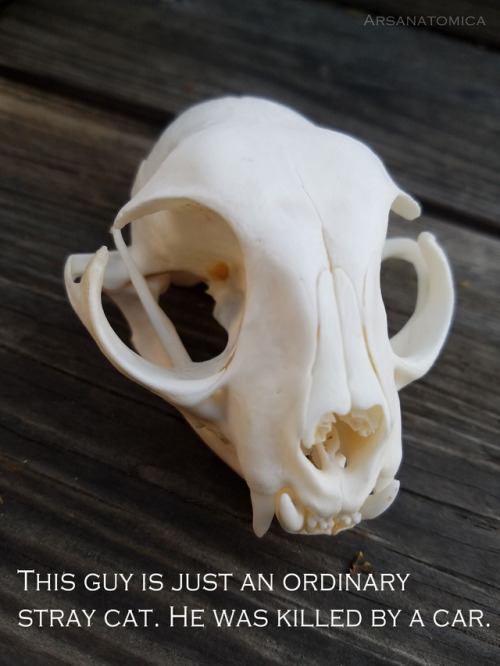
This Week In Chemistry: The World’s First Nanocar Race, And Making A Painkiller Last Longer Using A

This Week in Chemistry: The world’s first nanocar race, and making a painkiller last longer using a metal-organic framework: https://goo.gl/TaS7HG
More Posts from T-sci-eng and Others








Are Cloaking Devices Coming? Metalens-Shaped Light May Lead The Way
“The biggest challenge facing a real-life cloak has been the incorporation of a large variety of wavelengths, as the cloak’s material must vary from point-to-point to bend (and then unbend) the light by the proper amount. Based on the materials discovered so far, we haven’t yet managed to penetrate the visible light portion of the spectrum with a cloak. This new advance in metalenses, however, seems to indicate that if you can do it for a single, narrow wavelength, you can apply this nanofin technology to extend the wavelength covered tremendously. This first application to achromatic lenses covered nearly the full visible-light spectrum (from 470 to 670 nm), and fusing this with advances in metamaterials would make visible-light cloaking devices a reality.”
What would it take to have a true cloaking device? You’d need some way to bend the light coming from all across the electromagnetic spectrum around your cloaked object, and have it propagate off in the same direction once it moved past you. To an outside observer, it would simply seem like the cloaked object wasn’t there, and they’d only view the world in front of and behind them. Even with the recent advances that have been made in metamaterials, we have not yet been able to realize this dream in three dimensions, covering the entire electromagnetic spectrum, and from all directions. But a new advance in metalens technology might get you the full electromagnetic spectrum after all, as they appear to have solved the problem of chromatic aberration with a light, small, and inexpensive solution. If we can combine these two technologies, metalenses and metamaterials, we just might realize the dream of a true invisibility cloak.
Whether you’re a Star Trek or Harry Potter fan, the ability to turn yourself invisible would be Earth-shattering. Come see how transformation optics might transform the world!









