Aspirate Of A Mammary Mass From A 8 Year-old, Female-intact, Yorkshire Terrier. The Patient Was Found


Aspirate of a mammary mass from a 8 year-old, female-intact, Yorkshire Terrier. The patient was found wondering in a field by a good Samaritan-turned-owner over the 4th of July weekend. Although she was acting normally, the owner brought the little dog in for a ‘look over.’ On physical examination a 2cm mass was felt in the left mammary chain. No obvious spay scar was present.
*
On cytology there were copious clusters of epithelial cells. These epithelial cells (top picture) were very non-descript, making for large, jumbled piles of cells. Notice how you cannot see any well-defined cell borders between them?? Just a ton of nuclei (and nucleoli) blending in together! That’s a sign of cell craziness! Many clusters were surrounded by this gorgeous, pink-magenta material. Likely secretory product or matrix.
*
Cytologic diagnosis: Mammary tumor! Although the cells look quite malignant on cytology, many studies have shown you cannot reliably determine malignancy with cytology alone. Thus, you NEED a biopsy to determine if a mammary tumor is malignant or benign in a dog. And flip a coin on that - about 50% are malignant and 50% are benign. Intact female dogs have an almost 35% lifetime chance of developing one of these beasts!
More Posts from Thejoyofscience and Others

The central nervous system (CNS) in most vertebrates forms initially as a flat sheet of cells, which subsequently rolls up and fuses shut to form the hollow neural tube, which is the precursor to the CNS. The enriched apical actin in the closing neural tube (shown in green in the image) is central to cell shape changes that contribute to the rolling up process.
Image: Color micrograph showing a cross-sectional (transverse) view of the closing neural tube in a Xenopus embryo. Actin is shown in green.



the himalayan monal is a large member of the pheasant family found in parts of asia. while during the breeding season they mainly stay in pairs, in winter they form small communities and roost together. they feed on grasses, insects, seeds and berries. they are known for their vivid iridescent plumage, particularly colorful for a pheasant. x
Me whenever I see a corporate ad trying to say “we’re all in this together”:

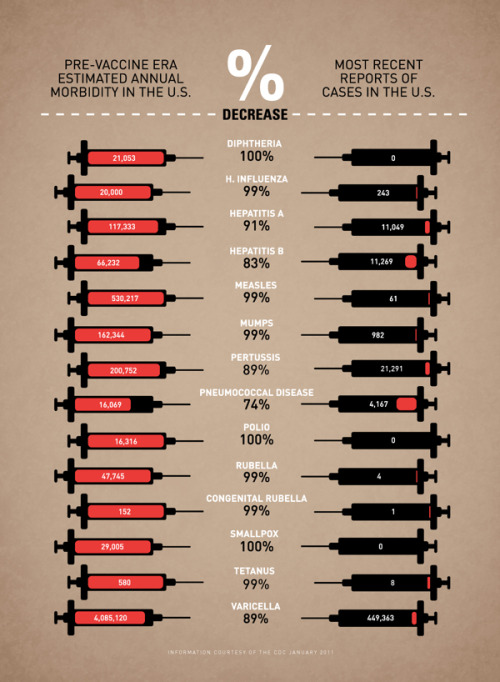
Vaccine Infographic by Leon Farrant.
I often speak with patients who tell me that they do not wish to be vaccinated because they do not see the point, that it is a farce, that it can cause autism (it does not), despite educating and informing them of the reasons behind it.
In the same way that people who did not grow up during the great wars of the mid-twentieth century have little frame of reference as to what the toll of total war can be, neither can a newer generation of people who have never seen the effects of polio, smallpox, and measles ravage humanity. For many people in the developed world, these are just distant, faded memories captured in the pages of medical textbooks.
I sincerely hope that the understanding of why we vaccinate does not become lost over time, that people need not fall victim to these preventable diseases; otherwise, the suffering, the challenges, and the research that went into developing these vaccines were all for nothing.
Pelvic Pain Research

Research link: https://wils9231.wixsite.com/website-1?fbclid=IwAR3dJS6LwJSbiTw3KE9D0nU-N81CQfHPrEfr52EWvk9i6sVqx8HScDSZLpA




“our work should equip the next generation of women to outdo us in every field this is the legacy we’ll leave.”
- rupi kaur








Journey to the Microcosmos- The Complicated Legacy of Lynn Margulis
Images originally captured by Jam’s Germs

Colonial rotifers showing eyespots and corona, magnification 200x - 500x. Ralph Grimm.

Hematopoietic stem cells ready for re-injection. Image from Steve Gschmeisserner.
-
 thejoyofscience reblogged this · 11 years ago
thejoyofscience reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 allunderskin-blog-blog reblogged this · 11 years ago
allunderskin-blog-blog reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 miamivets reblogged this · 11 years ago
miamivets reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 thetollerlover liked this · 11 years ago
thetollerlover liked this · 11 years ago -
 heckyeahcytos reblogged this · 11 years ago
heckyeahcytos reblogged this · 11 years ago
An assortment of scientific things from the wonderful world of biology
77 posts
