Latest Posts by maevetheeuropan - Page 4
NASA Technology in Your Life
How does NASA technology benefit life on Earth? It probably has an impact in more ways than you think! Since 1976, our Spinoff program has profiled nearly 2,000 space technologies that have transformed into commercial products and services. In celebration of Spinoff’s 40th year of publication, we’ve assembled a collection of spinoffs that have had the greatest impact on Earth.
Take a look and see how many you utilize on a regular basis:
Digital Image Sensors

Whether you take pictures and videos with a DSLR camera or a cell phone, or even capture action on the go with a device like a GoPro Hero, you’re using NASA technology. The CMOS active pixel sensor in most digital image- capturing devices was invented when we needed to miniaturize cameras for interplanetary missions. This technology is also widely used in medical imaging and dental X-ray devices.
Enriched Baby Formula

While developing life support for Mars missions, NASA-funded researchers discovered a natural source for an omega-3 fatty acid previously found primarily in breast milk that plays a key role in infant development. The ingredient has since been added to more than 90% of infant formula on the market and is helping babies worldwide develop healthy brains, eyes and hearts.
NASTRAN Software

NASTRAN is a software developed by our engineers that performs structural analysis in the 1960s. Still popular today, it’s been used to help design everything from airplanes and cars to nuclear reactors and even Disney’s Space Mountain roller coaster.
Food Safety Standards

Looking to ensure the absolute safety of prepackaged foods for spaceflight, we partnered with the Pillsbury Company to create a new, systematic approach to quality control. Now known as Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), the method has become an industry standard that benefits consumers worldwide by keeping food free from a wide range of potential chemical, physical and biological hazards.
Neutral Body Posture Specifications

What form does the human body naturally assume when all physical influences, including the pull of gravity, stop affecting it? We conducted research to find out using Skylab, America’s first space station, and later published specifications for what it called neutral body posture. The study has informed seat designs in everything from airplanes and office chairs to several models of Nissan automobiles.
Advanced Water Filtration

We recently discovered unexpected sources of water on the moon and Mars, but even so, space remains a desert for human explorers, and every drop must be recycled and reused. A nano filter devised to purify water in orbit is currently at work on Earth, in devices that supply water to remote villages as well as in a water bottle that lets hikers and adventurers stay hydrated using streams and lakes.
Swimsuit Designs

Wind-tunnel testing at our Langley Research Center played a key role in the development of Speedo’s LZR Racer swimsuit, proving which materials and seams best reduced drag as a swimmer cuts through the water. The swimsuit made a splash during its Olympic debut in 2008, as nearly every medal winner and world-record breaker wore the suit.
Air Purifier

When plants grow, they release a gas called ethylene that accelerates decay, hastening the wilting of flowers and the ripening of fruits and vegetables. Air circulation on Earth keeps the fumes from building up, but in the hermetically sealed environment of a spacecraft, ethylene poses a real challenge to the would-be space farmers. We funded the development of an ethylene scrubber for the International Space Station that has subsequently proved capable of purifying air on Earth from all kinds of pathogens and particulates. Grocery stores use it to keep produce fresh longer. It’s also been marketed for home use and has even been embraced by winemakers, who employ the scrubber to keep aging wine in barrels free from mold, mildew and musty odors.
Scratch-Resistant, UV-Reflective Lenses

Some of the earliest research into effective scratch-resistant coatings for prescription and sunglass lenses drew from work done at Ames Research Center on coatings for astronaut helmet visors and plastic membranes used in water purification systems. In the 1980s, we developed sunlight-filtering lenses to provide eye protection and enhance colors, and these lenses have found their way into sunglasses, ski goggles and safety masks for welders.
Dustbuster

An Apollo-era partnership with Black & Decker to build battery-operated tools for moon exploration and sample collection led to the development of a line of consumer, medical and industrial hand-held cordless tools. This includes the popular Dustbuster cordless vacuum.
To see even more of our spinoff technologies, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/offices/oct/40-years-of-nasa-spinoff
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Space Station Research: Cardiovascular Health
Each month, we highlight a different research topic on the International Space Station. In February, our focus is cardiovascular health, which coincides with the American Hearth Month.
Like bones and muscle, the cardiovascular system deconditions (gets weaker) in microgravity. Long-duration spaceflight may increase the risk of damage and inflammation in the cardiovascular system primarily from radiation, but also from psychological stress, reduced physical activity, diminished nutritional standards and, in the case of extravehicular activity, increased oxygen exposure.

Even brief periods of exposure to reduced-gravity environments can result in cardiovascular changes such as fluid shifts, changes in total blood volume, heartbeat and heart rhythm irregularities and diminished aerobic capacity.

