
Find out if your planet exists in a galaxy far, far away or all around you. And May the Fourth be with you!
Planets With Two Suns

From Luke Skywalker’s home world Tatooine, you can stand in the orange glow of a double sunset. The same could said for Kepler-16b, a cold gas giant roughly the size of Saturn, that orbits two stars. Kepler-16b was the Kepler telescopes’s first discovery of a planet in a “circumbinary” orbit (that is, circling both stars, as opposed to just one, in a double star system).

The best part is that Tatooine aka Kepler-16b was just the first. It has family. A LOT of family. Half the stars in our galaxy are pairs, rather than single stars like our sun. If every star has at least one planet, that’s billions of worlds with two suns. Billions! Maybe waiting for life to be found on them.
Desert Worlds

Mars is a cold desert planet in our solar system, and we have plenty of examples of scorching hot planets in our galaxy (like Kepler-10b), which orbits its star in less than a day)! Scientists think that if there are other habitable planets in the galaxy, they’re more likely to be desert planets than ocean worlds. That’s because ocean worlds freeze when they’re too far from their star, or boil off their water if they’re too close, potentially making them unlivable. Perhaps, it’s not so weird that both Luke Skywalker and Rey grew up on planets that look a lot alike.
Ice Planets

An icy super-Earth named OGLE-200-BLG-390Lb reminded scientists so much of the frozen Rebel base they nicknamed it “Hoth,” after its frozen temperature of minus 364 degrees Fahrenheit. Another Hoth-like planet was discovered last month; an Earth-mass icy world orbiting its star at the same distance as Earth orbits the sun. But its star is so faint, the surface of OGLE-2016-BLG-1195Lb is probably colder than Pluto.

Forest worlds

Both the forest moon of Endor and Takodana, the home of Han Solo’s favorite cantina in “Force Awakens,” are green like our home planet. But astrobiologists think that plant life on other worlds could be red, black, or even rainbow-colored!
In February 2017, the Spitzer Space Telescope discovered seven Earth-sized planets in the same system, orbiting the tiny red star TRAPPIST-1.

The light from a red star, also known as an M dwarf, is dim and mostly in the infrared spectrum (as opposed to the visible spectrum we see with our sun). And that could mean plants with wildly different colors than what we’re used to seeing on Earth. Or, it could mean animals that see in the near-infrared.
What About Moons?
In Star Wars, Endor, the planet with the cute Ewoks, is actually a habitable moon of a gas giant. Now, we’re looking for life on the moons of our own gas giants. Saturn’s moon Enceladus or Jupiter’s moon Europa are ocean worlds that may well support life. Our Cassini spacecraft has explored the Saturn system and its moons. Watch the video and learn more about the missions’s findings.
And Beyond

The next few years will see the launch of a new generation of spacecraft to search for planets around other stars. TESS and the James Webb Telescope are slated to launch in 2018, and WFIRST in the mid-2020s. That’s one step closer to finding life.

You might want to take our ‘Star Wars: Fact or Fiction?’ quiz. Try it! Based on your score you may obtain the title of Padawan, Jedi Knight, or even Jedi Master!
You don’t need to visit a galaxy far, far away to find wondrous worlds. Just visit this one … there’s plenty to see.
Discover more about exoplanets here: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
(via https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HU5kpIQ09Iw)
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
From observing our moon to Saturn’s mini solar system …here are a few things you should know about our solar system this week:
1. What a Long, Strange—and Revealing—Trip It’s Been

As the Cassini mission builds toward its climactic “Grand Finale,” we’re taking a look back at the epic story of its journey among Saturn’s mini-solar system of rings and moons.
+ Traverse the timeline
2. Our Very Own Moon

Unlike Saturn, Earth has only one moon. Let’s celebrate it! International Observe the Moon Night (InOMN) is a worldwide, public celebration of lunar science and exploration held annually. On Oct. 8, everyone on Earth is invited to observe and learn about the moon together, and to celebrate the cultural and personal connections we all have with it.
+ Join in
3. What’s Up, October?

