H. Pylori Infection
H. pylori Infection

Introduction
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a significant global health concern, affecting a substantial portion of the world’s population. The discussion aims to provide an in-depth exploration of various aspects of H. pylori infection, including its prevalence, transmission, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, complications, prevention strategies, and future research directions.
Prevalence and Transmission

H. pylori infection is widespread, with approximately two-thirds of the world’s population harboring the bacterium in their gastrointestinal tract. Various factors contribute to its prevalence, including socioeconomic status, living conditions, hygiene practices, and geographic location. The discussion indulges into the epidemiological trends of H. pylori infection across different populations and regions, highlighting disparities in prevalence rates and associated risk factors.
Transmission of H. pylori occurs primarily through interpersonal contact and ingestion of contaminated food or water. Saliva, fecal-oral transmission, and oral-oral transmission, including through kissing, are significant modes of spread. Poor sanitation and overcrowded living conditions facilitate the transmission of the bacterium, particularly in resource-limited settings. The discussion explores the mechanisms of H. pylori transmission and the implications for public health interventions aimed at reducing its spread.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

While many individuals with H. pylori infection remain asymptomatic, others experience a range of gastrointestinal symptoms, including stomach pain, bloating, nausea, and weight loss. The discussion elucidates the spectrum of clinical manifestations associated with H. pylori infection, emphasizing the importance of recognizing atypical presentations and considering differential diagnoses.
Diagnosing H. pylori infection presents several challenges due to the variability of symptoms and the limitations of available diagnostic tests. We critically evaluates the utility of different diagnostic modalities, including stool antigen tests, urea breath tests, and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, in detecting H. pylori infection. It also examines the role of serological tests and molecular techniques in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and guiding clinical management decisions.
Treatment Options

The standard treatment regimens for H. pylori infection typically involve a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). However, rising rates of antibiotic resistance pose significant challenges to effective eradication therapy. It explores the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in H. pylori and the implications for treatment outcomes.
Alternative treatment approaches, such as sequential therapy, concomitant therapy, and bismuth-based quadruple therapy, are also examined in the context of their efficacy and tolerability. Highlighting the importance of individualizing treatment regimens based on antibiotic susceptibility testing and patient-specific factors to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Complications

Peptic ulcers are a common complication of H. pylori infection, resulting from the bacterium’s ability to disrupt the gastric mucosal barrier and induce inflammation. The discussion elucidates the pathophysiology of peptic ulcer formation and the factors contributing to ulcer recurrence and complications.
In addition to peptic ulcers, H. pylori infection is associated with an increased risk of more serious complications, such as gastric cancer and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma. The discussion explores the molecular mechanisms underlying H. pylori-induced carcinogenesis and the strategies for early detection and management of gastric neoplasms.
Prevention

Preventive measures play a crucial role in reducing the burden of H. pylori infection and its associated complications. The discussion emphasizes the importance of promoting good hygiene practices, including handwashing and sanitation, to minimize the risk of transmission.
Furthermore, dietary factors may influence the risk of H. pylori infection and its clinical outcomes. The discussion evaluates the evidence regarding the impact of dietary habits, such as consumption of fruits, vegetables, and probiotics, on H. pylori colonization and disease progression. It also addresses the potential role of vaccination in preventing H. pylori infection and its complications, highlighting ongoing research efforts in vaccine development.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research efforts are focused on advancing our understanding of H. pylori pathogenesis, identifying novel therapeutic targets, and developing effective preventive strategies. The discussion highlights recent advancements in H. pylori research, including insights into bacterial virulence factors, host immune responses, and microbial interactions within the gastric microbiota.
Future directions in H. pylori research encompass a multidisciplinary approach, integrating molecular biology, epidemiology, immunology, and clinical medicine. The discussion outlines key areas for future investigation, such as the development of targeted antimicrobial agents, the role of host genetics in H. pylori susceptibility, and the impact of microbial dysbiosis on disease outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, H. pylori infection remains a significant public health challenge, with implications for gastrointestinal health and disease worldwide. A comprehensive understanding of the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of H. pylori infection is essential for guiding clinical practice and informing public health policies. By addressing the complexities of H. pylori infection through interdisciplinary research and collaborative efforts, we can strive towards reducing its global burden and improving patient outcomes.
In managing H. pylori infection, compassion, empathy, and a holistic approach are crucial alongside clinical expertise. Striving for excellence in knowledge and practice enables us to advance gastroenterology and improve patient outcomes.
As we address H. pylori infection and its broader implications on gastrointestinal health, let’s remain dedicated to providing optimal patient care. By working collaboratively and embracing interdisciplinary approaches, we can positively impact lives and contribute to a healthier future.
Email expertassignment46@gmail.com to explore how we can assist you in achieving your academic and professional aspirations. Wishing you continued success in your medical journey.
More Posts from Expertacademicassignmenthelp and Others
Blood cell

The blood cells serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricacies of hematopoiesis, the process through which various blood cell types are formed and function in the human body. This detailed discussion aims to unravel the key aspects presented in the article, delving into the structure, functions, and disorders associated with;
Red blood cells (erythrocytes),
2.White blood cells (leukocytes), and
platelets (thrombocytes).
Blood Cell Types and Composition
At the core of the circulatory system lie three major types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cellular components collectively contribute to 45% of blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% being plasma. This delicate balance underscores the dynamic nature of blood, serving as a conduit for various vital functions within the body.
1.Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
The discussion commences with a focus on red blood cells, the primary carriers of oxygen in the bloodstream. Erythrocytes, characterized by their unique biconcave shape and lack of a nucleus, play a crucial role in gas exchange facilitated by the iron-containing protein hemoglobin. The intricate details of erythropoiesis, the process of RBC formation in the red bone marrow, offer a glimpse into the remarkable physiological mechanisms that ensure a constant supply of oxygen carriers. The staggering production rate of 2.4 million RBCs per second in adults highlights the body’s continuous demand for these essential cells. The information regarding the lifespan of RBCs (100–120 days) and their subsequent removal by the spleen adds another layer to our understanding of the life cycle of these vital cells. The absence of a nucleus in mature red blood cells, a unique characteristic among human cells, is highlighted. The pathological conditions of anemia and polycythemia are thoroughly explored, shedding light on the consequences of an imbalance in red blood cell count. Additionally, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) provides valuable insights into the diagnostic tools used in assessing the health of red blood cells.
2.White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
The immune system, our body’s defense mechanism, relies on white blood cells to combat infectious diseases and foreign materials. These leukocytes, originating from multipotent cells in the bone marrow, are categorized into granulocytes (basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, mast cells) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes). The discussion delves into the roles these distinct white blood cell types play in the human immune system, offering a nuanced understanding of their functions. The conditions of leukopenia and leukocytosis, indicating low and high white blood cell counts, respectively, are explored, emphasizing the diagnostic significance of monitoring these counts. The increased white blood cell count during infections and its association with hematological cancers underscore the pivotal role leukocytes play in our overall health.
3.Platelets (Thrombocytes)
The section on platelets elucidates their role in hemostasis, the process of preventing and stopping bleeding. These small, irregularly shaped cell fragments, derived from megakaryocytes, circulate in the blood and are essential for the formation of blood clots. The average lifespan of platelets, a mere 5 to 9 days, emphasizes the continuous production required for maintaining hemostatic balance. The normal range of platelet counts and the potential consequences of low or high platelet numbers provide valuable insights into the delicate equilibrium necessary for preventing excessive bleeding or the formation of thrombosis. Thrombocytopathy, a broad term encompassing disorders related to platelets, is discussed, including thrombocytopenia, thrombasthenia, and thrombocytosis. The intricate relationship between platelets and growth factors, as well as their role in wound healing, showcases the multifaceted contributions of these small but crucial cellular fragments.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): The article introduces the Complete Blood Count (CBC) as a vital diagnostic tool providing a comprehensive analysis of blood cell composition. The historical transition from manual counting to automated analyzers reflects the evolving landscape of medical technology, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of blood cell analysis. The significance of CBC in offering an overview of a patient’s general health status is underscored, emphasizing its widespread use in medical diagnostics.
Historical Discoveries.
The historical perspective woven into the article traces the evolution of our understanding of blood cells. From Jan Swammerdam’s pioneering observation of red blood cells in 1658 to Paul Ehrlich’s techniques in staining blood films and differential blood cell counting in 1879, the narrative highlights key milestones in the establishment of hematology as a distinct field of medicine. The contributions of various scientists, including Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, Alfred Donne, and Gabriel Andal, collectively shaped our current knowledge of blood cells.
Conclusion
The blood cells provides a rich tapestry of information encompassing their structure, functions, and associated disorders. It serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding the dynamic nature of blood and the pivotal roles played by red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in maintaining homeostasis within the human body. The integration of historical discoveries adds depth to the narrative, highlighting the continuous quest for knowledge that has defined the field of hematology. This article not only serves as an educational tool but also showcases the remarkable advancements in medical science and technology that have propelled our understanding of blood cells to new heights. As we unravel the mysteries of hematopoiesis, we gain valuable insights into the machinery that sustains life within our veins.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
Viral Infection

