Solar System: Things To Know This Week
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Making every night science movie night with these amazing videos.

1. Pure Beauty
Our star sprouting coronal loops courtesy of the NASA sun team. See the full video: https://go.nasa.gov/2p47Lt2

2. Where’s the last place you'd expect to find enough ice to bury a city?
Answer: Mercury, the closest planet to the sun. Watch the video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11184

3. The Mars Fleet
Only Earth has more satellites studying it. Full video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/4414

4. A Star-Studded Cast
Check out NASA's satellite fleet of Earth observers. See the video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12586

5. Jupiter in Ultra HD
Thanks, Hubble Space Telescope! See the video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12021

6. A Tear Jerker
Our Cassini spacecraft starts her 4.5-month Grand Finale this week. Full video: https://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/resources/7628

7. Faster Than the Speed of Sound
Winds on Neptune travel faster than the speed of sound. Full video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11349

8. A Musical Number
This one features the planet Uranus doing pop and lock. Full video: https://youtu.be/CWuWoiHmXUs

9. Up Close and Personal
Thanks to our New Horizons mission, we’ve been able to get up close and with Pluto. Full video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12080

10: The Treasure Trove
TRAPPIST-1 is a treasure trove of seven Earth-sized planets orbiting a distant star. Full video: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/video/details.php?id=1459
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others

Hot New Planetary System Just Dropped.
We hope you like your planetary systems extra spicy. 🔥
A new system of seven sizzling planets has been discovered using data from our retired Kepler space telescope.
Named Kepler-385, it’s part of a new catalog of planet candidates and multi-planet systems discovered using Kepler.
The discovery helps illustrate that multi-planetary systems have more circular orbits around the host star than systems with only one or two planets.
Our Kepler mission is responsible for the discovery of the most known exoplanets to date. The space telescope’s observations ended in 2018, but its data continues to paint a more detailed picture of our galaxy today.
Here are a few more things to know about Kepler-385:

All seven planets are between the size of Earth and Neptune.

Its star is 10% larger and 5% hotter than our Sun.

This system is one of over 700 that Kepler’s data has revealed.
The planets’ orbits have been represented in sound.
Now that you’ve heard a little about this planetary system, get acquainted with more exoplanets and why we want to explore them.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Eclipse 2017 From Space
On Aug. 21, 2017, a total solar eclipse passed over North America. People throughout the continent captured incredible images of this celestial phenomenon. We and our partner agencies had a unique vantage point on the eclipse from space. Here are a few highlights from our fleet of satellites that observe the Sun, the Moon and Earth.

Our Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which watches the Sun nearly 24/7 from its orbit 3,000 miles above Earth, saw a partial eclipse on Aug. 21.
SDO sees the Moon cross in front of the Sun several times a year. However, these lunar transits don’t usually correspond to an eclipse here on Earth, and an eclipse on the ground doesn’t guarantee that SDO will see anything out of the ordinary. In this case, on Aug. 21, SDO did see the Moon briefly pass in front of the Sun at the same time that the Moon’s shadow passed over the eastern United States. From its view in space, SDO only saw 14 percent of the Sun blocked by the Moon, while most U.S. residents saw 60 percent blockage or more.

Six people saw the eclipse from the International Space Station. Viewing the eclipse from orbit were NASA’s Randy Bresnik, Jack Fischer and Peggy Whitson, the European Space Agency’s Paolo Nespoli, and Roscosmos’ Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin and Sergey Ryazanskiy. The space station crossed the path of the eclipse three times as it orbited above the continental United States at an altitude of 250 miles.

From a million miles out in space, our Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera, or EPIC, instrument captured 12 natural color images of the Moon’s shadow crossing over North America. EPIC is aboard NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory, or DSCOVR, where it photographs the full sunlit side of Earth every day, giving it a unique view of the shadow from total solar eclipses. EPIC normally takes about 20 to 22 images of Earth per day, so this animation appears to speed up the progression of the eclipse.

A ground-based image of the total solar eclipse – which looks like a gray ring – is superimposed over a red-toned image of the Sun’s atmosphere, called the corona. This view of the corona was captured by the European Space Agency and our Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. At center is an orange-toned image of the Sun’s surface as seen by our Solar Dynamics Observatory in extreme ultraviolet wavelengths of light.
During a total solar eclipse, ground-based telescopes can observe the lowest part of the solar corona in a way that can’t be done at any other time, as the Sun’s dim corona is normally obscured by the Sun’s bright light. The structure in the ground-based corona image — defined by giant magnetic fields sweeping out from the Sun’s surface — can clearly be seen extending into the outer image from the space-based telescope. The more scientists understand about the lower corona, the more they can understand what causes the constant outward stream of material called the solar wind, as well as occasional giant eruptions called coronal mass ejections.

