Thejoyofscience - This Is For All The Nerdy Girls


More Posts from Thejoyofscience and Others
Went out to a vernal pool today and saw some crazy toad action


Right lateral thoracic wall mass from a 10 year-old, female-spayed, Golden Retriever. Approximately six months ago the owner noticed a small, firm swelling on the patient’s right chest. No doubt it grew with time, as it finally got large enough for the owner to become truly concerned! The patient is clinically healthy otherwise.
*
The most prominent feature on the cytology were these gorgeous globules of magenta, streaming material! In fact, the entire slide was imbued with this color when you looked at it without a microscope. The substance is most likely matrix produced by cancer cells. Matrix of this color is commonly observed in chrondrosarcomas. Occasional malignant spindle-shaped cells were found imbedded in the matrix.
*
Diagnosis: Chondrosarcoma. Well , that’s the most likely diagnosis given the location and appearance of the neoplastic cells and matrix! Other possibilities include a myxosarcoma (which produces a mucous like material!) or osteosarcoma (malignant primary bone tumor). Chondrosarcomas are often regionally invasive but rarely metastasize. If the owner is on board with a chest wall resection, the patient will have a good prognosis :-)
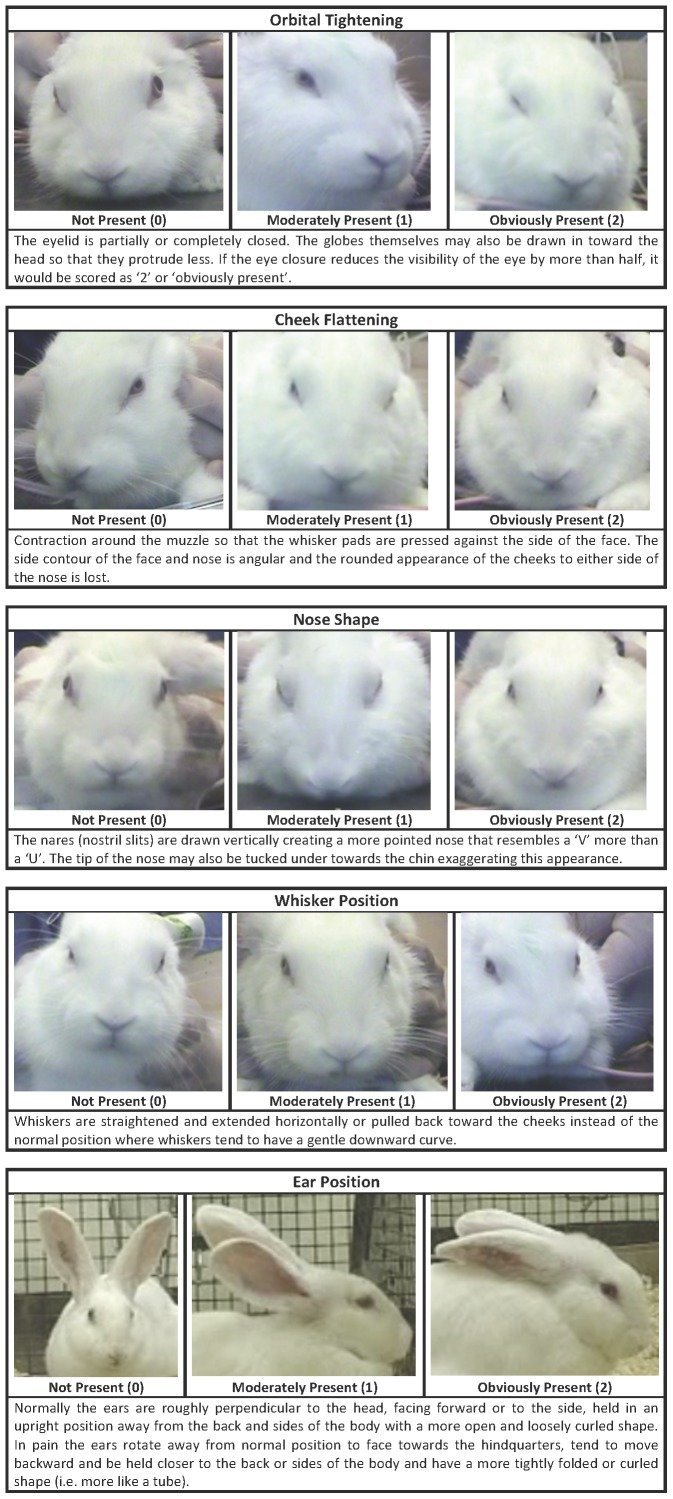



