What Is The Process Of Sleep?
What is The Process Of Sleep?

Introduction
Sleep is a complex physiological process that encompasses more than merely closing one’s eyes and drifting into unconsciousness. It is an active state of unconsciousness in which the brain, while relatively at rest, remains responsive primarily to internal stimuli. Despite extensive research, the precise purpose of sleep remains incompletely understood. Several prominent theories attempt to elaborate the purpose of sleep, including the Inactivity Theory, Energy Conservation Theory, Restoration Theory, and Brain Plasticity Theory.
Inactivity Theory involves that inactivity during nighttime reduces the risk of predation, offering an evolutionary advantage. This theory suggests that creatures that remained inactive during the night were less likely to fall victim to predators, thereby enhancing survival and reproductive success.
Energy Conservation Theory proposes that the primary function of sleep is to decrease energy demand during periods when it is less efficient to procure food, supported by evidence of a 10% reduction in metabolism during sleep. This theory aligns with the observation that many species exhibit lower metabolic rates during sleep, thereby conserving energy.
Restorative Theory asserts that sleep facilitates the repair and replenishment of cellular components, as evidenced by processes such as muscle repair, tissue growth, protein synthesis, and hormone release occurring predominantly during sleep. This theory is supported by findings that various restorative functions are activated during sleep, promoting physical health and well-being.
Brain Plasticity Theory suggests that sleep is essential for neural reorganization and brain development, particularly in infants and children who require extensive sleep. This theory underscores the role of sleep in cognitive functions, learning, and memory consolidation.
These theories collectively indicate that sleep serves multiple functions, and a combination of these concepts likely explains the necessity of sleep.
Function

Sleep follows a cyclical pattern, alternating between two major phases: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep is subdivided into stages 1 through 3, each representing different depths of sleep characterized by unique brain wave patterns, muscle tone, and eye movement patterns. NREM sleep comprises approximately 75–80% of total sleep time, while REM sleep accounts for the remaining 20–25%.
The sleep cycle begins with a short NREM stage 1 phase, progresses through NREM stages 2 and 3, and culminates in REM sleep. This cycle repeats throughout the night, with initial cycles lasting 70–100 minutes and subsequent cycles 90–120 minutes. As the night progresses, the duration of REM sleep increases, eventually comprising up to 30% of the sleep cycle later in the night. Typically, an individual undergoes 4 to 5 sleep cycles per night.
NREM Stage 1: A shallow sleep stage lasting 1–7 minutes, characterized by rhythmical alpha waves (8–13 Hz). This stage represents the transition from wakefulness to sleep, during which the individual can be easily awakened.
NREM Stage 2: A deeper sleep state lasting 10–25 minutes initially, progressing to encompass 50% of the total sleep cycle. EEG recordings during this stage show sleep spindles and K-complexes. Memory consolidation is believed to occur primarily in this stage.
NREM Stage 3: Lasting 20–40 minutes initially, characterized by high-voltage, slow-wave frequency on EEG. This stage, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), is crucial for restorative processes.
REM Sleep: Responsible for dreaming, characterized by muscle paralysis (except for the extraocular muscles) and sawtooth waveforms on EEG. REM sleep involves increased brain activity and is essential for cognitive functions such as learning, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation.
Mechanism

The regulation of sleep involves a delicate balance between homeostatic processes and circadian rhythms.
a) Homeostatic Processes
These processes reflect the body’s need for sleep, increasing the pressure to sleep the longer one stays awake. Sleep generation is initiated within the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO) of the anterior hypothalamus, which inhibits arousal regions in the brain, including the tuberomammillary nucleus, lateral hypothalamus, locus coeruleus, dorsal raphe, laterodorsally segmental nucleus. Hypocretin (orexin) neurons in the lateral hypothalamus facilitate this process synergistically.
b) Circadian Rhythm
The circadian rhythm, or the internal body clock, regulates the sleep-wake cycle and is influenced by light levels detected by the retina. The hypothalamus, particularly the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN),initiates this rhythm. Melatonin, produced by the pineal gland, modulates the circadian rhythm, with levels peaking at night and decreasing during the day. The circadian rhythm typically spans approximately 24.2 hours, and variations in body temperature also play a role, with lower temperatures in the morning and higher temperatures in the evening.
NREM sleep involves a functional disconnection between the brain stem, thalamus, and cortex, maintained by hyperpolarizing GABA neurons. During this phase, corticothalamic neurons signal the thalamus, causing hyperpolarization of thalamic reticular neurons, resulting in delta waves from both thalamic reticular and cortical pyramidal sources.
REM sleep is generated by “REM-on neurons” in the mesencephalic and pontine cholinergic neurons. The pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus and lateral dorsal tegmental neurons trigger desynchronized cortical waveforms. The tonic component of REM sleep is parasympathetically mediated, while the phasic component is sympathetically mediated.
Related Testing
Polysomnography is the primary modality used to study sleep. It is a comprehensive test that includes an electrocardiogram (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), electrooculography (EOG), electromyography (EMG), and oxygen saturation monitoring.
ECG: Measures the electrical activity of the heart to detect cardiac anomalies such as arrhythmias.
EEG: Non-invasively records brain wave activity to determine sleep stages and detect neurological abnormalities.
EOG: Measures eye movements to differentiate between NREM and REM sleep.
EMG: Assesses muscle activity, particularly in the respiratory muscles and peripheral limbs, to detect excessive movement or muscle tension during sleep.
Oxygen Saturation: Monitors respiratory function to ensure adequate oxygenation during sleep.
Clinical Significance

a) .Insomnia
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep and is the most common sleep disorder. It is often related to psychological stressors, poor sleep environments, irregular sleep schedules, or excessive mental, physical, or chemical stimulation. Treatment typically involves cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), sleep hygiene practices, and, in some cases, pharmacological interventions.
b) .Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
OSA is marked by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep due to airway obstruction, often caused by obesity or weak pharyngeal muscles. This condition leads to hypoxia and frequent awakenings, preventing restful sleep. OSA is classified into mild, moderate, and severe based on the frequency of apneic episodes per hour. Treatment options include Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) therapy, mandibular advancement devices, and surgical interventions such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, adenotonsillectomy, and maxillomandibular advancement.
c) .Central Sleep Apnea
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) results from a failure in the central respiratory drive, leading to diminished breathing effort during sleep. Conditions such as congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (Ondine’s curse) or congestive heart failure can cause CSA. Treatment includes CPAP, BiPAP, Adaptive-servo-ventilation, and medications like acetazolamide or theophylline.
d) .Mixed Sleep Apnea
Mixed Sleep Apnea, also known as Complex Sleep Apnea, involves symptoms of both OSA and CSA. This condition typically manifests when patients with OSA develop CSA symptoms upon treatment with CPAP. Treatment often involves low-pressure CPAP therapy.
d) .Ghrelin-Leptin Abnormalities
Sleep duration significantly influences hunger-regulating hormones, with reduced sleep linked to lower levels of leptin and higher levels of ghrelin. Leptin, produced by adipose cells, inhibits hunger, while ghrelin, produced in the gastrointestinal tract, stimulates appetite. Imbalances in these hormones due to inadequate sleep can increase appetite and contribute to higher body mass index (BMI), potentially leading to obesity. This phenomenon is particularly relevant in patients with OSA, where increased BMI is a risk factor.
e) .Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is characterized by a loss of orexin (hypocretin) neurons, leading to unstable transitions between sleep and wakefulness. Symptoms include excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, sleep paralysis, and hypnagogic hallucinations. Narcolepsy type 1 involves a significant loss of orexin neurons, while type 2 is less severe. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with medications such as stimulants, sodium oxybate, and selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs and SNRIs), along with lifestyle modifications.
f) .Somnambulism (Sleepwalking)
Somnambulism, or sleepwalking, involves performing activities while in a state of combined sleep and wakefulness. Sleepwalking is associated with increased slow-wave sleep and sleep deprivation, and there is evidence of a genetic predisposition. Treatment includes ensuring a safe sleep environment, improving sleep hygiene, and, in some cases, pharmacological interventions such as benzodiazepines.
Conclusion
Sleep is a physiological process essential for various bodily functions, including energy conservation, cellular repair, brain development, and cognitive function. The precise mechanisms and purposes of sleep remain areas of active research. Understanding the complexities of sleep and its disorders is crucial for promoting overall health and addressing various medical conditions. Ongoing research aims to fully understand the mechanisms of sleep and its broad implications for human health..
Navigating the rigorous demands of medical studies requires support and collaboration. Whether you’re a nursing student, medical doctor, clinical student, pharmacist, or any other medical practitioner, don’t hesitate to seek assistance. Utilize available resources and value teamwork and mentorship.
For personalized support, expert advice, and comprehensive resources, contact Expert Academic Assignment Help at expertassignment46@gmail.com With the right support and dedication, you can achieve your goals and make significant contributions to healthcare.
More Posts from Expertacademicassignmenthelp and Others
Cardiovascular System