Even more about Earth’s moon is the subject of this month’s video guide for sky watchers and includes a look at the moon’s phases and when to observe them. Also featured are a guide to upcoming meteor showers and tips on how to catch a glimpse of Saturn.
+ Take a look
4. Nine Lives

Dawn’s discoveries continue, even as the asteroid belt mission marks nine years in space. “For such an overachiever,” writes Dawn’s top scientist, “it’s fitting that now, on its ninth anniversary, the spacecraft is engaged in activities entirely unimagined on its eighth.”
+ Learn more
5. The Incredible Shrinking Mercury

It’s small, it’s hot, and it’s shrinking. Research funded by us suggests that Mercury is contracting even today. This means we now know that Mercury joins Earth as a tectonically active planet.
+ Get the small details
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Space Station Science: Biological Research

Each month, we highlight a different research topic on the International Space Station. In August, our focus is biological research. Learning how spaceflight affects living organisms will help us understand potential health risks related to humans on long duration missions, including our journey to Mars.

Cells, microbes, animals and plants are affected by microgravity, and studying the processes involved in adaptation to spaceflight increases our fundamental understanding of biological processes on Earth. Results on Earth from biological research in space include the development of new medications, improved agriculture, advancements in tissue engineering and regeneration, and more.
Take a look at a few of the biological research experiments performed on space station:
Biomolecule Sequencer

Living organisms contain DNA, and sequencing DNA is a powerful way to understand how they respond to changing environments. The Biomolecule Sequencer experiment hopes to demonstrate (for the first time) that DNA sequencing is feasible in an orbiting spacecraft. Why? A space-based DNA sequencer could identify microbes, diagnose diseases and understand crew member health, and potentially help detect DNA- based life elsewhere in the solar system.
Ant-stronauts

Yes, ant-stronauts…as in ants in space. These types of studies provide insights into how ants answer collective search problems. Watching how the colony adapts as a unit in the quest for resources in extreme environments, like space, provides data that can be used to build algorithms with varied applications. Understanding how ants search in different conditions could have applications for robotics.
TAGES

The TAGES experiment (Transgenic Arabidopsis Gene Expression System) looks to see how microgravity impacts the growth of plant roots. Fluorescent markers placed on the plant’s genes allow scientists to study root development of Arabidopsis (a cress plant) grown on the space station. Evidence shows that directional light in microgravity skews root growth to the right, rather than straight down from the light source. Root growth patters on station mimic that of plants grown at at 45% degree angle on Earth. Space flight appears to slow the rate of the plant’s early growth as well.
Heart Cells

Spaceflight can cause a suite of negative health effects, which become more problematic as crew members stay in orbit for long periods of time. Effects of Microgravity on Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomycytes (Heart Cells) studies the human heart, specifically how heart muscle tissue contracts, grows and changes in microgravity. Understanding how heart muscle cells change in space improves efforts for studying disease, screening drugs and conducting cell replacement therapy for future space missions.
Medaka Fish

Chew on these results…Jaw bones of Japanese Medaka fish in microgravity show decreased mineral density and increased volume of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone tissue. Results from this study improve our understanding of the mechanisms behind bone density and organ tissue changes in space.
These experiments, and many others, emphasize the importance of biological research on the space station. Understanding the potential health effects for crew members in microgravity will help us develop preventatives and countermeasures.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Life Among the Stars
Let us lead you on a journey of our solar system. Here are some things to know this week:
1. Amateur" Means “One Who Loves”

We release thousands of breathtaking solar system images every year and not all of them are the exclusive result of work by scientists. Amateur image processors around the world take raw data from deep space missions and turn it into striking visuals.
Amateur images from Cassini
Get current unprocessed images
2. Prepare to Weigh Anchor

OSIRIS-REx, our first spacecraft destined to rendezvous with, study and return a sample of an asteroid, will launch. The mission to asteroid Bennu will yield the largest sample returned from space since the Apollo era. Tune in four our media briefing about OSIRIS-REx for 2 p.m. EDT on Aug. 17.
Learn more and tune in.
3. Out for a Walk

Join us for live coverage on Aug. 19 as our astronauts Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins install a new gateway for American commercial crew spacecraft at the International Space Station.
Live coverage of the spacewalk.
4. The Weather Out There

