"I don't know who will read this. I guess someone will find it eventually. Maybe in a hundred years or so." -Mark Watney
174 posts
Latest Posts by inter-stellxr-blog - Page 3
@rasinblazin
this changes everything oh my god
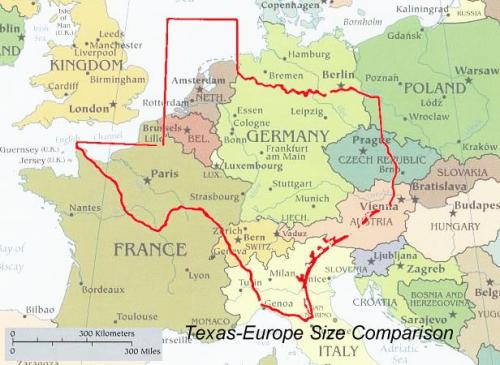
do you understand why it trips me out that people can drive 45 minutes and be in aNOTHER COUNTRY? I drive for 45 minutes and im like
a city over
I live in “Italy” and took a day trip to go to “Austria” and “Germany”
#it is literally impossible to leave texas #you will be in texas #FOREVER
Chums, that’s sweet, and all, but Australia just ate Texas for breakfast.

If you drive for 45 minutes in Australia you aren’t a city over, you’re just 45 minutes away from the city.
If you drive for 45 minutes in Australia you may not even leave the cattle station.

If you drive for 45 minutes in Canada you may not even leave your driveway.
If I drive 45 minutes in the us I’m just at another mcdonalds
If I drive for 45 minutes in Northern Ireland I’m 10 minutes into the sea.
I can’t drive.
I will use this post to explain tumblr


The first structural test article of Orion’s Service Module arrived at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio yesterday (November 9). Manufactured by Airbus Defense and Space in Europe, (the same company who built the Automated Transfer Vehicle), the European Service Module will provide Orion’s electrical, propulsion and umbilical capabilities during flight. A single Orbital Maneuvering System engine leftover from the Space Shuttle program will power the spacecraft, and four 11-kilowatt solar panels will generate electrical power. The STA will be used for fit checks and other engineering tests at NASA’s Plumb Brook facility, which is a sub-facility of Glenn. An Antonov-124 aircraft, the second largest cargo plane in the world delivered the ESM STA to Cleveland International Airport November 9.

Alpha Centauri bb, an Earth-like planet orbiting our closest star, has just vanished. In fact, a new study suggests it never actually existed outside of a blip in the data.
The planet was discovered in 2012, and it was a pretty big deal at the time. According to researchers’ best estimates, Alpha Centauri bb appeared to have a mass similar to Earth and was orbiting its star at a distance similar to Mercury.
Best of all, it was only 4.3 light-years away – a whole lot closer than most other Earth-like exoplanets – and existed in a star system that had housed the science-fiction characters of Avatar and Transformers.
But a year after its discovery, a separate group of researchers called the discovery into question, when they found only weak evidence that the planet existed. And now a new study suggests that Alpha Centauri bb was never more than a ‘ghost’ in the data.
The research serves as a cautionary tale to astrophysicists hunting for evidence of planets orbiting distant stars, and reminds us of how hard it is to work out what’s going on using sporadic data taken from distant star systems.
Continue Reading.

This is what happens when Two Black Holes Collide.
This is the animation of the final stages of a merger between two black holes. What is particularly interesting about this animation is that it highlights a phenomenon known as Gravitational Lensing.
What is Gravitational Lensing?
Mass bends Light. What?
Yeah, mass can bend Light. The gravitational field of a really massive object is super strong. And this causes light rays passing close to that object to be bent and refocused somewhere else.

The more massive the object, the stronger its gravitational field and hence the greater the bending of light rays - just like using denser materials to make optical lenses results in a greater amount of refraction.
Here’s an animation showing a black hole going past a background galaxy.

This effect is one of the predictions of Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity
PC: cfhtlens, Urbane Legend

The moon through my RC-16 http://space-pics.tumblr.com/ source:http://imgur.com/r/Astronomy/5fUyf89

A Quadruple Sky Over Great Salt Lake
@i-can-taste-the-sun
I CANT STOP LAUGHING
Mondays lmao @rasinblazin
@rasinblazin

That feel when you’re so drained of creativity that you have to ask your friend to just pick a number from 1-44. Yeah this hasn’t been my greatest week in terms of art so I’m very this isn’t that great. ANYWAYS Teddy Roosevelt is the literal embodiment the shark from the body building ad from that one spongebob episode (I overdosed my add meds today so I’d like to apologize ahead of time). But yeah, sick of being the scrawny asthmatic kid he was, Teedy (he was actually called that) wanted to buff up and oh my god did he freaking accomplish that. He turned out to be basically invincible stopping a bullet with his chest at one point while being charismatic as fuck, but he would basically just disappear into the void whenever someone would say a dick joke. Also, apparently he didn’t swear on the bible when taking office when McKinley was assassinated so that’s why he’s saying oh my god.
@wingmanoftheuniverse: thank

First time stacking a photo of the milky way! taken 30 miles from Fargo ND http://space-pics.tumblr.com/ source:http://imgur.com/r/Astronomy/hQfdwrV

What is this? http://space-pics.tumblr.com/ source:http://imgur.com/r/Astronomy/WhU2y3g
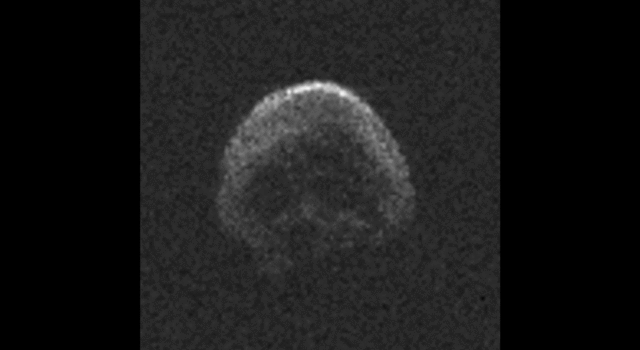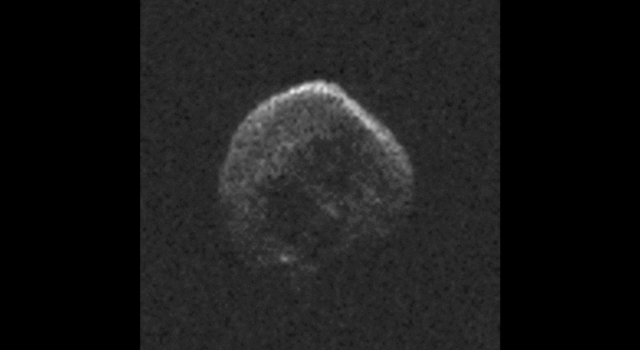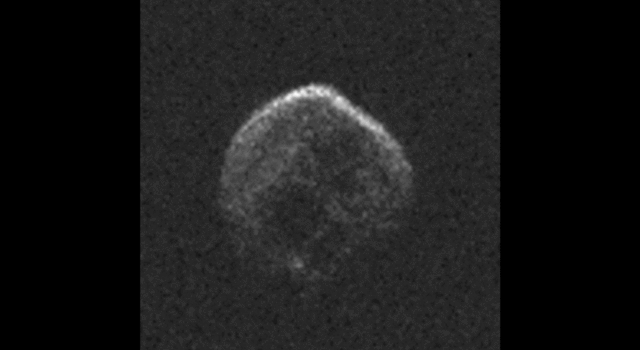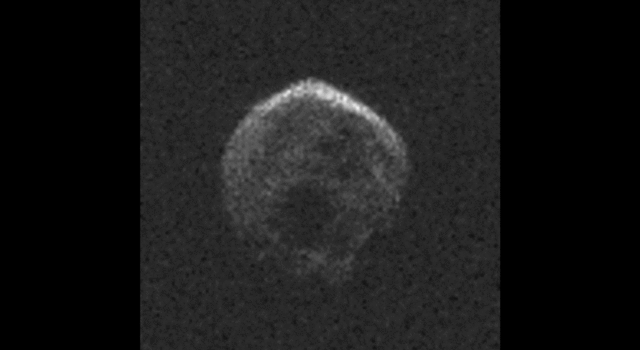
The large space rock that will zip past Earth this Halloween is most likely a dead comet that, fittingly, bears an eerie resemblance to a skull.
These first radar images from the National Science Foundation’s 1,000-foot (305-meter) Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico, indicate the near-Earth object is spherical in shape and approximately 2,000 feet (600 meters) in diameter. The radar images were taken on Oct. 30, 2015.
Scientists observing asteroid 2015 TB145 with NASA’s Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF) on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, have determined that the celestial object is more than likely a dead comet that has shed its volatiles after numerous passes around the sun.
For more information, click here.
Image Credit: NAIC-Arecibo/NSF
15 Years of Station Told in 15 Gifs
1. International Space Station Assembly Animation