Introduction
Viral infections, caused by small germs known as viruses, are prevalent and diverse. They can range from mild conditions such as the common cold to severe and life-threatening illnesses like Ebola or COVID-19. This comprehensive discussion aims to explore various aspects of viral infections, covering their overview, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, management, prevention, outlook, and living with these infections.
Overview
A viral infection occurs when a virus invades the body and utilizes the host’s cells to replicate. Viruses are microscopic pathogens with genetic material (DNA or RNA) encased in a protective protein coat. Unlike bacteria, viruses lack the cellular machinery necessary for self-replication. Instead, they rely on hijacking host cells to reproduce, causing illness in the process.
Understanding Viruses

Viruses, being smaller than bacteria, are visible only under a microscope. They carry genetic information that acts as instructions for replication. In contrast, human cells are complex factories containing the equipment to execute these instructions, such as building proteins and generating more cells. Viruses lack cells and the necessary machinery, making them obligate intracellular parasites.
Distinguishing Viral and Bacterial Infections
Symptoms of viral and bacterial infections often overlap, including fever, cough, and rashes. To differentiate between them, a healthcare provider’s assessment is crucial. Prolonged or worsening symptoms warrant professional evaluation. Various viruses, including herpes and adenoviruses, can cause diverse illnesses, making precise diagnosis crucial for effective treatment.
Types of Viral Infections

Viruses can infect different parts of the body, leading to various types of viral infections. Some common categories include respiratory infections (e.g., common cold, influenza, COVID-19), digestive system infections (e.g., norovirus, hepatitis), viral hemorrhagic fevers (e.g., Ebola, dengue), sexually transmitted infections (e.g., HIV, HPV), exanthemata's infections causing rashes (e.g., chickenpox, measles), neurological infections (e.g., West Nile virus, rabies), and congenital infections transmitted from mother to fetus (e.g., cytomegalovirus, Zika virus).
Risk Factors for Viral Infections
While everyone is susceptible to viral infections, certain factors increase the risk of severe illness. Infants, the elderly, individuals with specific health conditions (diabetes, asthma, COPD), those with weakened immune systems (HIV/AIDS, cancer patients), and pregnant individuals face elevated risks.
Symptoms and Causes
Symptoms of Viral Infections
The symptoms of viral infections vary based on the affected body part but commonly include flu-like symptoms such as fever, body aches, and fatigue. Respiratory infections manifest with sore throat, cough, and sneezing, while digestive system infections cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Skin conditions like rashes, sores, and warts are also prevalent.
Causes of Viral Infections
Various viruses cause infections in humans, entering the body through the nose, mouth, eyes, anus, genitals, or breaks in the skin. Transmission occurs through direct contact, respiratory droplets, contaminated surfaces, sexual contact, animal bites, or ingestion of contaminated food or water.
Contagious Nature
Almost all viral infections are contagious, relying on human-to-human transmission for survival. The need for living hosts to reproduce drives the contagious nature of viruses.
Diagnosis and Tests

Diagnosing Viral Infections
Healthcare providers can diagnose viral infections by assessing symptoms and conducting examinations. Specific viral identification often involves swabbing the nose or throat or obtaining blood samples. In cases of severe inflammation, imaging techniques like X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be employed to understand the infection’s impact on internal organs.
Tests for Viral Infections
Laboratory tests on body fluids or tissues, including blood, saliva, sputum, nasal swabs, skin samples, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, stool, and cervical cells (Pap smear), help identify viral DNA/RNA, antibodies, or antigens, aiding in the confirmation of viral infections.
Management and Treatment
Treatment Approaches
While specific antiviral medications are available for some viral infections (e.g., flu, COVID-19, HIV), many viral illnesses, particularly those causing mild symptoms, can be managed at home. Over-the-counter medications, rest, and proper hydration are commonly recommended.
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications impede virus replication and are crucial for managing chronic infections or shortening the duration of respiratory illnesses. Specific antivirals exist for influenza, COVID-19, hepatitis B and C, HIV, and certain other viral infections.
Convalescent Plasma and Prophylaxis
In severe cases, convalescent plasma, derived from recovered individuals, is used to introduce antibodies and aid in fighting the infection. Post-exposure prophylaxis, involving antiviral medications and immunoglobulin treatment, can prevent the onset of life-threatening viral infections if administered before symptoms appear.
Limitations of Antibiotics
Antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections and are only prescribed for bacterial infections. Their misuse contributes to antibiotic resistance, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis.
Prevention

Vaccinations
Vaccination is a cornerstone in preventing viral infections. Vaccines are available for numerous viruses, including chickenpox, COVID-19, hepatitis, HPV, influenza, measles, mumps, rubella, polio, rotavirus, rabies, and shingles. Seeking advice from healthcare providers helps determine the appropriate vaccinations based on individual risk factors.
Hygiene Practices
Frequent handwashing, especially during cold and flu seasons, is vital in preventing viral spread. Safe food practices, including proper storage and preparation, contribute to avoiding foodborne viruses. Consistent condom or dental dam use during sexual activity reduces the risk of sexually transmitted infections.
Vector-Borne Viruses
Protecting against vector-borne viruses involves using protective clothing, insect repellents, and mosquito nets. Avoiding contact with wild or aggressive animals and supervising pets outdoors reduces the risk of rabies.
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
In cases of potential exposure to life-threatening viruses like HIV, rabies, hepatitis B, or chickenpox, immediate post-exposure prophylaxis can prevent illness. Seeking prompt medical attention after exposure is crucial for effective prevention.
Prognosis
Expectations with Viral Infections
The prognosis of viral infections varies, ranging from self-limiting conditions like the common cold to severe and chronic illnesses. Managing less serious infections at home is often possible, while other infections may lead to life-threatening or long-lasting consequences.
Duration of Viral Infections
The duration of viral infections varies widely. Respiratory infections typically last a few days to two weeks, while chronic infections like hepatitis B and C can persist for years. HIV infections are lifelong, requiring ongoing management.
Complications
Viral infections can lead to complications, both immediate and delayed. Severe respiratory illnesses may result in pneumonia, requiring hospitalization. Inflammation in the brain or its lining (encephalitis or meningitis), severe bleeding, reactivation of dormant viruses, and the development of cancer are potential complications associated with viral infections.
Living With Viral Infections

When to Seek Medical Attention
Individuals experiencing viral infection symptoms that persist or worsen after several days should consult a healthcare provider. High-risk individuals with flu or COVID-19 symptoms may benefit from antiviral medications. Immediate medical attention is necessary for those exposed to HIV, rabies, hepatitis B, or chickenpox.
Emergency Situations
Signs of serious infection, such as high fever, difficulty breathing, chest pain, coughing up blood, severe abdominal pain, or mental changes, require immediate medical attention.
Questions for Healthcare Providers
Patients diagnosed with viral infections should inquire about preventing transmission, proper medication usage, expected recovery timelines, symptom management at home, and follow-up appointments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding viral infections is crucial for effective prevention, management, and timely medical intervention. With a focus on vaccination, hygiene practices, and post-exposure prophylaxis, individuals can minimize the risk of contracting and spreading viral infections. While many viral illnesses are self-limiting, recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate medical care is vital to prevent complications and ensure a healthier outcome. Embracing a proactive approach to viral infection prevention contributes to individual and public health.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help;
Email us at;
williamsliason@outlook.com
Drug metabolism