As millions of Americans watched the total solar eclipse that crossed the continental United States, the international Hinode solar observation satellite captured its own images of the awe-inspiring natural phenomenon. The images were taken with Hinode's X-ray telescope, or XRT, as it flew above the Pacific Ocean, off the west coast of the United States, at an altitude of approximately 422 miles. Hinode is a joint endeavor by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, the European Space Agency, the United Kingdom Space Agency and NASA.

During the total solar eclipse our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, in orbit around the Moon, turned one of its instruments towards Earth to capture an image of the Moon’s shadow over a large region of the United States.
As LRO crossed the lunar south pole heading north at 3,579 mph, the shadow of the Moon was racing across the United States at 1,500 mph. A few minutes later, LRO began a slow 180-degree turn to look back at Earth, capturing an image of the eclipse very near the location where totality lasted the longest. The spacecraft’s Narrow Angle Camera began scanning Earth at 2:25:30 p.m. EDT and completed the image 18 seconds later.

Sensors on the polar-orbiting Terra and Suomi NPP satellites gathered data and imagery in swaths thousands of miles wide. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, sensor on Terra and Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite, or VIIRS, on Suomi NPP captured the data used to make this animation that alternates between two mosaics. Each mosaic is made with data from different overpasses that was collected at different times.

This full-disk geocolor image from NOAA/NASA’s GOES-16 shows the shadow of the Moon covering a large portion of the northwestern U.S. during the eclipse.

Our Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, mission captured this view of the Moon passing in front of the Sun on Aug. 21.
Check out nasa.gov/eclipse to learn more about the Aug. 21, 2017, eclipse along with future eclipses, and follow us on Twitter for more satellite images like these: @NASASun, @NASAMoon, and @NASAEarth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
The As, Gs, Cs and Ts of the Space Station: First In-Space Microbe Identification
Being able to identify microbes in real-time aboard the International Space Station, without having to send them back to Earth for identification first, would be totally amazing for the world of microbiology and space exploration.

The Genes in Space 3 team turned that possibility into a reality this year, when it completed the first-ever sample-to-sequence process entirely aboard the space station.
The ability to identify microbes in space could aid in the ability to diagnose and treat astronauts in real time, as well as assisting in the identification of life on other planets. It could also benefit other experiments aboard the space station.
HELPFUL SCIENCE HINT: Identifying microbes involves isolating the DNA of samples, and then amplifying – or making lots and lots (and LOTS) of copies - of that DNA that can then be sequenced, or identified.
As part of regular monitoring, petri plates were touched to various surfaces of the space station. NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson transferred cells from growing bacterial colonies on those plates into miniature test tubes, something that had never been done before in space (first OMG moment!).

Once the cells were successfully collected, it was time to isolate the DNA and prepare it for sequencing, enabling the identification of the unknown organisms – another first for space microbiology.
Enter Hurricane Harvey. *thunder booms*

“We started hearing the reports of Hurricane Harvey the week in between Peggy performing the first part of collecting the sample and gearing up for the actual sequencing,” said Sarah Wallace, the project’s primary investigator.
When our Johnson Space Center (JSC) in Houston became inaccessible due hurricane conditions, Marshall Space Flight Center’s Payload Operations Integration Center in Huntsville, Alabama worked to connect Wallace to Whitson using Wallace’s personal cell phone.
With a hurricane wreaking havoc outside, Wallace and Whitson set out to make history.

The data were downlinked to the team in Houston for analysis and identification.
“Once we actually got the data on the ground we were able to turn it around and start analyzing it,” said Aaron Burton, the project’s co-investigator. “You get all these squiggle plots and you have to turn that into As, Gs, Cs and Ts.”
Those As, Gs, Cs and Ts are more than just a nerdy alphabet – they are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine – the four bases that make up each strand of DNA and can tell you what organism the strand of DNA came from.

“Right away, we saw one microorganism pop up, and then a second one, and they were things that we find all the time on the space station,” said Wallace. “The validation of these results would be when we got the sample back to test on Earth.”
Soon after, the samples returned to Earth aboard the Soyuz spacecraft, along with Whitson.
With the samples now in the team’s JSC lab, tests were completed in ground labs to confirm the findings from the space station. They ran the tests again and again, and then once more, to confirm accuracy. Each time, the results were exactly the same on the ground as in orbit. (second OMG moment!)

“We did it. Everything worked perfectly,” said Sarah Stahl, microbiologist.
This capability could change future space exploration.
“As a microbiologist,” said Wallace, “My goal is really so that when we go and we move beyond ISS and we’re headed towards Mars or the moon or wherever we are headed to, we have a process that the crew can have that great understanding of the environment, based on molecular technology.”
For more information, follow @ISS_Research.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Weathering the Storm with our Global Precipitation Measurement Mission
How much rain falls in a hurricane? How much snow falls in a nor’easter? What even is a nor’easter? These are the sorts of questions answered by our Global Precipitation Measurement Mission, or GPM.
GPM measures precipitation: Rain, snow, sleet, freezing rain, hail, ice pellets. It tells meteorologists the volume, intensity and location of the precipitation that falls in weather systems, helping them improve their forecasting, gather information about extreme weather and better understand Earth’s energy and water cycles.
And putting all that together, one of GPM’s specialties is measuring storms.
GPM is marking its fifth birthday this year, and to celebrate, we’re looking back on some severe storms that the mission measured in its first five years.
1. The Nor’easter of 2018

A nor’easter is a swirling storm with strong northeasterly winds and often lots of snow. In January 2018, the mission’s main satellite, the Core Observatory, flew over the East Coast in time to capture the development of a nor’easter. The storm dumped 18 inches of snow in parts of New England and unleashed winds up to 80 miles per hour!
2. Hurricane Harvey

Hurricane Harvey came to a virtual halt over eastern Texas in August 2017, producing the largest rain event in U.S. history. Harvey dropped up to 5 feet of rain, causing $125 billion in damage. The Core Observatory passed over the storm several times, using its radar and microwave instruments to capture the devastating deluge.
3. Typhoon Vongfong
In October 2014, GPM flew over one of its very first Category 5 typhoons – tropical storms with wind speeds faster than 157 miles per hour. The storm was Typhoon Vongfong, which caused $48 million in damage in Japan, the Philippines and Taiwan. We were able to see both the pattern and the intensity of Vongfong’s rain, which let meteorologists know the storm’s structure and how it might behave.
4. Near Real-Time Global Precipitation Calculations
The Core Observatory isn’t GPM’s only satellite! A dozen other satellites from different countries and government agencies come together to share their microwave measurements with the Core Observatory. Together, they are called the GPM Constellation, and they create one of its most impressive products, IMERG.
IMERG stands for “Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM,” and it uses the info from all the satellites in the Constellation to calculate global precipitation in near real time. In other words, we can see where it’s raining anywhere in the world, practically live.
5. Hurricane Ophelia
Hurricane Ophelia hit Ireland and the United Kingdom in October 2017, pounding them with winds up to 115 miles per hour, reddening the skies with dust from the Sahara Desert and causing more than $79 million in damages. Several satellites from the Constellation passed over Ophelia, watching this mid-latitude weather system develop into a Category 3 hurricane – the easternmost Category 3 storm in the satellite era (since 1970).
From the softest snow to the fiercest hurricanes, GPM is keeping a weather eye open for precipitation around the world. And we’re on cloud nine about that.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Does all capsules drops in Kazakhstan on return after every mission?
Since the US Space Shuttle retired in 2011, we launch to and return from the Space Station with the Russian Space Agency. So yes, these capsules (the Soyuz) land in Kazakhstan (or surrounding regions). However, different spacecrafts have different reentry trajectories, depending on where they aim to land. As you might recall, the Apollo mission capsules landed in the ocean. Since Space-X and Boeing are currently building new vehicles so that we will also launch from the US again to get to the International Space Station, these spacecraft will return to the US. For example, you may have seen footage of Space-X cargo vehicles splashing down into the Pacific over the last few years. The Boeing Starliner plans to land on land instead of water. NASA is also currently building the Orion spacecraft, which will take us to destinations beyond low earth orbit (where the Space Station is), whether that be the Moon or Mars or another target. Orion will also splash down in the ocean.
The Sun is not silent. The low, pulsing hum of our star's heartbeat allows scientists to peer inside, revealing huge rivers of solar material flowing around before their eyes — er, ears.
Data from ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO), sonified by the Stanford Experimental Physics Lab, captures the Sun’s natural vibrations and reveals what can’t be seen with the naked eye.
In this audiogram, our heliophysicist Alex Young explains how this simple sound connects us with the Sun and all the other stars in the universe.
This piece features low frequency sounds of the Sun. For the best listening experience, listen to this story with headphones. 🎧
Read more: https://go.nasa.gov/2LMW42o
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Launching Rockets from the Top of the World 🚀
Over the next 14 months, our scientists will join a group of international researchers to explore a special region — Earth's northern polar cusp, one of just two places on our planet where particles from the Sun have direct access to our atmosphere.

Earth is surrounded by a giant magnetic bubble known as a magnetosphere, which protects our planet from the hot, electrically charged stream of particles from the Sun known as the solar wind. The northern and southern polar cusps are two holes in this protection — here, Earth's magnetic field lines funnel the solar wind downwards, concentrating its energy before injecting it into Earth’s atmosphere, where it mixes and collides with particles of Earthly origin.

The cusp is the only place where dayside auroras are found — a special version of northern and southern lights, visible when the Sun is out and formed by a different process than the more familiar nighttime aurora. That's what makes this region so interesting for scientists to study: The more we learn about auroras, the more we understand about the fundamental processes that drive near-Earth space — including those processes that disrupt our technology and endanger our astronauts.

