Here Is Our Executive Director Using Big Red, Our Resident Red Rat Snake, For Our Virtual Education Program.
Here is our Executive Director using Big Red, our resident red rat snake, for our virtual education program. One of the SNC’s main missions is to spread environmental education throughout South Florida. We are excited to pivot to a virtual, safe platform. Big Red was just happy to have a warm body to thermoregulate with in this #FloridaCold!
More Posts from Sawgrassnaturecenter and Others
This year the SNC has rescued and rehabilitated over 900 wild animals in South Florida. Help us continue our mission by donating here https://sawgrassnaturecenter.org/ this #GivingTueday.
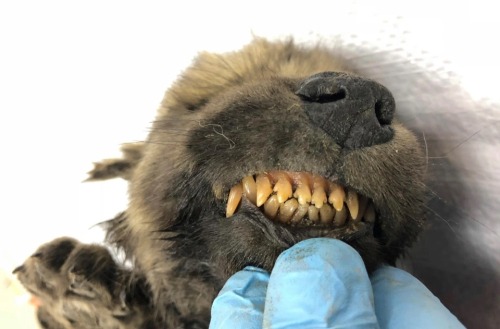

Dogor is the 18,000 year old pup that was found within the Siberian Permafrost, yet is not quite a dog nor a wolf, but a puzzling connection to both.
Dogor has been miraculously preserved within the permafrost, with its fur, teeth and even whiskers incredibly intact. Radiocarbon dating has placed the animal at 18,000 years old and researchers have suggested that the animal passed away at just 2 months old. The name Dogor means “Friend” in Yakut, a language spoken within Eastern Siberia.
Generally, genetic analysis can quite easily discern whether a discovered canine is a wolf or dog, but in this instance, the genetics suggest that it could be an ancestral link to both. Interestingly, Dogor lived at a time in canine evolutionary history when dogs and wolves began to branch off from each other.The general scientific consensus is that dogs and wolves split from a common ancestor, however, the process of how “dogs became dogs” is certainly contested, and Dogor could be a crucial piece in that puzzle.
If Dogor is determined to be a dog, it will be the oldest ever discovered. The next oldest, the Bonn-Oberkassel puppy, was discovered in Germany and was clearly determined to be a dog of around 14,000 years old, buried with a man and a woman.
The progression of climate change is melting the permafrost more rapidly, and discoveries like these are becoming more and more commonplace.
Images via Sergey Fedorov/The Siberian Times
Ocean Conservation Organizations: Help Save The Oceans & And Its Babies

Oceana:
A non-profit ocean conservation organization that focuses on influencing policy decisions on the national level to preserve and restore our oceans.
Shark Angels:
An organization focused on the conservation of sharks and using technology, education, media and local campaigns to conserve the oceans shark population.
Shark Savers:
Focuses on ending the slaughter of sharks and manta rays. They aim to motivate the end of shark fin soup and the consumption of sharks. They also work to create shark sanctuaries in different locations.

Sea Shepherd Conservation Society:
Sea Shepherd is well known for many things. One being their on going campaign against the dolphin hunts in Taiji and chasing Japanese whalers out of whale sanctuaries. They also have campaigns to vault poaching in Guatemala and advocating a ban on the West Australian shark cull.
Ocean Preservation Society:
They use cinematography to expose crimes against the environment and its creatures.
American Cetacean Society:
Their mission is to protect the habitats of whales, dolphins, and porpoises through public education and outreach programs.

Whale & Dolphin Conservation:
An organization devoted to the well being of both wild and captive cetaceans. They campaign for the end to the trade of captive cetaceans.
Project AWARE Foundation:
A non profit organization that works with scuba divers in 182 countries to implement lasting change in two core areas of shark conservation and marine litter.
Ocean Conservancy:
A non profit environmental advocacy group that helps formulate ocean policy at the federal and state levels based on peer review science.
Coral Reef Alliance:
A non profit organization aiming to save the world coral reefs.

Our oceans and its creatures are in danger and it is up to us to save them both. Let’s work together to save our oceans and it’s precious babies.
Mesozoic Monthly: Champsosaurus
Good news everyone: it’s September! We’ve made it to month nine of 12! Sometimes it feels like this year will never end. I take comfort in the idea that if life can survive the traumatic Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction that killed the non-avian dinosaurs, I can make it through 2020. One of the survival champs of the K-Pg extinction was Champsosaurus, a superficially crocodile-like reptile belonging to the extinct group Choristodera.