Aug. 17 marks 50 years since the launch of Pioneer 7, a robotic spacecraft that lived up to its name by exploring the solar magnetic field, the solar wind and cosmic rays in deep space. Along with Pioneers 6, 8, and 9, the spacecraft formed a ring of solar weather stations spaced along Earth’s orbit. Measurements by the craft were used to predict solar storms for organizations ranging from commercial airlines to power companies.
Learn more.
5. Destination: The Red Planet

The European Space Agency’s ExoMars/Trace Gas Orbiter mission to Mars performed a critical engine burn to keep it on course. The maneuver was a success, and ExoMars remains on target for an October arrival.
Learn more.
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Spacewalk Friday: Installing a New "Parking Spot" on Station
This Friday, Aug. 19, two U.S. astronauts will install a new gateway for American commercial crew spacecraft at the International Space Station.

Commercial crew flights from Florida’s Space Coast to the International Space Station will restore America’s human spaceflight launch capability and increase the time U.S. crews can dedicate to scientific research.

The adapter being installed (imaged below) was launched on a SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft and arrived on orbit July 20. NASA astronauts Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins will perform the spacewalk to install the equipment this Friday, Aug. 19. This will be the fourth spacewalk in Williams’ career and the first for Rubins.

Four previous spacewalks…like the one below…helped set the stage for installation of this docking adapter. During those previous spacewalks, other crew members laid hundreds of feet of power and data cables outside the space station.

On Wednesday, the robotics team using the Canadarm2 and its attached “Dextre” manipulator, will reach into the SpaceX Dragon trunk and pull out the docking adapter and position it for Friday’s spacewalk activities.

The morning of the spacewalk, while the astronauts are getting suited up, the robotic arm will position the docking adaptor near the port so that it will be ready for installation.

The two astronauts will venture outside the space station to install the first International Docking Adapter (IDA). This new adapter port will provide a parking space for U.S. Commercial Crew vehicles.
Watch LIVE!
Coverage of the spacewalk begins at 6:30 a.m. EDT on Friday, Aug. 19; with the spacewalk scheduled to begin at 8:05 a.m. EDT. Stream live online HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for April 2016?

Jupiter, Mars, the Lyrid meteor shower and 2016’s best views of Mercury are all visible in the sky this month.

Jupiter, where our Juno mission will begin orbiting on July 4, continues to shine almost as brightly this month as last. And eagle-eyed telescope viewers will see a transit, a shadow transit, an occultation and an eclipse of Jupiter’s moons- all in one night: April 6-7.

Io transits first, crossing the planet beginning at 9:52 p.m. EDT. It’s shadow can be seen less than an hour later.

Next Jupiter occults, or eclipses, Europa as Europa slips behind the giant planet at 10:48 p.m. EDT. At 3 a.m. Europa reappears from its eclipse, dramatically leaving the shadow of Jupiter.

Ganymede transits the planet beginning at 1:01 EDT April 7.
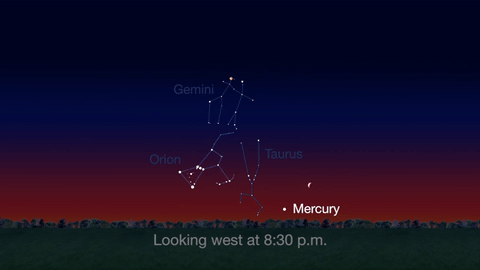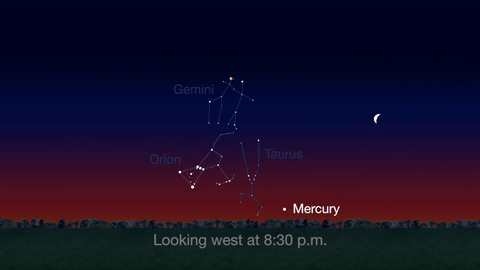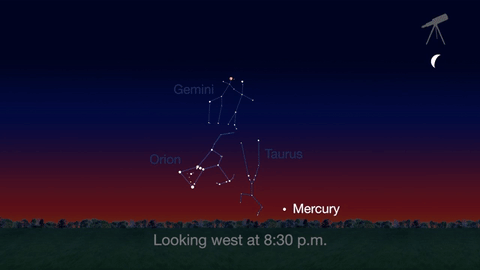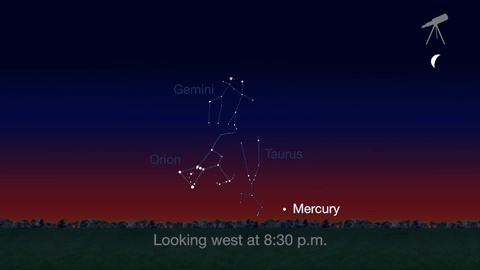
Check out the other planets in April, too! Mercury is always a challenging object to view, but this month you can spot it after sunset about 10 degrees above the horizon. Through a telescope you can see its phase. It will appear like a tiny crescent moon, with about 1/3 of its disk illuminated.

Mars is finally visible before midnight this month. It rises in the southeast at about 10 p.m. by the end of April. The best observing of Mars will be when it is highest in the sky. This means a few hours before dawn. Its brightness and apparent size increase dramatically this month. By month’s end, Mars appears nearly twice as bright as at the beginning of the month.

About mid-month you’ll see Mars near its rival in the sky: the similar-colored red supergiant star Antares. The name “Antares” means “equal to or rival of Mars”.
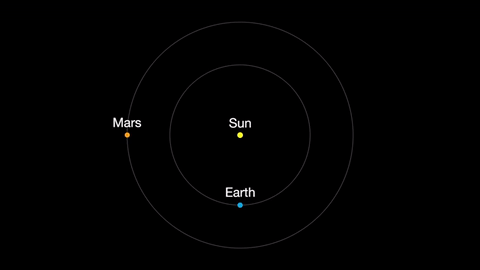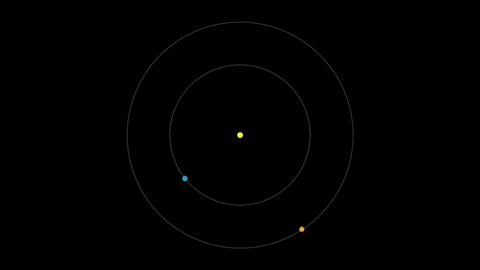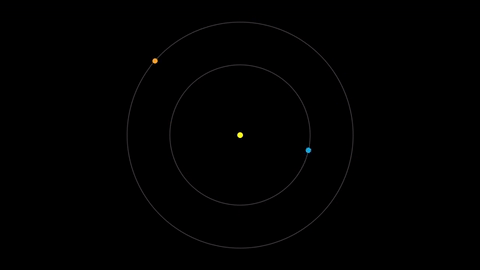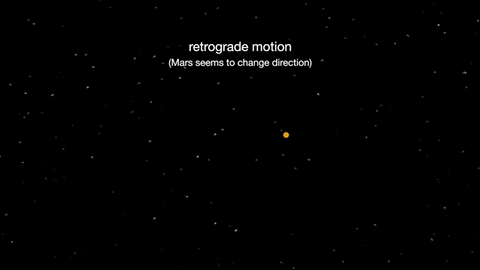
Earth moves almost twice as fast as Mars does, so it often passes Mars in their race around the sun. This causes “retrograde motion”: an illusion we see from our viewpoint on Earth.
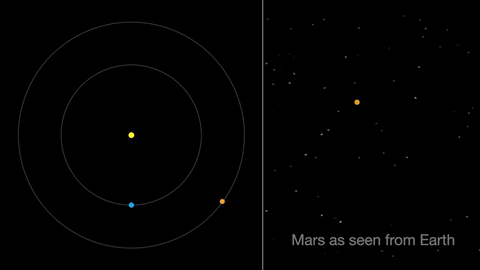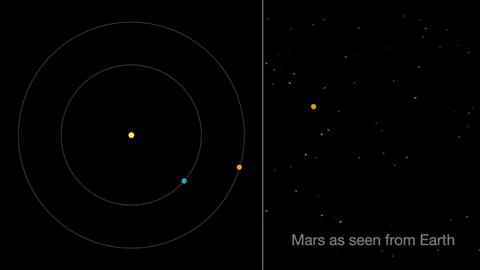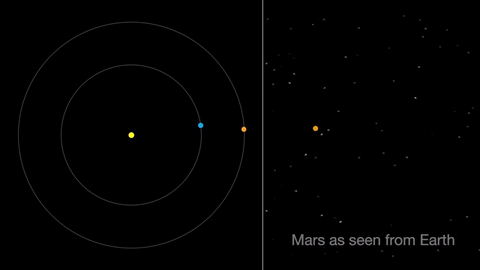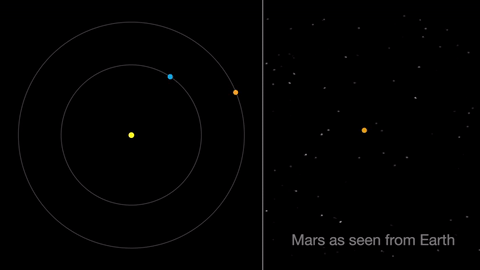
Retrograde motion happens as Earth catches up to Mars, causing Mars to appear slow to slow its eastward motion against the stars. After a few days, when Earth has overtaken Mars, the Red Planet seems to move westward. Eventually, Earth moves far enough around its orbit that Mars appears to be moving eastward again.
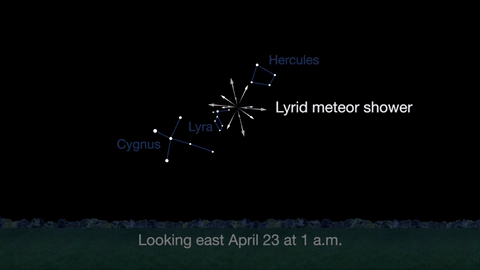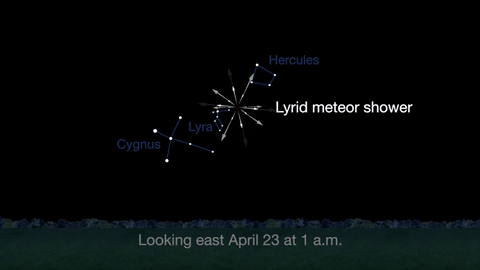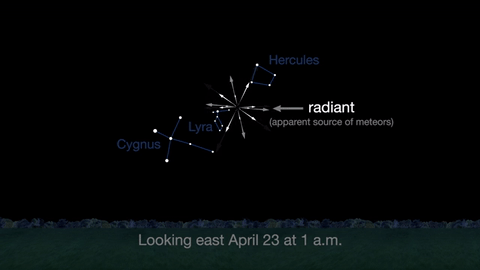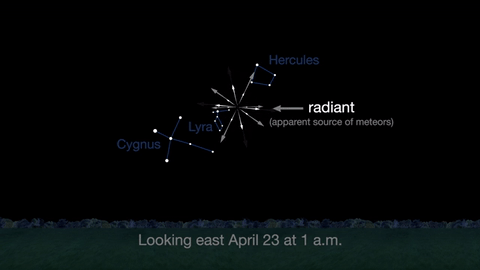