PERIODIC SPONGE SURFACES AND UNIFORM SPONGE POLYHEDRA IN NATURE AND IN THE REALM OF THE THEORETICALLY IMAGINABLE
By Michael Burt- Prof emeritus, Technion, I.I.T. Haifa Israel
The diversity of shapes and forms which meets the eye is overwhelming. They shape our environment: physical, mental, intellectual. Theirs is a dynamic milieu; time induced transformation, flowing with the change of light, with the relative movement to the eye, with physical and biological transformation and the evolutionary development of the perceiving mind. “Our study of natural form “the essence of morphology”, is part of that wider science of form which deals with the forms assumed by nature under all aspects and conditions, and in a still wider sense, with forms which are theoretically imaginable ..(On Growth and Form D'Arcy Thompson), “Theoretically” to imply that we are dealing with causal- rational forms. “It is the business of logic to invent purely artificial structures of elements and relations. Sometimes one of these structures is close enough to a real situation to be allowed to represent it. And then, because the logic is so tightly drawn, we gain insight into the reality which was previously withheld from us” (C. Alexander). A particular interest should be focused on those structures which are shaped like solids or containers, with continuous two-manifold enveloping surfaces, enclosing a volume of space and thus subdividing the entire space into two complementary sub-spaces, sometimes referred to as interior and exterior, although telling which is which, is a relativistic notion. On each of these envelopes, topologically speaking, an infinite number of different maps composed of polygonal regions (faces), which are bounded by sets of edge segments and vertices, could be drawn, to represent what we call polyhedra, or polyhedral envelopes. We come to know them by various names and notations, evolving through many historical cultures up to our present times; each representing an individual figure-polyhedron, or a family, a group, a class or a domain; convex-finite, Platonic and Archimedean polyhedra; pyramids, prisms; anti-prisms; star polyhedra; deltahedra; zonohedra; saddle polyhedra, dihedral, polydigonal, toroidal, sponge like, finite and infinite polyhedra; regular, uniform, quasi-regular, and so forth; all inscribable in our 3-dimensional space. It is these structures and their extended derivatives which shape our physical-natural or artificial man-conceived environment and provide for our mental pictures of its architecture. The number of forms which had acquired a name or a specific notation through the ages is amounting to infinity, although the number of those which comprise our day to day formal vocabulary and design imagery is extremely (and regretfully) limited by comparison, even amongst designers and architects, whose profession, by definition, compels them to manipulate and articulate forms and space. Here it is right to observe that name-giving is part of the creative and generative process. The number of polyhedral forms which did not receive, as yet a proper name or a notation is also infinite. Infinite is also the number of potentially existing and possible imaginary periodic forms, not envisaged yet. Conspicuous are those relating to sponge-like labyrinthian, polyhedral, space dividing surfaces, which until quite recently were not even considered as a research topic. The interest in these forms has been prompted by our growing awareness of their abundance in nature and their importance, not only in describing micro and macro-physical and biological phenomena, but also in coping with morphological complexity and nature of our built environment and its emerging new architecture and the order and formal character of our living spaces, on either the building or the urban scale. Nature is saturated with sponge structures on every possible scale of physical-biological reality. The term was first adopted in biology: “Sponge: any member of the phylum Porifera, sessile aquatic animals, with single cavity in the body, with numerous pores. The fibrous skeleton of such an animal, remarkable for its power of sucking up water”. (Wordsworth dictionary). the entire study here
© Michael Burt- Prof emeritus, Technion, I.I.T. Haifa Israel








Inside - Vadim Sadovski





Impressive artwork.
Dr. Greg Dunn (artist and neuroscientist) and Dr. Brian Edwards (artist and applied physicist) created Self Reflected to elucidate the nature of human consciousness, bridging the connection between the mysterious three pound macroscopic brain and the microscopic behavior of neurons. Self Reflected offers an unprecedented insight of the brain into itself, revealing through a technique called reflective microetching the enormous scope of beautiful and delicately balanced neural choreographies designed to reflect what is occurring in our own minds as we observe this work of art. Self Reflected was created to remind us that the most marvelous machine in the known universe is at the core of our being and is the root of our shared humanity.
h-t New Scientist: Brain images display the beauty and complexity of consciousness




The great esGape
Unlike most elemental metals, gallium will melt in the palm of your hand, or at temperatures above about 30 °C. And that’s not the only unusual thing about this element: It also expands when it freezes. In this video series, warm liquid gallium is poured into a glass vial (top), followed by a little clean-up. As the gallium cools back down to room temperature, it starts to bubble up as its volume expands (third video down). Overall, it expands 3%, shattering the vial (bottom). Water is a substance commonly used to demonstrate this sort of expansion, growing about 8% in volume when frozen, but other elements exhibit this behavior as well, including silicon and plutonium. The final two clips have been accelerated 200 times and 10 times, respectively.
Credit: Periodictable.ru (watch the whole video here; GIFs created by rudescience)
More ChemPics and C&EN stories:
Liquid metals take shape
A melting liquid
Rolling out liquid-metal motors
If you trace the orbits of Earth and Venus over 8 years, this is the pattern that emerges

Researchers build first deployable, walking, soft robot
Researchers have built the first robot made of soft, deployable materials that is capable of moving itself without the use of motors or any additional mechanical components. The robot “walks” when an electric current is applied to shape-memory alloy wires embedded in its frame: the current heats the wires, causing the robot’s flexible segments to contract and bend. Sequentially controlling the current to various segments in different ways results in different walking gaits.
The researchers expect that the robot’s ability to be easily deployed, along with its low mass, low cost, load-bearing ability, compact size, and ability to be reconfigured into different forms may make it useful for applications such as space missions, seabed exploration, and household objects.
The scientists, Wei Wang et al., at Seoul National University and Sungkyunkwan University, have published a paper on the new robot and other types of deployable structures that can be built using the same method in a recent issue of Materials Horizons.
“The main advantage of this modular robot is robustness in various environments due to lack of mechanical systems such as motors and gears,” coauthor Sung-Hoon Ahn at Seoul National University told Phys.org. “Thus, problems facing motor-based robots, such as sealing and lubrication of mechanical systems in water or space environments, are not a problem for the smart actuator.”
Read more.
How does sand from Sahara end up in your windshield ?