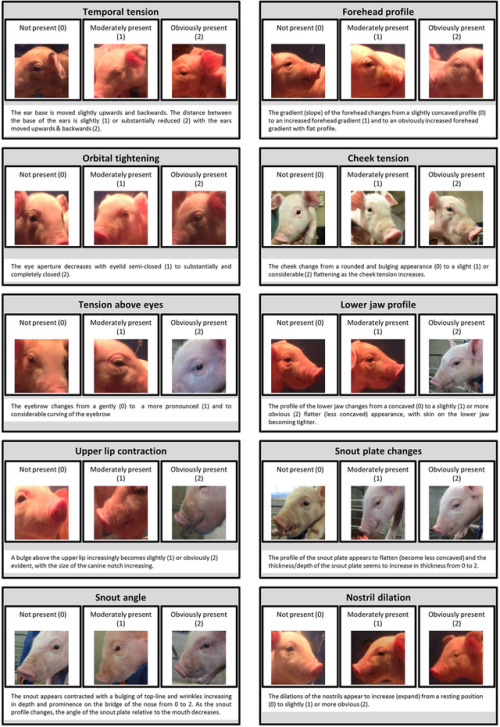





Recognising silent acute pain in animals - assorted species grimace scales:
Development of the Horse Grimace Scale (HGS) as a Pain Assessment Tool in Horses Undergoing Routine Castration
The composition and initial evaluation of a grimace scale in ferrets after surgical implantation of a telemetry probe
The Assessment of Facial Expressions in Piglets Undergoing Tail Docking and Castration: Toward the Development of the Piglet Grimace Scale
The Sheep Grimace Scale as an indicator of post-operative distress and pain in laboratory sheep and the Coding and quantification of a facial expression for pain in lambs
Mouse - How to be a pain management advocate for exotic and zoo animals (full text available - includes additional species)
The Rat Grimace Scale: A partially automated method for quantifying pain in the laboratory rat via facial expressions
Evaluation of EMLA Cream for Preventing Pain during Tattooing of Rabbits: Changes in Physiological, Behavioural and Facial Expression Responses
Pain evaluation in dairy cattle
Pain is subtle - we cannot depend on vocalisations or extreme abnormal behaviour to determine if an animal is on pain - animals can cover up pain while going about their daily life. Grimace scales have been found to be reliable indicators of pain (full text available)
Unfortunately, I could not find a clear visual grimace scale for dogs, cats or birds :(
Which is a shame, because perhaps I could have recognised my own dog’s discomfort for the acute pain it was sooner:

(left: dog in pain. See eyes, tension, cheeks, whiskers, ears compared to the multiple species grimace charts above. right: tired but not in pain dog)
Perhaps my new books that arrived today might have some on dogs at least. There’s this visual blog post of a stressed dog at the vet - stress in the absence of a trigger looks very much like pain.
Here is a small comparative cats, with the link going into more detail. Not a scale but better than nothing:


Bonus round - you can get free A3 posters on recognising pain for Rabbits, Mice and Rats from the National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research. My rabbit specialist vet has the rabbit one!
Pelvic Pain Research

Research link: https://wils9231.wixsite.com/website-1?fbclid=IwAR3dJS6LwJSbiTw3KE9D0nU-N81CQfHPrEfr52EWvk9i6sVqx8HScDSZLpA

Thunderstorm from space
This photo was taken from the International Space Station during a project to capture photos of clouds. Here a large anvil supercell (some 200 km across) is silhouetted against the limb of our blue orb, revealing clearly the layers of the atmosphere somewhere over northern Australia around 1,500 km from the station, which was then flying over Papua New Guinea.
Keep reading


(Image: U. Müeller)
New neurons (in green) are guided to the neocortex - responsible for controlling language and movement - not by glial cells, but by a protein called reelin.
Journal reference: Neuron, DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.003
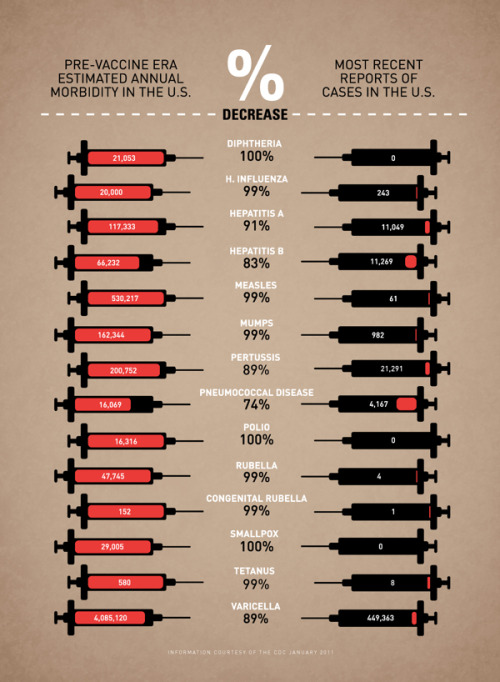
Vaccine Infographic by Leon Farrant.
I often speak with patients who tell me that they do not wish to be vaccinated because they do not see the point, that it is a farce, that it can cause autism (it does not), despite educating and informing them of the reasons behind it.
In the same way that people who did not grow up during the great wars of the mid-twentieth century have little frame of reference as to what the toll of total war can be, neither can a newer generation of people who have never seen the effects of polio, smallpox, and measles ravage humanity. For many people in the developed world, these are just distant, faded memories captured in the pages of medical textbooks.
I sincerely hope that the understanding of why we vaccinate does not become lost over time, that people need not fall victim to these preventable diseases; otherwise, the suffering, the challenges, and the research that went into developing these vaccines were all for nothing.

This bad little boy is super rare to find!!! This is a mitotically active cell present in peripheral blood circulation from a dog - only the second one I have ever seen!!
As a game, in the diagnostic lab we yell KABLAM! anytime we see a mitotic figure. The first one to say kablam wins :-P We should so turn it into a drinking game…
-
 kirkwahmmett liked this · 8 months ago
kirkwahmmett liked this · 8 months ago -
 censosrpg liked this · 1 year ago
censosrpg liked this · 1 year ago -
 contbamladict liked this · 1 year ago
contbamladict liked this · 1 year ago -
 fleuryheart liked this · 3 years ago
fleuryheart liked this · 3 years ago -
 certainangelthing liked this · 3 years ago
certainangelthing liked this · 3 years ago -
 inkyflygoesbzzzz liked this · 3 years ago
inkyflygoesbzzzz liked this · 3 years ago -
 regular-deli-meats liked this · 4 years ago
regular-deli-meats liked this · 4 years ago -
 perdidaenalgunlibro liked this · 4 years ago
perdidaenalgunlibro liked this · 4 years ago -
 evanescentnight liked this · 4 years ago
evanescentnight liked this · 4 years ago -
 wwickedwedgiewoman liked this · 4 years ago
wwickedwedgiewoman liked this · 4 years ago -
 panic-pain reblogged this · 4 years ago
panic-pain reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 panic-pain liked this · 4 years ago
panic-pain liked this · 4 years ago -
 kings-files liked this · 4 years ago
kings-files liked this · 4 years ago -
 steafire liked this · 4 years ago
steafire liked this · 4 years ago -
 markoftara reblogged this · 4 years ago
markoftara reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 lexielita liked this · 4 years ago
lexielita liked this · 4 years ago -
 yellowisalwaysahappycolour liked this · 4 years ago
yellowisalwaysahappycolour liked this · 4 years ago -
 royconner reblogged this · 4 years ago
royconner reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 anniephl liked this · 4 years ago
anniephl liked this · 4 years ago -
 missfrench14 liked this · 4 years ago
missfrench14 liked this · 4 years ago -
 a-loser-and-a-lover liked this · 4 years ago
a-loser-and-a-lover liked this · 4 years ago -
 whatiswrongwithpeople liked this · 4 years ago
whatiswrongwithpeople liked this · 4 years ago
An assortment of scientific things from the wonderful world of biology
77 posts
