Solar System: Top 5 Things To Know This Week
Solar System: Top 5 Things to Know This Week
1. A Ceres of Fortunate Events

Our Dawn mission continues its exploration at Ceres, and the team is working with the data coming back to Earth, looking for explanations for the tiny world’s strange features. Follow Dawn’s expedition HERE.
2. Icy Moon Rendezvous

One of the most interesting places in the entire solar system is Saturn’s moon Enceladus, with its underground ocean and spectacular geyser plume. This month, the Cassini spacecraft will be buzzing close by Enceladus several times, the last such encounters of the mission. On October 14, Cassini will perform a targeted flyby at a distance of just 1,142 miles (1,838 kilometers) over the moon’s northern latitudes. Ride along with Cassini HERE.
3. Make Your Own Mars Walkabout
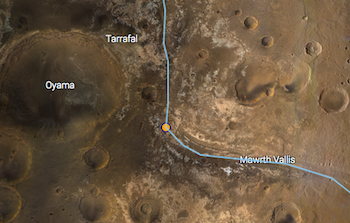
You can retrace Opportunity’s journey, see where the Curiosity rover is now, or even follow along with fictional astronaut Mark Watney from The Martian movie using the free online app MarsTrek. The app lets you zoom in on almost any part of the planet and see images obtained by our spacecraft, so you can plan your on Red Planet excursion. Take a hike HERE.
4. Elusive Features on Jupiter

New imagery from our Hubble Space Telescope is capturing details never before seen on Jupiter. High-resolution maps and spinning globes, rendered in the 4K Ultra HD format, reveal an elusive wave and changes to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. Explore Jupiter HERE.
5. Mr. Blue Sky

Another week, another amazing picture from Pluto. The first color images of Pluto’s atmospheric hazes, returned by our New Horizons spacecraft last week, reveal that the hazes are blue. Who would have expected a blue sky in the Kuiper Belt? Most of the data collected during July’s Pluto flyby remains aboard the spacecraft, but the team publishes new batches of pictures and other findings on a weekly basis. Keep up with the latest HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Inter-stellxr-blog and Others


Hubble’s Jupiter Maps Reveals Weird Structures
Over a 10 hour period, the Hubble Space Telescope gazed at the solar system’s largest planet to produce one of the most spectacular maps of Jupiter’s complex and dynamic atmosphere. Immediately astronomers were able to measure the size of the planet’s shrinking Great Red Spot and notice some mysterious structures along the way.
As the spot has shrunk, it’s color has also become more anemic, losing some of its redness. Also, as these new Hubble observations show, a strange wispy structure has formed inside the storm, becoming warped by the high-speed winds that have been clocked at a speed of 540 kilometers (335 miles) per hour. Astronomers, so far, have little explanation as to what this feature is or what caused it.
Another oddity has been spied just north of the planet’s equator — a wave-like structure has formed, something that hasn’t been seen since the Voyager 2 flyby in 1979. During that flyby, these waves were assumed to be a transient event and the fact the spacecraft imaged them was a fluke. But they’ve now returned, no doubt sparking some huge interest as to their origins.
Click to learn more
This is me
i dab every morning when i wake up
Astronomy Night at the White House
NASA took over the White House Instagram today in honor of Astronomy Night to share some incredible views of the universe and the world around us. Check out more updates from the astronauts, scientists, and students on South Lawn.

Here’s a nighttime view of Washington, D.C. from the astronauts on the International Space Station on October 17. Can you spot the White House?

Check out this look at our sun taken by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory. The SDO watches the sun constantly, and it captured this image of the sun emitting a mid-level solar flare on June 25. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare can’t pass through Earth’s atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground. But when they’re intense enough, they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.

Next up is this incredible view of Saturn’s rings, seen in ultraviolet by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft. Hinting at the origin of the rings and their evolution, this ultraviolet view indicates that there’s more ice toward the outer part of the rings than in the inner part.

Take a look at the millions of galaxies that populate the patch of sky known as the COSMOS field, short for Cosmic Evolution Survey. A portion of the COSMOS field is seen here by NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope. Even the smallest dots in this image are galaxies, some up to 12 billion light-years away. The picture is a combination of infrared data from Spitzer (red) and visible-light data (blue and green) from Japan’s Subaru telescope atop Mauna Kea in Hawaii. The brightest objects in the field are more than ten thousand times fainter than what you can see with the naked eye.

This incredible look at the Cat’s Eye nebula was taken from a composite of data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope. This famous object is a so-called planetary nebula that represents a phase of stellar evolution that the Sun should experience several billion years from now. When a star like the Sun begins to run out of fuel, it becomes what is known as a red giant. In this phase, a star sheds some of its outer layers, eventually leaving behind a hot core that collapses to form a dense white dwarf star. A fast wind emanating from the hot core rams into the ejected atmosphere, pushes it outward, and creates the graceful filamentary structures seen with optical telescopes.

This view of the International Space Station is a composite of nine frames that captured the ISS transiting the moon at roughly five miles per second on August 2. The International Space Station is a unique place—a convergence of science, technology, and human innovation that demonstrates new technologies and makes research breakthroughs not possible on Earth. As the third brightest object in the sky, the International Space Station is easy to see if you know when to look up. You can sign up for alerts and get information on when the International Space Station flies over you at spotthestation.nasa.gov. Thanks for following along today as NASA shared the view from astronomy night at the White House. Remember to look up and stay curious!

A Precocious Black Hole In July 2015, researchers announced the discovery of a black hole that grew much more quickly than its host galaxy. The discovery calls into question previous assumptions on development of galaxies. The black hole was discovered using the Hubble Space Telescope, and detected in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, by ESA’s XMM-Newton and NASA’s Chandra.






This volcano in Indonesia emits electric-blue “lava”
Kawah Ijen, in Indonesia’s Ijen volcano complex, is the biggest “acidic volcanic crater lake” in the world. It also happens to emit lava which appears luminescent and electric-blue. The lava, like all other lava, starts out red. Then it hits the “pockets.” (Photos via @reubenwu)
REBLOG IF A VIDEO GAME ENDING HAS EVER MADE YOU CRY
7 Things That Happen When You Go To Space
Told Through Astronaut Scott Kelly’s Tweets
Astronaut Scott Kelly is currently spending a year in space. Most expeditions to the space station last four to six months. By doubling the length of this mission, researchers hope to better understand how the human body reacts and adapts to long-duration spaceflight. During this one-year mission, Kelly is also participating in the Twins Study. While Kelly is in space, his identical twin brother, retired NASA Astronaut Mark Kelly, will participate in a number of comparative genetic studies.
Here are a few things that happen when astronauts go to the space station:
1. Your personal hygiene takes on a different form:


2. Sleeping arrangements might take some getting used to:



3. Internet services will remind you of the 90s:

4. You never have to do laundry:


5. You get to become immersed in a range of different cultures:

6. All of your water is recycled…yes…that means urine too:


7. You get to see the Earth like never before:



Follow Astronaut Scott Kelly’s Year in Space mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

One Last Look At The Space Shuttle Endeavour’s Cockpit Before It’s Shut Down Forever
What’s Enceladus?
Before we tell you about Enceladus, let’s first talk about our Cassini spacecraft…
Our Cassini mission to Saturn is one of the most ambitious efforts in planetary space exploration ever mounted. Cassini is a sophisticated robotic spacecraft orbiting the ringed planet and studying the Saturnian system in detail.

Cassini completed its initial four-year mission to explore the Saturn System in June 2008. It has also completed its first mission extension in September 2010. Now, the health spacecraft is making exciting new discoveries in a second extension mission!
Enceladus

Enceladus is one of Saturn’s many moons, and is one of the brightest objects in our solar system. This moon is about as wide as Arizona, and displays at least five different types of terrain. The surface is believed to be geologically “young”, possibly less than 100 million years old.
Cassini first discovered continually-erupting fountains of icy material on Enceladus in 2005. Since then, the Saturn moon has become one of the most promising places in the solar system to search for present-day habitable environments.

Scientists found that hydrothermal activity may be occurring on the seafloor of the moon’s underground ocean. In September, it was announced that its ocean –previously thought to only be a regional sea – was global!
Since Cassini is nearing the end of its mission, we are able to make a series of three close encounters with Enceladus, one of Saturn’s moons.
Close Encounters
On Oct. 14, Cassini performed a mid-range flyby of Enceladus, but the main event will take place on Oct. 28, when Cassini will come dizzyingly close to the icy moon. During this flyby, the spacecraft will pass a mere 30 miles above the moon’s south polar region!

This will be the deepest-ever dive through the moon’s plume of icy spray, where Cassini can collect images and valuable data about what’s going on beneath the frozen surface.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