The cardiovascular system, an intricate symphony of physiological marvels, stands as the linchpin of human existence. Woven intricately with the tapestry of life, it encompasses the heart, the rhythmic conductor, and a sprawling network of blood vessels navigating the human terrain. As we embark on this comprehensive expedition, our journey aims to unearth the multifaceted dimensions of the cardiovascular system, unraveling its nuanced functions, delving deep into its anatomical complexities, scrutinizing the spectrum of conditions it contends with, and exploring the exhaustive care practices imperative for the perpetual maintenance of its optimal health.
Overview and Function:
At the epicenter of biological vitality, the cardiovascular system unfurls its canvas, orchestrating a perpetual ballet of life-sustaining processes. Beyond the rudimentary task of blood transportation, this intricate network emerges as a dynamic conduit, ensuring the orchestrated delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and the expeditious removal of metabolic waste. The heart, a majestic organ with chambers that mirror the elegance of a grand ballroom, takes center stage, propelling nearly 2,000 volume of litters of life-essential fluid through the intricate channels of 1. Arteries, 2. veins, and 3. capillaries on a daily basis.
Anatomy:
Positioned majestically in the anatomical Centre of the chest, the heart assumes the role of the epicenter of the cardiovascular narrative. Intricately interwoven with blood vessels that traverse the entirety of the corporeal landscape, these conduits form a sophisticated network, ensuring the pervasive reach of oxygen, nutrients, and the removal of cellular detritus. This anatomical choreography mimics the intricate networks of water or sewer pipes, with large arteries and veins akin to main conduits beneath city streets, branching into diminishing tributaries that eventually culminate in microscopic capillaries facilitating the exchange of life’s essentials between blood and tissue cells.
Conditions and Disorders:
The robust fortitude of the cardiovascular system is not immune to the challenges posed by a diverse spectrum of conditions, frequently manifesting as impediments within the intricate vascular highways. These afflictions, akin to tempests in the circulatory teacup, include
1.Arrhythmia
2. myocardial infarction
3.malfunctioning heart valves
4.heart failure
5.Aneurysms
6.Strokes
7.Atherosclerosis
and an assortment of vascular abnormalities. The discernment of early warning signs, whether it be the thunderous symphony of chest pain, the breathless crescendo of shortness of breath, or the subtle nuances indicative of strokes, becomes the harbinger of timely intervention and meticulous management.
Tests and Treatments:
Within the echelons of cardiovascular health, the diagnostic arsenal assumes the mantle of an indispensable compass, navigating the terrain of system functionality. A cacophony of tests, including electrocardiograms capturing the heart’s melodic rhythm, blood tests unveiling biochemical orchestrations, echocardiograms crafting visual symphonies of the heart’s dynamics, and advanced imaging techniques such as cardiac CT and MRI, paints a comprehensive portrait of cardiovascular vitality. Treatments, akin to a therapeutic sonnet, are tailored with precision, embracing an expansive repertoire ranging from medical procedures like angioplasty, intricate surgeries addressing valvular intricacies, and the artistry of medication and lifestyle adjustments woven into the fabric of holistic care.
As we draw the curtains on this extensive odyssey through the labyrinthine landscapes of the cardiovascular system, the indomitable resilience of this physiological magnum opus comes to light. To comprehend its functions, to marvel at its anatomical symphony, and to acknowledge the variegated conditions it faces is to wield the reins of self-empowerment over cardiovascular well-being. In the realm of proactive health, the pillars of regular exercise, judicious blood pressure control, adherence to a heart-attuned diet, and the harmonious cadence of lifestyle adjustments stand as bulwarks fortifying the citadel of the heart and blood vessels. As we traverse this expansive exploration, let us not merely scrutinize but marvel at the complexity of the cardiovascular system, embracing the mantle of stewardship bestowed upon us to foster enduring health, vitality, and the pulsating rhythm of life itself.
The cardiovascular system, an intricate symphony of physiological marvels, stands as the linchpin of human existence. Woven intricately with the tapestry of life, it encompasses the heart, the rhythmic conductor, and a sprawling network of blood vessels navigating the human terrain. As we embark on this comprehensive expedition, our journey aims to unearth the multifaceted dimensions of the cardiovascular system, unraveling its nuanced functions, delving deep into its anatomical complexities, scrutinizing the spectrum of conditions it contends with, and exploring the exhaustive care practices imperative for the perpetual maintenance of its optimal health.
Overview and Function:
At the epicenter of biological vitality, the cardiovascular system unfurls its canvas, orchestrating a perpetual ballet of life-sustaining processes. Beyond the rudimentary task of blood transportation, this intricate network emerges as a dynamic conduit, ensuring the orchestrated delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and the expeditious removal of metabolic waste. The heart, a majestic organ with chambers that mirror the elegance of a grand ballroom, takes center stage, propelling nearly 2,000 volume of litters of life-essential fluid through the intricate channels of 1. Arteries, 2. veins, and 3. capillaries on a daily basis.
Anatomy:
Positioned majestically in the anatomical Centre of the chest, the heart assumes the role of the epicenter of the cardiovascular narrative. Intricately interwoven with blood vessels that traverse the entirety of the corporeal landscape, these conduits form a sophisticated network, ensuring the pervasive reach of oxygen, nutrients, and the removal of cellular detritus. This anatomical choreography mimics the intricate networks of water or sewer pipes, with large arteries and veins akin to main conduits beneath city streets, branching into diminishing tributaries that eventually culminate in microscopic capillaries facilitating the exchange of life’s essentials between blood and tissue cells.
Conditions and Disorders:
The robust fortitude of the cardiovascular system is not immune to the challenges posed by a diverse spectrum of conditions, frequently manifesting as impediments within the intricate vascular highways. These afflictions, akin to tempests in the circulatory teacup, include
1.Arrhythmia
2. myocardial infarction
3.malfunctioning heart valves
4.heart failure
5.Aneurysms
6.Strokes
7.Atherosclerosis
and an assortment of vascular abnormalities. The discernment of early warning signs, whether it be the thunderous symphony of chest pain, the breathless crescendo of shortness of breath, or the subtle nuances indicative of strokes, becomes the harbinger of timely intervention and meticulous management.
Tests and Treatments:
Within the echelons of cardiovascular health, the diagnostic arsenal assumes the mantle of an indispensable compass, navigating the terrain of system functionality. A cacophony of tests, including electrocardiograms capturing the heart’s melodic rhythm, blood tests unveiling biochemical orchestrations, echocardiograms crafting visual symphonies of the heart’s dynamics, and advanced imaging techniques such as cardiac CT and MRI, paints a comprehensive portrait of cardiovascular vitality. Treatments, akin to a therapeutic sonnet, are tailored with precision, embracing an expansive repertoire ranging from medical procedures like angioplasty, intricate surgeries addressing valvular intricacies, and the artistry of medication and lifestyle adjustments woven into the fabric of holistic care.
As we draw the curtains on this extensive odyssey through the labyrinthine landscapes of the cardiovascular system, the indomitable resilience of this physiological magnum opus comes to light. To comprehend its functions, to marvel at its anatomical symphony, and to acknowledge the variegated conditions it faces is to wield the reins of self-empowerment over cardiovascular well-being. In the realm of proactive health, the pillars of regular exercise, judicious blood pressure control, adherence to a heart-attuned diet, and the harmonious cadence of lifestyle adjustments stand as bulwarks fortifying the citadel of the heart and blood vessels. As we traverse this expansive exploration, let us not merely scrutinize but marvel at the complexity of the cardiovascular system, embracing the mantle of stewardship bestowed upon us to foster enduring health, vitality, and the pulsating rhythm of life itself.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help;
Email us at; williamsliason@outlook.com
Human musculoskeletal system.

Human musculoskeletal system, often referred to as the locomotor system, is a complex and integral component of human anatomy, enabling movement and providing structural support to the body. Comprising bones, muscles, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and other connective tissues, this intricate system plays a crucial role in maintaining form, stability, and mobility. This comprehensive article aims to explore the various components and functions of the musculoskeletal system, addressing the nuanced interplay between bones, muscles, and joints. Additionally, it delves into the classification of bones, the functions of the skeletal system, the role of muscles in movement, and the clinical significance of this system. Understanding the musculoskeletal system is fundamental to appreciating its profound significance in human anatomy and physiology.
The Skeletal System:
At the core of the musculoskeletal system lies the skeletal framework, serving as the foundation for the attachment of tissues and organs. This section provides an in-depth exploration of the skeletal system, elucidating its dynamic structure, classifications of bones, and the critical functions they perform. From supporting the body’s shape to acting as a storage site for essential minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, bones play a multifaceted role. The controversies surrounding the number of bones in the human skeleton are addressed, emphasizing the dynamic nature of the skeletal system, which evolves from birth to maturity.
2.The Muscular System:
The musculoskeletal system’s functionality is inherently intertwined with the muscular system, comprising skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. This section delves into the characteristics and roles of each muscle type, with a particular focus on the conscious control exerted by skeletal muscles. A comprehensive exploration of muscle contraction processes, initiation mechanisms, and the role of tendons in transmitting forces during contractions enriches our understanding of the system’s biomechanics. Recognizing the distinct attributes of cardiac and smooth muscles contributes to a holistic grasp of the musculoskeletal system’s dynamic nature.
3.Joints, Ligaments, and Bursae:
Movement within the musculoskeletal system is facilitated by joints, which connect bones and allow for a diverse range of motions. This section categorizes joints into diarthroses, amphiarthrosis, and synarthroses, elucidating their specific functions. A detailed examination of synovial joints, lubricated by synovial fluid, and the role of ligaments in limiting dislocation and controlling movement enhances our comprehension of joint dynamics. The significance of bursae, fluid-filled sacs providing cushioning around joints, is explored, emphasizing their role in minimizing friction and supporting efficient movement.
Clinical Significance:
The musculoskeletal system’s clinical significance extends to its susceptibility to disorders, impacting overall health. Diseases affecting this system can manifest as functional disorders, motion discrepancies, or complications arising from disorders in other body systems. This section explores the intricacies of musculoskeletal disorders, acknowledging the interconnections with the vascular, nervous, and integumentary systems that contribute to diagnostic challenges. Articular disorders are prevalent, but the musculoskeletal system is also affected by muscular diseases, neurologic deficits, toxins, endocrine abnormalities, metabolic disorders, infectious diseases, blood and vascular disorders, and nutritional imbalances. An exploration of inpatient procedures involving musculoskeletal interventions underscores the clinical importance of this system.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the human musculoskeletal system stands as a marvel of biological engineering, orchestrating movement, providing support, and safeguarding vital organs. This comprehensive exploration, spanning bones, muscles, joints, and clinical significance, highlights the intricate interplay of various components that contribute to the system’s overall functionality. Despite the challenges posed by disorders and diseases, advancements in medical science, particularly in fields like rheumatology and orthopedic surgery, continue to enhance our understanding and treatment of musculoskeletal issues. Recognizing the complexity and clinical significance of this system is crucial for healthcare professionals in providing comprehensive care. As we delve deeper into the intricacies of the human body, the musculoskeletal system stands as a testament to the harmonious coordination of various components for the fundamental purpose of movement and stability. This expansive exploration serves as a valuable resource for those seeking a profound understanding of the human musculoskeletal system.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help,
email us on, williamsliason@outlook.com
Interesting Nursing Research Topics To Choose

Childhood Nursing
Antibiotics Impact on Childhood Immunities
Antibiotics have revolutionized modern medicine, significantly improving the prognosis for many infectious diseases. However, the impact of antibiotics on childhood immunities is a multifaceted topic that warrants careful examination. While antibiotics target harmful bacteria, they may also affect the delicate balance of the immune system in developing children.
Research could delve into the long-term consequences of antibiotic use during childhood, exploring how it may influence the development of the immune system. Are there specific types of antibiotics that pose greater risks? What role do probiotics play in mitigating the potential negative effects of antibiotics on the immune system? Understanding these dynamics is crucial for optimizing pediatric care and ensuring the long-term health of children.
Effects of Childhood Exposure to Environmental Pollutants
Children are particularly vulnerable to environmental pollutants, and exposure during early life stages can have lasting health implications. Research in this area could focus on specific pollutants, such as air pollutants, heavy metals, or endocrine disruptors, and their impact on children’s health.
Exploring the effects of second-hand smoke inhalation during early life stages is particularly relevant. What are the respiratory and cardiovascular consequences of childhood exposure to second-hand smoke? How does environmental pollution contribute to respiratory conditions in children, and what preventive measures can be implemented?
Ethics of Pediatric Care
The ethical dimensions of pediatric care are intricate, involving considerations of autonomy, beneficence, and justice. Topics within this realm could include ethical dilemmas faced by pediatric nurses, such as decision-making in cases where parental and child interests may conflict.
Research may also explore the ethical implications of emerging technologies in pediatric care. For instance, what are the ethical considerations surrounding genetic testing in children? How can nurses navigate the ethical challenges posed by advances in pediatric treatments and interventions?
Genetic Factors of Diabetes in Children
The increasing prevalence of diabetes in children raises questions about the genetic factors contributing to this trend. Research in this area could delve into the genetic markers associated with pediatric diabetes, exploring the hereditary aspects of the disease.
Understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors is crucial. What role do lifestyle factors play in the manifestation of diabetes in genetically predisposed children? How can nurses incorporate genetic counseling into pediatric diabetes management to empower families with the knowledge needed for preventive strategies?
How Health in Children Can Affect Their Health Later in Life
The concept that early life experiences can shape health outcomes in adulthood is a key area of interest. Research could investigate the link between childhood health and long-term health trajectories. Are there specific childhood health indicators that serve as predictors of adult health issues?
Exploring the mechanisms through which childhood health influences adulthood health can guide nursing interventions. How can nurses promote healthy behaviors in children that have lasting effects on their well-being? What preventive measures can be implemented during childhood to mitigate the risk of chronic diseases in adulthood?
Adult Nursing
Analyzing the Benefits of Collaborative Nursing
Collaborative nursing involves interdisciplinary teamwork to enhance patient care outcomes. Research in this area could explore the benefits of collaborative nursing practices in diverse healthcare settings. What are the positive outcomes associated with collaborative care, such as improved patient satisfaction, reduced hospital readmissions, or enhanced treatment adherence?
Understanding the factors that contribute to successful collaboration is essential. How do effective communication and shared decision-making impact collaborative nursing efforts? What challenges do nurses face in interprofessional collaboration, and how can these challenges be addressed to optimize patient care?
Analyzing the Causes of Depression
Depression is a prevalent mental health concern affecting a significant portion of the adult population. Research into the causes of depression can provide valuable insights into preventive measures and targeted interventions. This could involve exploring the interplay between genetic, environmental, and psychological factors in the development of depression.
Investigating the role of adverse childhood experiences in predisposing individuals to depression in adulthood is a pertinent avenue. How can nurses identify individuals at risk based on early life experiences? What interventions can be implemented to break the cycle of depression rooted in childhood trauma?
Ethics of Data Collection in Adult Health Care
The ethical considerations surrounding data collection in adult health care are paramount, especially in the era of electronic health records and data-driven healthcare. Research could delve into the ethical challenges nurses face in collecting, storing, and utilizing patient data.
Exploring the perspectives of patients regarding data privacy and consent is crucial. How do patients perceive the use of their health data for research purposes? What safeguards can be implemented to ensure ethical data practices in adult health care settings?
Evolution of Nursing in a Specific Time Period
The evolution of nursing over time reflects changes in healthcare practices, societal attitudes, and technological advancements. Research in this area could focus on a specific time period, examining how nursing roles, responsibilities, and education have transformed.
For example, a study could explore the evolution of nursing during a period of significant healthcare reform. What were the key drivers of change, and how did nurses adapt to new models of care? Understanding historical contexts can inform current nursing practices and guide future developments in the profession.
Nonchemical Treatments for Bipolar Disorders
Bipolar disorders present unique challenges in terms of management and treatment. Research into nonchemical treatments for bipolar disorders can provide valuable alternatives or complementary approaches to medication-based interventions.
Exploring the efficacy of psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioral interventions, and lifestyle modifications in managing bipolar disorders is essential. How can nurses incorporate nonchemical treatments into holistic care plans for individuals with bipolar disorders? What role does patient education play in promoting self-management strategies for bipolar conditions?
Midwifery Nursing
Analysis of Caseload and Quality of Care for Underrepresented Groups
Midwives play a crucial role in maternal and infant care, yet disparities in care outcomes persist among underrepresented groups. Research in this area could investigate the caseloads and quality of care provided to women from marginalized communities.
Examining the experiences of midwives in catering to diverse caseloads can provide insights into challenges and opportunities. How do midwives adapt their care approaches to address the unique needs of underrepresented populations? What strategies can be implemented to ensure equitable access to high-quality midwifery care?
Analysis of Childbirth Experiences of Women with Autism
Pregnancy and childbirth can pose unique challenges for women with autism spectrum disorders. Research could explore the childbirth experiences of women with autism, considering factors such as sensory sensitivities, communication preferences, and support needs.
Understanding the specific needs of this population can inform midwifery practices and improve the overall childbirth experience. What adjustments can be made in maternity care settings to accommodate the needs of women with autism? How can midwives collaborate with other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care for pregnant individuals with autism?
Nonchemical Pain Management in Labor
Labor pain is a central aspect of childbirth, and nonchemical pain management approaches are gaining attention. Research in this area could focus on the effectiveness of non-pharmacological pain management methods during labor.
Exploring techniques such as hydrotherapy, massage, acupuncture, and mindfulness can provide valuable insights. How do these nonchemical methods influence pain perception and labor outcomes? What role can midwives play in promoting and facilitating the use of non-pharmacological pain management strategies during childbirth?
Role of Midwifery in Emergency Care
While childbirth is often a natural process, emergencies can arise, requiring swift and effective interventions. Research could investigate the role of midwives in emergency care.
Conclusion
In this expansive discussion, we have explored a variety of nursing research topics across different specializations. Each topic presents unique challenges, opportunities, and areas for further exploration within the field of nursing. Whether focusing on pediatric care, mental health, women’s health, or health care management, the diverse range of topics reflects the major areas to consider.
For further assistance and guidance, link to us on williamsliason@outlook.com
14 Common Lung Diseases

Introduction
Lung diseases represent some of the most severe health threats globally. The rise of industrialization, environmental pollution, and tobacco usage significantly contribute to the prevalence of these diseases. This article, outlines the most common lung diseases, their symptoms, causes, and treatments.
1. Pneumonia

Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other pathogens. It poses a significant risk to the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, and those with chronic conditions but can also affect healthy individuals. Pneumonia can be classified based on the causative agent, such as bacterial pneumonia (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae), viral pneumonia (e.g., influenza virus), or fungal pneumonia (e.g., Pneumocystis jirovecii).
Symptoms
Fever
Cough with sputum
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Sweating and shaking chills
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (less common)
Diagnosis Diagnosis of pneumonia typically involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures. Blood tests may also be conducted to identify the causative agent.
Treatment Depending on the cause, treatments may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia.
Antiviral medications for viral pneumonia.
Antifungal therapies for fungal pneumonia. Supportive care such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and manage pain can also alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to provide intravenous antibiotics, oxygen therapy, or mechanical ventilation.
2. Bronchitis

Bronchitis involves the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. It can be acute, often following colds or the flu, or chronic, usually resulting from smoking or long-term exposure to irritants like pollution or dust.
Symptoms
Persistent cough (productive or dry)
Sputum production (clear, white, yellowish-gray, or green)
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Slight fever and chills
Chest discomfort
Diagnosis Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, where a doctor listens to the patient’s lungs with a stethoscope. Additional tests, such as a chest X-ray, sputum tests, or pulmonary function tests, may be conducted to rule out other conditions like pneumonia or asthma.
Treatment
Acute bronchitis: Symptomatic treatment includes rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers and cough medications. Inhalers or nebulizers may be prescribed to ease breathing.
Chronic bronchitis: Management may involve bronchodilators, steroids, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Smoking cessation and avoiding lung irritants are crucial for treatment.
3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)

COPD is a progressive, irreversible disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways, primarily due to smoking, environmental pollutants, or long-term exposure to respiratory irritants. COPD includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, conditions that often coexist and lead to airflow obstruction.
Symptoms
Chronic cough
Sputum production
Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities
Wheezing
Chest tightness
Frequent respiratory infections
Fatigue
Unintended weight loss (in advanced stages)
Diagnosis COPD is diagnosed through a combination of patient history, physical examination, and spirometry, a test that measures the amount of air a person can exhale and how quickly they can do so. Chest X-rays, CT scans, and arterial blood gas analysis may also be used.
Prevention and Treatment Preventive measures include:
Smoking cessation
Vaccinations (influenza and pneumococcal vaccines)
Reducing exposure to lung irritants
Treatments involves;
Bronchodilators to relax the muscles around the airways
Inhaled steroids to reduce airway inflammation
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs
Oxygen therapy for severe cases
Surgery (e.g., lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplant) in advanced cases
4. Lung Cancer

Lung cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of malignant cells in the lung tissues. Major risk factors include smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, exposure to carcinogens (e.g., asbestos, radon), and genetic predisposition.
Types
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Often linked to heavy smoking, SCLC is aggressive and spreads quickly.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): More common and includes subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Symptoms
Persistent cough
Chest pain
Weight loss
Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
Shortness of breath
Hoarseness
Bone pain (in advanced stages)
Headache (if cancer spreads to the brain)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves imaging tests (chest X-rays, CT scans, PET scans), sputum cytology, and tissue biopsy. Molecular testing may be done to identify specific genetic mutations that can be targeted with specific treatments.
Treatment
Surgery to remove the tumor or part of the lung
Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells
Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors
Targeted drug therapies to attack specific genetic changes in cancer cells
Immunotherapy to help the immune system fight cancer
5. Pleurisy
Pleurisy, or pleuritis, is the inflammation of the pleura, the tissue lining the lungs and chest cavity. It can be caused by infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal), injuries, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), or other underlying conditions.
Symptoms
Sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens with breathing, coughing, or sneezing
Shortness of breath
Cough
Fever (if infection is present)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a physical examination, chest X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans, and blood tests to identify the underlying cause. Thoracentesis, a procedure to remove and analyze pleural fluid, may be performed.
Treatment Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial infections
Antiviral medications for viral infections
Anti-inflammatory medications (e.g., NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
Pain management with medications
Thoracentesis to drain excess fluid from the pleural space
6. Pulmonary Embolism

A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot, usually originating in the legs (deep vein thrombosis), travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow and causing tissue damage. Risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgery, cancer, and certain genetic conditions.
Symptoms
Sudden shortness of breath
Chest pain (may be sharp and worsen with deep breathing or coughing)
Cough (sometimes with bloody sputum)
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Lightheadedness or dizziness
Leg pain or swelling (if DVT is present)
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves imaging tests such as chest X-rays, CT pulmonary angiography, and ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scans. D-dimer blood tests and ultrasound of the legs may also be conducted.
Treatment Immediate treatment includes:
Anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent further clotting
Thrombolytics (clot-dissolving medications) for severe cases
Surgical or catheter-based procedures to remove the clot
Long-term anticoagulation therapy to prevent recurrence
7. Pulmonary Edema

Pulmonary edema is the accumulation of fluid in the lung alveoli, making breathing difficult. It can result from heart failure (cardiogenic pulmonary edema), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), or exposure to high altitudes (non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema).
Symptoms
Difficulty breathing (dyspnea), especially when lying down
Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
Wheezing or gasping for breath
Coughing up frothy, pink-tinged sputum
Excessive sweating
Cyanosis (bluish skin or lips)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves physical examination, chest X-rays, and blood tests. Echocardiography and pulmonary artery catheterization may be used to determine the underlying cause and severity.
Treatment Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause and may include:
Diuretics to remove excess fluid
Medications to improve heart function (for cardiogenic pulmonary edema)
Supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation
Treating underlying conditions such as infections or high altitude exposure
8. Pulmonary Fibrosis

Pulmonary fibrosis is the thickening and scarring of lung tissue, leading to reduced oxygen absorption. Causes include chronic exposure to environmental pollutants, infections, genetic factors, and autoimmune diseases (e.g., scleroderma).
Symptoms
Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
Persistent dry cough
Fatigue
Unexplained weight loss
Aching muscles and joints
Clubbing (widening and rounding) of the fingertips or toes
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, imaging tests (chest X-rays, high-resolution CT scans), pulmonary function tests, and sometimes lung biopsy. Blood tests may be used to identify underlying autoimmune diseases.
Treatment While there is no cure for pulmonary fibrosis, treatments focus on symptom management and slowing progression:
Medications such as pirfenidone and nintedanib to slow disease progression
Oxygen therapy
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Lung transplant in severe cases
9. Pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis is a lung disease caused by inhaling dust particles, such as asbestos, silica, or coal dust, leading to lung scarring. It is a type of occupational lung disease commonly seen in miners, construction workers, and industrial workers.
Symptoms:
Chronic cough
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Progressive loss of lung function
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed occupational history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess the extent of lung damage.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Avoiding further exposure to dust
Medications to manage symptoms, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids
Respiratory therapies
Pulmonary rehabilitation
10. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
PAH is a form of high blood pressure affecting the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart. It can be idiopathic, familial, or associated with other conditions such as connective tissue diseases, congenital heart disease, or chronic liver disease.
Symptoms
Breathing difficulties (dyspnea), especially during physical activities
Dizziness or fainting (syncope)
Chest pain
Fatigue
Swelling in the ankles, legs, and abdomen (edema)
Cyanosis (bluish lips and skin)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves echocardiography, right heart catheterization, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Blood tests and pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess lung and heart function.
Treatment Treatment strategies include:
Medications to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, such as endothelin receptor antagonists, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, and prostacyclin analogs
Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
Oxygen therapy
Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots
In severe cases, surgical procedures such as atrial septostomy or lung transplant
11. Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, leading to thick, sticky mucus buildup in the lungs and other organs. This results in frequent infections, respiratory issues, and digestive problems.
Symptoms
Persistent cough with thick mucus
Recurrent lung infections
Wheezing or shortness of breath
Poor growth and weight gain in children
Salty-tasting skin
Severe constipation
Frequent greasy, bulky stools
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves genetic testing, sweat chloride tests, and newborn screening. Pulmonary function tests, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures may also be conducted to assess lung health.
Treatment Management includes:
Medications to thin mucus, antibiotics to treat infections, and bronchodilators to open airways
Chest physiotherapy to clear mucus
Enzyme supplements and high-calorie diets to manage digestive issues
Newer therapies targeting the underlying genetic defect, such as CFTR modulators
12. Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
RDS primarily affects premature infants due to a lack of surfactant, a substance necessary to keep the lungs open and facilitate gas exchange. Risk factors include premature birth, maternal diabetes, and multiple births.
Symptoms
Rapid, shallow breathing
Grunting sounds while breathing
Nasal flaring
Chest retractions (pulling in of the chest muscles)
Cyanosis (bluish color of the skin and mucous membranes)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves clinical assessment, chest X-rays, and blood gas analysis to measure oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Prenatal tests can also help identify at-risk pregnancies.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Surfactant replacement therapy to improve lung function
Mechanical ventilation or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) to support breathing
Oxygen therapy
Supportive care such as fluids and nutrition
13. Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is characterized by the growth of granulomas (small clusters of inflammatory cells) in the lungs and other organs, likely as an immune response to unknown triggers. The exact cause remains unclear, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
Symptoms
Dry cough
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Fatigue
Fever
Swollen lymph nodes
Skin lesions (e.g., erythema nodosum)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, CT scans, and pulmonary function tests. Biopsy of affected tissues may be performed to confirm the presence of granulomas.
Treatment While sarcoidosis is often self-limiting and may resolve without treatment, severe cases may require:
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Immunosuppressive medications (e.g., methotrexate, azathioprine)
Antimalarial drugs (e.g., hydroxychloroquine) for skin lesions
Regular monitoring and follow-up care to manage chronic cases
14. Asthma
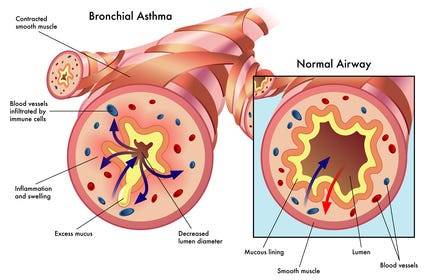
Definition and Causes: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways, causing episodes of wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, often triggered by allergens, exercise, cold air, or respiratory infections. Genetic and environmental factors contribute to its development.
Symptoms
Wheezing
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Coughing, especially at night or early morning
Increased mucus production
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests (spirometry, peak flow measurement). Allergy testing and chest X-rays may also be conducted to identify triggers and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Management includes:
Avoiding known triggers
Inhalers (bronchodilators for quick relief, corticosteroids for long-term control)
Long-term control medications (e.g., leukotriene modifiers, long-acting beta agonists)
Immunotherapy (allergy shots) for severe allergies
Asthma action plans to manage symptoms and prevent attacks
Conclusion
Lung diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments. Preventive measures such as avoiding smoking, reducing exposure to environmental pollutants, and timely vaccinations can significantly reduce the risk of developing many of these diseases. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by lung diseases. For personalized medical advice and treatment, consult with healthcare professionals.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Email us: expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional guidance.
Your Digestive System & How it Works

Introduction
The digestive system is a marvel of biological process that involves the breakdown of food into absorbable nutrients essential for sustaining life. Comprising a network of organs and tissues, it serves as the body’s processing center, converting ingested substances into energy, growth materials, and waste. Understanding the intricacies of this system provides profound insights into human physiology and health maintenance.
1. Anatomy of the Digestive System

The digestive system is a complex network of organs, glands, and tissues that work in harmony to facilitate the digestion and absorption of nutrients. At its core lies the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), a continuous tube extending from the mouth to the anus. Key components of the GI tract include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. Additionally, accessory organs such as the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder contribute crucial digestive enzymes and fluids to aid in the breakdown of food.
2. Functions of the Digestive System

The primary function of the digestive system is to process food and liquids to extract essential nutrients while eliminating waste products. Through a series of coordinated processes, including ingestion, digestion, absorption, and excretion, the digestive system ensures the body receives the necessary components for energy production, tissue repair, and growth. Moreover, it plays a vital role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance within the body.
3. Digestive process