From 1998 to 2011, five different space agencies representing 15 countries assembled the International Space Station, the largest structure ever built in space. Today humans are still living and work in the orbital laboratory. November 2, 2015 marks the 15th anniversary of continuous human presence onboard.
2. Entry of Expedition 1

Expedition 1 crew members including, Commander William Shepherd and Cosmonauts Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko arrive to the International Space Station for the first time on November 2, 2000.
3. September 11, 2001

Expedition 3 Commander Frank Culbertson was the only American living off the planet on September 11, 2001. He captured his view of the fateful day from the space station.
4. Kibo

The Japanese Experiment Module, or Kibo, is installed to the space station on June 3, 2008. Kibo means “hope” in Japanese, and it is the largest single space station module.
5. First 6-person Crew

The first 6 person crew on the space station gathers for a press conference in May 29, 2009. Because it was comprised of astronauts from NASA, CSA, ESA, JAXA, and Russia, this was the first and only time all international partners were represented on the space station at the same time.
6. SpaceX Dragon

The space station’s robotic arm captures the SpaceX Dragon during its demonstration flight on May 25, 2012, making it the first commercial vehicle ever to dock with the space station.
7. Olympic Torch

Russian Cosmonauts Sergey Ryanzanskiy and Oleg Kotov bring the Olympic torch outside the space station during a spacewalk on November 9, 2013. The torch traveled to the station as part of the Olympic torch relay ahead of the 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi, Russia.
8. Testing Fire in Space

Astronaut Reid Weisman captured a floating sphere of fire observed during the Flex-2 experiment on space station on July 18, 2014. The findings may lead to better engines here on Earth.
9. Aurora

Astronaut Reid Weisman’s timelapse of a flickering aurora seen from space station on August 28, 2014.
10. Sunrise

Astronaut Reid Weisman’s timelapse of what a sunrise looks like from the space station on September 23, 2014.
11. Water Bubbles

Astronaut Reid Weisman experiments with water bubbles in space on November 8, 2014.
12. GoPro

Astronauts Terry Virts and Barry “Butch” Wilmore capture the first GoPro footage of a spacewalk on February 25, 2015.
13. Lightning

Astronaut Terry Virts filmed a massive lightning storm over India from the space station on May 9, 2015.
14. Milky Way

Astronaut Terry Virts captured a stunning view of the Milky Way from space station on May 15, 2015.
15. Veggie

Astronauts Scott Kelly, Kjell Lindgren, and Kimiya Yui taste lettuce that had been grown and harvested in space for the very first time on August 10, 2015.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space:http://nasa.tumblr.com

Curiosity moved approximately 8.0m ESE (119º) on Sol 1151. Quick stitch of the available end-of-drive Navcams. More info to follow
http://space-pics.tumblr.com/

Funky Light Signal From Colliding Black Holes Explained
Entangled by gravity and destined to merge, two candidate black holes in a distant galaxy appear to be locked in an intricate dance. Researchers using data from NASA’s Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) and NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have come up with the most compelling confirmation yet for the existence of these merging black holes and have found new details about their odd, cyclical light signal.
The candidate black hole duo, called PG 1302-102, was first identified earlier this year using ground-based telescopes. The black holes are the tightest orbiting pair detected so far, with a separation not much bigger than the diameter of our solar system. They are expected to collide and merge in less than a million years, triggering a titanic blast with the power of 100 million supernovae.
Researchers are studying this pair to better understand how galaxies and the monstrous black holes at their cores merge – a common occurrence in the early universe. But as common as these events were, they are hard to spot and confirm.
PG 1302-102 is one of only a handful of good binary black hole candidates. It was discovered and reported earlier this year by researchers at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, after they scrutinized an unusual light signal coming from the center of a galaxy. The researchers, who used telescopes in the Catalina Real-Time Transient Survey, demonstrated that the varying signal is likely generated by the motion of two black holes, which swing around each other every five years. While the black holes themselves don’t give off light, the material surrounding them does.
In the new study, published in the Sept. 17 issue of Nature, researchers found more evidence to support and confirm the close-knit dance of these black holes. Using ultraviolet data from GALEX and Hubble, they were able to track the system’s changing light patterns over the past 20 years.
What’s causing the changes in light? One set of changes has to do with the “blue shifting” effect, in which light is squeezed to shorter wavelengths as it travels toward us in the same way that a police car’s siren squeals at higher frequencies as it heads toward you. Another reason has to do with the enormous speed of the black hole.
[Continue Reading→]

Integrated Space Plan, a 100-year plan to take mankind out of the solar system, has been updated.
The original Integrated Space Plan, created in 1989 >>

The Key to Colonizing Mars Could Be These Tiny Green Microbes
Long ago, a clan of hardy microbes called cyanobacteria helped terraform the lifeless Earth into a vibrant biosphere. Today, the very same critters could be the key to colonizing Mars.
Plants are going to have a tough time on the Red Planet’s hostile surface, but cyanobacteria have coped with extreme environments for eons. A paper led by astrobiologist Lynn Rothschild of NASA’s Ames Research Institute argues that we can harness these tiny photosynthesis machines to produce many of the resources we’ll need to survive, from food and oxygen to metals and medicine. Here are all the ways cyanobacteria can help us build a Martian colony.
Continue reading via Gizmodo and introduce yourself to biomining.

Rocket engine exhaust often contains a distinctive pattern known as shock diamonds or Mach diamonds. These are a series of shock waves and expansion fans that increase and decrease, respectively, the supersonic exhaust gases’ pressure until it equalizes with atmospheric pressure. The bright glowing spots visible to the naked eye are caused by excess fuel in the exhaust igniting. As awesome as shock diamonds look, they’re actually an indication of inefficiencies in the rocket: first, because the exhaust is over- or underexpanded, and second, because combustion inside the engine is incomplete. Both factors reduce a rocket engine’s efficiency (and both are, to some extent, inescapable). (Photo credit: XCOR)


New Horizons captures images of water ice and blue skies on Pluto
New Horizons, the spacecraft that keeps on giving.








NASA just released a brand new equirectangular projection of Jupiter, so I thought it would be fun to revisit the surface of some planetary bodies … IN CONTINUOUSLY LOOPING GIF FORM.
So here’s
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Earth’s moon
Mars
Jupiter
Ganymede (one of Jupiter’s moons)
Pluto
Credit: NASA/JPL, USGS

The large space rock that will zip past Earth this Halloween is most likely a dead comet that, fittingly, bears an eerie resemblance to a skull.
These first radar images from the National Science Foundation’s 1,000-foot (305-meter) Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico, indicate the near-Earth object is spherical in shape and approximately 2,000 feet (600 meters) in diameter. The radar images were taken on Oct. 30, 2015.
Scientists observing asteroid 2015 TB145 with NASA’s Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF) on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, have determined that the celestial object is more than likely a dead comet that has shed its volatiles after numerous passes around the sun.
For more information, click here.
Image Credit: NAIC-Arecibo/NSF

• Use the hand you write with.
• Make a fist with your thumb outside, not tucked inside. If it’s tucked inside your fist, when you punch someone, you might break your thumb. The thumb goes across your fingers, not on the side.
• Don’t be like in the movies—don’t aim for the face. Face punches don’t usually stop people, and you can miss when they duck their head or break your hand on their jaw. If you want to get away quickly, or end a fight, aim for the chest, or the ribs. If you really want to do some damage, e.g., you’re being attacked, aim for the throat, which will make it hard for your attacker to breathe for a hot minute.
• When you punch, you want to aim and hit with your first two knuckles. Not the flats of your fingers, and not your ring or pinky knuckles, which can break more easily. You can use your weight, if you’re on your feet, to add wallop, and spring into a punch with your feet and torso.


NASA in the 1970s expected to process the Space Shuttle after flights quickly, like an airliner. It didn’t work out that way.
Keep reading

T-39 days (October 26, 2015) - Technicians at the International Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center integrated the Cygnus spacecraft’s Pressurized Module with its Service Module late last week. The spacecraft spent last week being loaded with over 7,700 pounds of supplies for the orbiting laboratory. The PM arrived in mid-August while the SM arrived in early October. OA-4 is the first flight of a Cygnus spacecraft since October 2014′s launch failure of Orb-3. The Antares rocket is being redesigned, with its reflight slated to occur in spring, 2016. Until then, two Commercial Resupply Missions are scheduled to fly on United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rockets, OA-4 and OA-5. Launch of OA-4 is currently scheduled for 6:03 pm EST on Thursday, December 3.


Hubble’s Jupiter Maps Reveals Weird Structures
Over a 10 hour period, the Hubble Space Telescope gazed at the solar system’s largest planet to produce one of the most spectacular maps of Jupiter’s complex and dynamic atmosphere. Immediately astronomers were able to measure the size of the planet’s shrinking Great Red Spot and notice some mysterious structures along the way.
As the spot has shrunk, it’s color has also become more anemic, losing some of its redness. Also, as these new Hubble observations show, a strange wispy structure has formed inside the storm, becoming warped by the high-speed winds that have been clocked at a speed of 540 kilometers (335 miles) per hour. Astronomers, so far, have little explanation as to what this feature is or what caused it.
Another oddity has been spied just north of the planet’s equator — a wave-like structure has formed, something that hasn’t been seen since the Voyager 2 flyby in 1979. During that flyby, these waves were assumed to be a transient event and the fact the spacecraft imaged them was a fluke. But they’ve now returned, no doubt sparking some huge interest as to their origins.
Click to learn more
How you look at color is about to get all messed up…
A while back, I asked you to describe what color the moon appears to your eye. I got some pretty varied and entertaining answers, but you overwhelmingly agreed: The moon is essentially white or bright silver.
Well, you’re wrong.
The moon’s not white at all. It’s actually closer in color to an asphalt road, as we can clearly see in this 100% actually real series of images taken of the moon transiting Earth, courtesy of NOAA’s DSCOVR satellite:

That whole “the moon is white” thing? It’s just a nasty trick played on your brain by … well, another part of your brain. It has to do with the fact that our eyes perceive illumination in a scene relatively, not absolutely. It’s also why this GIF breaks your brain a little:

Watch this week’s It’s Okay To Be Smart video above to find out more!
Bonus: The PBS Digital Studios Science Squad™ brings you a double whammy of perceptual illusions this week! White isn’t the only light that messes with your visual system, not by a long shot. Did you know that red + green can look like… yellow?

Check out the video below from The Physics Girl and let Dianna teach you why, when it comes to colors, you should never quite believe your eyes:
NASA’s Fleet of Planet-hunters and World-explorers
Around every star is at least one planet, so we’re bound to find one that is rocky, like Earth, and possibly suitable for life. While we’re not quite to the point where we can zoom up and take clear snapshots of the thousands of distant worlds we’ve found outside our solar system, there are ways we can figure out what exoplanets light years away are made of, and if they have signs of basic building blocks for life. Here are a few current and upcoming missions helping us explore new worlds:
Kepler

Launched in 2009, the Kepler space telescope searched for planets by looking for telltale dips in a star’s brightness caused by crossing, or transiting, planets. It has confirmed more than 1,000 planets; of these, fewer than 20 are Earth-size (therefore possibly rocky) and in the habitable zone – the area around a star where liquid water could pool on the surface of an orbiting planet. Astronomers using Kepler data found the first Earth-sized planet orbiting in the habitable zone of its star.
In May 2013, a second pointing wheel on the spacecraft broke, making it not stable enough to continue its original mission. But clever engineers and scientists got to work, and in May 2014, Kepler took on a new job as the K2 mission. K2 continues the search for other worlds but has introduced new opportunities to observe star clusters, young and old stars, active galaxies and supernovae.
Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS)

Revving up for launch around 2017-2018, NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will find new planets the same way Kepler does, but right in the stellar backyard of our solar system while covering 400 times the sky area. It plans to monitor 200,000 bright, nearby stars for planets, with a focus on finding Earth and Super-Earth-sized planets.
Once we’ve narrowed down the best targets for follow-up, astronomers can figure out what these planets are made of, and what’s in the atmosphere. One of the ways to look into the atmosphere is through spectroscopy.
As a planet passes between us and its star, a small amount of starlight is absorbed by the gas in the planet’s atmosphere. This leaves telltale chemical “fingerprints” in the star’s light that astronomers can use to discover the chemical composition of the atmosphere, such as methane, carbon dioxide, or water vapor.
James Webb Space Telescope

Launching in 2018, NASA’s most powerful telescope to date, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), will not only be able to search for planets orbiting distant stars, its near-infrared multi-object spectrograph will split infrared light into its different colors- spectrum- providing scientists with information about an physical properties about an exoplanet’s atmosphere, including temperature, mass, and chemical composition.
Hubble Space Telescope

Hubble Space Telescope is better than ever after 25 years of science, and has found evidence for atmospheres bleeding off exoplanets very close to their stars, and even provided thermal maps of exoplanet atmospheres. Hubble holds the record for finding the farthest exoplanets discovered to date, located 26,000 light-years away in the hub of our Milky Way galaxy.
Chandra X-ray Observatory

Chandra X-ray Observatory can detect exoplanets passing in front of their parent stars. X-ray observations can also help give clues on an exoplanet’s atmosphere and magnetic fields. It has observed an exoplanet that made its star act much older than it actually is.
Spitzer Space Telescope

Spitzer Space Telescope has been unveiling hidden cosmic objects with its dust-piercing infrared vision for more than 12 years. It helped pioneer the study of atmospheres and weather on large, gaseous exoplanets. Spitzer can help narrow down the sizes of exoplanets, and recently confirmed the closest known rocky planet to Earth.
SOFIA

The Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) is an airplane mounted with an infrared telescope that can fly above more than 99 percent of Earth’s atmospheric water vapor. Unlike most space observatories, SOFIA can be routinely upgraded and repaired. It can look at planetary-forming systems and has recently observed its first exoplanet transit.
What’s Coming Next?
Analyzing the chemical makeup of Earth-sized, rocky planets with thin atmospheres is a big challenge, since smaller planets are incredibly faint compared to their stars. One solution is to block the light of the planets’ glaring stars so that we can directly see the reflected light of the planets. Telescope instruments called coronagraphs use masks to block the starlight while letting the planet’s light pass through. Another possible tool is a large, flower-shaped structure known as the starshade. This structure would fly in tandem with a space telescope to block the light of a star before it enters the telescope.
All images (except SOFIA) are artist illustrations.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