In first grade Jessica Meir made a drawing of herself standing on the moon. Turns out she underestimated her own ambition: Today, at 38, Meir could become the first human to touch down on an even farther destination: Mars. A next step for man? Yes, and a giant leap for womankind.
The mission itself is at least 15 years away—it will take that long to build and test every last piece of equipment. But it’s already the most hotly anticipated space-exploration effort ever. Governments around the world—in China, Europe, and Russia—have plans in the works to at least land robots on Mars, while in the U.S., private companies like SpaceX are partnering with NASA on a human mission and plotting their own commercial trips. And unlike the 1960s race to the moon, this time women are playing pivotal roles—building rockets, designing space suits, and controlling the remote rovers that are already sending momentous insights back from Mars.
A human landing will not, to put it mildly, be easy. The shortest route to our planetary neighbor is 35 million miles. Just getting there will take six to nine months; a round-trip, two to three years. “This will be the longest, farthest, and most ambitious space-exploration mission in history,” says Dava Newman, Ph.D., NASA’s deputy administrator. Once they’ve landed, the astronauts will have to navigate giant dust storms, temperatures that can plummet to minus 284 degrees Fahrenheit in winter, and an atmosphere filled with cancer-causing galactic radiation. If their equipment fails? NASA won’t hear an SOS for 10 minutes. And there’s no turning back. “It’s not like the moon; that’s a three-day trip,” says Jason Crusan, director of advanced exploration systems at the agency. “When you go to Mars, you’re going. You can’t abort.”
And yet the pull is irresistible: The rovers have revealed a land of swooping red dunes and craters. Evidence of water—not just ice, but actual flowing water—has surfaced, and water is often considered a sign of possible life. “Mars can teach us so much about the past, present, and future of our own planet,” says Meir. “That’s a phenomenal thing.”
Also phenomenal? For the first time NASA’s latest class of astronauts is 50 percent female. A fearless group, Meir and her colleagues Anne McClain, 36, Christina Hammock Koch, 37, and Nicole Aunapu Mann, 38, have already flown combat missions in Iraq, braved the South Pole, and dived under thick layers of ice in Antarctica. Last fall they gave Glamour exclusive access to watch them train at NASA’s facilities in Houston—and talked about their epic adventure.
Continue Reading.
-
 deathicus-sling reblogged this · 2 years ago
deathicus-sling reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 softeningandripening liked this · 5 years ago
softeningandripening liked this · 5 years ago -
 fredrick-smith liked this · 7 years ago
fredrick-smith liked this · 7 years ago -
 impala-moose liked this · 7 years ago
impala-moose liked this · 7 years ago -
 madokakaname1 reblogged this · 7 years ago
madokakaname1 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ageorgebir liked this · 8 years ago
ageorgebir liked this · 8 years ago -
 juliejuno reblogged this · 8 years ago
juliejuno reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 weeabooslut liked this · 8 years ago
weeabooslut liked this · 8 years ago -
 amigo155 liked this · 8 years ago
amigo155 liked this · 8 years ago -
 jaihind2110 liked this · 8 years ago
jaihind2110 liked this · 8 years ago -
 juliejuno reblogged this · 8 years ago
juliejuno reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 shippingtech-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
shippingtech-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 four-leaf-charm reblogged this · 9 years ago
four-leaf-charm reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 yeezynation8-blog liked this · 9 years ago
yeezynation8-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 aegisoracle liked this · 9 years ago
aegisoracle liked this · 9 years ago -
 happy420borderline liked this · 9 years ago
happy420borderline liked this · 9 years ago -
 seemply-d-best reblogged this · 9 years ago
seemply-d-best reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 annesully liked this · 9 years ago
annesully liked this · 9 years ago -
 megaradcollectionwolfthings-blog liked this · 9 years ago
megaradcollectionwolfthings-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 manicuredforwar reblogged this · 9 years ago
manicuredforwar reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 manicuredforwar liked this · 9 years ago
manicuredforwar liked this · 9 years ago -
 stormy-child reblogged this · 9 years ago
stormy-child reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tommie-james liked this · 9 years ago
tommie-james liked this · 9 years ago -
 theedsagroup-blog liked this · 9 years ago
theedsagroup-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 mobdividual liked this · 9 years ago
mobdividual liked this · 9 years ago -
 proffesionaldreamer reblogged this · 9 years ago
proffesionaldreamer reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 alpacachigga reblogged this · 9 years ago
alpacachigga reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 khaled-taleb-blog liked this · 9 years ago
khaled-taleb-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 anadeansky liked this · 9 years ago
anadeansky liked this · 9 years ago -
 faradayscandle liked this · 9 years ago
faradayscandle liked this · 9 years ago -
 iymerc01 liked this · 9 years ago
iymerc01 liked this · 9 years ago -
 grelse reblogged this · 9 years ago
grelse reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 fiamontague reblogged this · 9 years ago
fiamontague reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 thatgirlrobyn97 liked this · 9 years ago
thatgirlrobyn97 liked this · 9 years ago -
 melonssoup reblogged this · 9 years ago
melonssoup reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 fuyunoakegata reblogged this · 9 years ago
fuyunoakegata reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 prwtiapototelos liked this · 9 years ago
prwtiapototelos liked this · 9 years ago
"I don't know who will read this. I guess someone will find it eventually. Maybe in a hundred years or so." -Mark Watney
174 posts