Digestion begins in the mouth, where mechanical and chemical processes break down food into smaller particles. Chewing, or mastication, mechanically reduces food size, while saliva, secreted by salivary glands, initiates the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates through the action of enzymes like amylase. The bolus of food then travels down the esophagus via peristaltic contractions, entering the stomach for further processing.
In the stomach, gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid and pepsin begin the breakdown of proteins, while muscular contractions churn the food into a semi-liquid mixture known as chyme. From the stomach, chyme enters the small intestine, where the majority of nutrient absorption occurs. Enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver aid in the breakdown of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, allowing for absorption across the intestinal lining.
In the large intestine, water absorption occurs, leading to the formation of feces. Microbial fermentation within the colon further breaks down indigestible carbohydrates and produces essential nutrients like vitamin K and certain B vitamins. Finally, waste products are expelled through the anus during defecation.
4. Regulation of Digestive Processes

The intricate processes of digestion are tightly regulated by a combination of neural, hormonal, and local mechanisms. Neural signals originating from the brain and enteric nervous system (ENS) coordinate muscle contractions along the GI tract, ensuring the smooth passage of food and efficient mixing with digestive juices. Hormones such as gastrin, secretin, and cholecystokinin act as chemical messengers, modulating gastric acid secretion, pancreatic enzyme release, and bile production in response to dietary stimuli.
5. Clinical Implications and Disorders

Disruptions to the normal functioning of the digestive system can lead to a myriad of health disorders, ranging from minor discomforts to life-threatening conditions. Gastrointestinal disorders encompass a broad spectrum of diseases, including gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and colorectal cancer. These conditions often manifest with symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and rectal bleeding, necessitating thorough diagnostic evaluation and tailored treatment approaches.
6. Research and Advancements

Advancements in medical research continue to deepen our understanding of digestive physiology and pathology, paving the way for innovative diagnostic techniques and therapeutic interventions. Clinical trials conducted by academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies play a pivotal role in evaluating novel treatment modalities and improving patient outcomes. Areas of active investigation include microbiome research, targeted drug delivery systems, and minimally invasive surgical techniques for gastrointestinal disorders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the digestive system serves as a cornerstone of human biology, enabling the breakdown and assimilation of nutrients essential for life. Its intricate anatomy and physiological processes underscore the remarkable complexity of the human body. By elucidating the mechanisms of digestion and exploring the clinical implications of digestive disorders, we gain valuable insights into the maintenance of health and the management of disease. Continued research efforts hold the promise of further enhancing our understanding and treatment of gastrointestinal conditions, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals worldwide.
We wish you all the best in your medical education journey. In case you need any guidance or assistance during the learning process, do not hesitate to reach out to us.
Email at;
williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@gmail.com
10 Simple Tips for Caring for Your Heart.

The heart, a tireless worker at the core of our well-being, demands our attention and care. As we navigate through Heart Health Month this February, let’s explore ten simple yet impactful tips to ensure our hearts thrive. These practices, ranging from physical activity to laughter and dental hygiene, collectively contribute to a holistic approach to cardiovascular wellness.
1.Cardiovascular Exercise: A Heart’s Best Friend
Engaging in regular cardiovascular or aerobic activities is fundamental for heart health. Following the American Heart Association’s recommendations of 75 minutes of vigorous exercise or 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly can significantly boost cardiorespiratory fitness. Activities such as running, cycling, or brisk walking not only elevate heart rate but also enhance overall cardiovascular function. The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of muscles during exercise contribute to improved blood flow and reduced strain on the heart.
2.Embrace a Smoke-Free Lifestyle
Quitting smoking is a paramount step in safeguarding your heart. Smoking damages both the heart and blood vessels, escalating the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, avoiding second-hand smoke is crucial, as it has been linked to heart attacks and strokes. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke lead to the narrowing of blood vessels, increasing the workload on the heart and elevating the risk of high blood pressure.
3.Prioritize Quality Sleep
Adequate sleep, often underestimated, plays a pivotal role in heart health. With at least seven hours of nightly rest, blood pressure lowers, and the body undergoes essential repair processes. Research underscores the correlation between poor sleep and heightened risks of high blood pressure, subsequently increasing the likelihood of heart diseases. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a conducive sleep environment are crucial steps in promoting optimal cardiovascular health.
4.Regular Checkups: A Heart-Healthy Habit
Consistent visits to the doctor for heart health checkups are essential. Assessing risk factors such as diet, blood pressure, cholesterol, and family history enables early detection and management of potential issues. A proactive approach to heart health empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle choices. Regular checkups also provide an opportunity for healthcare professionals to offer personalized guidance on maintaining heart health through tailored interventions.
5.Laughter: The Heart’s Natural Tonic
Laughing, whether through entertainment or social interactions, yields surprising benefits for the heart. The act of laughter reduces artery inflammation, lowers stress hormones, and increases levels of good cholesterol. Integrating humor into daily life becomes a delightful prescription for heart health. Laughter promotes the release of endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good chemicals, which contribute to overall well-being and stress reduction.
6.Dental Hygiene and Heart Connection
Surprising as it may seem, maintaining good dental hygiene contributes to heart health. Studies reveal a link between poor dental health and the presence of bacteria in the bloodstream, impacting heart valves. Simple practices such as regular brushing can significantly decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, regular dental checkups not only preserve oral health but also serve as a preventive measure against potential cardiovascular complications.
7.Fuel Your Heart with a Healthy Diet
A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, whole grains, vegetables, and legumes significantly improves blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Steering clear of salty foods and saturated fats is crucial, as they contribute to elevated blood pressure and increased bad cholesterol. Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, further supports heart health by reducing inflammation and promoting optimal functioning of blood vessels.
8.Maintaining a Healthy Weight: A Heart’s Delight
Striving for and maintaining a healthy weight is a powerful defense against heart disease and high blood pressure. A combination of a balanced diet, regular exercise, and mindful calorie intake promotes overall well-being and cardiovascular health. Excess weight puts additional strain on the heart, leading to conditions such as hypertension and diabetes. Adopting sustainable lifestyle changes, including portion control and regular physical activity, contributes to achieving and sustaining a healthy weight.
9.Hydration: The Heart’s Elixir
Staying adequately hydrated is a simple yet often overlooked aspect of heart care. Considering the heart’s continuous effort in pumping around 2,000 gallons of blood daily, increased water intake supports its optimal functioning. Dehydration can lead to thicker blood, making the heart work harder to pump blood through the vessels. Maintaining proper hydration levels ensures the efficient transport of nutrients and oxygen to cells, promoting overall cardiovascular health.
10.Stay Active, Break Inactivity
Combatting sedentary lifestyles is crucial in preserving heart health. Incorporating simple changes like taking the stairs, walking, playing with pets, or engaging in household chores helps keep the heart active, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Prolonged sitting has been associated with various health risks, including obesity and heart disease. Regular physical activity not only supports cardiovascular health but also contributes to weight management and overall well-being.
In conclusion, adopting these ten heart-healthy habits provides a comprehensive approach to cardiovascular wellness. Whether it’s the joyous act of laughter, the discipline of regular exercise, or the mindfulness of a balanced diet, each step contributes to the harmonious symphony of a healthy heart. As we celebrate Heart Health Month, let’s embrace these practices and gift our hearts the care they deserve. Through consistent efforts and lifestyle modifications, we can ensure that our hearts continue to beat with vitality and resilience.
For health Sciences Assignment Help,
Email us on williamsliason@outlook.com
6 Simple Steps To Score ‘A’ Grade On Your Research Paper

1. Building Your Thesis
Your thesis serves as the bedrock of your research paper, providing a central focus and guiding principle for your investigation. It’s imperative to construct your thesis around a clear and concise idea, premise, or claim that you intend to explore and defend throughout your paper. In the introduction, articulate precisely what your thesis aims to address, ensuring clarity and coherence from the start outlining the scope and significance of your thesis, you not only distinguish your paper from others but also establish a compelling rationale for your research. Moreover, show case to your readers the insights they stand to gain by engaging with your thesis, thereby enhancing the relevance and impact of your work.
2. Preparing an Outline

Crafting a comprehensive outline is an indispensable organizational tool in the research paper writing process. It functions as a strategic roadmap, enlightening the structure and content of your paper while facilitating coherence and logical progression. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to outlining, it is essential to consider several key elements:
Content and Presentation Style: Determine the thematic framework and narrative structure for each section of your paper, ensuring alignment with your thesis.
Supporting Arguments and Evidence: Incorporate pertinent supporting arguments and empirical evidence to substantiate your thesis and bolster your overrating argument.
Cohesion and Conclusion: Ensure that your outline fosters cohesion by integrating disparate ideas and perspectives, culminating in a definitive conclusion that reinforces the significance of your research.
By vividly crafting an outline that contains these elements, you can streamline the writing process and maintain a cohesive and compelling narrative throughout your paper.
3. Conducting Research

Robust and thorough research is the cornerstone of a successful research paper, providing the empirical foundation and scholarly context necessary to substantiate your thesis. Begin by identifying a diverse array of potential sources that align with the theme focus and research objectives of your paper. With your outline serving as a strategic guide, embark on a systematic exploration of relevant literature, primary sources, and empirical data, prioritizing depth and breadth of coverage over superficiality. While evaluating sources, prioritize relevance and scholarly vigor over perfection, recognizing that the synthesis of diverse perspectives and methodologies can enrich your analysis and deepen the intellectual resonance of your paper.
4 . Writing Your Thesis

Armed with a comprehensive outline and an extensive body of research, it is time to translate your insights and arguments into a cognitive and compelling thesis. Drawing upon the scaffolding provided by your outline, into details craft each section of your paper, maintaining specificity to your thesis statement and overrated argument. Whether elucidating theoretical frameworks, analyzing empirical data, or synthesizing disparate perspectives, strive for consistency and coherence in your writing, ensuring that each subsection contributes meaningfully to the specific narrative of your paper. By adhering to the theme contours mentioned in your outline and showing the resilience of your thesis, you can construct a persuasive and intellectually rigorous argument that resonates with your readers.
5. Editing and Revision

The editing and revision process is an indispensable stage in refining the coherence, clarity, and scholarly rigor of your research paper. Upon completing the initial draft of your paper, undertake a comprehensive review and analysis, focusing on several key areas:
Structural Coherence: Evaluate the organizational coherence and logical progression of your paper, identifying opportunities to streamline transitions and enhance narrative flow.
Clarity and Precision: Scrutinize the clarity and precision of your prose, refining language and syntax to elucidate complex ideas and facilitate reader comprehension.
Scholarly Rigor: Verify the accuracy and integrity of your citations, ensuring adherence to established conventions of academic citation and attribution.
Grammar and Mechanics: Attend to grammatical errors, typographical inconsistencies, and syntactical ambiguities, rectifying any lapses in mechanics that deter from the scholarly integrity of your paper.
By subjecting your paper to rigorous scrutiny and revision, you can elevate the quality and scholarly resonance of your research, enhancing its capacity to engage and persuade your audience.
6. Creating a Checklist

As a culminating step, it is essential to create a comprehensive checklist to ensure that your research paper adheres to the highest standards of scholarly rigor and integrity. This checklist should encompass several key dimensions:
Content: Verify that your paper addresses all requisite components, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, findings, discussion, and conclusion.
Structure: Assess the structural coherence and narrative progression of your paper, ensuring that each section contributes meaningfully to the overarching argument.
Citation and Attribution: Confirm the accuracy and completeness of your citations, adhering to established conventions of academic citation and attribution.
Presentation: Review the formatting and presentation of your paper, attending to stylistic considerations such as font, spacing, and margins.
Proofreading: Conduct a final proofreading of your paper, scrutinizing for any lingering errors or oversights in grammar, syntax, or mechanics.
By rigorously adhering to this checklist, you can ensure that your research paper meets all necessary criteria for scholarly excellence and academic integrity, thereby maximizing its impact and credibility within the academic community.
By specifically following these six steps, you can consistently produce research papers of exceptional quality and academic rigor, irrespective of your current skill level or disciplinary background. Each step represents a critical juncture in the research paper writing process, providing a strategic framework for conceptualizing, organizing, and presenting your research in a compelling and intellectually rigorous manner. By embracing these principles and methodologies, you can elevate the caliber and excellent resonance of your research papers, thereby enhancing your academic proficiency and contributing meaningfully to the advancement of knowledge within your chosen field of study.
Crafting a top-notch research paper demands careful planning, thorough research, and diligent editing. Following the outlined steps can boost students’ writing skills and consistently lead to ‘A’ grades. Yet, academic writing complexities can overwhelm newcomers or those short on time.
Remember, seeking help isn’t weakness but a proactive strategy to ensure work quality. By utilizing available resources and seeking aid when necessary, students can ease academic writing stress and enrich their learning journey.
Therefore, I strongly encourage students to consider seeking assistance from Expert Academic Assignment Help by emailing expertassignment46@gmail.com With their expertise and support, students can receive tailored guidance, feedback, and assistance throughout the research paper writing process. By leveraging the expertise of academic professionals, students can overcome challenges, refine their writing skills, and achieve academic success more effectively.
Dementia in Old Age

Dementia is a complex medical condition characterized by a group of symptoms that affect memory, thinking, and social abilities, ultimately interfering with daily life. It is crucial to recognize that dementia is not a single disease but rather a set of symptoms resulting from various underlying causes. Memory loss is a common early sign, but its presence alone does not confirm dementia, as there can be different causes for memory issues.
1. Causes of Dementia
a. Alzheimer’s Disease
The most common cause of dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, is associated by the presence of plaques and tangles in the brain, impacting healthy brain cells.
b. Vascular Dementia
Caused by damage to blood vessels supplying the brain, often due to strokes or other vascular issues.
c. Lewy Body Dementia
Involves the presence of Lewy bodies i. e protein clumps found in the brains of affected individuals, leading to symptoms such as hallucinations and coordination problems.
d. Frontotemporal Dementia
A group of diseases affecting the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, influencing behavior, personality, language, and movement.
e. Mixed Dementia
A combination of various causes, such as Alzheimer’s, vascular dementia, and Lewy body dementia, making diagnosis and treatment more challenging.
2. Reversible Causes and Dementia-Like Conditions
a. Infections and Immune Disorders
Fever or immune responses can result in dementia-like symptoms.
b. Metabolic or Endocrine Problems
Thyroid issues, low blood sugar, and imbalances in sodium or calcium can contribute to dementia-like symptoms.
c. Nutrient Deficiencies
Lack of essential vitamins or minerals, such as B vitamins and vitamin D, can lead to cognitive decline.
d. Medication Side Effects
Some medications and their interactions can cause symptoms resembling dementia.
e .Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Repetitive head trauma, as seen in sports or accidents, can increase the risk of dementia.
3. Risk Factors
a .Non-Modifiable Factors
Age, family history, and Down syndrome are factors that increase the risk of dementia but cannot be changed.
b .Modifiable Factors:
Lifestyle choices, including diet, exercise, alcohol consumption, and cardiovascular health, can impact dementia risk.
4. Complications and Progression
Dementia can lead to complications affecting various body systems, including poor nutrition, pneumonia, self-care challenges, safety issues, and in late stages, coma and death.
5. Prevention Strategies
a. Engage in mentally stimulating activities to delay onset and reduce the impact of dementia.
b. Adopt a physically and socially active lifestyle, with at least 150 minutes of exercise per week.
c . Quit smoking to reduce the risk of dementia and associated vascular conditions.
d. Ensure adequate intake of essential vitamins, particularly vitamin D, through diet, supplements, and sunlight exposure.
e. Manage cardiovascular risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
f. Seek treatment for depression or anxiety, as these conditions may contribute to dementia risk.
g. Follow a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids.
h. Prioritize good-quality sleep and address sleep-related issues promptly.
i. Treat hearing problems early to decrease the risk of cognitive decline.
6. Conclusion
Understanding the pathophysiology of dementia, and potential prevention strategies is crucial for individuals and their families. By addressing modifiable risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle, one can contribute to maintaining cognitive health and potentially delaying the risk of dementia. Seeking medical attention for memory problems or dementia symptoms is vital to determine the underlying cause and explore appropriate treatments. Ongoing research continues to enhance our understanding of dementia, offering hope for effective interventions in the future.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help;
Email Us At;
williamsliason@outlook.com
10 Reasons Why Choose Assignment Help

1.Importance of Assignments
Assignments play a crucial role in reinforcing classroom learning and assessing students’ understanding of the subject matter. They serve as opportunities for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Additionally, assignments encourage students to actively engage with course materials and take ownership of their learning process.
2.Evolution of Assignments

As students progress through their academic journey, the complexity and scope of assignments tend to increase. In elementary school, assignments may focus on basic skills such as reading comprehension and arithmetic. However, in higher education, assignments often involve in-depth research, analysis, and synthesis of information from multiple sources. This progression reflects the development of students’ intellectual capabilities and prepares them for the rigors of professional life.
3. Efficiency of Applied Knowledge

Assignments serve as vehicles for applying theoretical knowledge in practical contexts, bridging the gap between classroom learning and real-world application. By working on assignments, students gain hands-on experience and develop transferable skills that are invaluable in their future careers. For example, a business student might analyze case studies to understand how theoretical concepts apply to real business challenges.
4. Benefits of Expert Help
Seeking assistance from assignment help experts offers numerous benefits to students. These experts possess subject matter expertise and can provide guidance and support tailored to students’ individual needs. Whether students require assistance with research, writing, or formatting, assignment help experts can offer valuable insights and resources to enhance the quality of their work.
5. Time-saving Approach

One of the primary advantages of online assignment help is its ability to save students time. With busy schedules and competing demands, students often struggle to find the time to complete assignments thoroughly. By outsourcing some of their academic tasks to experts, students can free up valuable time to focus on other priorities such as studying for exams or participating in extracurricular activities.
6. Procrastination and Stress Reduction
Procrastination is a common challenge that many students face, often leading to increased stress and anxiety as deadlines approach. Seeking professional help with assignments can alleviate some of this pressure by providing students with the support they need to get started and stay on track. Additionally, knowing that expert assistance is available can give students peace of mind and reduce feelings of overwhelm.
7. Quality Assurance

Assignment help experts are committed to delivering high-quality work that meets the academic standards and expectations of students’ instructors. They adhere to rigorous quality assurance processes to ensure that assignments are accurate, well-researched, and free from errors. By entrusting their assignments to experts, students can feel confident in the quality of their work and its potential to earn them high grades.
8. Customization and Flexibility
Online assignment help services offer a high degree of customization and flexibility to meet students’ individual needs and preferences. Whether students require assistance with a specific assignment or ongoing support throughout the semester, assignment help experts can tailor their services accordingly. This level of flexibility ensures that students receive the personalized attention and guidance they need to succeed academically.
9. Achieving Top Grades

The ultimate goal of seeking assistance from assignment help experts is to achieve top grades and academic success. By leveraging the expertise and support of these professionals, students can produce high-quality assignments that demonstrate their understanding of the course material and impress their instructors. This, in turn, can lead to improved academic performance and future opportunities.
10. Encouragement to Seek Help

It’s essential to encourage students to overcome any stigma or reluctance they may feel about seeking help with their assignments. Seeking assistance is a proactive step towards academic success and should be viewed as a valuable resource rather than a sign of weakness. By promoting a culture of support and collaboration, educational institutions can empower students to reach their full potential and excel in their studies.
In conclusion
The decision to seek assistance from assignment help experts is a strategic one that can greatly benefit students in their academic journey. By recognizing the importance of assignments, embracing the evolution of academic tasks, and leveraging the expertise of professionals, students can overcome challenges, save time, reduce stress, and achieve top grades. Encouraging a proactive approach to seeking help and fostering a culture of support within educational institutions can further enhance students’ academic success and well-being.
We wish you all the best in your studies as you Navigate the education journey,
In case you need any guidance or assistance during the learning process, do not hesitate to reach out to us.
Email at; williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@gmail.com
Breast Cancer

Introduction
Breast cancer, a multifaceted and prevalent disease, poses a significant health challenge globally, transcending gender lines with its potential impact. Characterized by the abnormal proliferation of cells within breast tissue, breast cancer’s complex etiology remains an area of intense study and concern. Despite notable advancements in medical science and increased awareness, it continues to be a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. This comprehensive discussion aims to delve into the intricacies of breast cancer, encompassing its causes, risk factors, prevention strategies, diagnostic modalities, treatment options, and the evolving landscape of supportive care.
Causes and Risk Factors

Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors associated with breast cancer is paramount in developing effective prevention and management strategies. While the precise etiology of breast cancer remains elusive, various genetic, hormonal, environmental, and lifestyle factors contribute to its onset and progression. Genetic predispositions, such as mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, significantly elevate the risk of developing breast cancer. Additionally, hormonal influences, including early onset of menstruation, late menopause, and hormone replacement therapy, play a crucial role in disease pathogenesis. Lifestyle factors such as excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, lack of physical activity, and exposure to environmental carcinogens further augment the risk profile.
Preventive Measures

Empowering individuals with knowledge about preventive measures is essential in mitigating the burden of breast cancer. Promoting regular breast self-examinations, clinical breast examinations, and mammographic screenings facilitates early detection and intervention. Emphasizing lifestyle modifications, including maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, limiting alcohol intake, and engaging in regular physical activity, can reduce the risk of breast cancer. For individuals with a heightened risk due to genetic predispositions or familial history, prophylactic surgeries, such as mastectomy or oophorectomy, and chemo preventive agents offer viable preventive options.
Diagnostic Modalities

Advances in diagnostic modalities have revolutionized the early detection and diagnosis of breast cancer, enabling prompt initiation of treatment and improved clinical outcomes. Mammography remains the cornerstone of breast cancer screening, capable of detecting abnormalities such as microcalcifications, masses, or architectural distortions. Complementary imaging techniques, including ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and molecular breast imaging (MBI), enhance diagnostic accuracy, particularly in women with dense breast tissue or high-risk profiles. Biopsy procedures, such as core needle biopsy or surgical excision, facilitate histopathological examination, enabling precise diagnosis and classification of breast lesions.
Treatment Options

Tailoring treatment strategies to individual patient characteristics and disease parameters is essential in optimizing therapeutic outcomes in breast cancer. The treatment landscape encompasses a multidisciplinary approach, integrating surgical, medical, and radiation oncology interventions. Surgical options range from breast-conserving surgeries, such as lumpectomy or segmental mastectomy, to radical procedures like total mastectomy or modified radical mastectomy, depending on tumor size, location, and extent of spread. Adjuvant therapies, including chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, aim to eradicate residual disease, prevent recurrence, and improve overall survival. Radiation therapy, administered either postoperatively or as a primary modality in selected cases, targets residual tumor cells, minimizing locoregional recurrence rates.
Supportive Care and Survivorship

Recognizing the holistic needs of breast cancer patients and survivors is integral in promoting comprehensive care and ensuring optimal quality of life. Supportive care interventions, including symptom management, psychosocial support, nutritional counseling, and rehabilitation services, address the multifaceted challenges associated with cancer diagnosis and treatment. Survivorship programs, focusing on survivorship care planning, surveillance for recurrence, long-term monitoring of treatment-related complications, and health promotion initiatives, facilitate the transition from active treatment to survivorship. Engaging patients and caregivers in survivorship care planning fosters empowerment, resilience, and a sense of agency in navigating the post-treatment phase.
Conclusion
In conclusion, breast cancer represents a formidable health challenge with profound implications for affected individuals, families, and communities worldwide. While significant strides have been made in understanding its pathophysiology, enhancing diagnostic capabilities, and expanding treatment options, concerted efforts are warranted to address existing gaps in prevention, early detection, and access to care. By fostering collaborative partnerships among stakeholders, advocating for evidence-based interventions, and promoting health equity, we can strive towards a future where breast cancer incidence and mortality rates are substantially reduced. Through continued innovation, education, and advocacy, we can transform the landscape of breast cancer care, offering hope, support, and healing to those impacted by this pervasive disease.
We wish you all the best in your medical education journey. In case you need any guidance or assistance during the learning process, do not hesitate to reach out to us.
Email at;
williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@gmail.com