The weightless environment of space also causes fluid shifts to occur in the body. This normal shift of fluids to the upper body in space causes increased inter-cranial pressure which could be reducing visual capacity in astronauts. We are currently testing how this can be counteracted by returning fluids to the lower body using a “lower body negative pressure” suit, also known as Chibis.
Spaceflight also accelerates the aging process, and it is important to understand this process to develop specific countermeasures. Developing countermeasures to keep astronauts’ hearts healthy in space is applicable to heart health on Earth, too!

On the space station, one of the tools we have to study heart health is the ultrasound device, which uses harmless sound waves to take detailed images of the inside of the body. These images are then viewed by researchers and doctors inside Mission Control. So with minimal training on ultrasound, remote guidance techniques allow astronauts to take images of their own heart while in space. These remote medicine techniques can also be beneficial on Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com








Very strange things happen to your body if you spend a year in space
NASA Astronaut Scott Kelly returns to Earth Tuesday night after spending almost a year in space.
But his 340 days aboard the International Space Station (ISS) haven’t been all fun and games.
Our bodies evolved on Earth, so they’re not built for weightlessness — which is exactly why NASA plans to use Kelly to study the long-term effects of spaceflight the human body.


Mars Pathfinder & Sojourner Rover (360 View) Explained
Thanks to new technology, we can take a 360-degree tour of the 1997 Pathfinder mission landing site, including Sojourner, the first Mars rover. Check out this interactive YouTube panorama, and then…
…keep scrolling to find out more about each point of interest, how the Pathfinder mission compares to “The Martian” and NASA’s real Journey to Mars.

Yogi
“Yogi” is a meter-size rock about 5 meters northwest of the Mars Pathfinder lander and the second rock visited by the Sojourner Rover’s alpha proton X-ray spectrometer (APXS) instrument. This mosaic shows super resolution techniques applied to help to address questions about the texture of this rock and what it might tell us about how it came to be.

Twin Peaks
The Twin Peaks are modest-size hills to the southwest of the Mars Pathfinder landing site. They were discovered on the first panoramas taken by the IMP camera on the July 4, 1997, and subsequently identified in Viking Orbiter images taken over 20 years ago. They’re about 30-35 meters tall.

Barnacle Bill
“Barnacle Bill” is a small rock immediately west-northwest of the Mars Pathfinder lander and was the first rock visited by the Sojourner Rover’s alpha proton X-ray spectrometer (APXS) instrument. If you have some old-school red-cyan glasses, put them on and see this pic in eye-popping 3-D.

Rock Garden
The Rock Garden is a cluster of large, angular rocks tilted in a downstream direction from ancient floods on Mars. The rocky surface is comprised of materials washed down from the highlands and deposited in this ancient outflow channel.

MOAR INFO
Pathfinder Lander & Sojourner Rover
Mission Facts [PDF]
Science Results
Rock & Soil Types


This vista was stitched together from many images taken in 1997 by Pathfinder.

Pathfinder and Sojourner figure into Mark Watney’s quest for survival on the Red Planet in the book and movie, “The Martian.” See JPL’s role in making “The Martian” a reality: http://go.nasa.gov/1McRrXw and discover nine real NASA technologies depicted in “The Martian”: http://go.nasa.gov/1QiyUiC.

So what about the real-life “Journey to Mars”? NASA is developing the capabilities needed to send humans to Mars in the 2030s. Discover more at http://nasa.gov/journeytomars and don’t forget to visit me when you make it to the Red Planet. Until then, stay curious and I’ll see you online.
What Did Astronaut Scott Kelly Do After a #YearInSpace?
Astronaut Scott Kelly just returned from his One-Year Mission aboard the International Space Station. After spending 340 days on orbit, you can imagine that he started to miss a few Earthly activities. Here are a few things he did after his return home:
Watched a Sunset

While on the International Space Station for his One-Year Mission, astronaut Scott Kelly saw 16 sunrises/sunsets each day…so he definitely didn’t miss out on the beauty. That said, watching a sunset while on Earth is something that he had to wait to see. Tweet available HERE.
Ate Fresh Food

After spending a year on the International Space Station, eating precooked food, anyone would be excited to dig into a REAL salad. Astronaut Scott Kelly was no exception, and posted about his first salad on Earth after his one-year mission. Learn more about what astronauts eat while in space HERE. Tweet available HERE.
Jumped into a Pool

Water is a precious resource in space. Unfortunately, that means that there isn’t a pool on the space station. Luckily, astronaut Scott Kelly was able to jump into some water after his return to Earth. Tweet/video available HERE.
Sat at a Dinner Table

While living on the International Space Station, crew members regularly enjoy their meals together, but do so while floating in microgravity. The comfort of pulling up a chair to the dinner table is something they can only experience once they’re back home on Earth. Tweet available HERE.
Enjoyed the Weather

When crew members live on the space station they can’t just step outside for a stroll. The only time they go outside the orbiting laboratory is during a spacewalk. Even then, they are confined inside a bulky spacesuit. Experiencing the cool breeze or drops of rain are Earthly luxuries. Tweet available HERE.
Stopped by the Doctor’s Office

The One-Year Mission doesn’t stop now that astronaut Scott Kelly is back on Earth. Follow-up exams and tests will help scientists understand the impacts of microgravity on the human body during long-duration spaceflight. This research will help us on our journey to Mars. Tweet available HERE.
Visited the Denist

When you spend a year in space, you’ll probably need to catch up on certain things when you return to Earth. Astronaut Scott Kelly made sure to include a visit to the dentist on his “return home checklist”. Tweet available HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Do You Stay Fit on a Mission to Mars?
This mini exercise device could be the key!
Onboard the International Space Station, astronauts need to work out to maintain their bone density and muscle mass, usually exercising 2 hours every single day. Throughout the week, they exercise on three different pieces of equipment–a bike, a treadmill and the Advanced Restive Exercise Device (ARED).

All these devices are needed to keep an astronaut healthy.
However, deep-space vehicles like our Orion Spacecraft aren’t as roomy as station, so everything — including exercise equipment — needs to be downsized. The Miniature Exercise Device (MED-2) is getting us one step closer to being able to keep astronauts’ bodies healthy on long journeys to the moon, Mars and beyond.

MED-2 is a compact, all-in-one exercise device that we developed and will be launching to the space station Tuesday, March 22. Onboard the station, we’ll see how MED-2 will perform in microgravity and how it will need to be further adapted for our Journey to Mars. However, it’s already pretty well equipped for deep space missions.
So what makes MED-2 so great for deep space travel and our Journey to Mars?
1. It is an all-in-one exercise device, meaning it can do both aerobic and resistive workouts. When we go to Mars, the less equipment we need, the better.

2. It’s incredibly light. The MED-2 weighs only 65 pounds, and every pound counts during space missions.

3. It has 5 - 350 pounds of resistance, despite weighing only 65 pounds. Astronauts don’t all lift the same amount, making the flexibility in MED-2’s “weights” essential.

4. It’s tiny. (Hence its name Miniature Exercise Device.) Not only is MED-2 incredibly light, but it also won’t take up a lot of space on any craft.

5. It powers itself. During an aerobic workout, the device charges, and then that power is used to run the resistive exercises. When traveling to space, it’s good when nothing goes to waste, and now astronauts’ workouts will help power the Journey to Mars.

MED-2 is only one of many devices and experiments flying on Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft. To find out more about the science on the space station, follow @ISS_Research and @Space_Station on Twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
The Five W’s of an Expandable Habitat in Space
Who: In this case, it’s really a “what.” The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is an expandable module developed by Bigelow Aerospace using a NASA patent conceptualized in the 1990s. It is made up of layers of fabric that will expand when installed and equalize with the pressure of the International Space Station.

What: Sensors inside BEAM will monitor temperature and radiation changes, as well as its resistance to potential orbital debris impacts. During its time on station, the airlock between BEAM and the rest of the space station will remained closed, and astronauts will enter only to collect data and help the experiment progress. If BEAM is punctured, the habitat is designed to slowly compress to keep the rest of the space station safe.
With the BEAM launch, deployment and time on station, Bigelow will demonstrate a number of expandable habitat capabilities, such as its folding and packing techniques, radiation protection capability and its thermal, structural and mechanical durability.

When: BEAM is set to launch on SpaceX’s eighth Dragon resupply mission April 8, and will be docked to the space station for a minimum two-year demonstration period.
Where: The International Space Station’s mechanical arm will transport BEAM from the spacecraft to a berthing port on the Tranquility module where it will then be expanded.

Why: These expandable modules take up less room on a rocket, but once set up, provide more volume for living and working in space.

When we’re traveling to Mars or beyond, astronauts need habitats that are both durable and easy to transport and to set up. That’s where expandable technology comes in. BEAM is one of the first steps to test expandable structures as a viable alternative to traditional space habitats.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
In addition to the Mercury transit of the sun today, there are a few other things you should know about our solar system this week:
1. Mars, Ready for its Close-Up

Mars will soon be closer to Earth than it has been for 11 years, presenting a great opportunity for backyard sky watchers.
2. Fire and Ice
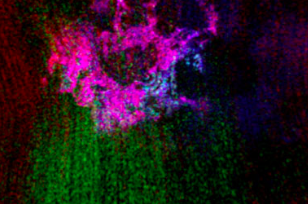
Our spacecraft have an even closer view of Mars, and that fact regularly leads to some intriguing discoveries. The latest: volcanoes may have erupted beneath an ice sheet there billions of years ago. The above image is a mineral map of part of the Martian surface.
3. Icy Hydra

Meanwhile, our New Horizons spacecraft has sent home the first compositional data about Pluto’s four small moons. The new data show the surface of Hydra is dominated by nearly pristine water ice–confirming hints that scientists picked up in images showing Hydra’s highly reflective surface.
4. Ceres, Ever Sharper

The mission director for our Dawn mission writes, “Ceres, which only last year was hardly more than a fuzzy blob against the stars, is now a richly detailed world, and our portrait grows more elaborate every day.”
5. Join us at Jupiter

Our Juno mission arrives at the giant planet on Jul. 4. Meanwhile, all amateur astronomers are invited to take part in a worldwide effort to identify potential observations for the spacecraft to make once it’s in orbit. Find out how to join HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


New Hubble Portrait of Mars (which will be at its closest to us on 30 May)
On May 12, 2016, the Hubble Space Telescope captured this vivid photo of Mars, when the planet was closer to Earth than usual and approaching the opposition (when the sun and Mars will be on exact opposite sides of Earth). Mars is especially photogenic during opposition because it can be seen fully illuminated by the sun as viewed from Earth. Mars will reach opposition on May 22.
Furthermore, the closest approach to Earth for the year will occur on 30 May, when Mars will be at a distance of 75.28 million km (46.78 million miles) from us. For comparison, the average distance between the two is 225 million km. These two events so close together make the coming week(s) the best time to observe the red planet with a telescope. You can already notice it in the night sky (check for your location) as one of the brightest dots with a red-orange glow near the Moon.
Read about the Hubble’s image here.
Image credits: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), J. Bell (ASU), and M. Wolff (Space Science Institute)


Scientists find another sign suggesting life existed on Mars
According to new research published in the Journal of Geophysical Research, scientists are getting even more indicators that life once existed on Mars. The latest proof? Carbonates found in 3.8 billion-year-old rock in the Huygens basin.
Follow @the-future-now

in 20-70 million years, Mars’ moon Phobos will get close enough to the surface of the planet that it will be ripped apart by the tidal forces. The resulting debris will most likely give Mars a planetary ring.

Mega-tsunamis in an ancient ocean on Mars may have shaped the landscape and left deposits that hint at whether the planet was once habitable, researchers say.
The giant waves, thought to have reached up to 120 metres in height as they raced over the land, could have been triggered by two large meteorites slamming into the surface.
The tsunamis may been powerful enough to shape much of the ancient coastlines on Mars, said J. Alexis Palmero Rodriguez, of the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, who led the study.
Writing in the journal Scientific Reports, the international team, which included scientists from the US, China and Germany, describe how they set out to probe a Martian mystery.
It has previously been proposed that the lowlands of the northern hemisphere of Mars were catastrophically flooded around 3.4 billion years ago, forming a vast ocean, potentially covering several million square kilometres. But scientists have been puzzled by the lack of an associated shoreline and its expected features.
Now Rodriguez and his team think they may have the answer- the fact that it is hard to make out such ancient shorelines is because huge tsunamis buried them, depositing sediments up to hundreds of kilometres inland.
Continue Reading.

Chasma Boreale and North Polar Ice Cap of Mars by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on Flickr.
Mars has bright polar caps of ice that are easily visible from telescopes on Earth. A seasonal cover of carbon-dioxide ice and snow is observed to advance and retreat over the poles during the Martian year. Scientists using radar data from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) have found a record of the most recent Martian ice age recorded in the planet’s north polar ice cap. This image is a simulated 3-D perspective view of Chasma Boreale, a canyon that reaches 570 kilometers (350 miles) into the north polar cap. It was created from image data taken by the THEMIS instrument on NASA’s Mars Odyssey spacecraft. Canyon walls rise about 1,400 meters (4,600 feet) above the floor of Chasma Boreale. Where the edge of the ice cap has retreated, sheets of sand are emerging that accumulated during earlier ice-free climatic cycles. Winds blowing off the ice have pushed loose sand into dunes, then driven them down-canyon in a westward direction.

Mars has many similarities to Earth. There are volcanoes, canyons, craters and - most importantly - water. Oh, and now NASA researchers have added another similarity to the list: ice ages.
Yup, thanks to radargrams taken from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), scientists now have physical measurements that suggest Mars is actually just now emerging from an ice age that ended some 400,000 years ago. That’s quite the cold spell!
According to the team, researchers have previously predicted that the Red Planet experienced ice ages in the past using complex computer models, but they lacked actual measurements to back them up.
Five human spaceflight missions to look forward to in the next decade
by Chris Arridge

From astronauts breaking records for the longest amount of time spent in space to experiments growing food and keeping bacteria in orbit, the past decade of human spaceflight has been fascinating. There has also been an explosion of privately-funded spaceflight companies providing access to space, including delivering supplies to the International Space Station (ISS).
The next decade will see a remarkable mix of countries and companies getting involved. Plans include taking humans from low-Earth orbit back to the moon and even an asteroid in the 2020s – all designed to help prepare for the ultimate goal of a human mission to Mars in the 2030s.
Keep reading

The Body’s Price on Space Exploration
It can be easy to get wrapped up in the dollar amount when talking about the price of sending humans to Mars but there is a factor that no amount of government or private funding can overcome: the human body.
Read more on Miss Aerospace

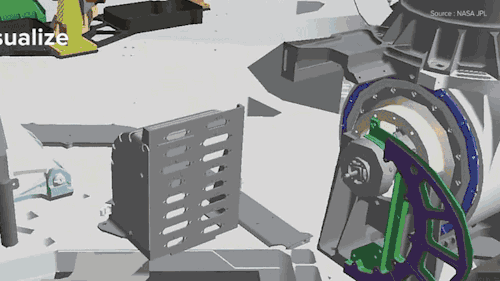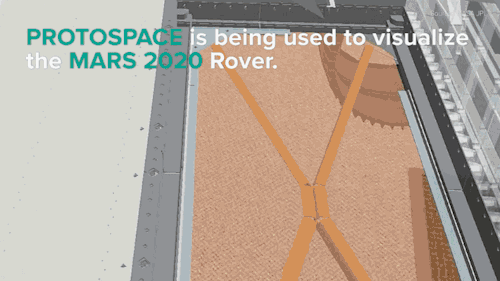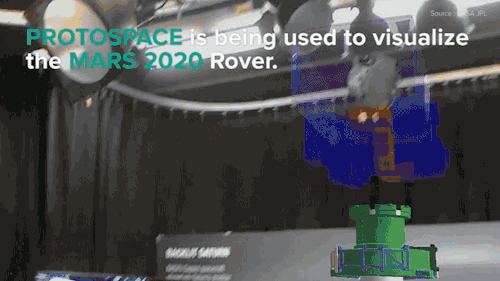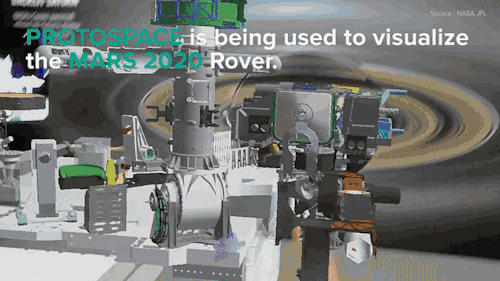
NASA is building the next Mars rover in mixed reality and It’s absolutely jaw-dropping!
When Can I Die on Mars?
Elon Musk recently announced SpaceX’s plans to send a spacecraft to the surface of Mars by 2018. It’s never been easier to die on Mars.
By: Fraser Cain. Support Universe Today on Patreon

Mars Orbiter Mission: April 11, 2016 Clouds over Olympus Mons, April 11th 2016
Olympus Mons is a large shield volcano on the planet Mars. It has a height of nearly 22 km. Olympus Mons stands almost three times as tall as Mount Everest’s height above sea level. It is the youngest of the large volcanoes on Mars, having formed during Mars’s Amazonian Period. Several meteorological factors contribute to cloud formation. This MCC image was taken on April 11, 2016 at an altitude of 22,794 km and resolution of 1,185 meters. The image shows cloud around Olympus Mons Region.

Lockheed Martin joins the space race to Mars
From China to NASA to Elon Musk, it seems everyone has their sights set on Mars exploration. But before we land on the Red Planet, we’ll probably orbit it. At this week’s Humans to Mars summit, Lockheed Martin unveiled its Mars Base Camp concept — an ambitious plan to send a manned space laboratory to orbit Mars by 2028.

Even after dozens of spacecraft have been sent to Mars, much remains unknown about that world. Here we have 7 fascinating yet unanswered questions about Mars.
Hearing: Next Steps to Mars: Deep Space Habitats
Subcommittee on Space (114th Congress) Next Steps to Mars: Deep Space Habitats