Drug metabolism is a complex and vital process within living organisms, involving the metabolic breakdown of pharmaceutical substances through specialized enzymatic systems. These enzymatic pathways, collectively known as xenobiotic metabolism, play a pivotal role in pharmacology and medicine. The modification of the chemical structure of xenobiotics, including drugs and poisons, occurs through a set of metabolic pathways. The study of drug metabolism, known as pharmacokinetics, is essential for comprehending the duration, intensity, and actions of pharmaceutical drugs.
Phases of Drug Metabolism
The metabolism of drugs is a multi-phase process.
In phase I
Enzymes such as cytochrome P450 oxidases introduce reactive or polar groups into xenobiotics, thereby facilitating subsequent modifications.
Phase II
Involves conjugation reactions, where activated xenobiotic metabolites are conjugated with charged species, making them less active and more readily excretable. The final phase,
phase III
Encompasses further modification and excretion of conjugates, crucial for eliminating these compounds from cells.
Factors Influencing Drug Metabolism
Diverse factors influence drug metabolism, ranging from
1.physiological variables
Like age and sex differences to genetic polymorphisms affecting enzyme activity. The Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase system, predominantly present in the liver, plays a crucial role in determining the rate of metabolism.
2 .Pathological factors
Including diseases affecting organs like the liver, kidney, or heart, can significantly impact drug metabolism.
Detoxification Mechanisms
Detoxification mechanisms within the body are sophisticated, utilizing physical barriers like cell membranes and low-specificity enzymatic systems. While physical barriers restrict the entry of hydrophilic molecules, enzymatic systems possess broad substrate specificities, metabolizing a wide array of non-polar compounds. The detoxification of endogenous reactive metabolites, such as peroxides and reactive aldehydes, often involves specific enzymatic systems that recognize and remove these potentially harmful substances.
Beyond Human Health
Drug metabolism extends beyond human health; it is essential in environmental science, influencing the fate of pollutants during bioremediation processes. Moreover, in agriculture, xenobiotic metabolism in microorganisms, particularly enzymes like glutathione S-transferases, contributes to resistance against pesticides and herbicides.
In conclusion, drug metabolism is a multifaceted and indispensable aspect of pharmacology, significantly influencing the effectiveness and safety of pharmaceutical drugs. Understanding the intricacies of xenobiotic metabolism is crucial not only for medical professionals but also for addressing environmental and agricultural challenges. As research continues to unravel the mysteries of drug metabolism, its impact on human health and the broader ecosystem becomes increasingly apparent. The continuous exploration of drug metabolism is vital for advancing medical knowledge, ensuring drug safety, and addressing environmental concerns in the ever-evolving field of pharmaceutical science.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help;
Email us on;
williamsliason@outlook.com
Digestive System

The digestive system is a marvel of biological engineering, orchestrating the journey of food through the body, from the moment it enters the mouth to its exit through the anus. This complex process involves a network of organs, each playing a crucial role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. In this detailed exploration, we delve into the anatomy, functions, common conditions, care practices, and the importance of seeking medical attention for digestive system issues.
Anatomy of the Digestive System

Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract:
1.Mouth:
Initiating Digestion: Salivary glands activate as the sight and scent of food trigger the digestive process.
Chewing and Mixing: Food is chewed into digestible pieces, mixed with saliva to facilitate breakdown.
Swallowing: The tongue propels the food into the throat and esophagus.
2. Esophagus:
Transportation: A muscular tube conducting food to the stomach through peristalsis.
Sphincter Function: The lower esophageal sphincter relaxes to allow food entry and contracts to prevent stomach content reflux.
3.Stomach:
Container and Mixer: A hollow organ holding and mixing food with stomach enzymes for further breakdown.
Acid Secretion: Cells in the stomach lining secrete powerful acids and enzymes crucial for digestion.
Release to Small Intestine: Processed stomach contents move to the small intestine for further digestion.
4.Small Intestine:
Segments and Functions: Comprising the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, each segment has distinct roles in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Enzymatic Breakdown: Pancreatic enzymes and bile from the liver aid in breaking down food.
Nutrient Absorption: The jejunum and ileum absorb nutrients into the bloodstream.
Consistency Changes: Contents transition from semi-solid to liquid as water, bile, enzymes, and mucus contribute to the process.
Biliary System

a. pancreas:
Enzyme Secretion: Releases digestive enzymes into the duodenum to break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Insulin Production: The pancreas produces insulin, a key hormone for sugar metabolism.
b. Liver:
Nutrient Processing: Processes nutrients absorbed by the small intestine.
Bile Production: Secretes bile into the small intestine, aiding in fat digestion and vitamin absorption.
Detoxification: Acts as the body’s chemical “factory,” detoxifying harmful substances.
c. Gallbladder:
Bile Storage: Stores and concentrates bile from the liver.
Release into Duodenum: Releases bile into the duodenum to assist in fat absorption.
Large Intestine (Colon):
Colon:
Waste Processing: Responsible for transforming waste into a convenient form for bowel movements.
Peristalsis: Propels stool through the colon, removing water and transitioning it from a liquid to a solid state.
Storage and Elimination: Stool is stored in the sigmoid colon until mass movements propel it into the rectum for elimination.
Rectum:
Chamber Function: A straight chamber connecting the colon to the anus.
Signaling and Holding: Signals the brain about stool presence and holds stool until evacuation.
Anus:
Final Elimination: The last part of the digestive tract, consisting of pelvic floor muscles and sphincters.
Sphincter Control: Surrounding sphincter muscles control stool release, preventing involuntary bowel movements.
Conditions and Disorders
Digestive system health can be affected by a spectrum of conditions, ranging from temporary issues to chronic diseases:
Temporary Conditions:
Constipation:
Frequency and Characteristics: Reduced bowel movements with dry and hard stool.
Difficulty and Pain: Straining during bowel movements, leading to discomfort.
2.Diarrhea:
Loose and Watery Stool: Abnormal stool consistency often caused by various factors.
Potential Causes: Bacterial infections, dietary issues, or unknown triggers.
3.Heartburn:
Misleading Name: Despite the name, heartburn is a digestive issue.
Acidic Backflow: Occurs when stomach acids move up the esophagus, causing discomfort in the chest.
4.Hemorrhoids:
Swollen Veins: Enlarged veins inside and outside the anus and rectum.
Symptoms: Pain, discomfort, and rectal bleeding.
5.Stomach Flu (Gastroenteritis):
Viral Infection: Infection of the stomach and upper part of the small intestine.
Duration: Typically lasts less than a week.
6.Ulcers:
Sore Development: Sores on the lining of the esophagus, stomach, or small intestine.
Causes: Helicobacter pylori infection and prolonged use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
7.Gallstones:
Solid Material Formation: Small pieces formed from digestive fluid in the gallbladder.
Chronic Diseases:
GERD (Chronic Acid Reflux):
Frequent Acid Backflow: Acid-containing contents in the stomach frequently leak into the esophagus.
Symptoms: Persistent heartburn and regurgitation.
2,Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
Colon Muscle Dysfunction: Irregular contractions leading to excessive gas, abdominal pain, and cramps.
Chronic Nature: A long-term condition affecting bowel function.
3.Lactose Intolerance:
Inability to Digest Lactose: Results in digestive discomfort after consuming milk and dairy products.
Common Symptoms: Bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
4.Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis:
Colon Pockets Formation: Diverticula (pockets) in the wall of the colon.
Complications: Inflammation (diverticulitis) can occur, causing pain and infection.
5.Gastrointestinal (GI) Cancers:
Tissue and Organ Affliction: Cancers affecting the digestive system, including esophageal, gastric, colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers.
6.Crohn’s Disease:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A lifelong condition causing inflammation in the digestive tract.
7.Celiac Disease:
Autoimmune Disorder: Gluten consumption damages the small intestine.
Trigger: Found in wheat, barley, and rye.
Care Practices for Digestive Health

Maintaining a healthy digestive system involves adopting proactive lifestyle and dietary habits:
1.Hydration:
Importance of Water: Drinking water facilitates smooth food flow, preventing dehydration-related constipation.
Dehydration Consequences: Insufficient water intake can lead to dry and hard stool.
2.Fiber-Rich Diet:
Benefits of Fiber: Supports digestion and regular bowel movements.
Soluble and Insoluble Fiber: Both types contribute to digestive health.
3.Balanced Nutrition:
Fruits and Vegetables: Multiple servings daily for essential vitamins and minerals.
Whole Grains: Choosing whole grains over processed grains.
Limiting Processed Foods: Reducing intake of processed and sugary foods.
4.Probiotics:
Role of Probiotics: Supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
Post-Antibiotic Use: Especially beneficial after antibiotic treatments.
5.Mindful Eating:
Chewing and Digestion: Thorough chewing aids in proper digestion.
Eating Pace: Slower eating allows the body to signal fullness.
6.Physical Activity:
Exercise and Digestion: Physical activity and gravity aid in moving food through the digestive system.
Post-Meal Walks: Taking a walk after meals can enhance digestion.
7.Avoiding Harmful Habits:
Alcohol and Smoking: Limiting alcohol intake to prevent acid-related issues.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking improves digestive symptoms.
8.Stress Management:
Stress and Digestive Issues: Association between stress and conditions like constipation, diarrhea, and IBS.
Stress Reduction Techniques: Incorporating stress-relief practices into daily life.
Seeking Medical Attention
While occasional digestive issues are common, persistent symptoms warrant attention:
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider:
Frequent Symptoms: Constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, excessive gas, or heartburn.
Potential Underlying Issues: Frequent occurrences may indicate a more serious digestive system problem.
2.Importance of Medical Evaluation:
Diagnostic Assessment: Identifying the cause of persistent symptoms.
Early Intervention: Timely treatment prevents potential complications.
3.Collaborative Approach:
Healthcare Professional Guidance: Seeking advice on managing and preventing digestive issues.
Individualized Care: Tailoring interventions based on the individual’s health status and conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the details of the digestive system provides a foundation for promoting digestive health. The collaboration of organs in the GI tract and the biliary system highlights the complexity of the digestive process. Awareness of common conditions, care practices, and the significance of seeking medical attention empowers individuals to prioritize their digestive well-being. Adopting a holistic approach that combines a healthy lifestyle, balanced nutrition, and regular medical check-ups ensures a resilient and well-functioning digestive system, contributing to overall health and vitality.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
14 Common Lung Diseases

Introduction
Lung diseases represent some of the most severe health threats globally. The rise of industrialization, environmental pollution, and tobacco usage significantly contribute to the prevalence of these diseases. This article, outlines the most common lung diseases, their symptoms, causes, and treatments.
1. Pneumonia

Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other pathogens. It poses a significant risk to the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, and those with chronic conditions but can also affect healthy individuals. Pneumonia can be classified based on the causative agent, such as bacterial pneumonia (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae), viral pneumonia (e.g., influenza virus), or fungal pneumonia (e.g., Pneumocystis jirovecii).
Symptoms
Fever
Cough with sputum
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Sweating and shaking chills
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (less common)
Diagnosis Diagnosis of pneumonia typically involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures. Blood tests may also be conducted to identify the causative agent.
Treatment Depending on the cause, treatments may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia.
Antiviral medications for viral pneumonia.
Antifungal therapies for fungal pneumonia. Supportive care such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and manage pain can also alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to provide intravenous antibiotics, oxygen therapy, or mechanical ventilation.
2. Bronchitis

Bronchitis involves the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. It can be acute, often following colds or the flu, or chronic, usually resulting from smoking or long-term exposure to irritants like pollution or dust.
Symptoms
Persistent cough (productive or dry)
Sputum production (clear, white, yellowish-gray, or green)
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Slight fever and chills
Chest discomfort
Diagnosis Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, where a doctor listens to the patient’s lungs with a stethoscope. Additional tests, such as a chest X-ray, sputum tests, or pulmonary function tests, may be conducted to rule out other conditions like pneumonia or asthma.
Treatment
Acute bronchitis: Symptomatic treatment includes rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers and cough medications. Inhalers or nebulizers may be prescribed to ease breathing.
Chronic bronchitis: Management may involve bronchodilators, steroids, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Smoking cessation and avoiding lung irritants are crucial for treatment.
3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)

COPD is a progressive, irreversible disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways, primarily due to smoking, environmental pollutants, or long-term exposure to respiratory irritants. COPD includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, conditions that often coexist and lead to airflow obstruction.
Symptoms
Chronic cough
Sputum production
Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities
Wheezing
Chest tightness
Frequent respiratory infections
Fatigue
Unintended weight loss (in advanced stages)
Diagnosis COPD is diagnosed through a combination of patient history, physical examination, and spirometry, a test that measures the amount of air a person can exhale and how quickly they can do so. Chest X-rays, CT scans, and arterial blood gas analysis may also be used.
Prevention and Treatment Preventive measures include:
Smoking cessation
Vaccinations (influenza and pneumococcal vaccines)
Reducing exposure to lung irritants
Treatments involves;
Bronchodilators to relax the muscles around the airways
Inhaled steroids to reduce airway inflammation
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs
Oxygen therapy for severe cases
Surgery (e.g., lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplant) in advanced cases
4. Lung Cancer

Lung cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of malignant cells in the lung tissues. Major risk factors include smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, exposure to carcinogens (e.g., asbestos, radon), and genetic predisposition.
Types
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Often linked to heavy smoking, SCLC is aggressive and spreads quickly.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): More common and includes subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Symptoms
Persistent cough
Chest pain
Weight loss
Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
Shortness of breath
Hoarseness
Bone pain (in advanced stages)
Headache (if cancer spreads to the brain)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves imaging tests (chest X-rays, CT scans, PET scans), sputum cytology, and tissue biopsy. Molecular testing may be done to identify specific genetic mutations that can be targeted with specific treatments.
Treatment
Surgery to remove the tumor or part of the lung
Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells
Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors
Targeted drug therapies to attack specific genetic changes in cancer cells
Immunotherapy to help the immune system fight cancer
5. Pleurisy
Pleurisy, or pleuritis, is the inflammation of the pleura, the tissue lining the lungs and chest cavity. It can be caused by infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal), injuries, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), or other underlying conditions.
Symptoms
Sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens with breathing, coughing, or sneezing
Shortness of breath
Cough
Fever (if infection is present)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a physical examination, chest X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans, and blood tests to identify the underlying cause. Thoracentesis, a procedure to remove and analyze pleural fluid, may be performed.
Treatment Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial infections
Antiviral medications for viral infections
Anti-inflammatory medications (e.g., NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
Pain management with medications
Thoracentesis to drain excess fluid from the pleural space
6. Pulmonary Embolism

A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot, usually originating in the legs (deep vein thrombosis), travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow and causing tissue damage. Risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgery, cancer, and certain genetic conditions.
Symptoms
Sudden shortness of breath
Chest pain (may be sharp and worsen with deep breathing or coughing)
Cough (sometimes with bloody sputum)
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Lightheadedness or dizziness
Leg pain or swelling (if DVT is present)
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves imaging tests such as chest X-rays, CT pulmonary angiography, and ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scans. D-dimer blood tests and ultrasound of the legs may also be conducted.
Treatment Immediate treatment includes:
Anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent further clotting
Thrombolytics (clot-dissolving medications) for severe cases
Surgical or catheter-based procedures to remove the clot
Long-term anticoagulation therapy to prevent recurrence
7. Pulmonary Edema

Pulmonary edema is the accumulation of fluid in the lung alveoli, making breathing difficult. It can result from heart failure (cardiogenic pulmonary edema), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), or exposure to high altitudes (non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema).
Symptoms
Difficulty breathing (dyspnea), especially when lying down
Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
Wheezing or gasping for breath
Coughing up frothy, pink-tinged sputum
Excessive sweating
Cyanosis (bluish skin or lips)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves physical examination, chest X-rays, and blood tests. Echocardiography and pulmonary artery catheterization may be used to determine the underlying cause and severity.
Treatment Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause and may include:
Diuretics to remove excess fluid
Medications to improve heart function (for cardiogenic pulmonary edema)
Supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation
Treating underlying conditions such as infections or high altitude exposure
8. Pulmonary Fibrosis

Pulmonary fibrosis is the thickening and scarring of lung tissue, leading to reduced oxygen absorption. Causes include chronic exposure to environmental pollutants, infections, genetic factors, and autoimmune diseases (e.g., scleroderma).
Symptoms
Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
Persistent dry cough
Fatigue
Unexplained weight loss
Aching muscles and joints
Clubbing (widening and rounding) of the fingertips or toes
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, imaging tests (chest X-rays, high-resolution CT scans), pulmonary function tests, and sometimes lung biopsy. Blood tests may be used to identify underlying autoimmune diseases.
Treatment While there is no cure for pulmonary fibrosis, treatments focus on symptom management and slowing progression:
Medications such as pirfenidone and nintedanib to slow disease progression
Oxygen therapy
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Lung transplant in severe cases
9. Pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis is a lung disease caused by inhaling dust particles, such as asbestos, silica, or coal dust, leading to lung scarring. It is a type of occupational lung disease commonly seen in miners, construction workers, and industrial workers.
Symptoms:
Chronic cough
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Progressive loss of lung function
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed occupational history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess the extent of lung damage.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Avoiding further exposure to dust
Medications to manage symptoms, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids
Respiratory therapies
Pulmonary rehabilitation
10. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
PAH is a form of high blood pressure affecting the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart. It can be idiopathic, familial, or associated with other conditions such as connective tissue diseases, congenital heart disease, or chronic liver disease.
Symptoms
Breathing difficulties (dyspnea), especially during physical activities
Dizziness or fainting (syncope)
Chest pain
Fatigue
Swelling in the ankles, legs, and abdomen (edema)
Cyanosis (bluish lips and skin)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves echocardiography, right heart catheterization, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Blood tests and pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess lung and heart function.
Treatment Treatment strategies include:
Medications to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, such as endothelin receptor antagonists, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, and prostacyclin analogs
Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
Oxygen therapy
Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots
In severe cases, surgical procedures such as atrial septostomy or lung transplant
11. Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, leading to thick, sticky mucus buildup in the lungs and other organs. This results in frequent infections, respiratory issues, and digestive problems.
Symptoms
Persistent cough with thick mucus
Recurrent lung infections
Wheezing or shortness of breath
Poor growth and weight gain in children
Salty-tasting skin
Severe constipation
Frequent greasy, bulky stools
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves genetic testing, sweat chloride tests, and newborn screening. Pulmonary function tests, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures may also be conducted to assess lung health.
Treatment Management includes:
Medications to thin mucus, antibiotics to treat infections, and bronchodilators to open airways
Chest physiotherapy to clear mucus
Enzyme supplements and high-calorie diets to manage digestive issues
Newer therapies targeting the underlying genetic defect, such as CFTR modulators
12. Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
RDS primarily affects premature infants due to a lack of surfactant, a substance necessary to keep the lungs open and facilitate gas exchange. Risk factors include premature birth, maternal diabetes, and multiple births.
Symptoms
Rapid, shallow breathing
Grunting sounds while breathing
Nasal flaring
Chest retractions (pulling in of the chest muscles)
Cyanosis (bluish color of the skin and mucous membranes)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves clinical assessment, chest X-rays, and blood gas analysis to measure oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Prenatal tests can also help identify at-risk pregnancies.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Surfactant replacement therapy to improve lung function
Mechanical ventilation or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) to support breathing
Oxygen therapy
Supportive care such as fluids and nutrition
13. Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is characterized by the growth of granulomas (small clusters of inflammatory cells) in the lungs and other organs, likely as an immune response to unknown triggers. The exact cause remains unclear, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
Symptoms
Dry cough
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Fatigue
Fever
Swollen lymph nodes
Skin lesions (e.g., erythema nodosum)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, CT scans, and pulmonary function tests. Biopsy of affected tissues may be performed to confirm the presence of granulomas.
Treatment While sarcoidosis is often self-limiting and may resolve without treatment, severe cases may require:
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Immunosuppressive medications (e.g., methotrexate, azathioprine)
Antimalarial drugs (e.g., hydroxychloroquine) for skin lesions
Regular monitoring and follow-up care to manage chronic cases
14. Asthma
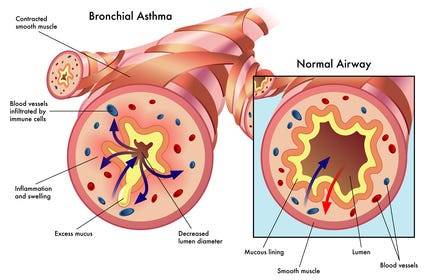
Definition and Causes: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways, causing episodes of wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, often triggered by allergens, exercise, cold air, or respiratory infections. Genetic and environmental factors contribute to its development.
Symptoms
Wheezing
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Coughing, especially at night or early morning
Increased mucus production
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests (spirometry, peak flow measurement). Allergy testing and chest X-rays may also be conducted to identify triggers and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Management includes:
Avoiding known triggers
Inhalers (bronchodilators for quick relief, corticosteroids for long-term control)
Long-term control medications (e.g., leukotriene modifiers, long-acting beta agonists)
Immunotherapy (allergy shots) for severe allergies
Asthma action plans to manage symptoms and prevent attacks
Conclusion
Lung diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments. Preventive measures such as avoiding smoking, reducing exposure to environmental pollutants, and timely vaccinations can significantly reduce the risk of developing many of these diseases. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by lung diseases. For personalized medical advice and treatment, consult with healthcare professionals.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Email us: expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional guidance.

Thank you @expertacademicassignmenthelp and everyone who got me to 10 reblogs!
The pathophysiology of hypertension

Introduction
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a complex medical condition affecting a significant proportion of the global population. Despite its prevalence, there remains uncertainty regarding its pathophysiology, with essential hypertension constituting a substantial portion where no single identifiable cause is found. This comprehensive discussion aims to delve into the physiological mechanisms involved in the development of hypertension, exploring factors such as cardiac output, peripheral resistance, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, the autonomic nervous system, endothelial dysfunction, genetic factors, and intrauterine influences.
Cardiac Output and Peripheral Resistance

Maintaining normal blood pressure relies on the delicate balance between cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance. Essential hypertension often involves a normal cardiac output but elevated peripheral resistance, primarily determined by small arterioles. The role of smooth muscle cells, calcium concentration, and structural changes in arteriolar vessel walls contribute to the irreversible rise in peripheral resistance.
Renin-Angiotensin System

The renin-angiotensin system plays a crucial role in blood pressure regulation. Renin, released in response to various stimuli, initiates the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is then converted to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. This system also stimulates aldosterone release, promoting sodium and water retention. While the circulating system may not be directly responsible for essential hypertension, local renin-angiotensin systems in organs like the kidney, heart, and arterial tree gain significance in regulating regional blood flow.
Autonomic Nervous System

Sympathetic nervous system stimulation affects arteriolar constriction and dilation, playing a pivotal role in maintaining normal blood pressure. Although the exact role of epinephrine and norepinephrine in hypertension etiology remains unclear, drugs blocking the sympathetic nervous system demonstrate therapeutic efficacy.
Endothelial Dysfunction

Vascular endothelial cells, producing vasoactive agents like nitric oxide and endothelin, play a key role in cardiovascular regulation. Endothelial dysfunction, implicated in essential hypertension, involves impaired production of nitric oxide. This dysfunction, once established, becomes irreversible, highlighting its primary nature in hypertension.
Vasoactive Substances

Various vasoactive substances, such as bradykinin, endothelin, atrial natriuretic peptide, and ouabain, influence sodium transport and vascular tone. These substances contribute to the delicate balance in maintaining normal blood pressure.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition significantly contributes to hypertension, with specific mutations linked to disorders like Liddle’s syndrome, glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism, and others. The intricate interplay of multiple genes makes it challenging to pinpoint individual contributions.
Intrauterine Influences
Fetal influences, particularly birth weight, emerge as determinants of adult blood pressure. The Barker hypothesis suggests a link between low birth weight, metabolic abnormalities, and hypertension in later life. However, the role of genetic factors in this relationship requires further exploration.
Diastolic Dysfunction

Hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy leads to impaired diastolic relaxation, affecting ventricular input during exercise. This dysfunction contributes to increased atrial pressure, pulmonary congestion, atrial fibrillation, and potential complications like pulmonary edema.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the pathophysiology of hypertension involves a multifaceted exploration of various physiological mechanisms. While essential hypertension remains a complex and often multifactorial condition, advancements in research shed light on factors such as cardiac output, peripheral resistance, the renin-angiotensin system, the autonomic nervous system, endothelial dysfunction, genetic influences, and intrauterine factors. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies and preventive measures against the global burden of hypertension.
We hope this helps in improving our comprehension of the Hypertension condition. All the best in your journey in the medical field.
Incase of any challenges' and in need of professional guidance, contact;
Expert Academic Assignment Help at;
williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@gmail.com
Pneumonia In Children And Adults

Introduction
Pneumonia stands as a prevalent respiratory infection, exerting a significant burden on global public health. Its impact extends beyond mere morbidity, contributing to substantial healthcare costs and socioeconomic consequences. This discussion aims to elucidate the general nature of pneumonia, encompassing its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic modalities, treatment strategies, complications, and preventive measures. By indulging into these factors, we aim to provide a better understanding of pneumonia’s complexity and underscore the importance of timely recognition and management.
Pathophysiology

Pneumonia ensues from the infiltration of infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and less commonly, parasites, into the lower respiratory tract. Upon inhalation or aspiration of these pathogens, they gain access to the alveoli, where they incite an inflammatory response. This inflammatory cascade triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, recruiting immune cells to the site of infection. Neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes converge to eradicate the invading pathogens, leading to the characteristic consolidation and exudate formation within the affected lung tissue. As the infection progresses, alveolar edema, impaired gas exchange, and parenchymal damage ensue, culminating in the clinical manifestations of pneumonia.
Clinical Presentation

The clinical presentation of pneumonia encompasses a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild respiratory complaints to life-threatening respiratory failure. Common symptoms include cough, productive sputum production, fever, chills, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, and systemic manifestations such as malaise and fatigue. The severity of symptoms varies depending on factors such as the underlying pathogen, the extent of lung involvement, the host’s immune status, and comorbidities. In pediatric populations, pneumonia may present with nonspecific symptoms such as feeding difficulties, lethargy, and irritability, posing diagnostic challenges. Conversely, elderly individuals may exhibit atypical presentations characterized by confusion, hypothermia, and exacerbations of underlying chronic conditions.
Diagnostic Modalities

The diagnosis of pneumonia hinges on a comprehensive clinical assessment, augmented by various diagnostic modalities to confirm the presence of pulmonary infection and reveal its etiology. A thorough history and physical examination provide invaluable insights into the patient’s symptomatology, risk factors, and clinical trajectory. Symptomatic findings such as crackles, wheezes, and diminished breath sounds may aid in localizing the site of infection and assessing disease severity. Radiographic imaging, notably chest X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, serves as the cornerstone of pneumonia diagnosis, revealing characteristic radiographic findings such as airspace opacities, lobar consolidation, and interstitial infiltrates. Laboratory investigations, including complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin levels, may corroborate the clinical suspicion of pneumonia and guide therapeutic decisions. Additionally, microbiological testing of respiratory specimens through techniques such as sputum culture, blood cultures, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays facilitates pathogen identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing, thereby informing targeted therapy.
Treatment Strategies

The management of pneumonia hinges on prompt initiation of empiric antimicrobial therapy tailored to the likely causative pathogen(s) and disease severity. Antibiotics represent the mainstay of treatment for bacterial pneumonia, with the choice of agent dictated by factors such as local antimicrobial resistance patterns, patient age, comorbidities, and recent antibiotic exposure. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include beta-lactam agents (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, and combination regimens for severe or healthcare-associated infections. Conversely, viral pneumonia necessitates supportive care measures, given the limited efficacy of antiviral agents in most cases. Influenza-associated pneumonia may benefit from neuraminidase inhibitors such as oseltamivir, while respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia may warrant ribavirin therapy in select cases. Adjunctive therapies such as oxygen supplementation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids may mitigate respiratory distress and improve clinical outcomes, particularly in severe or hypoxemic patients. The duration of antimicrobial therapy varies depending on factors such as the causative pathogen, clinical response, radiographic resolution, and the presence of complications. Close monitoring of clinical parameters and serial imaging studies guide the decision-making process, enabling clinicians to tailor therapy to individual patient needs.
Complications

Pneumonia harbors the potential for various complications, ranging from mild to life-threatening sequelae, necessitating vigilant monitoring and timely intervention. Common complications include pleural effusion, empyema, lung abscess, respiratory failure, septic shock, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Pleural effusion denotes the accumulation of fluid within the pleural space, secondary to inflammation or impaired lymphatic drainage, manifesting as dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and dullness to percussion on physical examination. Empyema represents a purulent collection within the pleural cavity, often complicating bacterial pneumonia and necessitating drainage via thoracentesis or chest tube placement. Lung abscesses manifest as circumscribed cavities containing necrotic debris and pus within the lung parenchyma, triggered by persistent fever, productive cough, and hemoptysis. Respiratory failure ensues from impaired gas exchange and alveolar hypoventilation, caused by worsening hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and respiratory acidosis, necessitating mechanical ventilation and intensive care support. Septic shock represents a life-threatening complication of severe pneumonia, characterized by systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and end-organ dysfunction, requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. ARDS denotes a severe form of acute lung injury, characterized by diffuse alveolar damage, refractory hypoxemia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, necessitating lung-protective ventilation and supportive care in the intensive care unit (ICU). The occurrence of complications portends a poor prognosis and underscores the need for early recognition and intervention to mitigate adverse outcomes.
Preventive Measures

Preventing pneumonia entails a broad approach encompassing vaccination, infection control measures, and health promotion strategies aimed at reducing the risk of respiratory infections and their sequelae. Vaccination stands as a cornerstone of pneumonia prevention, targeting common bacterial and viral pathogens implicated in pneumonia pathogenesis. Vaccines such as the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) confer protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae, the leading bacterial cause of pneumonia, particularly in high-risk populations such as young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals. Influenza vaccination remains paramount in mitigating influenza-associated pneumonia and reducing disease transmission, underscoring the importance of annual vaccination campaigns targeting vulnerable populations. Additionally, adherence to infection control measures, including hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and environmental sanitation, plays a pivotal role in reducing the spread of respiratory pathogens in healthcare settings and the community at large. Health promotion efforts aimed at smoking cessation, optimizing nutrition, and addressing underlying comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and immunodeficiency bolster immune resilience and mitigate pneumonia risk. Furthermore, early identification and management of predisposing factors such as malnutrition, homelessness, and overcrowded living conditions attenuate pneumonia susceptibility and enhance overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pneumonia emerges as a formidable respiratory infection, posing significant challenges to global public health. Its diverse etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, treatment modalities, complications, and preventive measures underscore the nature of pneumonia management. Timely recognition and intervention are imperative in mitigating the morbidity and mortality associated with pneumonia, necessitating a collaborative approach among healthcare providers, public health authorities, and policymakers. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of pneumonia’s manifest and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can strive towards reducing its burden and improving patient outcomes. Through ongoing research, education, and advocacy efforts, we can envision a future where pneumonia-related morbidity and mortality are substantially diminished, paving the way for enhanced respiratory health and well-being worldwide.
In managing pneumonia, compassion, empathy, and a holistic approach are essential alongside clinical expertise. Striving for excellence in knowledge and practice allows us to enhance respiratory medicine and patient outcomes.
As we address pneumonia and broader cardiovascular health complexities, let’s remain committed to optimal patient care. Together, we can impact lives positively and foster a healthier future.
Email expertassignment46@gmail.com to discover how we can support your academic and professional goals. Wishing you ongoing success in your medical journey.
Digestive System

The digestive system is a marvel of biological engineering, orchestrating the journey of food through the body, from the moment it enters the mouth to its exit through the anus. This complex process involves a network of organs, each playing a crucial role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. In this detailed exploration, we delve into the anatomy, functions, common conditions, care practices, and the importance of seeking medical attention for digestive system issues.
Anatomy of the Digestive System
Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract:
1.Mouth:
Initiating Digestion: Salivary glands activate as the sight and scent of food trigger the digestive process.
Chewing and Mixing: Food is chewed into digestible pieces, mixed with saliva to facilitate breakdown.
Swallowing: The tongue propels the food into the throat and esophagus.
2. Esophagus:
Transportation: A muscular tube conducting food to the stomach through peristalsis.
Sphincter Function: The lower esophageal sphincter relaxes to allow food entry and contracts to prevent stomach content reflux.
3.Stomach:
Container and Mixer: A hollow organ holding and mixing food with stomach enzymes for further breakdown.
Acid Secretion: Cells in the stomach lining secrete powerful acids and enzymes crucial for digestion.
Release to Small Intestine: Processed stomach contents move to the small intestine for further digestion.
4.Small Intestine:
Segments and Functions: Comprising the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, each segment has distinct roles in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Enzymatic Breakdown: Pancreatic enzymes and bile from the liver aid in breaking down food.
Nutrient Absorption: The jejunum and ileum absorb nutrients into the bloodstream.
Consistency Changes: Contents transition from semi-solid to liquid as water, bile, enzymes, and mucus contribute to the process.
Biliary System:
a. pancreas:
Enzyme Secretion: Releases digestive enzymes into the duodenum to break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Insulin Production: The pancreas produces insulin, a key hormone for sugar metabolism.
b. Liver:
Nutrient Processing: Processes nutrients absorbed by the small intestine.
Bile Production: Secretes bile into the small intestine, aiding in fat digestion and vitamin absorption.
Detoxification: Acts as the body’s chemical “factory,” detoxifying harmful substances.
c. Gallbladder:
Bile Storage: Stores and concentrates bile from the liver.
Release into Duodenum: Releases bile into the duodenum to assist in fat absorption.
Large Intestine (Colon):
Colon:
Waste Processing: Responsible for transforming waste into a convenient form for bowel movements.
Peristalsis: Propels stool through the colon, removing water and transitioning it from a liquid to a solid state.
Storage and Elimination: Stool is stored in the sigmoid colon until mass movements propel it into the rectum for elimination.
Rectum:
Chamber Function: A straight chamber connecting the colon to the anus.
Signaling and Holding: Signals the brain about stool presence and holds stool until evacuation.
Anus:
Final Elimination: The last part of the digestive tract, consisting of pelvic floor muscles and sphincters.
Sphincter Control: Surrounding sphincter muscles control stool release, preventing involuntary bowel movements.
Conditions and Disorders
Digestive system health can be affected by a spectrum of conditions, ranging from temporary issues to chronic diseases:
Temporary Conditions:
Constipation:
Frequency and Characteristics: Reduced bowel movements with dry and hard stool.
Difficulty and Pain: Straining during bowel movements, leading to discomfort.
2.Diarrhea:
Loose and Watery Stool: Abnormal stool consistency often caused by various factors.
Potential Causes: Bacterial infections, dietary issues, or unknown triggers.
3.Heartburn:
Misleading Name: Despite the name, heartburn is a digestive issue.
Acidic Backflow: Occurs when stomach acids move up the esophagus, causing discomfort in the chest.
4.Hemorrhoids:
Swollen Veins: Enlarged veins inside and outside the anus and rectum.
Symptoms: Pain, discomfort, and rectal bleeding.
5.Stomach Flu (Gastroenteritis):
Viral Infection: Infection of the stomach and upper part of the small intestine.
Duration: Typically lasts less than a week.
6.Ulcers:
Sore Development: Sores on the lining of the esophagus, stomach, or small intestine.
Causes: Helicobacter pylori infection and prolonged use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
7.Gallstones:
Solid Material Formation: Small pieces formed from digestive fluid in the gallbladder.
Chronic Diseases:
GERD (Chronic Acid Reflux):
Frequent Acid Backflow: Acid-containing contents in the stomach frequently leak into the esophagus.
Symptoms: Persistent heartburn and regurgitation.
2,Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
Colon Muscle Dysfunction: Irregular contractions leading to excessive gas, abdominal pain, and cramps.
Chronic Nature: A long-term condition affecting bowel function.
3.Lactose Intolerance:
Inability to Digest Lactose: Results in digestive discomfort after consuming milk and dairy products.
Common Symptoms: Bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
4.Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis:
Colon Pockets Formation: Diverticula (pockets) in the wall of the colon.
Complications: Inflammation (diverticulitis) can occur, causing pain and infection.
5.Gastrointestinal (GI) Cancers:
Tissue and Organ Affliction: Cancers affecting the digestive system, including esophageal, gastric, colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers.
6.Crohn’s Disease:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A lifelong condition causing inflammation in the digestive tract.
7.Celiac Disease:
Autoimmune Disorder: Gluten consumption damages the small intestine.
Trigger: Found in wheat, barley, and rye.
Care Practices for Digestive Health
Maintaining a healthy digestive system involves adopting proactive lifestyle and dietary habits:
1.Hydration:
Importance of Water: Drinking water facilitates smooth food flow, preventing dehydration-related constipation.
Dehydration Consequences: Insufficient water intake can lead to dry and hard stool.
2.Fiber-Rich Diet:
Benefits of Fiber: Supports digestion and regular bowel movements.
Soluble and Insoluble Fiber: Both types contribute to digestive health.
3.Balanced Nutrition:
Fruits and Vegetables: Multiple servings daily for essential vitamins and minerals.
Whole Grains: Choosing whole grains over processed grains.
Limiting Processed Foods: Reducing intake of processed and sugary foods.
4.Probiotics:
Role of Probiotics: Supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
Post-Antibiotic Use: Especially beneficial after antibiotic treatments.
5.Mindful Eating:
Chewing and Digestion: Thorough chewing aids in proper digestion.
Eating Pace: Slower eating allows the body to signal fullness.
6.Physical Activity:
Exercise and Digestion: Physical activity and gravity aid in moving food through the digestive system.
Post-Meal Walks: Taking a walk after meals can enhance digestion.
7.Avoiding Harmful Habits:
Alcohol and Smoking: Limiting alcohol intake to prevent acid-related issues.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking improves digestive symptoms.
8.Stress Management:
Stress and Digestive Issues: Association between stress and conditions like constipation, diarrhea, and IBS.
Stress Reduction Techniques: Incorporating stress-relief practices into daily life.
Seeking Medical Attention
While occasional digestive issues are common, persistent symptoms warrant attention:
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider:
Frequent Symptoms: Constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, excessive gas, or heartburn.
Potential Underlying Issues: Frequent occurrences may indicate a more serious digestive system problem.
2.Importance of Medical Evaluation:
Diagnostic Assessment: Identifying the cause of persistent symptoms.
Early Intervention: Timely treatment prevents potential complications.
3.Collaborative Approach:
Healthcare Professional Guidance: Seeking advice on managing and preventing digestive issues.
Individualized Care: Tailoring interventions based on the individual’s health status and conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the details of the digestive system provides a foundation for promoting digestive health. The collaboration of organs in the GI tract and the biliary system highlights the complexity of the digestive process. Awareness of common conditions, care practices, and the significance of seeking medical attention empowers individuals to prioritize their digestive well-being. Adopting a holistic approach that combines a healthy lifestyle, balanced nutrition, and regular medical check-ups ensures a resilient and well-functioning digestive system, contributing to overall health and vitality.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help;
Email us on;
williamsliason@outlook.com
How to Write a Case Study

The case study indulges into the ideal process of rehabilitating a semi-professional cyclist who underwent a traumatic transfemoral amputation due to a road traffic accident. This comprehensive analysis aims to shed light on the complexities of limb loss rehabilitation, emphasizing the importance of tailored interventions and evidence-based practice in optimizing outcomes for individuals facing similar challenges.
Client Characteristics

In this section, a detailed exploration of the patient’s background, lifestyle, and medical history provides crucial insights into his unique rehabilitation needs. Emphasis is placed on the impact of the accident on the patient’s physical and psychological well-being, as well as his aspirations for returning to an active lifestyle post-amputation.
The patient, a previously healthy 24-year-old male, was actively engaged in semi-professional cycling and held a physically demanding job at a bicycle shop. The road traffic accident resulted in a traumatic transfemoral amputation, significantly altering his physical capabilities and emotional state. His aspirations to return to his previous level of physical activity underscore the importance of addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of his rehabilitation journey.
Examination Findings
A thorough examination is conducted to assess the patient’s physical condition and identify areas of impairment resulting from the amputation. Objective measurements, including strength assessments and gait analysis, complement subjective reports of phantom limb pain and functional limitations, forming the basis for the subsequent formulation of a clinical hypothesis.
The examination reveals significant impairments in strength and mobility, as well as the presence of phantom limb pain, which negatively impacts the patient’s daily life and rehabilitation progress. These findings highlight the need for a comprehensive treatment approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the patient’s condition.
Clinical Hypothesis/Impression

Drawing on current research and clinical expertise, the clinical hypothesis focuses on addressing the patient’s complex pain experience and psychological distress following the amputation. The identification of neuropathic pain mechanisms and the potential efficacy of interventions such as mirror therapy and mental imagery inform the development of a tailored treatment plan aimed at promoting pain relief and enhancing functional recovery.
The clinical hypothesis highlights the importance of addressing the underlying causes of the patient’s pain and implementing evidence-based interventions to optimize his rehabilitation outcomes. By targeting both the physical and psychological aspects of his condition, the treatment plan aims to improve the patient’s overall quality of life and facilitate his successful return to daily activities.
Intervention
The intervention plan is majorly crafted to address the patient’s unique rehabilitation goals and challenges. A multi-disciplinary approach, incorporating pharmacological interventions, prosthetic care, and psychological support, is implemented to optimize outcomes and empower the patient in his journey towards recovery. Detailed descriptions of specific treatment modalities and their rationale are provided, highlighting the importance of individualized care and ongoing monitoring throughout the rehabilitation process.
The intervention plan includes a combination of pharmacological management, prosthetic fitting and training, and psychological support to address the patient’s physical and psychological needs. Each component of the plan is tailored to the patient’s specific goals and challenges, with regular monitoring and adjustments made to ensure optimal outcomes.
Outcome
Objective measures are used to track the patient’s progress and evaluate the effectiveness of the intervention plan. Significant improvements in pain management, functional mobility, and quality of life are observed over the course of treatment, with particular emphasis on the transformative impact of mirror therapy on the patient’s pain experience and overall well-being. The importance of ongoing follow-up and support is emphasized as integral to maintaining long-term gains and facilitating the patient’s successful reintegration into daily activities.
The patient demonstrates significant improvements in pain management, functional mobility, and overall quality of life following the implementation of the intervention plan. Objective measures, including pain intensity ratings and functional assessments, demonstrate tangible improvements in the patient’s physical and psychological well-being, highlighting the effectiveness of the multi-disciplinary approach employed in his rehabilitation.
Discussion
A comprehensive discussion examines the broader implications of the case study for physiotherapy practice, highlighting the importance of holistic rehabilitation approaches that address the complex interplay of physical, psychological, and social factors in individuals with limb loss. Key lessons learned from the case study, including the value of evidence-based practice and the need for ongoing collaboration between healthcare professionals, are discussed in relation to optimizing outcomes and promoting patient-centered care.
The discussion explores the broader implications of the case study for physiotherapy practice, emphasizing the importance of adopting a holistic approach to rehabilitation that addresses the complex needs of individuals with limb loss. By integrating evidence-based interventions and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, healthcare professionals can enhance the effectiveness of rehabilitation interventions and improve outcomes for patients with limb loss.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the extended case study provides a detailed exploration of the rehabilitation journey of a semi-professional cyclist following a traumatic limb amputation. Through a comprehensive analysis of client characteristics, examination findings, intervention strategies, and outcomes, valuable insights are gained into the complexities of limb loss rehabilitation and the importance of personalized, evidence-based care in achieving optimal outcomes for individuals facing similar challenges.
The case study underscores the importance of adopting a holistic approach to rehabilitation that addresses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of limb loss by focusing on interventions to the unique needs of each patient and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, healthcare professionals can optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for individuals with limb loss.
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at expertassignment46@gmail.com and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
Osteoporosis in Aging

Introduction
Osteoporosis, a progressive skeletal disorder characterized by reduced bone mass and deteriorating bone quality, poses significant health challenges, especially among the aging population. This discussion involves dynamics of bone health, the factors contributing to osteoporosis, and proactive measures individuals can adopt to protect and strengthen their bones as they age.
1.Understanding Bone Structure and Dynamics
Bones, seemingly solid, have an internal honeycomb-like structure. This structural framework undergoes constant remodeling, with cells building new bone tissue while others dissolve existing bone to release essential minerals. As individuals age, this delicate balance shifts, resulting in a gradual loss of bone density and an increased susceptibility to fractures.
2.Prevalence and Impact of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a widespread concern, affecting over 10 million people nationwide. Its consequences, particularly in Adults, extend beyond fractures, leading to a variety of issues such as disability and loss of dependence. The vulnerability of specific areas, including the;
hips, wrists, and spine, underscores the importance of understanding and addressing this condition.
3.Hormonal Influence and Screening
Estrogen, a crucial hormone, plays a major role in bone formation and regeneration. Postmenopausal women, experiencing a decline in estrogen levels, face a high risk of an increased bone loss. Regular screening, typically recommended for women aged 65 and older, involves non-invasive tests like;
Bone density scan(DXA), measuring bone mineral density. A total score of -2.5 or lower is indicative of osteoporosis.
4.Nutritional Factors
The role of nutrition in maintaining bone health cannot be overstated. Calcium, an essential mineral for bone strength and formation, is obtainable from various dietary sources such as, dairy products and leafy greens. Vitamin D, facilitating calcium absorption, becomes increasingly critical with age. This emphasizes the importance of adequate nutrient intake, either through dietary means or supplements. Specific daily calcium requirements for women over 50 and men over 70 are outlined.
5.Exercise as a Protective Measure
Physical activity, especially weight-bearing exercises like jogging, walking, tennis, and dancing, significantly contributes to bone health. These exercises serve as signals to bone cells, promoting density and reducing the risk of fractures. Conversely, lifestyle choices such as smoking and heavy drinking weaken bones, while certain medications may increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Medical Interventions and Future Prospects
Medical interventions, including medications like bisphosphonates, are commonly prescribed to combat bone loss. Ongoing research is exploring drugs aimed at stimulating bone growth, with parathyroid hormone being a current option. The article discusses the potential of these interventions and highlights the importance of timely medical advice and interventions, even after an osteoporosis diagnosis, to positively impact bone health.
Fall Prevention and Fracture Avoidance
More than 2 million fragility fractures occur annually due to falls, highlighting the need for a comprehensive approach to bone health. Combining efforts to enhance bone strength with fall prevention strategies is crucial. Factors such as balance, environmental hazards, and the type of fall play significant roles in fracture risk. The discussion underscores the effectiveness of exercises that improve balance and coordination, such as slow intentional movement in preventing fractures.
Conclusion
Maintaining optimal bone health is a course that involves a combination of nutrition, exercise, and proactive healthcare measures. Given the critical impact of osteoporosis on aging populations, raising awareness and implementing early intervention strategies are paramount. This comprehensive approach empowers individuals to foresee the risks associated with osteoporosis, ensuring a resilient and active lifestyle in their later years. The discussion concludes by encouraging individuals concerned about their bone health to engage or consult with their healthcare specialists, pressing on the importance of personalized guidance and bone density testing for proactive management.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help;
Email us at;
williamsliason@outlook.com