April features one meteor shower, the Lyrids. This year the Lyrids are marred by the full moon. The best time to view will be just before dawn on April 23, when the constellation Lyra is overhead and the moon will be near to setting.
With all of these great things to spot in the sky this month, be sure to get outside and look up!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What Have We Learned About Pluto?
This month (March 2016), in the journal Science, New Horizons scientists have authored the first comprehensive set of papers describing results from last summer’s Pluto system flyby. These detailed papers completely transform our view of Pluto and reveal the former “astronomer’s planet” to be a real world with diverse and active geology, exotic surface chemistry, a complex atmosphere, puzzling interaction with the sun and an intriguing system of small moons.
Here’s a breakdown of what we’ve learned about Pluto:

1. Pluto has been geologically active throughout the past 4 billion years. The age-dating of Pluto’s surface through crater counts has revealed that Pluto has been geologically active throughout the past 4 billion years. Further, the surface of Pluto’s informally-named Sputnik Planum, a massive ice plain larger than Texas, is devoid of any detectable craters and estimated to be geologically young – no more than 10 million years old.

2. Pluto’s moon Charon has been discovered to have an ancient surface. As an example, the great expanse of smooth plains on Charon is likely a vast cryovolcanic flow or flows that erupted onto Charon’s surface about 4 billion years ago. These flows are likely related to the freezing of an internal ocean that globally ruptured Charon’s crust.