Photo credit: Violaene Kaeser
The teams working on the Grand Challenge Initiative — Cusp will fly sounding rockets from two Norwegian rocket ranges that fall under the cusp for a short time each day. Sounding rockets are sub-orbital rockets that shoot up into space for a few minutes before falling back to Earth, giving them access to Earth's atmosphere between 30 and 800 miles above the surface. Cheaper and faster to develop than large satellite missions, sounding rockets often carry the latest scientific instruments on their first-ever flights, allowing for unmatched speed in the turnaround from design to implementation.

Each sounding rocket mission will study a different aspect of Earth's upper atmosphere and its connection to the Sun and particles in space. Here's a look at the nine missions coming up.
1. VISIONS-2 (Visualizing Ion Outflow via Neutral Atom Sensing-2) — December 2018
The cusp isn’t just the inroad into our atmosphere — it’s a two-way street. Counteracting the influx of particles from the Sun is a process called atmospheric escape, in which Earthly particles acquire enough energy to escape into space. Of all the particles that escape Earth’s atmosphere, there’s one that presents a particular mystery: oxygen.
At 16 times the mass of hydrogen, oxygen should be too heavy to escape Earth’s gravity. But scientists have found singly ionized oxygen in near-Earth space, which suggests that it came from Earth. The two VISIONS-2 rockets, led by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, will create maps of the oxygen outflow in the cusp, tracking where these heavy ions are and how they’re moving to provide a hint at how they escape.
2. TRICE-2 (Twin Rockets to Investigate Cusp Electrodynamics 2) — December 2018
If the cusp is like a funnel, then magnetic reconnection is what turns on the faucet. When the solar wind collides with Earth’s magnetic field, magnetic reconnection breaks open the previously closed magnetic field lines, allowing some solar wind particles to stream into Earth’s atmosphere through the cusp.
But researchers have noticed that the stream of particles coming in isn’t smooth: instead, it has abrupt breaks in it. Is magnetic reconnection turning on and off? Or is the solar wind shooting in from different locations? TRICE-2, led by the University of Iowa in Iowa City, will fly two separate rockets through a single magnetic field line in the cusp, to help distinguish these possibilities. If reconnection sputters on and off over time, then the two rockets should get quite different measurements, like noting how it feels to run your finger back and forth under a faucet that is being turned on and off. If instead reconnection happens consistently in multiple locations — like having ten different faucets, all running constantly — then the two rockets should have similar measurements whenever they pass through the same locations.

Magnetic reconnection is a process by which magnetic field lines explosively realign
3. CAPER-2 (Cusp Alfvén and Plasma Electrodynamics Rocket) — January 2019
The CAPER-2 rocket, led by Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire, will examine how fast-moving electrons — particles that can trigger aurora — get up to such high speeds. The team will zero in on the role that Alfvén waves, a special kind of low-frequency wave that oscillates along magnetic field lines, play in accelerating auroral electrons.

An illustration of rippling Alfvén waves
4. G-CHASER (Grand Challenge Student Rocket) — January 2019
G-CHASER is made up entirely of student researchers from universities in the United States, Norway and Japan, many of whom are flying their experiments for the first time. The mission, led by the Colorado Space Grant Consortium at the University of Colorado Boulder, is a collaboration between seven different student-led missions, providing a unique opportunity for students to design, test and ultimately fly their experiment from start to finish. The students involved in the mission — mostly undergraduates but including some graduate teams — are responsible for all aspects of the mission, from developing the initial idea, to securing the funding, to making sure it passes all the tests before flight.
5 & 6. AZURE (Auroral Zone Upwelling Rocket Experiment) and CHI (Cusp Heating Investigation) — April & November/December 2019
When the aurora shine, they don’t just emit light — they also release thermal and kinetic energy into the atmosphere. Some of this energy escapes back into space, but some of it stays with us. Which way this balance tips depends, in part, on the winds in the cusp. AZURE, led by Clemson University in South Carolina, will measure the vertical winds that swish energy and particles around within the auroral oval, the larger ring around the pole where the aurora are most common.
Later that year, the same team will launch the CHI mission, using a methodology similar to AZURE to measure the flow of charged and neutral gases inside the cusp. The goal is to better understand how particles, flowing in horizontal and vertical directions, interact with each other to produce heating and acceleration.
7. C-REX-2 (Cusp-Region Experiment) — November 2019
The cusp is a place where strange physics happens, producing some anomalies in the physical structure of the atmosphere that can make our technology go haywire. For satellites that pass through the cusp, density increases act like potholes, shaking up their orbits. Scientists don’t currently understand what causes these density increases, but they have some clues. C-REX-2, led by the University of Alaska Fairbanks, aims to figure out which variables — wind, temperature or ion velocity — are responsible.
8. ICI-5 (Investigation of Cusp Irregularities-5) — December 2019
Recent research has uncovered mysterious hot patches of turbulent plasma inside the auroral region that rain energetic particles towards Earth. GPS signals become garbled as they pass through these turbulent plasma patches, affecting so many of today’s technologies that depend on them. ICI-5, led by the University of Oslo, will launch into the cusp to take measurements from inside these hot patches. To measure their structure as several scales, the rocket will eject 12 daughter payloads in concentric squares which will achieve a variety of different separations.

9. JAXA's SS-520-3 mission — January 2020
Exploring the phenomenon of atmospheric escape, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's SS-520-3 mission will fly 500 miles high over the cusp to take measurements of the electrostatic waves that heat ions up and get them moving fast enough to escape Earth.
For updates on the Grand Challenge Initiative and other sounding rocket flights, visit nasa.gov/soundingrockets or follow along with NASA Wallops and NASA heliophysics on Twitter and Facebook.
@NASA_Wallops | NASA's Wallops Flight Facility | @NASASun | NASA Sun Science
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Discovering the Universe Through the Constellation Orion
Do you ever look up at the night sky and get lost in the stars? Maybe while you’re stargazing, you spot some of your favorite constellations. But did you know there’s more to constellations than meets the eye? They’re not just a bunch of imaginary shapes made up of stars — constellations tell us stories about the universe from our perspective on Earth.

What is a constellation?
A constellation is a named pattern of stars that looks like a particular shape. Think of it like connecting the dots. If you join the dots — stars, in this case — and use your imagination, the picture would look like an object, animal, or person. For example, the ancient Greeks believed an arrangement of stars in the sky looked like a giant hunter with a sword attached to his belt, so they named it after a famous hunter in their mythology, Orion. It’s one of the most recognizable constellations in the night sky and can be seen around the world. The easiest way to find Orion is to go outside on a clear night and look for three bright stars close together in an almost-straight line. These three stars represent Orion's belt. Two brighter stars to the north mark his shoulders, and two more to the south represent his feet.

Credit: NASA/STScI
Over time, cultures around the world have had different names and numbers of constellations depending on what people thought they saw. Today, there are 88 officially recognized constellations. Though these constellations are generally based on what we can see with our unaided eyes, scientists have also invented unofficial constellations for objects that can only be seen in gamma rays, the highest-energy form of light.
Perspective is everything
The stars in constellations may look close to each other from our point of view here on Earth, but in space they might be really far apart. For example, Alnitak, the star at the left side of Orion's belt, is about 800 light-years away. Alnilam, the star in the middle of the belt, is about 1,300 light-years away. And Mintaka, the star at the right side of the belt, is about 900 light-years away. Yet they all appear from Earth to have the same brightness. Space is three-dimensional, so if you were looking at the stars that make up the constellation Orion from another part of our galaxy, you might see an entirely different pattern!

The superstars of Orion
Now that we know a little bit more about constellations, let’s talk about the supercool cosmic objects that form them – stars! Though over a dozen stars make up Orion, two take center stage. The red supergiant Betelgeuse (Orion's right shoulder) and blue supergiant Rigel (Orion's left foot) stand out as the brightest members in the constellation.

Credit: Derrick Lim
Betelgeuse is a young star by stellar standards, about 10 million years old, compared to our nearly 5 billion-year-old Sun. The star is so huge that if it replaced the Sun at the center of our solar system, it would extend past the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter! But due to its giant mass, it leads a fast and furious life.

Betelgeuse is destined to end in a supernova blast. Scientists discovered a mysterious dimming of Betelgeuse in late 2019 caused by a traumatic outburst that some believed was a precursor to this cosmic event. Though we don’t know if this incident is directly related to an imminent supernova, there’s a tiny chance it might happen in your lifetime. But don't worry, Betelgeuse is about 550 light-years away, so this event wouldn't be dangerous to us – but it would be a spectacular sight.
Rigel is also a young star, estimated to be 8 million years old. Like Betelgeuse, Rigel is much larger and heavier than our Sun. Its surface is thousands of degrees hotter than Betelgeuse, though, making it shine blue-white rather than red. These colors are even noticeable from Earth. Although Rigel is farther from Earth than Betelgeuse (about 860 light-years away), it is intrinsically brighter than its companion, making it the brightest star in Orion and one of the brightest stars in the night sky.

Credit: Rogelio Bernal Andreo
Buckle up for Orion’s belt
Some dots that make up constellations are actually more than one star, but from a great distance they look like a single object. Remember Mintaka, the star at the far right side of Orion's belt? It is not just a single star, but actually five stars in a complex star system.

Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/GSFC/M. Corcoran et al.; Optical: Eckhard Slawik
Sword or a stellar nursery?
Below the three bright stars of Orion’s belt lies his sword, where you can find the famous Orion Nebula. The nebula is only 1,300 light-years away, making it the closest large star-forming region to Earth. Because of its brightness and prominent location just below Orion’s belt, you can actually spot the Orion Nebula from Earth! But with a pair of binoculars, you can get a much more detailed view of the stellar nursery. It’s best visible in January and looks like a fuzzy “star” in the middle of Orion’s sword.

More to discover in constellations
In addition to newborn stars, Orion also has some other awesome cosmic objects hanging around. Scientists have discovered exoplanets, or planets outside of our solar system, orbiting stars there. One of those planets is a giant gas world three times more massive than Jupiter. It’s estimated that on average there is at least one planet for every star in our galaxy. Just think of all the worlds you may be seeing when you look up at the night sky!
It’s also possible that the Orion Nebula might be home to a black hole, making it the closest known black hole to Earth. Though we may never detect it, because no light can escape black holes, making them invisible. However, space telescopes with special instruments can help find black holes. They can observe the behavior of material and stars that are very close to black holes, helping scientists find clues that can lead them closer to discovering some of these most bizarre and fascinating objects in the cosmos.

Next time you go stargazing, remember that there’s more to the constellations than meets the eye. Let them guide you to some of the most incredible and mysterious objects of the cosmos — young stars, brilliant nebulae, new worlds, star systems, and even galaxies!

To keep up with the most recent stellar news, follow NASA Universe on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
What’s Up for April 2016?

Jupiter, Mars, the Lyrid meteor shower and 2016’s best views of Mercury are all visible in the sky this month.

Jupiter, where our Juno mission will begin orbiting on July 4, continues to shine almost as brightly this month as last. And eagle-eyed telescope viewers will see a transit, a shadow transit, an occultation and an eclipse of Jupiter’s moons- all in one night: April 6-7.

Io transits first, crossing the planet beginning at 9:52 p.m. EDT. It’s shadow can be seen less than an hour later.

Next Jupiter occults, or eclipses, Europa as Europa slips behind the giant planet at 10:48 p.m. EDT. At 3 a.m. Europa reappears from its eclipse, dramatically leaving the shadow of Jupiter.

Ganymede transits the planet beginning at 1:01 EDT April 7.
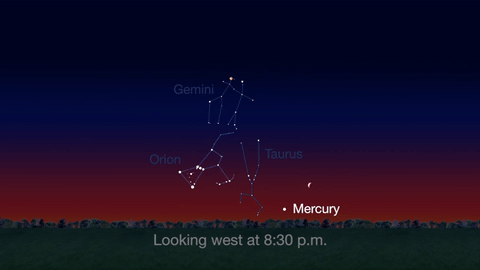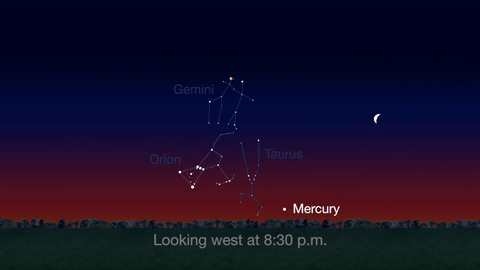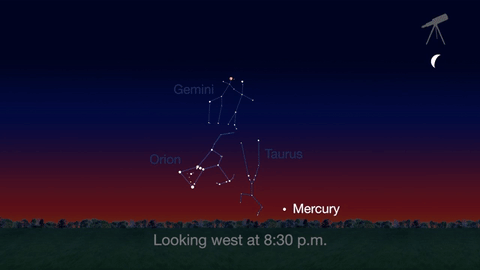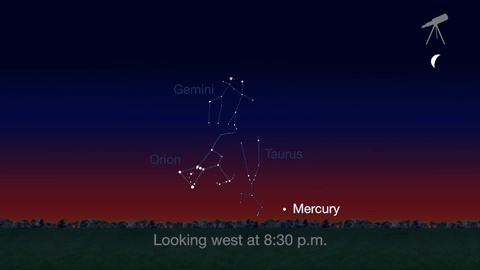
Check out the other planets in April, too! Mercury is always a challenging object to view, but this month you can spot it after sunset about 10 degrees above the horizon. Through a telescope you can see its phase. It will appear like a tiny crescent moon, with about 1/3 of its disk illuminated.

Mars is finally visible before midnight this month. It rises in the southeast at about 10 p.m. by the end of April. The best observing of Mars will be when it is highest in the sky. This means a few hours before dawn. Its brightness and apparent size increase dramatically this month. By month’s end, Mars appears nearly twice as bright as at the beginning of the month.