TBH cleaning your car is a rather mundane task. But when you fill your head with some interesting physics the task actually gets rather pretty interesting. Here’s some good for thought on such an occasion :
The dust on your windshield might actually be from the Sahara desert
To understand how, lets start with some simple physics.
The stacked ball drop
You basically take couple of balls, align them up and drop them to the ground. The ball at the top reaches the most highest due to the subsequent transfer of energy from the other balls.

Source Video : Physics Girl
Here is an exaggerated but amazing slow motion of the same energy transfer with a water balloon. Notice how the transfer of energy takes place between the water balloon and the tennis ball.

Source Video : Slow Mo Lab
Sandstorms in the desert

Sandstorms/ Dust storms as you might be aware, are pretty common in the desert. . Dust storms arise when a gust front or other strong wind blows loose sand and dirt from a dry surface.

And this can cause something phenomenal to happen:
If the wind speed is sufficient then larger sand particles can propel finer ones high into the atmosphere. ( just like the stacked ball )
Then these fine particles are caught in the global wind pattern and are transported across the globe until they fall down to the earth as rain.
How cool is that ! Have a great day!
* Tracking saharan dust in 3D - NASA video
** All the World’s a Stage … for Dust - NASA article
** Wiki on Saltation
-
 pretty-butterfly16 liked this · 4 years ago
pretty-butterfly16 liked this · 4 years ago -
 oneinquisitivechild liked this · 6 years ago
oneinquisitivechild liked this · 6 years ago -
 ash-moztaza liked this · 6 years ago
ash-moztaza liked this · 6 years ago -
 fractal-fluctuation liked this · 6 years ago
fractal-fluctuation liked this · 6 years ago -
 banginbabe88-blog liked this · 7 years ago
banginbabe88-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 kno19131677 liked this · 7 years ago
kno19131677 liked this · 7 years ago -
 chatelaine-panda liked this · 7 years ago
chatelaine-panda liked this · 7 years ago -
 end-of-the-rabbithole reblogged this · 7 years ago
end-of-the-rabbithole reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 end-of-the-rabbithole liked this · 7 years ago
end-of-the-rabbithole liked this · 7 years ago -
 quantumfuckery liked this · 7 years ago
quantumfuckery liked this · 7 years ago -
 yogesh531035sharma liked this · 7 years ago
yogesh531035sharma liked this · 7 years ago -
 damnsmartblueboxes liked this · 7 years ago
damnsmartblueboxes liked this · 7 years ago -
 t-sci-eng reblogged this · 7 years ago
t-sci-eng reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 fabulouisday liked this · 7 years ago
fabulouisday liked this · 7 years ago -
 pinkheartfest liked this · 7 years ago
pinkheartfest liked this · 7 years ago -
 ravenslash-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago
ravenslash-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago -
 toonvailo reblogged this · 8 years ago
toonvailo reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 amarilloblancorosa-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
amarilloblancorosa-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 alanamiss liked this · 8 years ago
alanamiss liked this · 8 years ago -
 thingsaccordingtogroup5a-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
thingsaccordingtogroup5a-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 thingsaccordingtogroup5a-blog liked this · 8 years ago
thingsaccordingtogroup5a-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 pallid-etoiles liked this · 8 years ago
pallid-etoiles liked this · 8 years ago -
 andthatremindsme reblogged this · 8 years ago
andthatremindsme reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mfennec-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
mfennec-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tixs reblogged this · 8 years ago
tixs reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 aberadolflincler-blog liked this · 8 years ago
aberadolflincler-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 rkbetancourt reblogged this · 8 years ago
rkbetancourt reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 intheeyeofadiamond liked this · 8 years ago
intheeyeofadiamond liked this · 8 years ago -
 winking-owl reblogged this · 8 years ago
winking-owl reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 gottablastoff reblogged this · 8 years ago
gottablastoff reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 gottablastoff liked this · 8 years ago
gottablastoff liked this · 8 years ago -
 malazan-warren-mastermage reblogged this · 8 years ago
malazan-warren-mastermage reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 keepinitreal787 liked this · 8 years ago
keepinitreal787 liked this · 8 years ago -
 ununnilium liked this · 8 years ago
ununnilium liked this · 8 years ago -
 geneticwitch reblogged this · 8 years ago
geneticwitch reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 d1ckqueen reblogged this · 8 years ago
d1ckqueen reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 scrmnviking liked this · 8 years ago
scrmnviking liked this · 8 years ago -
 dialmformara liked this · 8 years ago
dialmformara liked this · 8 years ago -
 no-good-omens liked this · 8 years ago
no-good-omens liked this · 8 years ago -
 fredscience-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
fredscience-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 estrellada66-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
estrellada66-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago