Latest Posts by maevetheeuropan - Page 3

@little-laced Here are some test shots I took of the moon. It’s hard to tell because I had to reduce the image size drastically but the telescope was extremely difficult to keep focused. The image quality loss I incurred uploading this only adds to the ‘out-of-focus’ness
Also shout out to the Sea of Crises visible as the circular, dark-gray splotch on the right
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn about the science of photonics to create space communications, get updates on Juno, mining data from Voyager for new discoveries and more.

1. Carried on a Beam of Light
One of our major priorities is to make space communications more efficient. While our communications systems have matured over the decades, they still use the same radio-frequency system developed in the earliest days of the agency. After more than 50 years, we’re investing in new ways to increase data rates while also finding more efficient communications systems. Photonics–generating, detecting and manipulating particles of light–may provide the solution.
+ See how it works

2. It’s No Joke: Two New Moons for the Seventh Planet
Voyager 2 spacecraft flew by Uranus 30 years ago, but researchers are still making discoveries using the data it gathered. A new study led by University of Idaho researchers suggests there could be two tiny, previously undiscovered moonlets orbiting near two of the planet’s rings.
+ Find out how they were discovered

3. Vortex of Mystery
As southern winter solstice approaches in the Saturn system, our Cassini spacecraft has revealed dramatic seasonal changes in the atmospheric temperature and composition of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. Winter is taking a grip on Titan’s southern hemisphere, and a strong, whirling vortex has intensified in the upper atmosphere over the south pole.
+See more

4. The Spiders of Mars
Ten thousand volunteers viewing images of Martian south polar regions have helped identify targets for closer inspection, yielding new insights about seasonal slabs of frozen carbon dioxide and erosional features known as “spiders.” From the comfort of home, the volunteers have been exploring the surface of Mars by reviewing images from the Context Camera on our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and identifying certain types of seasonal terrains near Mars’ south pole.
+ Learn more and see how you can join in

7. Better Safe than Sorry
Juno entered safe mode last week and early indications are a software performance monitor induced a reboot of the spacecraft’s onboard computer. In this case, the safe mode turned off instruments and a few non-critical spacecraft components, and it confirmed the spacecraft was pointed toward the sun to ensure the solar arrays received power.The spacecraft acted as expected during the transition into safe mode, restarted successfully and is healthy. High-rate data has been restored, and the spacecraft is conducting flight software diagnostics. Meanwhile, the Juno science team continues to analyze returns from the first close Jupiter flyby on Aug. 27. Revelations so far include that Jupiter’s magnetic fields and aurora are bigger and more powerful than thought. Scientists have also had their first glimpse below the planet’s swirling cloud deck. The next close flyby is scheduled on Dec. 11, with all science instruments on.
+ Get the details
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
@laurathia -YES these are my favorite kind of articles to read!
@maevemauvaise










Thoughts that will change the way you think about the universe and your existence




Dynamic projection mapping onto deforming non-rigid surface
Truly impressive technology from Ishikawa Watanabe Laboratory, University of Tokyo, can accurately projection map on moving, loose, dynamic surfaces:
We realize dynamic projection mapping onto deforming non-rigid surface based on two original technologies. The first technology is a high-speed projector “DynaFlash” that can project 8-bit images up to 1,000 fps with 3 ms delay. The second technology is a high-speed non-rigid surface tracking at 1,000 fps. Since the projection and sensing are operated at a speed of 1,000 fps, a human cannot perceive any misalignment between the dynamically-deforming target and the projected images. Especially, focusing on new paradigms in the field of user interface and fashion, we have demonstrated dynamic projection mapping onto a deformed sheet of paper and T-shirt. Also we show that projection to multiple targets can be controlled flexibly by using our recognition technique.
More Here
Living and Working Aboard Station
Join us on Facebook Live for a conversation with astronaut Kate Rubins and the director of the National Institutes for Health on Tuesday, October 18 at 11:15 a.m. ET.
Astronaut Kate Rubins has conducted out of this world research aboard Earth’s only orbiting laboratory. During her time aboard the International Space Station, she became the first person to sequence DNA in space. On Tuesday, she’ll be live on Facebook with National Institute of Health director Francis Collins, who led the effort to map the human genome. You can submit questions for Kate using the hashtag #SpaceChat on Twitter, or during the live event. Here’s a primer on the science this PhD astronaut has been conducting to help inspire your questions:

Kate has a background in genomics (a branch of molecular genetics that deals with the study of genomes,specifically the identification and sequencing of their constituent genes and the application of this knowledge in medicine, pharmacy,agriculture, and other fields). When she began her tenure on the station, zero base pairs of DNA had been sequenced in space. Within just a few weeks, she and the Biomolecule Sequencer team had sequenced their one billionth base of DNA aboard the orbital platform.
“I [have a] genomics background, [so] I get really excited about that kind of stuff,” Rubins said in a downlink shortly after reaching the one billion base pairs sequenced goal.
Learn more about this achievement:
+First DNA Sequencing in Space a Game Changer
+Science in Short: One Billion Base Pairs Sequenced
Why is DNA Sequencing in Space a Big Deal?
A space-based DNA sequencer could identify microbes, diagnose diseases and understand crew member health, and potentially help detect DNA-based life elsewhere in the solar system.
+Why Sequencing DNA in Space is a Big Deal
https://youtu.be/1N0qm8HcFRI
Miss the Reddit AMA on the subject? Here’s a transcript:
+NASA AMA: We just sequenced DNA in space for the first time. Ask us anything!
NASA and Its Partnerships

We’re not doing this alone. Just like the DNA sequencing was a collaborative project with industry, so is the Eli Lilly Hard to Wet Surfaces investigation. In this experiment aboard the station, astronauts will study how certain materials used in the pharmaceutical industry dissolve in water while in microgravity. Results from this investigation could help improve the design of tablets that dissolve in the body to deliver drugs, thereby improving drug design for medicines used in space and on Earth. Learn more about what we and our partners are doing:
+Eli Lilly Hard to Wet Surfaces – been happening the last week and a half or so
Researchers to Test How Solids Dissolve in Space to Design Better Tablets and Pills on Earth
With our colleagues at the Stanford University School of Medicine, we’re also investigating the effects of spaceflight on stem cell-derived heart cells, specifically how heart muscle tissue, contracts, grows and changes in microgravity and how those changes vary between subjects. Understanding how heart muscle cells change in space improves efforts for studying disease, screening drugs and conducting cell replacement therapy for future space missions. Learn more:
+Heart Cells
+Weekly Recap From the Expedition Lead Scientist for Aug. 18, 2016
It’s Not Just Medicine

Kate and her crew mates have also worked on the combustion experiments.
Kate has also worked on the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM), an experimental expandable capsule that docks with the station. As we work on our Journey to Mars, future space habitats are a necessity. BEAM, designed for Mars or other destinations, is a lightweight and relatively simple to construct solution. Kate has recently examined BEAM, currently attached to the station, to take measurements and install sensors.

Kate recently performed a harvest of the Plant RNA Regulation experiment, by removing seed cassettes and stowing them in cold stowage.

The Plant RNA Regulation investigation studies the first steps of gene expression involved in development of roots and shoots. Scientists expect to find new molecules that play a role in how plants adapt and respond to the microgravity environment of space, which provides new insight into growing plants for food and oxygen supplies on long-duration missions. Read more about the experiment:
+Plant RNA Harvest
NASA Astronaut Kate Rubins is participating in several investigations examining changes in her body as a result of living in space. Some of these changes are similar to issues experienced by our elderly on Earth; for example, bone loss (osteoporosis), cardiovascular deconditioning, immune dysfunction, and muscle atrophy. Understanding these changes and how to prevent them in astronauts off the Earth may help improve health for all of us on the Earth. In additional, the crew aboard station is also working on more generalized studies of aging.
+ Study of the effects of aging on C. elegans, a model organism for a range of biological studies.
lol sometimes science publications are like 20 pages of gibberish. It feels like an alien language I’m learning slowly as I stare at the pages…
—___—







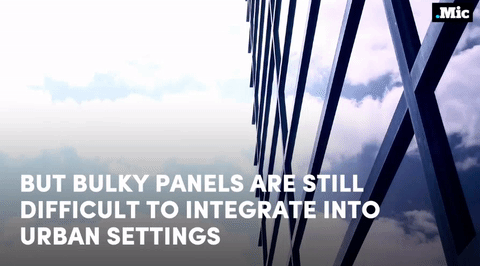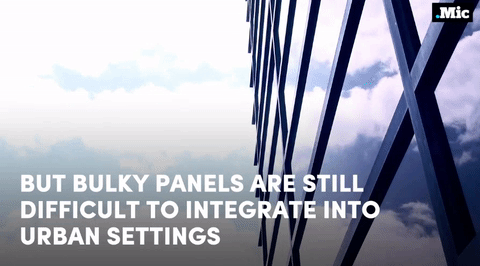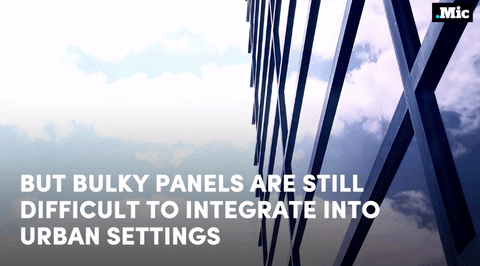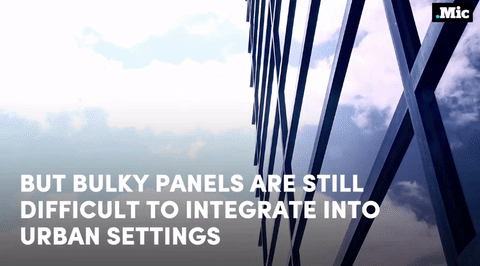


this is a massive step forward for renewable energy (x) | follow @the-future-now
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
There’s even more to Mars.

1. Batten Down the Hatches
Good news for future astronauts: scientists are closer to being able to predict when global dust storms will strike the Red Planet. The winds there don’t carry nearly the same force that was shown in the movie “The Martian,” but the dust lofted by storms can still wreak havoc on people and machines, as well as reduce available solar energy. Recent studies indicate a big storm may be brewing during the next few months.
+ Get the full forecast

2. Where No Rover Has Gone Before
Our Opportunity Mars rover will drive down an ancient gully that may have been carved by liquid water. Several spacecraft at Mars have observed such channels from a distance, but this will be the first up-close exploration. Opportunity will also, for the first time, enter the interior of Endeavour Crater, where it has worked for the last five years. All this is part of a two-year extended mission that began Oct. 1, the latest in a series of extensions going back to the end of Opportunity’s prime mission in April 2004. Opportunity landed on Mars in January of that year, on a mission planned to last 90 Martian days (92.4 Earth days). More than 12 Earth years later, it’s still rolling.
+ Follow along + See other recent pictures from Endeavour Crater

3. An Uphill Climb
Opportunity isn’t the only NASA Mars rover getting a mission extension. On the other side of the planet, the Curiosity rover is driving and collecting samples amid some of the most scenic landscapes ever visited on Mars. Curiosity’s two-year mission extension also began Oct. 1. It’s driving toward uphill destinations, including a ridge capped with material rich in the iron-oxide mineral hematite, about a mile-and-a-half (two-and-a-half kilometers) ahead. Beyond that, there’s an exposure of clay-rich bedrock. These are key exploration sites on lower Mount Sharp, which is a layered, Mount-Rainier-size mound where Curiosity is investigating evidence of ancient, water-rich environments that contrast with the harsh, dry conditions on the surface of Mars today.
+ Learn more

4. Keep a Sharp Lookout
Meanwhile, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter continues its watch on the Red Planet from above. The mission team has just released a massive new collection of super-high-resolution images of the Martian surface.
+ Take a look

5. 20/20 Vision for the 2020 Rover
In the year 2020, Opportunity and Curiosity will be joined by a new mobile laboratory on Mars. In the past week, we tested new “eyes” for that mission. The Mars 2020 rover’s Lander Vision System helped guide the rocket to a precise landing at a predesignated target. The system can direct the craft toward a safe landing at its primary target site or divert touchdown toward better terrain if there are hazards in the approaching target area.
+ Get details
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

This is a picture from the Curiosity Rover on Mars showing Earth from the Perspective of Mars. You are literally looking at your home from the Perspective of another planet. Epic times indeed



Creepy or adorable? Researchers at Harvard University have demonstrated the first autonomous, untethered, entirely soft robot: the octobot.
Instead of being controlled by electronics, the robot’s logic board is powered by chemical reactions and fluid passing along tiny channels. Scientist have struggled to create completely soft robots because rigid components like circuit boards, power sources and electronic controls are difficult to replace.
Learn more about the octobot and soft robotics here and see the full study published in Nature here.
Videos Credit: Harvard SEAS/Image Credit Lori Sanders

A 25-year-old student has just come up with a way to fight drug-resistant superbugs without antibiotics.
The new approach has so far only been tested in the lab and on mice, but it could offer a potential solution to antibiotic resistance, which is now getting so bad that the United Nations recently declared it a “fundamental threat” to global health.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria already kill around 700,000 people each year, but a recent study suggests that number could rise to around 10 million by 2050.
In addition to common hospital superbug, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), scientists are now also concerned that gonorrhoea is about tobecome resistant to all remaining drugs.
But Shu Lam, a 25-year-old PhD student at the University of Melbourne in Australia, has developed a star-shaped polymer that can kill six different superbug strains without antibiotics, simply by ripping apart their cell walls.
“We’ve discovered that [the polymers] actually target the bacteria and kill it in multiple ways,” Lam told Nicola Smith from The Telegraph. “One method is by physically disrupting or breaking apart the cell wall of the bacteria. This creates a lot of stress on the bacteria and causes it to start killing itself.”
The research has been published in Nature Microbiology, and according to Smith, it’s already being hailed by scientists in the field as “a breakthrough that could change the face of modern medicine”.
Before we get too carried away, it’s still very early days. So far, Lam has only tested her star-shaped polymers on six strains of drug-resistant bacteria in the lab, and on one superbug in live mice.
But in all experiments, they’ve been able to kill their targeted bacteria - and generation after generation don’t seem to develop resistance to the polymers.
Continue Reading.
OMG congrats! How exciting! I can't wait to see your photos! I've tried with my SLR and uh it has NOT gone well lol.
I did it.
After a year of talking I finally bit the bullet and got a DSLR camera (Nikon D5300) for astrophotography. Will be using it at the observatory (16″ Cassegrain) as well as during hikes for sweeping vistas under the Milky Way. Very excited to explore astrophotography as a hobby and can’t wait to start uploading pictures
//screams// THIS IS LOVELY OMG
Finally
HUGE ANNOUNCEMENT!
Elon Musk is set to announce his plans for Mars colonization in an hour, at 2:30 Eastern Time.
Please watch it because this could be history in the making.
Why Sequencing DNA in Space is a Big Deal
… And How You Can Talk to the Scientists Who Made It Happen

Less than one month ago, DNA had never been sequenced in space. As of today, more than one billion base pairs of DNA have been sequenced aboard the International Space Station, Earth’s only orbiting laboratory. The ability to sequence the DNA of living organisms in space opens a whole new world of scientific and medical possibilities. Scientists consider it a game changer.

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins, who has a background in genomics, conducted the sequencing on the space station as part of the Biomolecule Sequencer investigation. A small, commercial, off-the-shelf device called MinION (min-EYE-ON), manufactured by Oxford Nanopore Technologies in the UK, was used to sequence the DNA of bacteria, a virus and rodents. Human DNA was not sequenced, and there are no immediate plans to sequence human DNA in space.

(Image Credit: Oxford Nanopore Technologies)
The MinION is about the size of a candy bar, and plugs into a laptop or tablet via USB connection, which also provides power to the device. The tiny, plug and play sequencer is diminutive compared to the large microwave-sized sequencers used on Earth, and uses much less power. Unlike other terrestrial instruments whose sequencing run times can take days, this device’s data is available in near real time; analysis can begin within 10-15 minutes from the application of the sample.

Having real-time analysis capabilities aboard the space station could allow crews to identify microbes, diagnose infectious disease and collect genomic and genetic data concerning crew health, without having to wait long periods of time to return samples to Earth and await ground-based analysis.
The first DNA sequencing was conducted on Aug. 26, and on Sept. 14, Rubins and the team of scientists back at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston hit the one-billionth-base-pairs-of-DNA-sequenced mark.

Have more questions about how the Biomolecule Sequencer works, or how it could benefit Earth or further space exploration? Ask the team of scientists behind the investigation, who will be available for questions during a Reddit Ask Me Anything on /r/science on Wednesday, Sept. 29 at 2 p.m. EDT.
The participants are:
Dr. Aaron Burton, NASA Johnson Space Center, Planetary Scientist and Principal Investigator
Dr. Sarah Castro-Wallace, NASA Johnson Space Center, Microbiologist and Project Manager
Dr. David J. Smith, NASA Ames Research Center, Microbiologist
Dr. Mark Lupisella, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Systems Engineer
Dr. Jason P. Dworkin, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Astrobiologist
Dr. Christopher E. Mason, Weill Cornell Medicine Dept. of Physiology and Biophysics, Associate Professor
this website pisses me off, everyones always like “space is so cool!” not its not, space is bullshit and i hate everything about it, i genuinely just saw the phrase “a black hole with a mass two billion times the mass of the sun” im so pissed off, shut the fuck up, dont patronise me scientists you know i dont know what the fuck that means, my sad little brain cant comprehend the mass of one sun let alone two fucking billion, i cant even count past 10 without getting confused and youre out here talking about the mass of two billion fucking suns, shut the hell up. and dont even get me started about black holes or the expansion of the universe because thats another two seperate rants entierly. oh and apparently theres a planet made of ice except the ice is also on fire??? yeah sure fucking thing, scientists. and this is just the shit i know about. i purposely dont research space because it pisses me off so much, god knows what other fucking bullshit exists out there that ive yet to read a fucking wikipedia article about. i dont think space is real, literally everything about space is so fucking fake, this is just some elaborate fucking practicle joke. two billion times the mass of the sun, fuck you

Fantastic success story for the astronomy community of China, congratulations!
People can’t anticipate how much they’ll miss the natural world until they are deprived of it. I have read about submarine crewmen who haunt the sonar room, listening to whale songs and colonies of snapping shrimp. Submarine captains dispense “periscope liberty” - a chance to gaze at clouds and birds and coastlines - and remind themselves that the natural world still exists. I once met a man who told me that after landing in Christchurch, New Zealand, after a winter at the South Pole research station, he and his companions spent a couple of days just wandering around staring in awe at flowers and trees. At one point, one of them spotted a woman pushing a stroller. “A baby!” he shouted, and they all rushed across the street to see. The woman turned the stroller and ran. Nothing tops space as a barren, unnatural environment. Astronauts who had no prior interest in gardening spend hours tending experimental greenhouses. “They are our love,” said cosmonaut Vladislav Volkov of the tiny flax plants - with which they shared the confines of Salyut 1, the first Soviet space station. At least in orbit, you can look out the window and see the natural world below. On a Mars mission, once astronauts lose sight of Earth, they’ll be nothing to see outside the window. “You’ll be bathed in permanent sunlight, so you won’t even see any stars,” astronaut Andy Thomas explained to me. “All you’ll see is black.”
Mary Roach. Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the Void.
This is a really interesting read - it’s got a lot of information that I would never have thought to think of (such as - will astronauts eyeballs become different shapes without gravity - weird), but it also has really good chapters about the psychology of space.
(via psycholar)
this is wonderful - and def something I've thought about!







Here’s a comic on something flaming hot!
This week’s comic: Firewall Theory
http://www.sciencealert.com/try-to-escape-a-black-hole-and-you-ll-be-burnt-to-a-crisp-new-paper-cautions
https://profmattstrassler.com/articles-and-posts/relativity-space-astronomy-and-cosmology/black-holes/black-hole-information-paradox-an-introduction/

You Can Now Access All Of NASA’s Research Online For Free
Geeks and wannabe astronauts rejoice – NASA has announced they’re making all their research publicly available on a new online portal.
The new site PubSpace will put up any research or data that NASA has funded within one year of publication. That also includes any peer-reviewed scholarly journals and papers, which are often barred by paywalls.
“At NASA, we are celebrating this opportunity to extend access to our extensive portfolio of scientific and technical publications,” NASA Deputy Administrator Dava Newman said in a press release. “Through open access and innovation we invite the global community to join us in exploring Earth, air and space.”
The pledge is in light of the government’s request to make science agencies more transparent and accessible. NASA hopes this increased public access accelerates the spread of information, fosters interest, and ultimately advances scientific knowledge.
The European Union recently said they also hope to make all of their scientific research free and accessible by 2020.
“Making our research data easier to access will greatly magnify the impact of our research,” said NASA Chief Scientist Ellen Stofan. “As scientists and engineers, we work by building upon a foundation laid by others.”
You can check it all out here: https://www.nihms.nih.gov/db/sub.cgi
~ IFL Science
Ooooh very cool!
Constellations and the Calendar
Did you recently hear that NASA changed the zodiac signs? Nope, we definitely didn’t…
…Here at NASA, we study astronomy, not astrology. We didn’t change any zodiac signs, we just did the math. Here are the details:
First Things First: Astrology is NOT Astronomy…
Astronomy is the scientific study of everything in outer space. Astronomers and other scientists know that stars many light years away have no effect on the ordinary activities of humans on Earth.
Astrology is something else. It’s not science. No one has shown that astrology can be used to predict the future or describe what people are like based on their birth dates.

Some curious symbols ring the outside of the Star Finder. These symbols stand for some of the constellations in the zodiac. What is the zodiac and what is special about these constellations?

Imagine a straight line drawn from Earth though the sun and out into space way beyond our solar system where the stars are. Then, picture Earth following its orbit around the sun. This imaginary line would rotate, pointing to different stars throughout one complete trip around the sun – or, one year. All the stars that lie close to the imaginary flat disk swept out by this imaginary line are said to be in the zodiac.

The constellations in the zodiac are simply the constellations that this imaginary straight line points to in its year-long journey.
What are Constellations?
A constellation is group of stars like a dot-to-dot puzzle. If you join the dots—stars, that is—and use lots of imagination, the picture would look like an object, animal, or person. For example, Orion is a group of stars that the Greeks thought looked like a giant hunter with a sword attached to his belt. Other than making a pattern in Earth’s sky, these stars may not be related at all.

Even the closest star is almost unimaginably far away. Because they are so far away, the shapes and positions of the constellations in Earth’s sky change very, very slowly. During one human lifetime, they change hardly at all.
A Long History of Looking to the Stars
The Babylonians lived over 3,000 years ago. They divided the zodiac into 12 equal parts – like cutting a pizza into 12 equal slices. They picked 12 constellations in the zodiac, one for each of the 12 “slices.” So, as Earth orbits the sun, the sun would appear to pass through each of the 12 parts of the zodiac. Since the Babylonians already had a 12-month calendar (based on the phases of the moon), each month got a slice of the zodiac all to itself.

But even according to the Babylonians’ own ancient stories, there were 13 constellations in the zodiac. So they picked one, Ophiuchus, to leave out. Even then, some of the chosen 12 didn’t fit neatly into their assigned slice of the pie and crossed over into the next one.

When the Babylonians first invented the 12 signs of zodiac, a birthday between about July 23 and August 22 meant being born under the constellation Leo. Now, 3,000 years later, the sky has shifted because Earth’s axis (North Pole) doesn’t point in quite the same direction.

The constellations are different sizes and shapes, so the sun spends different lengths of time lined up with each one. The line from Earth through the sun points to Virgo for 45 days, but it points to Scorpius for only 7 days. To make a tidy match with their 12-month calendar, the Babylonians ignored the fact that the sun actually moves through 13 constellations, not 12. Then they assigned each of those 12 constellations equal amounts of time.
So, we didn’t change any zodiac signs…we just did the math.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

NASA Is Considering A Deep Sleep Option for Mars Mission Crew
A NASA-backed study is exploring an innovative way to dramatically cut the cost of a human expedition to Mars — put the crew in stasis.
The deep sleep, called torpor, would reduce astronauts’ metabolic functions with existing medical procedures. Torpor also can occur naturally in cases of hypothermia.
“Therapeutic torpor has been around in theory since the 1980s and really since 2003 has been a staple for critical care trauma patients in hospitals,” aerospace engineer Mark Schaffer, with SpaceWorks Enterprises in Atlanta, said at the International Astronomical Congress in Toronto this week. “Protocols exist in most major medical centers for inducing therapeutic hypothermia on patients to essentially keep them alive until they can get the kind of treatment that they need.”
Coupled with intravenous feeding, a crew could be put in hibernation for the transit time to Mars, which under the best-case scenario would take 180 days one-way.
So far, the duration of a patient’s time in torpor state has been limited to about one week.
“We haven’t had the need to keep someone in (therapeutic torpor) for longer than seven days,” Schaffer said. “For human Mars missions, we need to push that to 90 days, 180 days. Those are the types of mission flight times we’re talking about.”
Impressive Payoffs
Economically, the payoff looks impressive. Crews can live inside smaller ships with fewer amenities like galleys, exercise gear and of course water, food and clothing. One design includes a spinning habitat to provide a low-gravity environment to help offset bone and muscle loss.
SpaceWorks’ study, which was funded by NASA, shows a five-fold reduction in the amount of pressurized volume need for a hibernating crew and a three-fold reduction in the total amount of mass required, including consumables like food and water.
Overall, putting a crew in stasis cuts the baseline mission requirements from about 400 tons to about 220 tons.
“That’s more than one heavy-lift launch vehicle,” Schaffer said.
The Big Chill
The study looked at a two-part system for putting Mars-bound astronauts in stasis and bringing them out. The cooling would be done through an internasal system, which Schaffer admits is “not very comfortable,” but inhaling a coolant has several advantages over reducing body temperatures with external cooling pads. Cooled from the outside, the body is more susceptible to shivering and possible tissue damage, Schaffer notes.
The so-called RhinoChill System lowers body temperature about 1 degree Fahrenheit per hour. Reaching torpor state — between 89 degrees and 93 degrees Fahrenheit — takes about six hours.
Simply stopping the flow of coolant will bring a person out of stasis, though the SpaceWorks study included rewarming pads as a backup and to speed up the waking process in case of an emergency.
An alternative to having the whole crew in stasis is to have one person awake for two to three days, then hibernate for 14 days. By staggering the shifts, no one person would be in stasis for more than 14 days at a time and one crewmember would be awake to monitor the ship, conduct science experiments and handle maintenance chores.
Schaffer also points to a potential psychological advantage to stasis.
“Rather than being stuck in a can for 180 days, you go to sleep, you wake up and you’re there,” he said. More research is needed to assure prolonged stasis is safe, but initial results are promising, Schaffer added.
“We have not seen any show-stoppers on the medical side or on the engineering side,” he said.

What’s hard about Mars?
Mars, unlike the Moon, is far away. It also has an atmosphere - but not a useful one. Atmospheric density, wind, dust storms… all of these things contribute to a larger list of circumstances that any given mission needs to be ready for.
All those circumstances contribute heavily to the cost, time and hard resources needed to be poured into the mission preparation. In addition, the vast distance to Mars means the cost of carrying all this prepared hardware must be covered.
The atmosphere of Mars is such that if you’re going too fast during entry, you’ll burn up. It’s such a low density however that parachutes aren’t tremendously useful.
During the Curiosity rover’s landing it needed a heat shield, a supersonic parachute, rocket boosters to slow it down, a sky-crane to allow Curiosity to drop to the surface like an interplanetary spider and then explosive propulsion to send the platform it dropped from a safe distance away to crash into the surface.
During this landing, the rover experienced a force of about 15 g’s. That force would make a 200 lb man weigh 3000 lbs. Without proper precautions it would make the average head snap down at about 150 to 165 lbs.
NASA’s developing a new type of parachute and it’s being attached to a flying saucer-like spacecraft known as the Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator. This is currently hoped to provide NASA with a stable go-to architecture for future Mars missions.
The red planet’s killed most missions sent there. Power for solar-panels on rovers get covered during planet-wide dust storms. Some missions smashed into its moons. Some have smashed into its surface. Others have simply missions the planet entirely only to drift away as Mars dances around the Sun.
The world is an untamed place and has sought to buck all attempts to temper its mysteries.
(Image credit: ESA / DLR / FU Berlin (G. Neukum) / animation by Emily Lakdawalla)

NASA scientists have reported that they’ve successfully tested an engine called the electromagnetic propulsion drive, or the EM Drive, in a vacuum that replicates space. The EM Drive experimental system could take humans to Mars in just 70 days without the need for rocket fuel, and it’s no exaggeration to say that this could change everything.
But before we get too excited (who are we kidding, we’re already freaking out), it’s important to note that these results haven’t been replicated or verified by peer review, so there’s a chance there’s been some kind of error. But so far, despite a thorough attempt to poke holes in the results, the engine seems to hold up.
Continue Reading.