3. Pluto’s surface has many types of terrain. The distribution of compositional units on Pluto’s surface – from nitrogen-rich, to methane-rich, to water-rich – has been found to be surprisingly complex, creating puzzles for understanding Pluto’s climate and geologic history. The variations in surface composition on Pluto are unprecedented elsewhere in the outer solar system.

4. Pluto’s atmosphere is colder than we thought. Pluto’s upper atmospheric temperature has been found to be much colder (by about 70 degrees Fahrenheit) than had been thought from Earth-based studies, with important implications for its atmospheric escape rate. Why the atmosphere is colder is a mystery.

5. We know what Pluto’s atmosphere is made of. The New Horizon spacecraft made observations of sunlight passing through Pluto’s atmosphere. We see absorption features that indicate an atmosphere made up of nitrogen (like Earth’s) with methane, acetylene and ethylene as minor constituents.

6. We might have an idea for how Pluto’s haze formed. For first time, a plausible mechanism for forming Pluto’s atmospheric haze layers has been found. This mechanism involves the concentration of haze particles by atmospheric buoyancy waves, created by winds blowing over Pluto’s mountainous topography. Pluto’s haze extends hundreds of kilometers into space, and embedded within it are over 20 very thin, but far brighter, layers.

7. There isn’t much dust around Pluto. Before the flyby, there was concern that a small piece of debris (even the size of a grain of sand) could cause great damage to (or even destroy) the spacecraft. But the Venetia Burney Student Dust Counter (an instrument on the New Horizons spacecraft) only counted a single dust particle within five days of the flyby. This is similar to the density of dust particles in free space in the outer solar system – about 6 particles per cubic mile – showing that the region around Pluto is, in fact, not filled with debris.

8. Pluto’s atmosphere is smaller than we expected. The uppermost region of Pluto’s atmosphere is slowly escaping to space. The hotter the upper atmosphere, the more rapid the gasses escape. The lower the planet’s mass, the lower the gravity, and the faster the atmospheric loss. As molecules escape, they are ionized by solar ultraviolet light. Once ionized, the charged molecules are carried away by the solar wind. As more Pluto-genic material is picked up by the solar wind, the more the solar wind is slowed down and deflected around Pluto. So - the net result is a region (the interaction region), which is like a blunt cone pointed toward the sun, where the escaping ionized gasses interact with the solar wind. The cone extends to a distance about 6 Pluto radii from Pluto toward the sun, but extend behind Pluto at least 400 Pluto radii behind Pluto - like a wake behind the dwarf planet.

9. Pluto’s moons are brighter than we thought. The high albedos (reflectiveness) of Pluto’s small satellites (moons) – about 50 to 80 percent – are entirely different from the much lower reflectiveness of the small bodies in the general Kuiper Belt population, which range from about 5 to 20 percent. This difference lends further support to the idea that these moons were not captured from the general Kuiper Belt population, but instead formed by the collection of material produced in the aftermath of the giant collision that created the entire Pluto satellite system.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
It’s a U.S. Record! Cumulative Days in Space: 383

Today, Astronaut Scott Kelly has broken the record for longest time spent in space by a U.S. astronaut! Over the course of his four missions, Kelly has spent 383 cumulative days in space. This record was previously held by Astronaut Mike Fincke, with 382 days in space over three flights. Here are some more fun facts about this milestone:
4: The number of humans that have spent a year or more in orbit on a single mission
215 Days: The record currently held by Mike Lopez-Alegria for most time on a single spaceflight by U.S. astronaut. On Oct. 29, Kelly will break this record
377 Days: The current record for most days in space by a U.S. female astronaut, held by Peggy Whitson
879 Days: The record for most cumulative days in space by a human, currently held by Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka

Why Spend a Year in Space?
Kelly’s One-Year Mission is an important stepping stone on our journey to Mars and other deep space destinations. These investigations are expected to yield beneficial knowledge on the medical, psychological and biomedical challenges faced by astronauts during long-duration spaceflight.
Kelly is also involved in the Twins Study, which consists of ten separate investigations that are being conducted with his twin brother, who is on Earth. Since we are able to study two individuals who have the same genetics, but are in different environments for one year, we can gain a broader insight into the subtle effects and changes that may occur in spaceflight.
For regular updates on Kelly’s one-year mission aboard the space station, follow him on social media: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Fun Facts About Mars

Mars is a cold desert world, and is the fourth planet from the sun. It is half the diameter of Earth and has the same amount of dry land. Like Earth, Mars has seasons, polar ice caps, volcanoes, canyons and weather, but its atmosphere is too thin for liquid water to exist for long on the surface. There are signs of ancient floods on the Red Planet, but evidence for water now exists mainly in icy soil and thin clouds.

