
167 posts
Latest Posts by jackasslope - Page 3

Cryptid of the Day: Wanjilanko
Description: The Wanjilanko is a massive feline seen in the Casamance Forest of Senegal. It’s described as reddish with faint stripes, long fangs and a negligible tail. Cryptozoologists think that the creature is a living Saber Tooth Tiger.
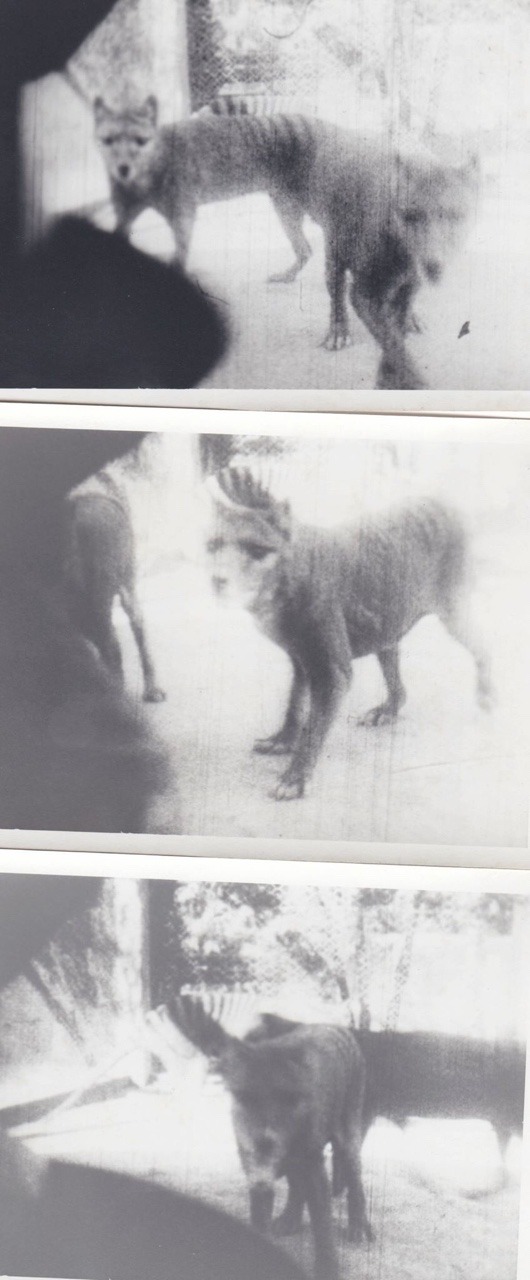


Some beautiful 35mm stills from a 1928 film of three thylacines residing at the Beaumaris Zoo, Hobart. Stills taken by James Malley.

Here’s a nice thylacine photograph I personally hadn’t seen before. From Eric Guiler’s book “Tasmanian Tiger: A Lesson to be Learnt.”
Photo caption in the book states that it’s a male at the Beaumaris Zoo.

The story of the Black Dog of Aylesbury dates back to the 1890s. The legend tells of a milkman who would travel the same path to get to his field of cattle every day. However, one day, while walking his normal path, the milkman stopped and noted the way was being blocked by an enormous black dog with blazing red eyes. He got the sense that this was no ordinary dog and he backtracked and took the longer route to his cattle. Each day thereafter, the milkman would try to go his shortcut, only to be blocked by that black dog. The milkman felt less and less fear of the dog as the days went by; on one fateful night, when he had a companion with him and he felt braver, the milkman decided enough was enough. He charged at the dog, using the pole that carried his milk pails as a weapon. When he struck at the dog, it simply vanished into thin air.

Inktober day 17 is the Black Dog. The black dog is a spectral or demonic entity found primarily in the folklore of the British Isles. The black dog is essentially a nocturnal apparition, in some cases a shapeshifter, and is often said to be associated with the Devil or described as a ghost or hellhound. It’s appearance was regarded as a portent of death. It is generally larger than a normal dog and often has large glowing eyes. It is sometimes associated with electrical storms, crossroads, places of execution and ancient pathways.

#20 - Dobhar-chú
The Dobhar-chú is a vicious lake cryptid of Irish folklore. Roughly translated as “water hound” is described as being half-dog, half-fish, or as something resembling a very large otter, up to two metres in length. The creature is said to be extremely aggressive and capable of killing humans. There even exists a grave in Conwall cemetary in County Leitrim, Ireland of a woman supposedly killed by the Dobhar-chú, with a carving of the creature featured on her headstone.

Beebe’s Manta Ray was first reported by William Beebe nearby the Galapagos Islands on April 27th, 1923. He described the manta as having a 10 foot wingspan. Its back is a dark brown with distinctive white bands that go halfway down its back to either side of its head. The very tips of the wings are also white in color. The manta supposedly collided with Beebe’s vessel briefly before quickly retreating from it.

The story of the Wolf Woman of Mobile was first published in newspapers on April 8th, 1971. This Alabama monster was reported over 50 times in one week. Witnesses claim that the top half of the creature was that of a human woman, but the bottom half was that of a wolf. Many people described the creature as “pretty and hairy”. Some believe that this creature may have been a werewolf. However, after 10 days of sightings, calls stopped and the creature was never seen again.

Some of the things that Gef the Talking Mongoose had said were written word for word in James Irving’s personal diary. It is thought that Voirrey Irving was behind it all using ventriloquism.
“I am not evil. I could be if I wanted. You don’t know what damage or harm I could do if I were roused. I could kill you all, but I won’t.”
“I am a ghost in the form of a weasel, and I shall haunt you with weird noises and clanking chains.”
“Of course I know what I am, and you are not going to get to know, and you are only grizzled because I won’t tell you. I might let you see me some time, but thou wilt never get to know what I am.”
“I have three attractions. I follow Voirrey, Mam gives me food, and Jim answers my questions.”
“I’ll split the atom! I am the fifth dimension! I am the eighth wonder of the world!”
“If you are kind to me, I will bring you good luck. If you are not kind, I shall kill all your poultry. I can get them wherever you put them!”

Inktober Day 12: The Ahuizotl
The ahuizotl is an amphibious creature, and when on land its fur dries into spikes as hard as steel. Its main prey is humans, although it only consumes the hair, fingernails, and teeth of its victims, leaving the rest of the body unscathed.
Jackalopes are my favorite cryptid, so I decided to stitch one featuring the night sky!


The oldest Thylacine illustration I have found yet, from Animal Life Throughout The Globe, Nelson and Sons, 1876.

Tatzelwurm The tatzelwurm has a snake-like body between 2 and 6 feet in length, with two clawed front legs, but no hind legs. It has smooth hairless skin covered with delicate scales. Its most distinctive trait is a large head with big eyes similar to the head of a cat, except for it having scales instead of fur. The tatzelwurm can grow to at least six feet long, but some specimens, possibly juveniles, are considerably smaller. Local folklore holds that the Tatzelwurm is able to defend itself by expelling poisonous fumes that are capable of killing a human
One claimed photograph of the Tatzelwurm exists. It was taken in 1934 by Swiss photographer named Balkin who took a photo of what he thought was a very peculiar log. When the camera flashed, the “log” darted away.

Cryptid of the Day: Snow Worm
Description: In Spring of 1978, in California’s San Gabriel Mountains, two cryptozoologists found a worm-like creature wiggling along a bank near a creek. They took it home and kept it for three months without feeding it. Miraculously, it lived. They believe the worm was a new species, since no worm expert could identify the species.
Tsuchinoko

Tsuchinoko:
Tsuchinoko are described as being between 30 and 80 centimetres in length, similar in appearance to a snake, but with a central girth that is much wider than its head or tail, and as having fangs and venom similar to that of a viper. Some accounts also describe the tsuchinoko as being able to jump up to a meter in distance.
According to legend, some tsuchinoko have the ability to speak and a propensity for lying, and is also said to have a taste for alcohol

The Cù Sìth (ku-shuh) by Manecoon
According to Scottish folklore, the cù-sìth is said to be the size of a young bull with the appearance of a dog. Its fur is shaggy, and usually cited as being dark green though sometimes white. Its tail is described as being long and either coiled up or plaited (braided). Its paws are described as being the width of a man’s hand.
The cù-sìth was feared as a harbinger of death and would appear to bear away the soul of a person to the afterlife, similar to the manner of the Grim Reaper.

Tasmanian wolf woven blanket design by MarcoNavarro on Threadless. I wish this had actually been made!
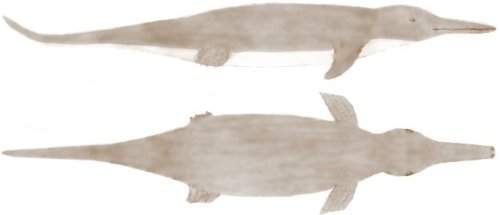
These sketches were drawn by Owen Burnham of a globster known as Gambo. The 15 year old measured the strange creature on June 12, 1983, when he found it on a beach in Islamic Republic of The Gambia. It measured to be “15 - 16 feet long”. While some believed the creature to be a dolphin, it had two nostrils at the tip of its snout, which dolphins do not. The body was not DNA tested as Burnham claims he did not think to take samples until he realized he could not identify the creature in any books.

Rods
A much overlooked cryptid, rods are believed to be extradimensional creatures. Some believe these undulating, serpent-like creatures move at a rate that is faster than the “framerate” of the human eye, but are sometimes captured on film. Rods have been known to measure from just a few centimetres, to over a mile in length. The largest of rods are believed to be connected to UFOs and alien life.
Rods are widely discredited as being regular flying insects that appear strange on-camera due to motionblur. However, some sightings are not so easily explained.

The Last Thylacine: September 7, 1936
Hey everyone! This may be a little late depending on your time zone (as I’m in Los Angeles / PST, I’m behind practically everyone). Sorry about that!
Today, September 7th, 2019, marks the 83rd Anniversary of the death of the last known thylacine in the Hobart Zoo. This animal is pictured above.
There are a lot of myths and misconceptions surrounding the thylacine - and this individual in particular - so I thought I’d make a post to correct a few of these. Keep in mind that new facts and evidence do occasionally come to light, so this is of course subject to change!
MYTH #1: The last thylacine was named Benjamin.
FACT: The name “Benjamin” was allegedly given to the animal by a keeper named Frank Darby. Darby later claimed to have worked with this animal in an interview that took place in 1968. However, no record exists of Darby ever working at the Hobart Zoo, and the zoo curator’s daughter Alison Reid denied that Darby ever worked there.** [Source]
** Note: Although the nickname “Benjamin” was likely made up by Darby after the fact, it has stuck, so many thylacine enthusiasts (including me) still use it to refer to the last individual.
MYTH #2: The last thylacine was actually female.
FACT: Zoologist David Fleay, who took much of the film footage of this individual, stated in a newspaper article and diary entry that the animal was male, referring to it as a “fine male marsupial wolf.” Furthermore, in 2011, careful video analysis by Dr. Stephen Sleightholme (director of the ITSD) confirmed the presence of a scrotal sac, indicating that the last thylacine was indeed a male. [Source, Source]
MYTH #3: “Benjamin” was part of the Mullins family group.
FACT: The Mullins female was snared while her young were still in the pouch. This assertion would assume that “Benjamin” was one of the pups, grew up in captivity, and was the last surviving member of the family. However, in photos (including the one on this post), the snare mark is clearly visible on the animal’s hind leg, indicating that it was wild caught. It is more likely that “Benjamin” was snared by a man named Elias Churchill, though this is also debated. [Source]
MYTH #4: The carcass of “Benjamin” was immediately discarded after death because it was in poor condition.
FACT: The carcass was in fact sent to the Tasmanian Museum. What happened to it after that is unknown. [Source]

The more modern interest in the legendary Loch Ness Monster was ignited after several sightings that took place in 1933. One of the sightings was recorded in the Inverness Courier in May. The witnesses of the May encounter reported “an enormous animal rolling and plunging” on the surface of the water. In June of the same year, George Spicer and his wife claimed to have seen an unknown creature cross the road on which they were traveling until it reached the waters of the loch and vanished. Spicer said that the creature was about 4 feet tall and 25 feet long with a strangely long neck that was a little thicker than an elephant’s trunk. The creature had no visible legs.




Colourised footage of Benjamin, the last know Tasmanian Tiger (Thylacine).
Benjamin died on September 7th, 1936 in Hobart zoo. It is believed that he died out of neglect, as he was locked out of his shelter and was exposed to the searing hot sun and freezing cold night of Tasmania.
The Thylacine was one of the last large marsupials left on Australia (the other being the Kangaroo) after a great extinction event occurred around 40 thousand years ago. This extinction event, caused mainly by the arrival of humans, wiped out 90% of Australia’s terrestrial vertebrates, including the famous Megafauna.
The Thylacine was around 15-30kg (33-66lbs), were carnivorous, and had numerous similarities to other species like dogs, despite not being related and purely by chance, in a phenomenon known as convergent evolution (just like the ability to fly of bats and birds, despite following different evolutionary paths). Not only that, they could open their jaws up to 120 degrees, could hop around on two legs like a kangaroo, and both males and females had pouches.
Lastly in a cruel twist, the Tasmanian government decided to protect the Thylacine - just 59 days before the last one died, in a very notable case case of “Too little too late”. To date, many biologists believe that there are still Thylacine roaming the wild plains of Australia.

The Irving family posed many questions to Gef the Talking Mongoose to try and get his answers. Once, among all their questions, the Irvings asked Gef if he knew what death was. To which, his voice replied simply, “Yes, a changeover.”







