10 Research Methods In Psychology
10 Research Methods in Psychology

Psychology is a complex field that indulges into the realms of human behavior and mental processes. In the pursuit of understanding these aspects, psychologists employ a myriad of research methods, each tailored to unravel specific dimensions of the human psyche. Whether engaged in experimental investigations or qualitative explorations, these methodologies serve as invaluable tools for therapists, clinicians, and researchers aiming to decipher the complexities of the human mind.
Surveys
Surveys stand as stalwart instruments in the psychologist’s toolkit, facilitating the study of mental health disorders’ prevalence and causative factors. Offering both quantitative and qualitative insights, these inquiries employ random selection techniques to ensure a representative sample. The resultant data not only aids in comprehending human behavior but also serves as a cornerstone for crafting effective treatment strategies.
Tip: Craft well-structured questions and employ random sampling for robust and reliable results.

In the core of qualitative exploration, case studies emerge as profound investigations into the lives of individuals, groups, or communities. By immersing themselves in the core of a subject, psychologists gain miles perspectives on behavior and mental health. Beyond clinical applications, case studies find relevance in diverse fields such as finance, sales, and advertising, offering insights into consumer behavior and decision-making.
Tip: Combine multiple case studies for a comprehensive understanding and ensure triangulation for heightened reliability.
3. Experimental Study
Quantitative in essence, experimental studies play a main role in establishing causal relationships between variables. By manipulating independent variables and observing resultant changes in dependent variables, psychologists gain valuable insights into the external causes of behaviors, both in communities and broader societal contexts.
Tip: Prioritize random assignment for internal validity, strengthening the credibility of causal relationships.
4. Content Analysis:
Involving into the realm of text-based data, content analysis emerges as a powerful method for extracting patterns and themes from patient communication. Whether analyzing interview transcripts or business emails, this technique aids in the development of targeted psychological treatments and proves instrumental in forensic psychology when solving complex behavioral issues.
Tip: Ensure intercoder reliability to enhance the validity of your content analysis.

In the pursuit of synthesizing knowledge, psychologists turn to meta-analysis, a quantitative approach that combines findings from diverse studies. By consolidating information on a specific topic, meta-analysis serves as a comprehensive resource, offering recommendations for future research endeavors and advancing the frontiers of psychology.
Tip: Encompass studies with diverse methodologies for a robust and holistic analysis.
6. Correlational Research
Navigating the unknown landscape of nonexperimental methods, correlational research illuminates relationships between two variables. While not establishing causation, this approach is instrumental in identifying connections, prompting researchers to complement it with causal studies for more nuanced conclusions.
Tip: Clearly communicate the distinction between correlation and causation in research findings.
7. Quasi-Experiment
Akin to traditional experiments but devoid of random participant assignment, quasi-experiments find their niche in studying non-random traits. Particularly valuable when exploring innate qualities, this method enables psychologists to delve into traits that cannot be randomly assigned.
Tip: Transparently acknowledge the limitations associated with quasi-experiments, especially in terms of establishing causal relationships.

Capturing the essence of behavior in its natural habitat, naturalistic observation, a qualitative method, provides a nuanced understanding of how individuals behave in their accustomed settings. Beyond psychology, this method’s applications extend to diverse fields, including technology, sales, and business, offering insights for innovation.
Tip: Integrate naturalistic observation with other methods for a comprehensive grasp of human behavior.
9. Structured Observation
In the controlled environs of a laboratory, structured observation unfolds as a qualitative method to evaluate human behavior systematically. Applied extensively in clinical and medical research, this method aids in understanding how new therapies or medications influence patient behaviors.
Tip: Ensure the relevance of the structured setting to the behavior under scrutiny for heightened external validity.

Harnessing cutting-edge technology, neuroimaging serves as a quantitative method, unveiling the intricacies of the human brain. Techniques like CT scans and MRI enable psychologists to map brain functions, offering profound insights into the interplay between neural processes, thoughts, emotions, and behavior.
Tip: Stay abreast of technological advancements in neuroimaging for continually refined insights into brain activity.
Tips for Conducting Effective Research
Maintain Research Ethics: Uphold ethical standards, ensuring that both research teams and participants are well-versed in procedures, policies, and confidentiality agreements.
Apply the Scientific Method: Consistently adhere to the scientific method, facilitating organized data collection and analysis to enhance result accuracy.
Report Findings: Disseminate research, theories, and analysis within the scientific community. This not only fosters collaboration but also establishes professional authority in the field.
This comprehensive guide encapsulates the diverse array of research methods in psychology, illustrating their applications, nuances, and tips for effective execution. Whether through quantitative experiments or qualitative explorations, psychologists navigate the terrain of human behavior, contributing to the continual evolution of the field.
Wishing you all the best in your Psychology Research and related studies,
For any Challenges or Guidance during the education journey,
Email us at;williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@gmail.com
More Posts from Expertacademicassignmenthelp and Others
14 Reasons to become a Doctor

Introduction
Embarking on a career as a doctor is a monumental commitment, requiring an extensive education, unwavering dedication, and resilience. This detailed exploration aims to involve deep into the 14 compelling reasons to choose the noble profession of a medical doctor. Each reason represents a reality of the face and nature of the medical field, elucidating the diverse experiences, responsibilities, and its rewards associated with this esteemed profession.
1.To Help Others
At the core of a doctor’s vocation lies the fundamental responsibility to save lives and enhance the health of their patients. Exploring through challenging moments in patients’ lives, doctors have a unique opportunity to contribute significantly to their recovery and overall well-being. This shown aspect forms the very heart of the medical profession, acting as a profound motivator for those who choose this career path
2. To Explore Science

The steps involving to become a doctor unfolds as a rigorous educational stages across various scientific disciplines. From foundational studies in physics, chemistry, and biology during undergraduate education to the exploration of specialized subjects like pharmacology, anatomy, pathology, and neurology in medical school, doctors engage with an expansive array of scientific knowledge. This profession not only broadens their understanding but also empowers them to apply scientific principles practically in the life of patient care.
3 .To Have Variety in Your Work
A career in medicine is anonymously dynamic, promising a different experience each day. Doctors find themselves at the forefront of a diverse condition of illnesses and injuries, prompting the utilization of various skills and treatments. This extends beyond the medical cases to include interactions with a wide group of people, including patients, families, and colleagues, making the profession continuously admiring and intellectually engaging.
4. To Collaborate
The medical profession thrives on a team-oriented environment, fostering collaboration with nurses, orderlies, administrators, specialists, and pharmacists. This collaborative ethos not only promotes continuous learning as doctors share insights but also serves as a critical for finding collective solutions to complex medical conditions. Effective teamwork emerges as a cornerstone for successful patient care.
5.To Have Purpose in Your Work

Doctors occupy a crucial role in society, profoundly impacting the lives of individuals and their families. By promoting healthier lifestyles and improving patient health, doctors become stewards in contributing to the well-being of their communities. This sense of purpose adds a profound dimension to the daily work of a doctor.
6. To Educate
With their detailed study, doctors become experts of knowledge, which they can share with patients and colleagues as well. Patient education on health management and lifestyle improvements becomes a crucial aspect of a doctor’s responsibilities. Additionally, some doctors have the unique opportunity to contribute to medical education by mentoring and teaching medical students in teaching hospitals to get the best knowledge.
7. To Have Job Security
The universal demand for medical expertise provides doctors with a reassuring sense of job security. Unlike some professions, doctors rarely face concerns about a lack of competition for their skills. This extensive demand allows for greater flexibility when choosing a work location, catering to a broader spectrum of professional opportunities.
8. To Earn a Good Salary
While salaries in the medical field may vary based on factors such as location, experience, and specialization, doctors generally enjoy competitive remuneration coupled with excellent benefits. Specialized fields, particularly surgery, can qualify for even higher incomes. The financial rewards reflect the substantial investment of time and dedication required in pursuing of a medical career.
9. To Be a Leader

A medical career aligns seamlessly with the aspirations of individuals attached towards leadership roles. Physicians and surgeons often find themselves leading large teams of medical personnel, providing vital and main guidance while taking responsibility for patient outcomes. Exceptional leadership skills may present opportunities for doctors to pursue supervisory roles, further enriching their professional journey.
10. To Learn
Medical professionals encounter many challenges facing new medical conditions and dangers regularly. Liaising with experienced physicians and exposure to diverse cases contribute to a continuous learning environment. This commitment to lifelong learning renders a medical career particularly appealing to those with an insatiable passion for acquiring knowledge.
11. To Test Yourself
The study towards being a doctor is worth undertaking, marked by numerous challenges. Overcoming these challenges becomes a crucial for personal and professional growth. Adapting and continuous self-improvement emerge as integrated face of a physician’s journey, contributing to the development of resilient and resourceful medical professionals.
12. To Solve Problems
Critical thinking stands as a cornerstone of medical practice. Physicians accurately analyze symptoms, review patient conditions, and develop precise diagnosis, considering individual’s symptoms and clinical presentation of a disease condition. The expertise skills required in medicine demand cautiousness , structured thinking, and a balanced approach to well being , proofing the analytical competency of doctors.
13. To Contribute to Breakthroughs
Medicine, like many other scientific fields, is in a delicate state of expanding aided by technological advancements. Staying ahead of recent developments is not just a professional necessity but also an opportunity for doctors to contribute actively to breakthroughs in medical science. Those with an admiration towards medical innovation can explore positions in research hospitals, where their contributions may shape the future of healthcare.
14. To Find New Opportunities
Upon completing the rigorous phases of medical school and residency, doctors find themselves at a point of diverse opportunities. The array of choices includes pursuing specialization in a preferred field, opening a private practice, engaging in community work overseas, majoring into scientific research, contributing to public health initiatives, or transitioning into teaching positions, exploiting the versatility of a medical career.
Conclusion:
A career as a doctor is a field attached with diverse experiences, responsibilities, and opportunities. The 14 reasons explored in this discussion shed light on the main rewards and challenges that accompany the study of a medical profession. From the known satisfaction derived from helping others to the demand for knowledge and the potential to actively contribute to important developments, a medical career beckons those with indriven passion, full dedication, and a commitment to the continuous evolution of their professional journey. The resilience, adaptability, and sense of purpose implanted in the medical profession form the foundation of a vocation that extends far beyond the sense of a mere job, defining a passion that motivates those who aspire to make a meaningful impact on the lives of others through the practice of medicine.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for assistance guidance.
How Does The Brain Work?

The brain stands as a marvel of biological engineering, Composing of a multitude of bodily functions ranging from cognition and memory to emotions and sensory perception. Together with the spinal cord, it constitutes the central nervous system (CNS), the command center of the human body.
Composition of the Brain

Weighing approximately 3 pounds in adults, the brain’s main structure comprises about 60% fat, interspersed with water, protein, carbohydrates, and salts. Unlike muscles, it houses a complex network of blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
a) Gray and White Matter
Within the central nervous system, gray matter and white matter occupies distinct regions. In the brain, gray matter forms the outer layer, rich in neuron somas, while white matter constitutes the inner section, primarily composed of axons unsheathed in myelin. Conversely, in the spinal cord, this arrangement is reversed.
b) Brain Functionality
The brain operates by transmitting and receiving chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. These signals regulate a myriad of processes, with the brain disseminating each input. Some signals remain confined within the brain, while others traverse the spinal cord and nerves, disseminating information across the body’s expanse. This composes neural network relies on billions of interconnected neurons.
Major Brain Regions and Their Functions

1.Cerebrum
Dominating the brain’s landscape, the cerebrum encompasses the cerebral cortex and underlying white matter. It governs a spectrum of functions, including motor coordination, temperature regulation, language processing, emotional regulation, and sensory perception.
2. Brainstem
Serving as the bridge between the cerebrum and spinal cord, the brainstem comprises the midbrain, pons, and medulla. It regulates vital autonomic functions such as heart rate, breathing, and reflexive responses.
3. Cerebellum
Nestled at the posterior aspect of the brain, the cerebellum coordinates voluntary muscle movements, posture, balance, and motor learning.
Brain Coverings

a) Meninges
Three layers of protective membranes, collectively known as meninges, enshroud the brain and spinal cord. These layers — dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater — shield the delicate neural tissue from physical trauma and infection.
b) Lobes of the Brain
Each hemisphere of the brain comprises four lobes, each harboring distinct functional domains:
Frontal Lobe: Governing executive functions, motor control, and higher cognitive processes.
Parietal Lobe: Integrating sensory information, spatial awareness, and perception of pain and touch.
Occipital Lobe: Specialized for visual processing and perception.
Temporal Lobe: Involved in auditory processing, language comprehension, and memory consolidation.
Deeper Brain Structures
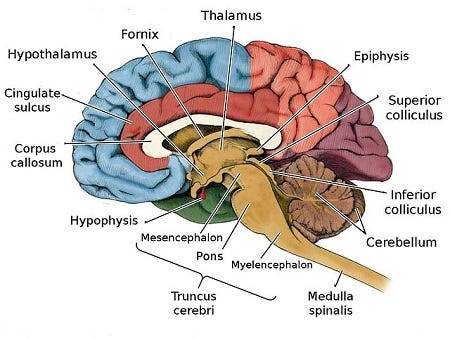
These encompass important structures such as the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, and pineal gland, orchestrating hormone secretion, emotional regulation, memory consolidation, and circadian rhythms.
Blood Supply
The brain receives its oxygenated blood supply through the vertebral and carotid arteries, ensuring adequate perfusion of neural tissue. The main network of blood vessels, including the Circle of Willis, safeguards against ischemic insults and facilitates intraarterial communication.
Cranial Nerves

The twelve pairs of cranial nerves, originating from the brainstem, mediate a diverse array of sensory and motor functions, encompassing olfaction, vision, facial expression, and auditory perception.
Comprehending the anatomy and functionality of the brain fosters a deeper appreciation of its complexity and facilitates advances in neuroscientific research and therapeutic interventions aimed at diminishing neurological disorders.
Understanding the detailed anatomy and functionality of the brain is crucial for medical students embarking on their journey of study. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers invaluable assistance in navigating the complexities of neuroscience and related subjects. By leveraging expert guidance and support, students can excel in their medical education and contribute to advancements in the field of Medicine. Email us at expertassignment46@gmail.com to embark on your path to scholarly excellence and professional competency.
10 Strategies For Handling Online Exams.

Online examinations have emerged as a reliable method for evaluating students in today’s digital era. However, navigating through these virtual assessments can present challenges, particularly for individuals new to the format or struggling to adapt. Fortunately, online exam assignment assistance services like Expert Academic Assignment Help provide invaluable guidance to students, empowering them not only to approach examinations with confidence but also to excel in them. Let’s focuses into ten effective strategies recommended by assignment assistance experts to successfully ace online examinations.
1. Familiarize Yourself With The Exam Format
Understanding the structure and format of the examination is paramount. By comprehending what to anticipate, students can better prepare their study approach and manage their time effectively during the examination.
2. Create A Study Schedule
Effective time management is imperative. Establishing a study schedule that encompasses dedicated time for reviewing course materials, practicing sample questions, and undertaking mock examinations ensures comprehensive preparation.
3. Utilize Online Resources
Exploit the varieties of online resources available to supplement learning. Websites, forums, and educational platforms offer a treasure trove of information, including study guides and interactive quizzes, augmenting students’ understanding of the examination material.
4. Practice Regularly
Practice breeds perfection. Allocating time each day to tackle examination questions under timed conditions not only enhances speed and accuracy but also diminishes anxiety by acquainting students with the examination interface.
5. Seek Clarification
Do not hesitate to seek clarification from instructors or peers when encountering difficulties or questions about the examination material. Engaging in discussions through online forums or study groups can enrich understanding and boost confidence.
6. Minimize Distractions
Cultivating a conducive study environment by minimizing distractions is imperative. Identifying a tranquil, well-lit space and disabling electronic device notifications optimize concentration and information retention.
7. Take Regular Breaks
Striking a balance between study sessions and short breaks is crucial for sustaining focus and preventing burnout. Rejuvenating the mind with stretching and relaxation exercises ensures optimal performance.
8. Develop Exam Strategies
Mastery of effective examination strategies can significantly enhance performance. Learning to prioritize questions, manage time efficiently, and utilize available resources enriches examination outcomes.
9. Review And Revise
Thoroughly reviewing course materials in the days leading up to the examination reinforces comprehension and aids retention. Crafting summary notes and mnemonic devices facilitates the recall of key concepts and definitions.
10. Stay Calm And Confident

On the day of the examination, maintaining composure and confidence is paramount. Trusting in one’s preparation, staying focused, and approaching each question methodically are important contributors to success.
In conclusion, mastering online examinations necessitates thorough preparation, consistent practice, and strategic thinking. By adhering to these ten strategies and availing themselves of support from online exam assignment assistance services like Expert Academic Assignment Help, students can elevate their performance, surmount challenges, and attain academic success. With dedication, perseverance, and the right support system in place, excelling in online examinations is entirely attainable.
The strategies for handling online exams is essential for achieving academic success in the digital era. If you’re aiming to enhance your performance and ensure success in your online examinations, don’t hesitate to reach out to Expert Academic Assignment. Connect with us via email: expertassignment46@gmail.com to explore how our specialized assistance can elevate your exam preparation and performance. Remember, seeking support when needed is a wise decision, particularly when it comes to excelling in challenging assessments like online exams.
Pneumonia In Children And Adults

Introduction
Pneumonia stands as a prevalent respiratory infection, exerting a significant burden on global public health. Its impact extends beyond mere morbidity, contributing to substantial healthcare costs and socioeconomic consequences. This discussion aims to elucidate the general nature of pneumonia, encompassing its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic modalities, treatment strategies, complications, and preventive measures. By indulging into these factors, we aim to provide a better understanding of pneumonia’s complexity and underscore the importance of timely recognition and management.
Pathophysiology

Pneumonia ensues from the infiltration of infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and less commonly, parasites, into the lower respiratory tract. Upon inhalation or aspiration of these pathogens, they gain access to the alveoli, where they incite an inflammatory response. This inflammatory cascade triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, recruiting immune cells to the site of infection. Neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes converge to eradicate the invading pathogens, leading to the characteristic consolidation and exudate formation within the affected lung tissue. As the infection progresses, alveolar edema, impaired gas exchange, and parenchymal damage ensue, culminating in the clinical manifestations of pneumonia.
Clinical Presentation

The clinical presentation of pneumonia encompasses a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild respiratory complaints to life-threatening respiratory failure. Common symptoms include cough, productive sputum production, fever, chills, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, and systemic manifestations such as malaise and fatigue. The severity of symptoms varies depending on factors such as the underlying pathogen, the extent of lung involvement, the host’s immune status, and comorbidities. In pediatric populations, pneumonia may present with nonspecific symptoms such as feeding difficulties, lethargy, and irritability, posing diagnostic challenges. Conversely, elderly individuals may exhibit atypical presentations characterized by confusion, hypothermia, and exacerbations of underlying chronic conditions.
Diagnostic Modalities

The diagnosis of pneumonia hinges on a comprehensive clinical assessment, augmented by various diagnostic modalities to confirm the presence of pulmonary infection and reveal its etiology. A thorough history and physical examination provide invaluable insights into the patient’s symptomatology, risk factors, and clinical trajectory. Symptomatic findings such as crackles, wheezes, and diminished breath sounds may aid in localizing the site of infection and assessing disease severity. Radiographic imaging, notably chest X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, serves as the cornerstone of pneumonia diagnosis, revealing characteristic radiographic findings such as airspace opacities, lobar consolidation, and interstitial infiltrates. Laboratory investigations, including complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin levels, may corroborate the clinical suspicion of pneumonia and guide therapeutic decisions. Additionally, microbiological testing of respiratory specimens through techniques such as sputum culture, blood cultures, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays facilitates pathogen identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing, thereby informing targeted therapy.
Treatment Strategies

The management of pneumonia hinges on prompt initiation of empiric antimicrobial therapy tailored to the likely causative pathogen(s) and disease severity. Antibiotics represent the mainstay of treatment for bacterial pneumonia, with the choice of agent dictated by factors such as local antimicrobial resistance patterns, patient age, comorbidities, and recent antibiotic exposure. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include beta-lactam agents (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, and combination regimens for severe or healthcare-associated infections. Conversely, viral pneumonia necessitates supportive care measures, given the limited efficacy of antiviral agents in most cases. Influenza-associated pneumonia may benefit from neuraminidase inhibitors such as oseltamivir, while respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia may warrant ribavirin therapy in select cases. Adjunctive therapies such as oxygen supplementation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids may mitigate respiratory distress and improve clinical outcomes, particularly in severe or hypoxemic patients. The duration of antimicrobial therapy varies depending on factors such as the causative pathogen, clinical response, radiographic resolution, and the presence of complications. Close monitoring of clinical parameters and serial imaging studies guide the decision-making process, enabling clinicians to tailor therapy to individual patient needs.
Complications

Pneumonia harbors the potential for various complications, ranging from mild to life-threatening sequelae, necessitating vigilant monitoring and timely intervention. Common complications include pleural effusion, empyema, lung abscess, respiratory failure, septic shock, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Pleural effusion denotes the accumulation of fluid within the pleural space, secondary to inflammation or impaired lymphatic drainage, manifesting as dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and dullness to percussion on physical examination. Empyema represents a purulent collection within the pleural cavity, often complicating bacterial pneumonia and necessitating drainage via thoracentesis or chest tube placement. Lung abscesses manifest as circumscribed cavities containing necrotic debris and pus within the lung parenchyma, triggered by persistent fever, productive cough, and hemoptysis. Respiratory failure ensues from impaired gas exchange and alveolar hypoventilation, caused by worsening hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and respiratory acidosis, necessitating mechanical ventilation and intensive care support. Septic shock represents a life-threatening complication of severe pneumonia, characterized by systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and end-organ dysfunction, requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. ARDS denotes a severe form of acute lung injury, characterized by diffuse alveolar damage, refractory hypoxemia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, necessitating lung-protective ventilation and supportive care in the intensive care unit (ICU). The occurrence of complications portends a poor prognosis and underscores the need for early recognition and intervention to mitigate adverse outcomes.
Preventive Measures

Preventing pneumonia entails a broad approach encompassing vaccination, infection control measures, and health promotion strategies aimed at reducing the risk of respiratory infections and their sequelae. Vaccination stands as a cornerstone of pneumonia prevention, targeting common bacterial and viral pathogens implicated in pneumonia pathogenesis. Vaccines such as the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) confer protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae, the leading bacterial cause of pneumonia, particularly in high-risk populations such as young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals. Influenza vaccination remains paramount in mitigating influenza-associated pneumonia and reducing disease transmission, underscoring the importance of annual vaccination campaigns targeting vulnerable populations. Additionally, adherence to infection control measures, including hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and environmental sanitation, plays a pivotal role in reducing the spread of respiratory pathogens in healthcare settings and the community at large. Health promotion efforts aimed at smoking cessation, optimizing nutrition, and addressing underlying comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and immunodeficiency bolster immune resilience and mitigate pneumonia risk. Furthermore, early identification and management of predisposing factors such as malnutrition, homelessness, and overcrowded living conditions attenuate pneumonia susceptibility and enhance overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pneumonia emerges as a formidable respiratory infection, posing significant challenges to global public health. Its diverse etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, treatment modalities, complications, and preventive measures underscore the nature of pneumonia management. Timely recognition and intervention are imperative in mitigating the morbidity and mortality associated with pneumonia, necessitating a collaborative approach among healthcare providers, public health authorities, and policymakers. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of pneumonia’s manifest and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can strive towards reducing its burden and improving patient outcomes. Through ongoing research, education, and advocacy efforts, we can envision a future where pneumonia-related morbidity and mortality are substantially diminished, paving the way for enhanced respiratory health and well-being worldwide.
In managing pneumonia, compassion, empathy, and a holistic approach are essential alongside clinical expertise. Striving for excellence in knowledge and practice allows us to enhance respiratory medicine and patient outcomes.
As we address pneumonia and broader cardiovascular health complexities, let’s remain committed to optimal patient care. Together, we can impact lives positively and foster a healthier future.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance

Thank you @kitteena and everyone who got me to 5 reblogs!
The pathophysiology of hypertension

Introduction
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a complex medical condition affecting a significant proportion of the global population. Despite its prevalence, there remains uncertainty regarding its pathophysiology, with essential hypertension constituting a substantial portion where no single identifiable cause is found. This comprehensive discussion aims to delve into the physiological mechanisms involved in the development of hypertension, exploring factors such as cardiac output, peripheral resistance, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, the autonomic nervous system, endothelial dysfunction, genetic factors, and intrauterine influences.
Cardiac Output and Peripheral Resistance

Maintaining normal blood pressure relies on the delicate balance between cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance. Essential hypertension often involves a normal cardiac output but elevated peripheral resistance, primarily determined by small arterioles. The role of smooth muscle cells, calcium concentration, and structural changes in arteriolar vessel walls contribute to the irreversible rise in peripheral resistance.
Renin-Angiotensin System

The renin-angiotensin system plays a crucial role in blood pressure regulation. Renin, released in response to various stimuli, initiates the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is then converted to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. This system also stimulates aldosterone release, promoting sodium and water retention. While the circulating system may not be directly responsible for essential hypertension, local renin-angiotensin systems in organs like the kidney, heart, and arterial tree gain significance in regulating regional blood flow.
Autonomic Nervous System

Sympathetic nervous system stimulation affects arteriolar constriction and dilation, playing a pivotal role in maintaining normal blood pressure. Although the exact role of epinephrine and norepinephrine in hypertension etiology remains unclear, drugs blocking the sympathetic nervous system demonstrate therapeutic efficacy.
Endothelial Dysfunction

Vascular endothelial cells, producing vasoactive agents like nitric oxide and endothelin, play a key role in cardiovascular regulation. Endothelial dysfunction, implicated in essential hypertension, involves impaired production of nitric oxide. This dysfunction, once established, becomes irreversible, highlighting its primary nature in hypertension.
Vasoactive Substances

Various vasoactive substances, such as bradykinin, endothelin, atrial natriuretic peptide, and ouabain, influence sodium transport and vascular tone. These substances contribute to the delicate balance in maintaining normal blood pressure.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition significantly contributes to hypertension, with specific mutations linked to disorders like Liddle’s syndrome, glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism, and others. The intricate interplay of multiple genes makes it challenging to pinpoint individual contributions.
Intrauterine Influences
Fetal influences, particularly birth weight, emerge as determinants of adult blood pressure. The Barker hypothesis suggests a link between low birth weight, metabolic abnormalities, and hypertension in later life. However, the role of genetic factors in this relationship requires further exploration.
Diastolic Dysfunction

Hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy leads to impaired diastolic relaxation, affecting ventricular input during exercise. This dysfunction contributes to increased atrial pressure, pulmonary congestion, atrial fibrillation, and potential complications like pulmonary edema.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the pathophysiology of hypertension involves a multifaceted exploration of various physiological mechanisms. While essential hypertension remains a complex and often multifactorial condition, advancements in research shed light on factors such as cardiac output, peripheral resistance, the renin-angiotensin system, the autonomic nervous system, endothelial dysfunction, genetic influences, and intrauterine factors. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies and preventive measures against the global burden of hypertension.
We hope this helps in improving our comprehension of the Hypertension condition. All the best in your journey in the medical field.
Incase of any challenges' and in need of professional guidance, contact;
Expert Academic Assignment Help at;
williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@gmail.com
How Can You Make Your Assignment Better?

Crafting high-quality assignments is a fundamental aspect of academic success, requiring a strategic approach and attention to detail. Let’s involve into a detailed discussion on each of the provided guidelines for improving assignment writing skills:
1. Understanding the Assignment Prompt
The assignment prompt serves as a roadmap for your task, outlining the expectations and requirements set by your instructor. Without a clear understanding of the prompt, you risk deviating from the intended focus and missing key elements necessary for a successful assignment. To ensure comprehension, it’s essential to break down the prompt into manageable components, identify keywords, and clarify any uncertainties with your instructor. By mastering this step, you lay a solid foundation for the rest of your assignment.
2. Thorough Research

Research is the backbone of academic writing, providing the necessary evidence and context to support your arguments. However, effective research goes beyond a simple gathering of information; it involves critical evaluation and synthesis of diverse sources to construct a coherent narrative. By consulting a variety of reputable sources, such as academic journals, books, and credible websites, you can deepen your understanding of the topic and bolster the credibility of your arguments. Additionally, employing advanced search strategies, such as Boolean operators and database filters, can streamline the research process and yield more targeted results.
3. Clear Thesis Statement
The thesis statement serves as the central claim or argument of your assignment, guiding the direction of your analysis and providing a roadmap for your readers. A strong thesis statement is concise, specific, and debatable, offering a clear stance on the topic while leaving room for exploration and interpretation. To craft an effective thesis statement, it’s crucial to conduct preliminary research, identify key themes or patterns, and articulate a focused argument that aligns with the scope of your assignment. By establishing a solid thesis statement early on, you can maintain clarity and coherence throughout your writing process.
4. Creating an Outline

An outline is a roadmap that organizes your ideas and structures your assignment in a logical sequence. By outlining the main points, arguments, and supporting evidence, you can ensure that your assignment flows cohesively and addresses all necessary components. Additionally, an outline provides a visual representation of your assignment’s structure, allowing you to identify gaps in your argumentation or areas that require further development. To create an effective outline, consider using a hierarchical format, such as Roman numerals or bullet points, to delineate the main sections and subtopics of your assignment. By investing time in outlining, you can streamline the writing process and produce a more polished final product.
5. Adhering to Formatting Guidelines
Formatting guidelines dictate the presentation and organization of your assignment, ensuring consistency and professionalism across academic work. While formatting requirements may vary depending on the discipline or institution, common elements include font size, margins, spacing, and citation style. By familiarizing yourself with the specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution, you can avoid unnecessary errors and present your work in a standardized format. Additionally, utilizing formatting tools or templates, such as Microsoft Word’s built-in styles or citation managers like EndNote, can simplify the formatting process and save time during document preparation.
6. Writing Clear and Concise Sentences
Clarity is paramount in academic writing, as it enhances comprehension and facilitates effective communication of ideas. Clear and concise sentences convey information efficiently, minimizing ambiguity and maximizing impact. To achieve clarity, it’s essential to use precise language, avoid unnecessary jargon or complex syntax, and structure sentences logically. Additionally, incorporating transition words and phrases, such as “however,” “therefore,” and “in addition,” can enhance coherence and flow between ideas. By prioritizing clarity and conciseness in your writing, you can engage your readers more effectively and convey your arguments with precision.
7. Supporting Arguments with Evidence

Evidence serves as the backbone of persuasive writing, providing support for your claims and lending credibility to your arguments. Whether in the form of empirical data, scholarly research, or real-world examples, evidence should be relevant, reliable, and effectively integrated into your assignment. To effectively support your arguments with evidence, it’s essential to critically evaluate sources, consider alternative perspectives, and provide sufficient context for interpretation. Additionally, employing proper citation techniques, such as direct quotations or paraphrasing, ensures academic integrity and acknowledges the contributions of other scholars. By prioritizing evidence-based reasoning, you can strengthen the persuasiveness of your arguments and demonstrate your mastery of the subject matter.
8. Proper Source Citation
Accurate citation of sources is essential for maintaining academic integrity and avoiding plagiarism. Proper citation acknowledges the contributions of other scholars, provides context for your arguments, and allows readers to locate the original source material. Depending on the citation style specified by your instructor or institution, you may be required to include in-text citations, footnotes, or a bibliography/reference list. To ensure proper source citation, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the conventions of your chosen citation style and apply them consistently throughout your assignment. Additionally, utilizing citation management tools, such as Zotero, Mendeley, can streamline the citation process and minimize errors.
9. Revision and Editing

Revision and editing are essential stages of the writing process, allowing you to refine your ideas, clarify your arguments, and improve the overall quality of your assignment. Revision involves reviewing your work from a macro perspective, focusing on content, structure, and argumentation, while editing focuses on micro-level elements such as grammar, punctuation, and style. To effectively revise and edit your assignment, it’s helpful to approach the task systematically, taking breaks between drafts to gain fresh perspective and utilizing feedback from peers, instructors, or writing tutors. Additionally, employing self-editing techniques, such as reading your work aloud or using grammar-checking software, can help identify errors and inconsistencies that may have been overlooked.
9. Careful Proofreading

Proofreading is the final step before submission, ensuring that your assignment is free from errors and polished to perfection. While it may seem tedious, careful proofreading is essential for maintaining professionalism and credibility in academic writing. To effectively proofread your assignment, it’s helpful to approach the task methodically, focusing on one aspect at a time (e.g., spelling, grammar, punctuation) and utilizing tools such as spell-checkers or style guides for assistance. Additionally, seeking feedback from peers or mentors can provide valuable insights and help identify areas for improvement. By dedicating time and attention to proofreading, you can ensure that your assignment meets the highest standards of quality and excellence.
Incorporating these guidelines into your writing process can significantly enhance the quality of your assignments and contribute to your academic success. By prioritizing clarity, coherence, and evidence-based reasoning, you can effectively communicate your ideas, engage your readers, and achieve your academic goals. Additionally, seeking assistance from resources such as Expert Academic Assignment Help can provide valuable support and guidance, helping you navigate complex assignments and overcome challenges along the way. Remember, improvement takes time and effort, but with dedication and practice, you can elevate your assignment writing skills to new heights and achieve academic excellence.
Incase of need for any guidance or facing challenges during the study period, just email: expertassignment46@gmail.com
First Aid Instructions for 10 Medical Emergencies

Introduction
First aid is the immediate care provided to a sick or injured person, often serving as a crucial bridge until professional medical help arrives. While formal first aid training is ideal, there are basic life-saving steps that everyone should be aware of. This article outlines first aid instructions for 10 common medical emergencies, along with practical tips and a comprehensive first aid kit list.
1.Stopped Heart (Cardiac Arrest)

In the event of a stopped heart, immediate action is crucial:
Initiate CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) to maintain blood circulation.
Use an AED (automated external defibrillator) if available to shock the heart.
Call 911 and continue care until professional help arrives.
2. Bleeding

Effective bleeding control is essential
Apply direct pressure with a clean cloth or bandage to control bleeding.
Elevate the bleeding body part if possible to reduce blood flow.
Seek immediate medical help for severe bleeding.
3. Choking
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*acrWmV_gxPmZh9JX
Swift response is vital when someone is choking:
Perform the Heimlich maneuver for a conscious choking victim.
If unconscious, initiate CPR and call for help.
Monitor airway and breathing.
4. Burns
Proper handling of burns is crucial for minimizing damage:
Stop the burning process by cooling the burn with running water.
For minor burns, use a light gauze bandage and avoid breaking blisters.
Seek medical attention for severe burns.
5. Blisters
Appropriate care can aid in the healing of blisters:
Leave small, unopened blisters alone to promote healing.
For larger, painful blisters, clean, drain, and apply antibiotic ointment.
Monitor for signs of infection.
6. Broken Bone/Fracturey
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*4NouIgQSR_QHj-t6.jpeg
Careful management of fractures is essential:
Call 911 for severe fractures and avoid moving the person if a spinal injury is suspected.
Immobilize the injured area with a splint, elevate, and apply a cold pack for pain.
Seek prompt medical attention.
7. Sprains
Proper first aid can alleviate symptoms of sprains:
Rest the injured limb, apply a cold pack, and elevate if possible.
Seek medical attention for severe pain, inability to bear weight, or signs of infection.
Follow R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) principles.
8. Nosebleeds
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*jJd3qZg5Q8xI_IHf
Effective nosebleed management is essential:
Lean forward and pinch the nose just below the bridge to control bleeding.
Apply a cold pack and seek medical attention for persistent or frequent nosebleeds.
Address underlying causes such as dry air or trauma.
9. Frostbite
Timely response is critical to treating frostbite:
Get out of the cold and gradually warm the affected area with warm water.
Avoid rubbing the affected area, and do not use dry heat sources.
Seek medical attention for severe cases.
10. Bee Sting
Proper care for bee stings is vital, especially for allergic reactions:
Remove the stinger immediately using a straight-edged object.
Monitor for signs of an allergic reaction and call 911 if necessary.
Clean the area, apply a cold pack, and use antihistamines for swelling.
First Aid Kit List
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*WM_HfAvd_-O5fZMC
A well-prepared first aid kit is an essential tool for handling emergencies. The kit should include:
Adhesive bandages in various sizes and shapes
Gauze pads and compress dressings
Adhesive cloth tape, latex gloves, and antiseptic wipes
Antibiotic ointment and hydrocortisone ointment
A breathing barrier for performing CPR
Instant cold compress, tweezers, and an oral thermometer
Emergency blanket for warmth and comfort
Conclusion
While formal first aid training is highly recommended, understanding the basics of immediate care can make a significant difference in emergencies. The outlined first aid instructions cover a range of medical situations, and having a well-stocked first aid kit further enhances preparedness. Quick and appropriate action can be a crucial factor in saving lives during medical emergencies. Remember, being informed and ready can make you a valuable first responder in times of need.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance and guidance
Gangrene

Introduction
Gangrene, a condition marked by tissue death due to insufficient blood flow or bacterial infection, poses significant risks to affected individuals. Understanding the complexities surrounding gangrene, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment modalities, and preventive measures, is paramount for healthcare professionals and the general public alike. This comprehensive discussion aims into the aspects of gangrene, providing insights into its various dimensions and fostering awareness for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes.
Overview of Gangrene
Gangrene manifests when tissues are deprived of adequate blood supply, leading to necrosis or cell death. Whether triggered by compromised circulation or bacterial invasion, gangrene can affect diverse anatomical regions, from the extremities to internal organs. Diabetes, atherosclerosis, and other vascular disorders heighten susceptibility to gangrene, underscoring the importance of vascular health in mitigating its onset.
Symptoms of Gangrene

Recognizing the subtle yet ominous signs of gangrene is critical for timely intervention. Symptoms encompass a spectrum of manifestations, including changes in skin color, swelling, blister formation, intense pain followed by numbness, malodorous discharge, skin texture alterations, and coolness upon touch. Systemic indicators such as fever, tachycardia, and hypotension may herald severe infection or septic shock, necessitating urgent medical attention.
When to See a Doctor
Prompt medical evaluation is imperative upon the onset of persistent, unexplained pain coupled with skin discoloration, discharge, or trauma-related symptoms. Delayed intervention can exacerbate tissue damage and precipitate life-threatening complications, underscoring the urgency of seeking professional care without delay.
Causes of Gangrene

Gangrene can arise from a constellation of etiological factors, ranging from vascular insufficiency to microbial infiltration. Conditions like diabetes, atherosclerosis, traumatic injury, or surgical interventions predispose individuals to gangrene by compromising tissue perfusion or facilitating pathogen colonization. Various subtypes of gangrene, including dry, wet, gas, internal, Fournier’s, and Maloney's gangrene, exhibit distinct pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical presentations, necessitating tailored therapeutic approaches.
Diagnosis and Treatment