Earth has one, Mars has two…moons of course! Phobos (fear) and Deimos (panic) are the Red Planet’s two small moons. They are named after the horses that pulled the chariot of the Greek war god Ares, the counterpart to the Roman war god Mars.

The diameter of Mars is 4220 miles (6792 km). That means that the Red Planet is twice as big as the moon, but the Earth is twice as big as Mars.

Since Mars has less gravity than Earth, you would weigh 62% less than you do here on our home planet. Weigh yourself here on the Planets App. What’s the heaviest thing you’ve ever lifted? On Mars, you could have lifted more than twice that! Every 10 pounds on Earth only equals 4 pounds on the Red Planet. Find out why HERE.

Mass is the measurement of the amount of matter something contains. Mars is about 1/10th of the mass of Earth.

Mars and Earth are at their closest point to each other about every two years, with a distance of about 33 million miles between them at that time. The farthest that the Earth and Mars can be apart is: 249 million miles. This is due to the fact that both Mars and Earth have elliptical orbits and Mars’ orbit is tilted in comparison with the Earth’s. They also orbit the sun at different rates.

The temperature on Mars can be as high as 70 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) or as low as about –225 degrees Fahrenheit (-153 degrees Celsius). How hot or cold the surface varies between day and night and among seasons. Mars is colder than Earth because it is farther from the sun.

You know that onions have layers, but did you know that Mars has layers too? Like Earth, Mars has a crust, a mantle and a core. The same stuff even makes up the planet layers: iron and silicate.

Ever wonder why it’s so hard launching things to space? It’s because the Earth has a log of gravity! Gravity makes things have weight, and the greater the gravity, the more it weights. On Mars, things weigh less because the gravity isn’t as strong.

Take a deep breath. What do you think you just breathed in? Mostly Nitrogen, about a fifth of that breath was Oxygen and the rest was a mix of other gases. To get the same amount of oxygen from one Earth breath, you’d have to take around 14,500 breaths on Mars! With the atmosphere being 100 times less dense, and being mostly carbon dioxide, there’s not a whole lot of oxygen to breathe in.

Mars has about 15% of Earth’s volume. To fill Earth’s volume, it would take over 6 Mars’ volumes.
For more fun Mars facts, visit HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

A map of our galaxy the Milky Way, showing pulsars (red), planetary nebulae (blue), globular clusters (yellow), and the orbits of several stars

The Andromeda Galaxy is 2 million light years away from us so what we see now is how it appeared 2 million years ago. It will collide with our Milky Way in 2 billions years from now. The two galaxies are heading towards each other at a rate of 430 km/hr. A billion years from now Andromeda will loom as a spectacular site, eventually swelling to fill half of the night sky.
Chasing Storms at 17,500mph
Flying 250 miles above the Earth aboard the International Space Station has given me the unique vantage point from which to view our planet. Spending a year in space has given me the unique opportunity to see a wide range of spectacular storm systems in space and on Earth.
The recent blizzard was remarkably visible from space. I took several photos of the first big storm system on Earth of year 2016 as it moved across the East Coast, Chicago and Washington D.C. Since my time here on the space station began in March 2015, I’ve been able to capture an array of storms on Earth and in space, ranging from hurricanes and dust storms to solar storms and most recently a rare thunder snowstorm.

Blizzard 2016

Hurricane Patricia 2015

Hurricane Joaquin 2015

Dust Storm in the Red Sea 2015

Dust Storm of Gobi Desert 2015

Aurora Solar Storm 2015

Aurora Solar Storm 2016

Thunderstorm over Italy 2015

Lightning and Aurora 2016

Rare Thunder Snowstorm 2016
Follow my Year In Space on Twitter, Facebook and Instagram.
Just another great training with educators using NASA Education resources for the classroom.
How Well Do you Know Neptune?

Dark, cold and whipped by supersonic winds, Neptune is the last of the hydrogen and helium gas giants in our solar system. More than 30 times as far from the sun as Earth, the planet takes almost 165 Earth years to orbit our sun! In fact, in 2011, Neptune completed its first orbit since its discovery in 1846.

Here are a few things you might not know about the windiest planet:
If the sun were as tell as a typical front door, the Earth would be the size of a nickel and Neptune would be about as big as a baseball.
Neptune orbits our sun, a star. Neptune is the eighth planet from the sun at a distance of about 4.5 billion km (2.8 billion miles) or 30.07 AU.
One day on Neptune takes about 16 hours (the time it takes for Neptune to rotate or spin once)
Neptune makes a complete orbit around the sun (a year in Neptunian time) in about 165 Earth years (60,190 Earth days)
Neptune has six rings
Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to have visited Neptune
Neptune has 13 moons. They are named after various sea gods and nymphs in Greek mythology
Did you know that Neptune has storms?

Similar to Jupiter, Neptune has storms that create gigantic spots in its atmosphere…well, it did. When Voyager 2 flew past Neptune in 1989, it tracked and imaged the “Great Dark Spot” — a storm larger than the entire Earth! When the Hubble Space Telescope imaged Neptune the spot had disappeared, only to be replaced with two smaller storms, which in turn also disappeared.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Orion Nebula in Oxygen, Hydrogen, and Sulfur Image Credit Copyright: César Blanco González
The Orion Nebula is among the most intensely studied celestial features.The nebula has revealed much about the process of how stars and planetary systems are formed from collapsing clouds of gas and dust.
Astronomers have directly observed protoplanetary disks, brown dwarfs, intense and turbulent motions of the gas, and the photo-ionizing effects of massive nearby stars in the nebula.
We’re With You When You Fly

Did you know that “We’re With You When You Fly”? Thanks to our advancements in aeronautics, today’s aviation industry is better equipped than ever to safely and efficiently transport millions of passengers and billions of dollars worth of freight to their destinations. In fact, every U.S. Aircraft flying today and every U.S. air traffic control tower uses NASA-developed technology in some way. Here are some of our objectives in aeronautics:
Making Flight Greener

From reducing fuel emissions to making more efficient flight routes, we’re working to make flight greener. We are dedicated to improving the design of airplanes so they are more Earth friendly by using less fuel, generating less pollution and reducing noise levels far below where they are today.
Getting you safely home faster

We work with the Federal Aviation Administration to provide air traffic controllers with new tools for safely managing the expected growth in air traffic across the nation. For example, testing continues on a tool that controllers and pilots can use to find a more efficient way around bad weather, saving thousands of pounds of fuel and an average of 27 minutes flying time per tested flight. These and other NASA-developed tools help get you home faster and support a safe, efficient airspace.
Seeing Aviation’s Future

Here at NASA, we’re committed to transforming aviation through cutting edge research and development. From potential airplanes that could be the first to fly on Mars, to testing a concept of a battery-powered plane, we’re always thinking of what the future of aviation will look like.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

M8 M16 M17 And M20 Gems Of The Summer Milky Way by Martin Campbell on Flickr.

NASA Gemini Mission Spacewalk. Famous shot. Note the hand held maneuvering gun
Elementary GLOBE is designed to introduce K-4 students to the study of Earth System Science. The complete instructional unit includes:
Science-based storybooks designed to introduce students to key concepts in water, soil, clouds, seasons, aerosols, and Earth system studies.
Classroom learning activities complementing the science content covered in each storybook that are designed to further engage students in GLOBE's 5 investigation areas.
(via https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wEHNfIUA6gM)
A 3D tour of the path taken by Mark Watney in “The Martian” was recently added to the Mars Trek page. It includes commentary from NASA experts. Use the tutorial to learn how to navigate. @NASAEPDC

Not to spoil the movie, because it & the book are awesome. This is just something you can learn about Mars before or after you watch the movie, “The Martian.”