About mid-month you’ll see Mars near its rival in the sky: the similar-colored red supergiant star Antares. The name “Antares” means “equal to or rival of Mars”.
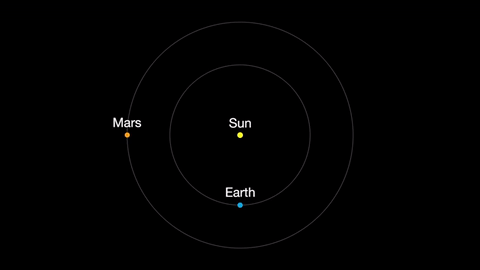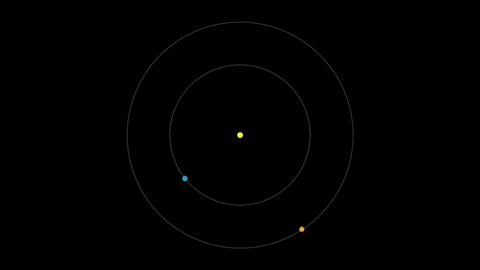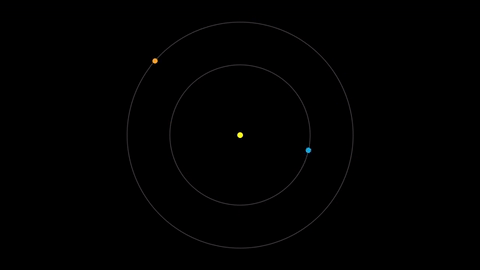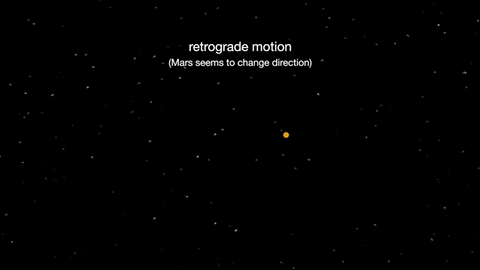
Earth moves almost twice as fast as Mars does, so it often passes Mars in their race around the sun. This causes “retrograde motion”: an illusion we see from our viewpoint on Earth.
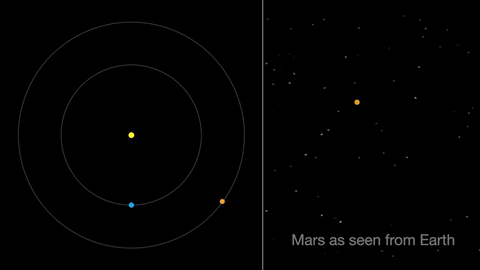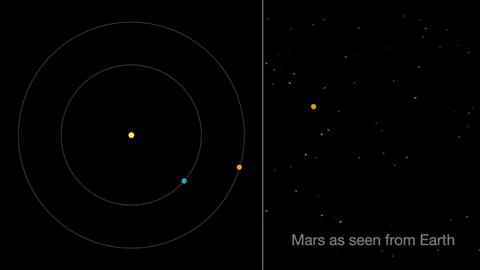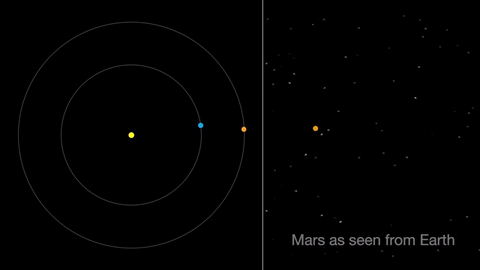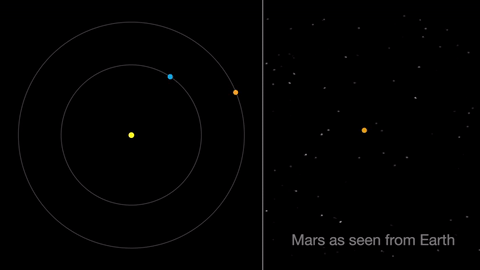
Retrograde motion happens as Earth catches up to Mars, causing Mars to appear slow to slow its eastward motion against the stars. After a few days, when Earth has overtaken Mars, the Red Planet seems to move westward. Eventually, Earth moves far enough around its orbit that Mars appears to be moving eastward again.
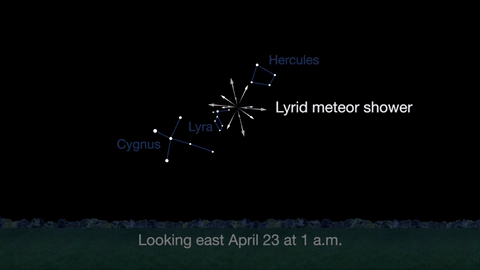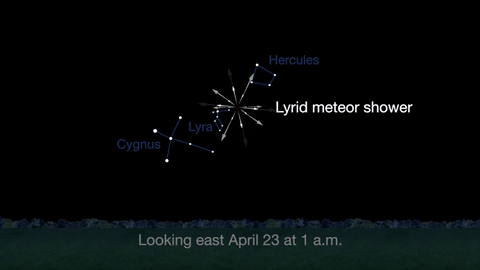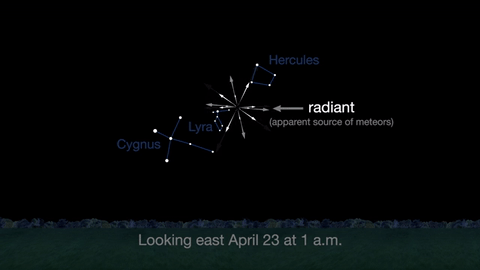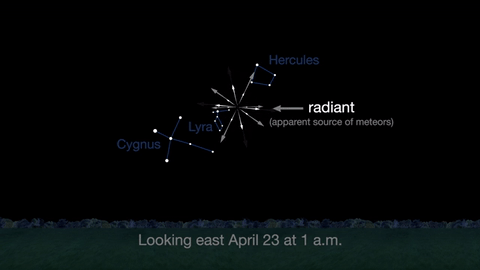
April features one meteor shower, the Lyrids. This year the Lyrids are marred by the full moon. The best time to view will be just before dawn on April 23, when the constellation Lyra is overhead and the moon will be near to setting.
With all of these great things to spot in the sky this month, be sure to get outside and look up!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Blowing Bubbles in the Gamma-ray Sky

Did you know our Milky Way galaxy is blowing bubbles? Two of them, each 25,000 light-years tall! They extend above and below the disk of the galaxy, like the two halves of an hourglass. We can’t see them with our own eyes because they’re only apparent in gamma-ray light, the highest-energy light in the universe.

We didn’t even know these humongous structures were smack in the middle of our galaxy until 2010. Scientists found them when they analyzed the first two years of data from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. They dubbed them the “Fermi bubbles” and found that in addition to being really big and spread out, they seem to have well-defined edges. The bubbles’ shape and the light they give off led scientists to think they were created by a rapid release of energy. But by what? And when?

One possible explanation is that they could be leftovers from the last big meal eaten by the supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy. This monster is more than 4 million times the mass of our own Sun. Scientists think it may have slurped up a big cloud of hydrogen between 6 and 9 million years ago and then burped jets of hot gas that we see in gamma rays and X-rays.

Another possible explanation is that the bubbles could be the remains of star formation. There are massive clusters of stars at very the center of the Milky Way — sometimes the stars are so closely packed they’re a million times more dense than in the outer suburb of the galaxy where we live. If there was a burst of star formation in this area a few million years ago, it could have created the surge of gas needed to in turn create the Fermi bubbles.

It took us until 2010 to see these Fermi bubbles because the sky is filled with a fog of other gamma rays that can obscure our view. This fog is created when particles moving near light speed bump into gas, dust, and light in the Milky Way. These collisions produce gamma rays, and scientists had to factor out the fog to unveil the bubbles.

Scientists continue to study the possible causes of these massive bubbles using the 10 years of data Fermi has collected so far. Fermi has also made many other exciting discoveries — like the the collision of superdense neutron stars and the nature of space-time. Learn more about Fermi and how we’ve been celebrating its first decade in space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 cloudsurfer84 liked this · 1 year ago
cloudsurfer84 liked this · 1 year ago -
 luvbandit007 liked this · 2 years ago
luvbandit007 liked this · 2 years ago -
 bama4life reblogged this · 2 years ago
bama4life reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 bama4life liked this · 2 years ago
bama4life liked this · 2 years ago -
 appro880 reblogged this · 2 years ago
appro880 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 fad6a5 liked this · 4 years ago
fad6a5 liked this · 4 years ago -
 ruinatlantis reblogged this · 4 years ago
ruinatlantis reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 ruinatlantis liked this · 4 years ago
ruinatlantis liked this · 4 years ago -
 m808vthetank liked this · 5 years ago
m808vthetank liked this · 5 years ago -
 ivysrebloggings reblogged this · 5 years ago
ivysrebloggings reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 somewhat-eternal liked this · 5 years ago
somewhat-eternal liked this · 5 years ago -
 yellowmagicalgirl reblogged this · 5 years ago
yellowmagicalgirl reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 imagesharer liked this · 5 years ago
imagesharer liked this · 5 years ago -
 violettabluee reblogged this · 5 years ago
violettabluee reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 nevadaoftheforest liked this · 5 years ago
nevadaoftheforest liked this · 5 years ago -
 sonicsoundscapes liked this · 6 years ago
sonicsoundscapes liked this · 6 years ago -
 worldart1 reblogged this · 6 years ago
worldart1 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 about-mindmischief liked this · 6 years ago
about-mindmischief liked this · 6 years ago -
 radondom liked this · 6 years ago
radondom liked this · 6 years ago -
 supperlunary reblogged this · 6 years ago
supperlunary reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 appro880 reblogged this · 6 years ago
appro880 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 jobryon liked this · 6 years ago
jobryon liked this · 6 years ago -
 marina880 liked this · 6 years ago
marina880 liked this · 6 years ago -
 c-n-dub liked this · 6 years ago
c-n-dub liked this · 6 years ago -
 isbbc liked this · 6 years ago
isbbc liked this · 6 years ago -
 naxal reblogged this · 6 years ago
naxal reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 normanijanehansen liked this · 6 years ago
normanijanehansen liked this · 6 years ago -
 momentfalife reblogged this · 6 years ago
momentfalife reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 rodyroco reblogged this · 6 years ago
rodyroco reblogged this · 6 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts