Some Of You May Have Heard About Monarch Butterflies Being Added To The Threatened Species List In The
Some of you may have heard about Monarch butterflies being added to the Threatened species list in the US and be planning to immediately rush out in spring and buy all the milkweed you can manage to do your part and help the species.
And that's fantastic!! Starting a pollinator garden and/or encouraging people and businesses around you to do the same is an excellent way to help not just Monarchs but many other threatened and at-risk pollinator species!
However.
Please please PLEASE do not obtain Tropical Milkweed for this purpose!
Tropical milkweed (Asclepias curassavica)--also commonly known as bloodflower, Mexican butterflyweed, and scarlet milkweed--will likely be the first species of milkweed you find for sale at most nurseries. It'll be fairly cheap, too, and it grows and propagates so easily you'll just want to grab it! But do not do that!
Tropical milkweed can cause a host of issues that can ultimately harm the butterflies you're trying to help, such as--
Harboring a protozoan parasite called OE (which has been linked to lower migration success, reductions in body mass, lifespan, mating success, and flight ability) for long periods of time
Remaining alive for longer periods, encouraging breeding during migration time/overwintering time as well as keeping monarchs in an area until a hard freeze wherein which they die
Actually becoming toxic to monarch caterpillars when exposed to warmer temperatures associated with climate change
However--do not be discouraged!! There are over 100 species of milkweed native to the United States, and plenty of resources on which are native to your state specifically! From there, you can find the nurseries dedicated to selling native milkweeds, or buy/trade for/collect seeds to grow them yourself!!
The world of native milkweeds is vast and enchanting, and I'm sure you'll soon find a favorite species native to your area that suits your growing space! There's tons of amazing options--whether you choose the beautiful pink vanilla-smelling swamp milkweed, the sophisticated redring milkweed, the elusive purple milkweed, the alluring green antelopehorn milkweed, or the charming heartleaf milkweed, or even something I didn't list!
And there's tons of resources and lots of people willing to help you on your native milkweed journey! Like me! Feel free to shoot me an ask if you have any questions!
Just. PLEASE. Leave the tropical milkweed alone. Stay away.
TLDR: Start a pollinator garden to help the monarchs! Just don't plant tropical milkweed. There's hundreds of other milkweeds to grow instead!
More Posts from Calystegia and Others



Ghost Pipe Monotropa uniflora
"Unlike most plants, it is white and does not contain chlorophyll. Instead of generating food using the energy from sunlight, it is parasitic, and more specifically a mycoheterotroph. Its hosts are in the Russulaceae family. Most fungi are mycorrhizal. Meaning, through the fungal web of mycorrhizae the M. uniflora roots ultimately sap food from where the host fungi are connected to the photosynthetic trees. The clustered node roots of this plant are covered in hairs called cystidium. The cystidia found on these roots allow easy attachment to fungi hyphae, such as can be seen in ectomycorrhiza. Since it is not dependent on sunlight to grow, it can grow in very dark environments like in the understory of dense forests. The complex relationship that allows this plant to grow makes propagation difficult."

THE OLD FRIENDSHIP OF BLUEBERRIES AND SWEET FERN:
"In the time before refrigeration, Ojibwe folks kept their blueberry harvest fresh by lining their birchbark storage containers with a plant called sweet fern that often grows right alongside blueberry bushes!
The leaves of sweet fern produce a compound called gallic acid, which is a potent anti-microbial and keeps harmful bacteria like salmonella from growing on the berries.
It's name in the Ojibwe dialect I've learned is "giba`iganiminzh" meaning "it covers the berries" because of this usage and its contribution to keeping the precious staple food of minan (blueberries) fresh!
I don't use a birchbark container but I do pop a few sprigs of sweet fern into my gathering bag when out picking and then into my tupperware when storing berries to remember and utilize the gifts of this wonderful plant!
(Sweet fern can also be used as a medicinal tea to help the intestines and colon! And when added to a fire, the smoke will help keep away mosquitos and horse flies--in addition to smelling lovely!)" - The Native Nations Museum, founded by Chippewa Bonnie Jones



Yareta (Azorella compacta) in Bolivia (elevation of 14,000 ft.).
This may look like a moss, but it isnt! This is a broad-leafed plant in the carrot family, Apiaceae.
These plants can grow to bve over 3000 years old. This large specimen may be over 1000 years old.
photographs by Mark Dwyer
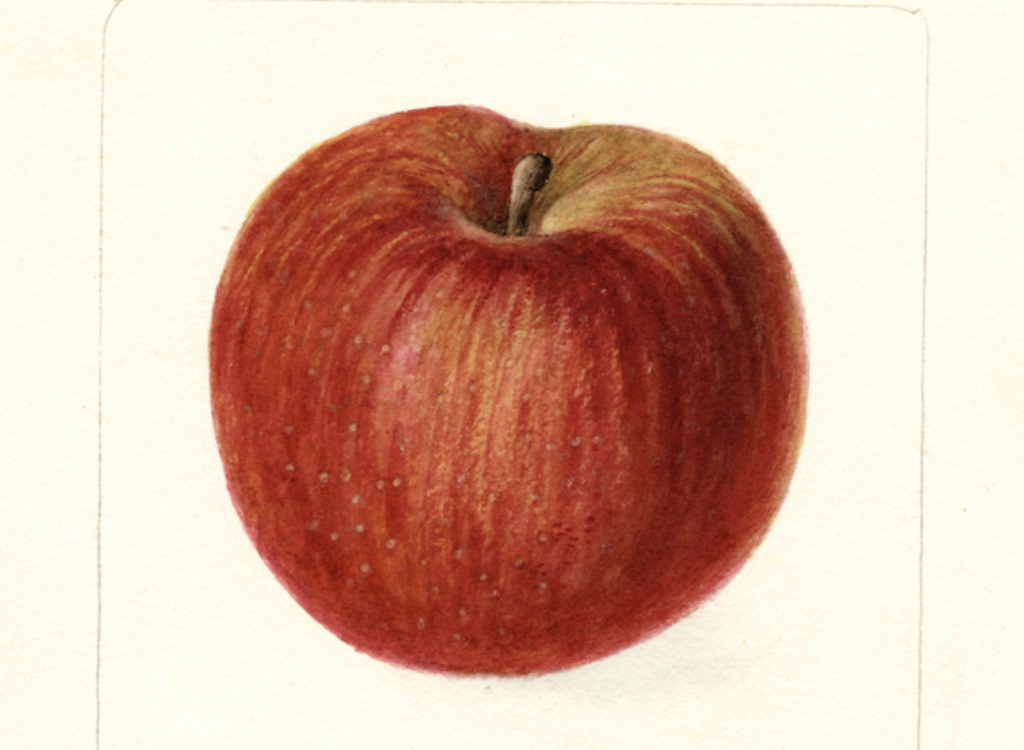

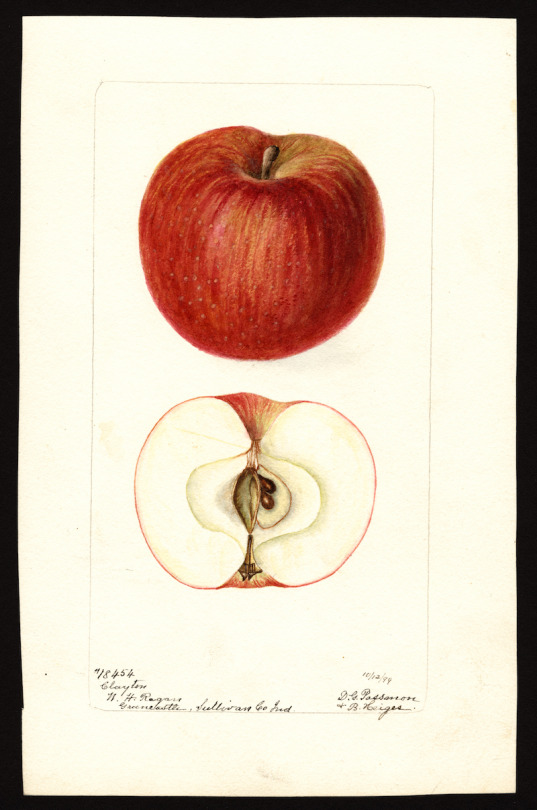

At what point does an exploration of these images tip from information into knowledge? It’s hard to say, but it’s unlikely we would pursue either one if that pursuit didn’t also include its share of pleasure. Enter the USDA’s Pomological Watercolor Collection here to [view] and download over 7,500 high-resolution digital images like those above.
I wonder how many of these fruits & vegetables have changed since 1886?


Erica pyramidalis, the pyramid heath, was a species of Erica (also sometimes known as heath/heather) that was endemic to the city of Cape Town, South Africa. Erica is a genus of roughly 857 species of flowering plants in the family Ericaceae. The Pyramid Heath was restricted to what today is the city of Cape Town in the Western Cape Province, South Africa.The species disappeared due to the destruction of its habitat by the expanding city, and, despite the fact that the species was even cultivated for some time it is now considered extinct.






FINALLY the buttonbush pictures. These are just about the coolest flowers in the world. And they grow all over the riverbanks and are swarmed with pollinators right now it’s amazing. My mom and I couldn’t canoe 10 feet without spotting another one and of course we couldn’t not check out every single one.
I learned that the fruit of the [mesquite] tree was one of many in our landscape that had evolved to be eaten by the giant mammals who disappeared from this continent not long after humans showed up, one of those factual nuggets that punctuate a truth about the deep history of the Anthropocene in ways reading alone cannot. […] [W]e will soon need to learn not to take for granted things like the wild food that goes uneaten due to the absence of the animals whose extinction our dominion coincided with.
I wonder what kind of cake we will make, if we have to make it from the fruit of the old tree that grew up in the brownfield.
Christopher Brown, A Natural History of Vacant Lots: Field Notes from Urban Edgelands, Back Alleys, and Other Wild Places (2024)
-
 oliebollen69 liked this · 1 week ago
oliebollen69 liked this · 1 week ago -
 tighnarithebotanynerd reblogged this · 1 week ago
tighnarithebotanynerd reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 glossytopaz liked this · 1 week ago
glossytopaz liked this · 1 week ago -
 coolghostie reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
coolghostie reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 coolghostie liked this · 2 weeks ago
coolghostie liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 a-couple-of-scheming-hornets liked this · 2 weeks ago
a-couple-of-scheming-hornets liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 orangesodaspirit liked this · 2 weeks ago
orangesodaspirit liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 gay-as-tree liked this · 2 weeks ago
gay-as-tree liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 avaraydrake liked this · 2 weeks ago
avaraydrake liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 ratduude reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
ratduude reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 depthsofmysol reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
depthsofmysol reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 sleepaspirant reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
sleepaspirant reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 jerkuelyn reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
jerkuelyn reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 615andbeyond liked this · 2 weeks ago
615andbeyond liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 sassy-saves-stuff reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
sassy-saves-stuff reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 bumblebee-supreme liked this · 2 weeks ago
bumblebee-supreme liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 pallid-etoiles liked this · 2 weeks ago
pallid-etoiles liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 razette reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
razette reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 fandomcringebucket reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
fandomcringebucket reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 liquidmooniight liked this · 2 weeks ago
liquidmooniight liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 conlainn reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
conlainn reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 conlainn liked this · 3 weeks ago
conlainn liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 whositsandwhatits reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
whositsandwhatits reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 mimingnuns reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
mimingnuns reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 tontonnot liked this · 3 weeks ago
tontonnot liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 narutomaki reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
narutomaki reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 abowlofbeans liked this · 3 weeks ago
abowlofbeans liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 bleedinghearthypocrit reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
bleedinghearthypocrit reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 bleedinghearthypocrit liked this · 3 weeks ago
bleedinghearthypocrit liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 cherry-flakes liked this · 3 weeks ago
cherry-flakes liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 renee561 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
renee561 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 a-peculiar-potoo reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
a-peculiar-potoo reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 a-peculiar-potoo liked this · 3 weeks ago
a-peculiar-potoo liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 edibletrees2 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
edibletrees2 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 smartasspikachu reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
smartasspikachu reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 ghostapple8 liked this · 3 weeks ago
ghostapple8 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 theuselessnonstopscreamer liked this · 3 weeks ago
theuselessnonstopscreamer liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 sablenitez liked this · 3 weeks ago
sablenitez liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 gengaritez reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
gengaritez reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 51nn0n reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
51nn0n reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 51nn0n liked this · 3 weeks ago
51nn0n liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 moth-lover-not-mother reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
moth-lover-not-mother reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 lollipoppersposts liked this · 3 weeks ago
lollipoppersposts liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 moth-lover-not-mother liked this · 3 weeks ago
moth-lover-not-mother liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 vinguist reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
vinguist reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 legallytired reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
legallytired reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 helperbot-5000 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
helperbot-5000 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 bigcheesevik reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
bigcheesevik reblogged this · 3 weeks ago

icon: Cressida Campbell"I know the human being and fish can co-exist peacefully."
35 posts