Accurate diagnosis of gangrene entails a special evaluation of clinical symptoms, medical history, and ancillary investigations such as imaging and laboratory tests. Treatment strategies aim to restore tissue perfusion, eradicate infection, and remove necrotic tissue. Antibiotics, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and surgical interventions like debridement or amputation constitute cornerstone modalities, guided by the severity and anatomical extent of gangrene.
Doctors and Departments
A multidisciplinary approach involving primary care physicians, vascular surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and wound care experts is indispensable for comprehensive management of gangrene. Collaborative efforts encompass diagnostic precision, therapeutic synergy, and rehabilitative support, ensuring holistic care tailored to individual patient needs.
Prevention
Preventing gangrene necessitates proactive measures targeting predisposing factors and promoting vascular health. Effective strategies encompass glycemic control in diabetes, lifestyle modifications, smoking cessation vigorous wound care, and early recognition of ischemic or infectious triggers. Vigilant surveillance and timely intervention mitigate the risk of gangrene development, fostering tissue preservation and optimizing long-term outcomes.
Conclusion
Gangrene epitomizes a formidable clinical challenge leading to various approach consisting of prevention, early recognition, and prompt intervention. Heightened awareness of gangrene’s clinical spectrum, coupled with proactive measures targeting predisposing factors, is important for mitigating its morbidity and mortality. By fostering collaboration among healthcare providers and empowering individuals with knowledge and preventive strategies, we can confront the scourge of gangrene and safeguard tissue viability, thereby promoting optimal health and well-being for all.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for assistance.
Pneumonia In Children And Adults

Introduction
Pneumonia stands as a prevalent respiratory infection, exerting a significant burden on global public health. Its impact extends beyond mere morbidity, contributing to substantial healthcare costs and socioeconomic consequences. This discussion aims to elucidate the general nature of pneumonia, encompassing its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic modalities, treatment strategies, complications, and preventive measures. By indulging into these factors, we aim to provide a better understanding of pneumonia’s complexity and underscore the importance of timely recognition and management.
Pathophysiology

Pneumonia ensues from the infiltration of infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and less commonly, parasites, into the lower respiratory tract. Upon inhalation or aspiration of these pathogens, they gain access to the alveoli, where they incite an inflammatory response. This inflammatory cascade triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, recruiting immune cells to the site of infection. Neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes converge to eradicate the invading pathogens, leading to the characteristic consolidation and exudate formation within the affected lung tissue. As the infection progresses, alveolar edema, impaired gas exchange, and parenchymal damage ensue, culminating in the clinical manifestations of pneumonia.
Clinical Presentation

The clinical presentation of pneumonia encompasses a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild respiratory complaints to life-threatening respiratory failure. Common symptoms include cough, productive sputum production, fever, chills, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, and systemic manifestations such as malaise and fatigue. The severity of symptoms varies depending on factors such as the underlying pathogen, the extent of lung involvement, the host’s immune status, and comorbidities. In pediatric populations, pneumonia may present with nonspecific symptoms such as feeding difficulties, lethargy, and irritability, posing diagnostic challenges. Conversely, elderly individuals may exhibit atypical presentations characterized by confusion, hypothermia, and exacerbations of underlying chronic conditions.
Diagnostic Modalities

The diagnosis of pneumonia hinges on a comprehensive clinical assessment, augmented by various diagnostic modalities to confirm the presence of pulmonary infection and reveal its etiology. A thorough history and physical examination provide invaluable insights into the patient’s symptomatology, risk factors, and clinical trajectory. Symptomatic findings such as crackles, wheezes, and diminished breath sounds may aid in localizing the site of infection and assessing disease severity. Radiographic imaging, notably chest X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, serves as the cornerstone of pneumonia diagnosis, revealing characteristic radiographic findings such as airspace opacities, lobar consolidation, and interstitial infiltrates. Laboratory investigations, including complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin levels, may corroborate the clinical suspicion of pneumonia and guide therapeutic decisions. Additionally, microbiological testing of respiratory specimens through techniques such as sputum culture, blood cultures, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays facilitates pathogen identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing, thereby informing targeted therapy.
Treatment Strategies

The management of pneumonia hinges on prompt initiation of empiric antimicrobial therapy tailored to the likely causative pathogen(s) and disease severity. Antibiotics represent the mainstay of treatment for bacterial pneumonia, with the choice of agent dictated by factors such as local antimicrobial resistance patterns, patient age, comorbidities, and recent antibiotic exposure. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include beta-lactam agents (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, and combination regimens for severe or healthcare-associated infections. Conversely, viral pneumonia necessitates supportive care measures, given the limited efficacy of antiviral agents in most cases. Influenza-associated pneumonia may benefit from neuraminidase inhibitors such as oseltamivir, while respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia may warrant ribavirin therapy in select cases. Adjunctive therapies such as oxygen supplementation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids may mitigate respiratory distress and improve clinical outcomes, particularly in severe or hypoxemic patients. The duration of antimicrobial therapy varies depending on factors such as the causative pathogen, clinical response, radiographic resolution, and the presence of complications. Close monitoring of clinical parameters and serial imaging studies guide the decision-making process, enabling clinicians to tailor therapy to individual patient needs.
Complications

Pneumonia harbors the potential for various complications, ranging from mild to life-threatening sequelae, necessitating vigilant monitoring and timely intervention. Common complications include pleural effusion, empyema, lung abscess, respiratory failure, septic shock, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Pleural effusion denotes the accumulation of fluid within the pleural space, secondary to inflammation or impaired lymphatic drainage, manifesting as dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and dullness to percussion on physical examination. Empyema represents a purulent collection within the pleural cavity, often complicating bacterial pneumonia and necessitating drainage via thoracentesis or chest tube placement. Lung abscesses manifest as circumscribed cavities containing necrotic debris and pus within the lung parenchyma, triggered by persistent fever, productive cough, and hemoptysis. Respiratory failure ensues from impaired gas exchange and alveolar hypoventilation, caused by worsening hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and respiratory acidosis, necessitating mechanical ventilation and intensive care support. Septic shock represents a life-threatening complication of severe pneumonia, characterized by systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and end-organ dysfunction, requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. ARDS denotes a severe form of acute lung injury, characterized by diffuse alveolar damage, refractory hypoxemia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, necessitating lung-protective ventilation and supportive care in the intensive care unit (ICU). The occurrence of complications portends a poor prognosis and underscores the need for early recognition and intervention to mitigate adverse outcomes.
Preventive Measures

Preventing pneumonia entails a broad approach encompassing vaccination, infection control measures, and health promotion strategies aimed at reducing the risk of respiratory infections and their sequelae. Vaccination stands as a cornerstone of pneumonia prevention, targeting common bacterial and viral pathogens implicated in pneumonia pathogenesis. Vaccines such as the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) confer protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae, the leading bacterial cause of pneumonia, particularly in high-risk populations such as young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals. Influenza vaccination remains paramount in mitigating influenza-associated pneumonia and reducing disease transmission, underscoring the importance of annual vaccination campaigns targeting vulnerable populations. Additionally, adherence to infection control measures, including hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and environmental sanitation, plays a pivotal role in reducing the spread of respiratory pathogens in healthcare settings and the community at large. Health promotion efforts aimed at smoking cessation, optimizing nutrition, and addressing underlying comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and immunodeficiency bolster immune resilience and mitigate pneumonia risk. Furthermore, early identification and management of predisposing factors such as malnutrition, homelessness, and overcrowded living conditions attenuate pneumonia susceptibility and enhance overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pneumonia emerges as a formidable respiratory infection, posing significant challenges to global public health. Its diverse etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, treatment modalities, complications, and preventive measures underscore the nature of pneumonia management. Timely recognition and intervention are imperative in mitigating the morbidity and mortality associated with pneumonia, necessitating a collaborative approach among healthcare providers, public health authorities, and policymakers. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of pneumonia’s manifest and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can strive towards reducing its burden and improving patient outcomes. Through ongoing research, education, and advocacy efforts, we can envision a future where pneumonia-related morbidity and mortality are substantially diminished, paving the way for enhanced respiratory health and well-being worldwide.
In managing pneumonia, compassion, empathy, and a holistic approach are essential alongside clinical expertise. Striving for excellence in knowledge and practice allows us to enhance respiratory medicine and patient outcomes.
As we address pneumonia and broader cardiovascular health complexities, let’s remain committed to optimal patient care. Together, we can impact lives positively and foster a healthier future.
Email expertassignment46@gmail.com to discover how we can support your academic and professional goals. Wishing you ongoing success in your medical journey.
Blood cell

The blood cells serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricacies of hematopoiesis, the process through which various blood cell types are formed and function in the human body. This detailed discussion aims to unravel the key aspects presented in the article, delving into the structure, functions, and disorders associated with;
Red blood cells (erythrocytes),
2.White blood cells (leukocytes), and
platelets (thrombocytes).
Blood Cell Types and Composition
At the core of the circulatory system lie three major types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cellular components collectively contribute to 45% of blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% being plasma. This delicate balance underscores the dynamic nature of blood, serving as a conduit for various vital functions within the body.
1.Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
The discussion commences with a focus on red blood cells, the primary carriers of oxygen in the bloodstream. Erythrocytes, characterized by their unique biconcave shape and lack of a nucleus, play a crucial role in gas exchange facilitated by the iron-containing protein hemoglobin. The intricate details of erythropoiesis, the process of RBC formation in the red bone marrow, offer a glimpse into the remarkable physiological mechanisms that ensure a constant supply of oxygen carriers. The staggering production rate of 2.4 million RBCs per second in adults highlights the body’s continuous demand for these essential cells. The information regarding the lifespan of RBCs (100–120 days) and their subsequent removal by the spleen adds another layer to our understanding of the life cycle of these vital cells. The absence of a nucleus in mature red blood cells, a unique characteristic among human cells, is highlighted. The pathological conditions of anemia and polycythemia are thoroughly explored, shedding light on the consequences of an imbalance in red blood cell count. Additionally, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) provides valuable insights into the diagnostic tools used in assessing the health of red blood cells.
2.White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
The immune system, our body’s defense mechanism, relies on white blood cells to combat infectious diseases and foreign materials. These leukocytes, originating from multipotent cells in the bone marrow, are categorized into granulocytes (basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, mast cells) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes). The discussion delves into the roles these distinct white blood cell types play in the human immune system, offering a nuanced understanding of their functions. The conditions of leukopenia and leukocytosis, indicating low and high white blood cell counts, respectively, are explored, emphasizing the diagnostic significance of monitoring these counts. The increased white blood cell count during infections and its association with hematological cancers underscore the pivotal role leukocytes play in our overall health.
3.Platelets (Thrombocytes)
The section on platelets elucidates their role in hemostasis, the process of preventing and stopping bleeding. These small, irregularly shaped cell fragments, derived from megakaryocytes, circulate in the blood and are essential for the formation of blood clots. The average lifespan of platelets, a mere 5 to 9 days, emphasizes the continuous production required for maintaining hemostatic balance. The normal range of platelet counts and the potential consequences of low or high platelet numbers provide valuable insights into the delicate equilibrium necessary for preventing excessive bleeding or the formation of thrombosis. Thrombocytopathy, a broad term encompassing disorders related to platelets, is discussed, including thrombocytopenia, thrombasthenia, and thrombocytosis. The intricate relationship between platelets and growth factors, as well as their role in wound healing, showcases the multifaceted contributions of these small but crucial cellular fragments.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): The article introduces the Complete Blood Count (CBC) as a vital diagnostic tool providing a comprehensive analysis of blood cell composition. The historical transition from manual counting to automated analyzers reflects the evolving landscape of medical technology, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of blood cell analysis. The significance of CBC in offering an overview of a patient’s general health status is underscored, emphasizing its widespread use in medical diagnostics.
Historical Discoveries.
The historical perspective woven into the article traces the evolution of our understanding of blood cells. From Jan Swammerdam’s pioneering observation of red blood cells in 1658 to Paul Ehrlich’s techniques in staining blood films and differential blood cell counting in 1879, the narrative highlights key milestones in the establishment of hematology as a distinct field of medicine. The contributions of various scientists, including Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, Alfred Donne, and Gabriel Andal, collectively shaped our current knowledge of blood cells.
Conclusion
The blood cells provides a rich tapestry of information encompassing their structure, functions, and associated disorders. It serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding the dynamic nature of blood and the pivotal roles played by red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in maintaining homeostasis within the human body. The integration of historical discoveries adds depth to the narrative, highlighting the continuous quest for knowledge that has defined the field of hematology. This article not only serves as an educational tool but also showcases the remarkable advancements in medical science and technology that have propelled our understanding of blood cells to new heights. As we unravel the mysteries of hematopoiesis, we gain valuable insights into the machinery that sustains life within our veins.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help;
Email us on;
williamsliason@outlook.com