The skeleton of Champsosaurus laramiensis looks superficially like that of a crocodilian, but this is the result of convergent evolution. Choristoderes (like Champsosaurus) and crocodilians lived contemporaneously for at least 150 million years, until the choristoderes said “after a while, crocodile!” and went extinct. Photo by Triebold Paleontology, Inc., used with permission.
The class Reptilia encompasses an incredible variety of animals: lizards, snakes, turtles, crocodilians, pterosaurs, dinosaurs, and even birds are just a few of its members. In addition to the familiar reptiles that live today, many other reptile groups thrived for millions of years before eventually going extinct. It’s easy to think of dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus or Triceratops when we talk about extinct reptile groups, but in reality, many extinct groups of animals with no living relatives escape the public eye. Choristodera, an order within the class Reptilia, is one of these groups. Choristoderes were semi-aquatic or aquatic carnivorous reptiles that evolved during the Mesozoic Era (the Age of Dinosaurs) and died out in the Cenozoic Era (the Age of Mammals). Just because they went extinct does not mean they were unsuccessful; the group survived for at least 150 million years! Like many animals, a rapidly shifting environment was probably the source of their demise. Until that point, choristodere evolution was able to ‘keep up’ with the changing times, including the monumental global changes that came with the K-Pg extinction. The combination of a massive asteroid impact in what’s now Mexico, extensive volcanic activity in India, and worldwide climatic shifts resulted in the extinction of over 75% of all species. Research on choristodere teeth suggests that they beat the odds by adapting to new prey.
When you think of an aquatic carnivorous reptile, you probably think of a crocodilian – and that’d be right! The crocodilian body plan is a very successful build for hunting prey in the water. As another aquatic carnivorous reptile, Champsosaurus evolved similar traits. This is an example of convergent evolution, in which unrelated species develop similar characteristics to deal with comparable circumstances. (You can read about more examples of convergent evolution in the January edition of Mesozoic Monthly about the sauropodomorph dinosaur Ledumahadi.) Some of the shared features between Champsosaurus and crocodilians include long, muscular jaws for catching fish, eyes at the top of the head for peering out of the water, and a flattened tail that was paddled side-to-side for propulsion. Of course, Champsosaurus and the rest of the choristoderes had many features that set them apart as well. Unlike crocodilians, which have bony armor called osteoderms embedded in their skin, choristoderes just had skin covered with tiny scales. In addition, crocodilians have nostrils on top of their snouts so that they can breathe while lurking beneath the surface of the water; choristodere nostrils were at the end of their snouts, so that they could stick the tip of their nose out of the water like a snorkel and breathe from down below.

A right dentary (tooth-bearing lower jaw bone) of Champsosaurus sp. from the Upper Cretaceous of Wyoming in Carnegie Museum of Natural History’s Vertebrate Paleontology collection (specimen number CM 96509). The bone is facing upwards, so you’re looking down on the teeth. Check out the dark ‘stripes’ on the enamel of each tooth. These unusual enamel striations are a hallmark of neochoristoderes, the particular choristodere subgroup to which Champsosaurus belongs. Photo by Joe Sawchak.
The traits we see in the skeleton of Champsosaurus help paleontologists paint a picture of its behavior. Instead of lurking at the surface of the water, Champsosaurus would wait on the bottom of a shallow lake or stream for prey to come close, lifting the tip of its snout out of the water to breathe. When a tasty fish approached, it would spring off the bottom with its powerful legs and snatch it with its toothy jaws. Despite having strong legs, Champsosaurus was not adapted to a terrestrial lifestyle. In fact, adult males may not have been able to leave the water at all! Fossils attributed to females have more robust hips and hind limbs, allowing them to crawl onto land to lay eggs. According to this hypothesis, the less-robust males would have been restricted to an aquatic-only lifestyle.
Some of the freshwater environments that Champsosaurus inhabited were relatively cold, but that wasn’t a big deal; choristoderes may have been able to regulate their body temperature (a talent known as endothermy or ‘warm-bloodedness’). Crocodilians, by contrast, live in warm, tropical habitats because they are not capable of regulating their body temperature and rely on the sun to warm their bodies (aka ectothermy or ‘cold-bloodedness’). This would explain why choristoderes were able to live further north than crocodilians. However, it seems that crocodilians had the right idea; temperatures around the tropics change less during cooling and warming periods than those at higher latitudes. So, when the current Antarctic ice sheets began to form and the planet started cooling, the temperate choristoderes had to deal with more environmental change than the tropical crocodilians, and finally went extinct. I think the moral of the story is, we would all be handling 2020 better if we lived in the tropics!
Lindsay Kastroll is a volunteer and paleontology student working in the Section of Vertebrate Paleontology at Carnegie Museum of Natural History. Museum staff, volunteers, and interns are encouraged to blog about their unique experiences and knowledge gained from working at the museum.
Our resident yellow-naped parrots love talking to the SNC’s Executive Director, probably because they’ve known her longer than any other staff here! Their incredible memory and bonding behaviors lead to some interesting dynamics.
Parrots are known for their impressive mimicry. Vocal mimicry is the ability to imitate speech or noises. There are many possible reasons why vocal mimicry abilities could be an evolutionary advantage. Improved communication could help with the mating process and imitating predators might scare away competition.

Our turtles are wondering where the sun is today

Tomorrow an incredible natural phenomenon known as the super blood moon lunar eclipse will take place at 5:45AM EST. “In the United States, the total eclipse will begin at 7:11 a.m. ET and end at 7:26 a.m. ET, but will be partially visible from 5:45 a.m. ET to 8:52 a.m. ET,” (https://www.cnn.com/2021/05/25/world/may-full-moon-lunar-eclipse-scn/index.html). A lunar eclipse is described as an event where the Earth’s shadow blocks the sun’s light that reflects off the moon.
Celestial events like a lunar eclipse have long caught the attention of humans throughout history. There are also many myths and legends about the full moon affecting human behavior. Whether it’s just a really cool event to watch, or something more, what is the connection between the moon and us?
Scientifically speaking, the moon has a gravitational pull on the Earth’s oceans. The moon’s pull is what is responsible for creating the tides. The tide is essentially the rising and lowering of the ocean against the shore. The change in period between higher and lower local ocean levels is referred to as high and low tide. As the moon circles the Earth, it’s gravitational pull gets greater and weaker in the areas it moves closer to or further from. The greater the pull, the higher the tide, and vice-versa.
Find your local high and low tide here: https://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/map/index.html?region=Florida/
In nature, many animal species have oriented themselves to respond to high and low tide. For example, sea turtles will come up to shore during a high tide to lay their eggs. Since other animal species have developed behavior that responds to certain aspects of the moon, it isn’t too crazy to believe that at some point down the evolutionary line, humans may have done something similar. However, there aren’t too many studies to prove this.
While many studies have been done on how the Full Moon can affect sleep cycles in humans (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25266502/), this might be better chalked up to the slow adaptation to artificial light in the 21st century. And while there are many who believe that hospitals, emergency rooms, and even classrooms get crazier than usual on the day of a full moon, there isn’t much to prove that either. A better question to ask might be, is the superstition around the full moon becoming a self-fulfilling prophecy? Let us know what you think!
This juvenile red tailed hawk was brought to the SNC a few weeks ago after being found injured on a golf course. On Sep. 27 the hawk was successfully released back into the wild!
Red tailed hawks are native to Florida and, like all hawks, considered a bird of prey. Their large talons and sharp beaks are perfect for ripping and tearing their prey. It also makes them difficult patients. Luckily, our experienced rehabber was able to get the hawk all patched up and back into the wild in record time!
This African Spur Thigh Tortoise is named Bubba and he is a permanent resident at the Sawgrass Nature Center. He was previously kept as a pet, but his owners did not realize that he would get this large. And since he is an exotic species to Florida, he is non-releasable.
The African Spur-Thigh is a native species of tortoise to Northern Africa, specifically along the southern edge of the Sahara Desert. They dig burrows in the ground to spend the hottest parts of the day in. This is known as aestivation.
Fun fact: The African Spur Thigh Tortoise is the third largest tortoise in the world. Surpassed only by the Galapagos Tortoise and the Aldabra Giant Tortoise.

This is a reminder that tortoises can NOT swim like other turtles. If tortoises are dropped in water, they will drown. You can tell the difference between a swimming turtle and a tortoise by looking at their feet. Turtles will have webbed feet that help them swim, or flippers. Tortoises do not have webbed feet.
-
 errorx429 reblogged this · 4 years ago
errorx429 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 errorx429 liked this · 4 years ago
errorx429 liked this · 4 years ago -
 straymongrel liked this · 4 years ago
straymongrel liked this · 4 years ago -
 captain-awesome03 liked this · 4 years ago
captain-awesome03 liked this · 4 years ago -
 shygardenstudentthing-blog liked this · 4 years ago
shygardenstudentthing-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 bookwyrmth1rt33n liked this · 4 years ago
bookwyrmth1rt33n liked this · 4 years ago -
 nealmcclure liked this · 4 years ago
nealmcclure liked this · 4 years ago -
 sawgrassnaturecenter reblogged this · 4 years ago
sawgrassnaturecenter reblogged this · 4 years ago

The Sawgrass Nature Center (SNC) is a nonprofit located in South Florida. Our mission is to educate the public about native wildlife and environmental stewardship. We also rescue, rehabilitate, and release injured, orphaned, or sick wildlife. Animals that cannot be released due to permanent injuries or disabilities are given a forever home on site with animal keepers that know how to properly care for them. We are able to operate due to donations from generous patrons. If you are interested in helping us further our mission, check us out at: https://sawgrassnaturecenter.org/
202 posts