Writing Notes: Stages Of Decomposition
Writing Notes: Stages of Decomposition

The decomposition process occurs in several stages following death:
Pallor mortis
Algor mortis
Rigor mortis
Cadaveric spasm
Lividity
Putrefaction
Decomposition
Skeletonization
PALLOR MORTIS
The first stage of death.
Occurs once blood stops circulating in the body.
The cessation of an oxygenated blood flow to the capillaries beneath the skin causes the deceased to pale in appearance.
In non-Caucasians, the pallor may appear to develop an unusual hue; the skin will lose any natural lustre and appears more waxen.
Occurs quite quickly, within about 10 minutes after death.
ALGOR MORTIS
The cooling of the body after death.
The cooling process will be influenced by many factors, including the deceased’s clothing, or whether they are covered with bed linen such as blankets or duvets.
The body will typically cool to the ambient room temperature, but this alters if there is heating in the room or if there is a constant draught cooling the body.
RIGOR MORTIS
Can occur between 2 and 6 hours after death.
Factors including temperature can greatly affect this.
Caused by the muscles partially contracting, and the lack of aerobic respiration means that the muscles cannot relax from the contraction, leaving them tense, subsequently resulting in the stiffening we associate with rigor mortis.
This stage typically begins in the head, starting with the eyes, mouth, jaw and neck, and progresses right through the body.
The process is concluded approximately 12 hours after death (although, again, certain variables may occur) and lasts between 24 and 72 hours depending on circumstances.
Contrary to popular belief, rigor mortis is not a permanent state and is in fact reversed, with the muscles relaxing in the same order in which they initially stiffened.
The reversing process also takes approximately 12 hours, when the body returns to its un-contracted state.
It is possible to ‘break’ rigor mortis by manipulating and flexing the limbs. This is usually done by undertakers, pathologists or crime scene investigators who are attempting to examine or move a body – or by a murderer trying to hide their victim in the closet or the boot of a car.
CADAVERIC SPASM
A phenomenon that can be misinterpreted as rigor mortis.
The instantaneous stiffening of the body (most commonly the hands) following a traumatic death.
Unlike rigor mortis, the stiffening of the affected limb is permanent and is not reversed, causing the deceased to maintain the rigidity until such time as putrefaction causes breakdown of the particular muscle group.
Examples:
The deceased following an air crash were later discovered still clutching their seatbelts or arm rests in a final, desperate act of survival.
In a drowning case, the victim was discovered with grass from the riverbank still grasped in their hand.
Perhaps the most famous case of cadaveric spasm involves the rock band Nirvana’s lead singer, Kurt Cobain. Cobain reportedly committed suicide in April 1994. His body was discovered a few days after his death with a shotgun wound to the head, and tests revealed he had large traces of heroin in his system. He was reportedly discovered still clutching the gun in his left hand, due to cadaveric spasm. However, a great deal of controversy surrounds the veracity of this latter assumption, and indeed the cause of his death, with many people insisting and attempting to prove that he died as the result of foul play rather than suicide.
LIVIDITY
Also known as livor mortis, hypostasis, or suggillation.
Once blood can no longer circulate, it will gravitate towards the lowest point of the body.
Example: A supine body will display pinkish/purple patches of discoloration where the blood has settled in the back and along the thighs.
Occurs about 30 minutes after death, but will not necessarily be noticeable until at least 2 hours afterwards as the pooling process intensifies and becomes visible, finally peaking up to between 8 and 12 hours later.
Once it is complete, the lividity process cannot be reversed.
Therefore a body discovered lying on its side, but with staining evident in the back and shoulders, must have been moved at some point from what would have been a supine position at the time of death.
It is worth noting that if the body has had contact with the floor, a wall or other solid surface, lividity would not occur at the points of contact as the pressure would not allow the blood to seep through the capillaries and pool. The specific area of pressure will be the same colour as the rest of the body and a pattern of contact may well be evident.
PUTREFACTION
Derives from the Latin putrefacere, meaning ‘to make rotten’.
The body becomes rotten through the process known as autolysis, which is the liquefaction of bodily tissue and organs and the breakdown of proteins within the body due to the increased presence of bacteria.
The first visible sign is the discoloration of the skin in the area of the abdomen.
Bacteria released from the intestine cause the body to become bloated with a mixture of gases; over time these will leak out, and the smell will intensify to unbearable proportions.
Typically, this will attract flies that will lay eggs, which develop into maggots.
Bloating is most evident in the stomach area, genitals and face, which can become unrecognizable as the tongue and eyes are forced to protrude due to the pressure of the build-up of gases in the body.
At this stage, the body will also begin to lose hair.
The organs typically decompose in a particular order: starting with the stomach, followed by the intestines, heart, liver, brain, lungs, kidney, bladder and uterus/prostate.
Once all the gases have escaped the skin begins to turn black: this stage is called ‘black putrefaction’.
As with all the other stages of death so far, the rate of putrefaction depends on temperature and location. A body exposed to the air above ground will decompose more quickly than a body left in water or buried below ground.
During putrefaction, blistering of the skin and fermentation can also occur:
Fermentation - a type of mould that will grow on the surface of the body. This mould appears white, and is slimy or furry in texture. It also releases a very strong, unpleasant, cheesy smell.
As the putrefaction process comes to an end, fly and maggot activity will become less, which leads to the next stage.
DECOMPOSITION
The body is an organic substance comprising organisms that can be broken down by chemical decomposition.
If the body is outside, any remains that have not been scavenged or consumed by maggots will liquefy and seep into the surrounding soil.
Thus when the body decomposes it is effectively recycled and returned to nature.
SKELETONIZATION
The final stage of death is known as ‘dry decay’, when the cadaver has all but dried out: the soft tissue has all gone and only the skeleton remains.
If the cadaver is outside, not only is it exposed to the elements but it also becomes food for scavengers such as rats, crows or foxes.
As the remains are scavenged, the body parts become dispersed so it is not unusual to find skeletal remains some distance from where the body lay at the point of death.
The way in which skeletal remains are scattered in such cases is of interest to archaeologists, and is referred to as taphonomy.
Where a body has lain undiscovered at home for a period of time it has also been known for family pets, typically dogs, to feed on the body. The natural instinct of a pet is to attempt to arouse the deceased by licking them, but once it gets hungry, its survival instinct will take over and it will consider the body as little more than carrion: it will act with the same natural instinct as a scavenger in the wild, which will feed on any corpse, be it animal or human, if it is starving.
Obviously the number of pets, the body mass of the deceased and the time lapse before the body is discovered will influence to what extent it has been devoured.
For further research on the stages of decomposition and the factors that affect it, look up body farms. These are medical facilities where bodies are donated for research purposes so scientists can specifically observe the decomposition process. However, be aware that some of the images are quite graphic.
Source ⚜ More: References ⚜ Autopsy ⚜ Pain & Violence ⚜ Injuries Bereavement ⚜ Death & Sacrifice ⚜ Cheating Death ⚜ Death Conceptions
More Posts from Watergeus and Others
So... I found this and now it keeps coming to mind. You hear about "life-changing writing advice" all the time and usually its really not—but honestly this is it man.
I'm going to try it.

Writing Body Language
How to Improve your writing
This is something that happens every day in your life. A shift of your eyebrow in skepticism, or the way your lip may twitch to a half smile cause you’re trying not to laugh. These behaviors are vital for writing in character, because not only do the allow you to visually see what is happening but it is also reaffirming whatever emotion your character is showing.
So why should you write it?
Much of human communication is non-verbal which means you need to also translate this non-verbal reaction in a post. It allows you to greatly enhance the emotions of another character and always another person to ‘visually’ see how they feel in a post. Most of all, this will add depth and volume to your post to make it feel more real. IT will make your character feel like a human instead of just another fictional person you look at from above.
Below you will find a list different type of emotions and what sort of body language can be exhibited to them.
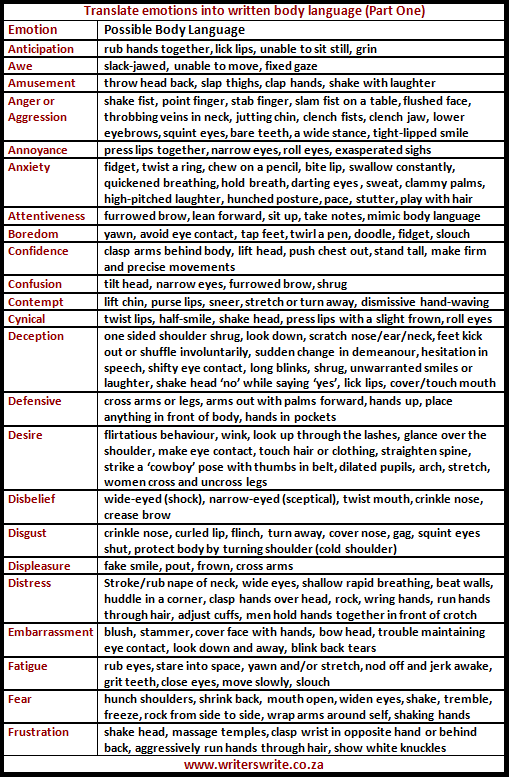
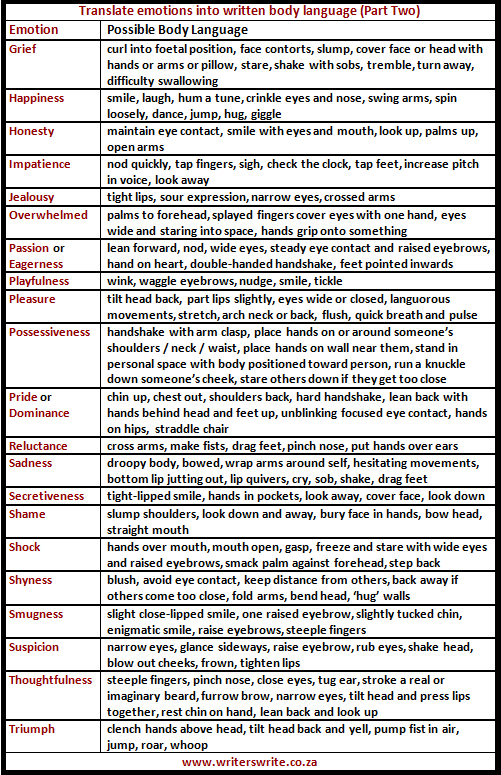
Three ways to accent an action.
When writing about emotions, there are different ways to verbally write them out. Each one is unique in their own way, allowing you to show more about the emotion.
Emphasize the Emotion. But doing this, you are expressing both the emotion and the body language. We’ll use a simple example. It’s short and simple yet you can sense he is happy. John felt so happy that he was humming a tune while walking down the hall.
Complicate the Emotion. Sometimes, even when you are feeling one emotion, deep down rooted underneath the facade of it all, there is actually an underlining emotion they feel. This is something you have to truly express otherwise no one will know. John felt so happy that he was humming a tune while walking down the hall. However, it was obvious by the way his nose crinkled that he was disgusted by the actions beforehand. Instead, John covered it up by appearing pleased today.
Contradict the Emotion. This is a little different than complicate. Contradicting means that you are claiming one thing when in fact its the other. In many ways, this has a variety of uses, from inner depth of the truth to what you see in person, or someone creating a wall. It could be considered a lie, but when is anything that easy? John felt so happy that he was humming a tune while walking down the hall. In truth, once he was in the classroom, his shoulders slumped and a pout crossed his lips when no one was around, showing just how displeased he was with the situation.
Remember that you do not always have to contradict or complicate anything. Sometimes all you need to do is emphasize and that will be just fine. You don’t always have to have an underlining complicated for an emotion to make it more enhanced.
Do be afraid to use the Thesaurus to also improve an emotion. Such things as “happy” is a nice emotional word, but think of how much more powerful it is when you heard some is “overjoyed” or “content.” She how these emotions matched up with a body language can give two different styles of happiness? Mix and match to find what works best for your character at the time.
More In Depth Information
What I’ve stated above is more of a simplistic overview. IF you truly want to improve yourself, go to this
LINK HERE
To see just how much body language can reveal about a person. You will find things such as how a person lies, how the eyes reaction, the positioning of a person in personal space, mouth, and head body language and so much more.
Use these resources to greatly increase the reactions of your character to another and create a more life-like world.
Pirate Terms and Phrases
-> Pirate Lingo
-> A Pirate's Glossary
Batten Down The Hatches - tie everything down and put stuff away for a coming storm.
Brig - a prison on a ship.
Bring a Spring Upon 'er - turn the ship in a different direction
Broadside - the most vulnerable angle of a ship that runs the length of the boat.
Cutlass - a thick, heavy and rather short sword blade.
Dance with Jack Ketch - to hang; death at the hands of the law (Jack Ketch was a famed English executioner).
Davy Jones's Locker - a mythical place at the bottom of the ocean where drowned sailors are said to go.
Dead Men Tell No Tales - the reason given for leaving no survivors.
Flogging - severe beating of a person.
Gangplank - removable ramp between the pier and ship.
Give No Quarter - show no mercy.
Jack - flag flown at the front of the ship to show nationality.
Jolly Roger - black pirate flag with a white skull and crossbones.
Keelhaul - a punishment where someone is dragged under the ship. They are cut by the planks and barnacles on the bottom of the ship.
Landlubber - an inexperienced or clumsy person who doesn't have any sailing skills.
Letters of Marque - government-issued letters allowing privateers the right to piracy of another ship during wartime.
Man-O-War - a pirate ship that is decked out and prepared for battle.
Maroon - to leave someone stranded on a. deserted island with no supplies, typically a punishment for any crew members who disrespected the captain.
Mutiny - a situation in which the crew chooses a new captain, sometimes by forcibly removing the old one.
No Prey, No Pay - a common pirate law that meant crew members were not paid, but rather received a share of whatever loot was taken.
Old Salt - experienced pirate or sailor.
Pillage - to steal/rob a place using violence.
Powder Monkeys - men that performed the most dangerous work on the ship. They were treated harshly, rarely paid, and were expendable.
Privateer - government-appointed pirates.
Run A Shot Across the Bow - fire a warning shot at another boat's Captain.
Scurvy - a disease caused by Vitamin C Deficiency.
Sea Legs - when a sailor adjusts his balance from riding on a boat for a long time.
Strike Colors - lower a ship's flag to indicate surrender.
Weigh Anchor and Hoist the Mizzen - an order to the crew to pull up the anchor and get the ship sailing.
If you like what I do and want to support me, please consider buying me a coffee! I also offer editing services and other writing advice on my Ko-fi! Become a member to receive exclusive content, early access, and prioritized writing prompt requests.
Emotions in writing
The following examples have been taken from the book The Emotion Thesaurus: A Writer's Guide To Character Expression by Angela Ackerman & Becca Puglisi - make sure to get the book!
Confidence
Definition: having faith in one’s own influence and ability
Physical signals: Strong posture (shoulders back, chest out, chin high) Walking with wide steps Strong hygiene and personal grooming Holding the hands loosely behind the back Touching one’s fingertips together (tapping, forming a steeple) A gleam in one’s eye, an inner light Smiling, a playful grin Winking or giving someone an easy nod Keeping one’s hands out of the pockets Appearing relaxed (drumming fingers against a leg, humming) Taking up space (legs spread wide, arms loose at the sides) Approaching people with ease Looking others directly in the eye Arms swinging while walking Choosing the middle, not the sides (be it a couch or a room) Using exaggerated movements to draw attention to oneself A booming laugh Showing comfort in the close proximity of others Initiating contact Telling jokes, adding to or steering a conversation Hosting events (getting the guys together for a football game) Openness when dealing with people Appearing unbothered by what others may think Leaning in to talk or listen Increased physical contact, becoming touchy-feely Running hands through one’s hair or flipping the hair back Assuming a pose that draws attention to one’s best attributes Wearing clothes that are flashy or dramatic
Internal sensations: Relaxed muscles Easy breaths Lightness in the chest
Cues of acute or long-term confidence: Doing or saying things outside of the norm without anxiety or concern Obsessively talking about an achievement or material object Reacting with anger or jealousy if one’s reputation is impugned Bragging, showing off
Cues of suppressed confidence: Minimizing compliments Modesty Changing the topic to bring others into the spotlight Downplaying one’s own comfort level to make others feel better Asking for opinions or advice
Oh my gosh. I just found this website that walks you though creating a believable society. It breaks each facet down into individual questions and makes it so simple! It seems really helpful for worldbuilding!
Character Traits & Quirks (For Writers)
Peace and blessings upon everyone!
I hope life's treating you well. I’m Esmeray and I welcome you to this post on my blog Dear Esmeray.
Ever wondered what makes your OC truly unforgettable? I believe it is the character traits. Character traits are what bring a character to life, or else you just have a flat, one-dimensional everyman as your OC. So today I'll be sharing with you a list of character traits that I compiled to help you develop better OCs.
Positive Traits:
Agreeable
Brave
Caring
Cheerful
Confident
Cooperative
Creative
Dedicated
Devotion
Diligent
Disciplined
Dutiful
Easygoing
Efficient
Fairness
Forgiveness
Friendly
Funny
Generous
Hard-Working
Honest
Honorable
Humble
Kind
Leadership
Love of learning
Loyal
Passionate
Persuasive
Prudent
Principled
Punctual
Reasonable
Reliable
Respectful
Responsible
Self-regulation
Social Intelligence
Supportive
Trust-worthy
Well-mannered
Witty
Wise
Neutral Traits & Quirks:
Raises Eyebrows
Blinks rapidly
Avoids eye contact
Maintains eye contact
Blinks rapidly
Slouches
Stares off into the distance
Shrugs often
Touches their scars or wounds often
Chews lips
Paces around
Smiles a lot
Rarely smiles
Gestures with hands while speaking
Often is distracted
Hums
Negative Traits:
Absentminded
Abusive
Acts superior
Alcoholic
Aggressive
Always plays the victim
Aimless
Apathetic
Arrogant
Argumentive
Avoids their problems
Bossy
Blunt
Boring
Careless
Can't take criticism
Can't take a joke
Clumsy
Conceited
Controlling
Cunning
Childish
Cruel
Deceptive
Defiant
Demanding
Disloyal
Dishonest
Dramatic
Dependent
Disorganized
Disrespectful
Distracted easy
Extravagant
Envious
Forgetful
Greedy
Holds grudges
Makes up excuses for everything
Has a reason for why nothing is ever their fault
No accountability
Hostile
Hypopocrite
Immature
Impatient
Impractical
Impressionable
Impulsive
Insensitive
Irresponsible
Not a team player
Incompetent
Irritable
Inconsiderate
Indulgent
Insecure
Jealous
Know-It-All
Lazy
Liar
Loud
Manipulative
Makes everything about them
Makes everything a joke
Their way or the highway
Mean
Meddlesome
Messy
Naive
Nosy
Obnoxious
Obbssesive
Offended easily
Overdramatic
Overreacts
Patronizing
Power-hungry
Pretentious
Rebellious
Reckless
Rude
Sarcastic
Selfish
Sensitive
Stingy
Sexist
Spoiled
Stubborn
Superstitious
Talks over others/interrupts
Too loyal
Too forgiving
Undependable
Unreliable
Unsympathetic
Unorganized
Unreasonable
Violent
Weak
Remember, there are no one-dimensional characters in real life, and there shouldn't be in your stories either. The possibilities for your characters are endless – so get creative and have fun writing!
With Love, Esmeray ♡
30 Questions for your Dark Urge
These questions can be used as an Ask Game or just answering them all for fun character development!
(Tav edition here)
What circumstances led to your Dark Urge becoming their Class/Subclass?
Did your Dark Urge have any romantic and/or sexual relationships prior to their illithid adventure? If yes, who was it with and what was it like? If no, how did they feel about being single?
What would your Dark Urge consider to be their greatest skill? Is this accurate?
What would your Dark Urge consider to be their greatest flaw? Is this accurate?
What opinion does your Dark Urge have about the Gods?
How does your Dark Urge react to waking up with memory loss?
Did your Dark Urge recall any childhood memories? If yes, how do they feel about the revelations? If no, was it by choice or lack of options?
How does your Dark Urge feel about the wilderness?
How does your Dark Urge feel about the city?
What motivates your Dark Urge to either embrace or resist the tadpole?
What motivates your Dark Urge to either embrace or resist the Urge?
How does your Dark Urge feel about being a bhaalspawn?
How does your Dark Urge feel about killing?
How good of a liar is your Dark Urge? How do they feel about lying?
What is your Dark Urge’s greatest fear?
What is your Dark Urge’s greatest desire?
What is your Dark Urge’s greatest regret?
How does your Dark Urge feel about love?
Has your Dark Urge become particularly close to anyone romantically and/or platonically in their journey? If so, who, and what is the relationship like? If no, why not?
Is your Dark Urge open about their Urge or do they try to hide it? Why?
What are 2-3 songs that your Dark Urge would relate to?
What first impression does your Dark Urge give off to strangers?
How does your Dark Urge feel about what others think of them?
Does your Dark Urge have a treasured item with them? If yes, what is it and why is it special? If no, how do they feel about item sentimentality in general?
How does your Dark Urge feel about Sceleritas Fel?
How does your Dark Urge feel about Bhaal?
How does your Dark Urge feel about giving and receiving orders?
How well does your Dark Urge function under pressure?
What advice would you give to your Dark Urge?
What are your Dark Urge’s intentions/goals after the end of the game?
10 Tips for Crafting Authentic Characters
Give them depth: Create characters with multidimensional personalities, including strengths, weaknesses, quirks, and flaws. They should have a mix of virtues and vices that make them relatable and interesting.
Provide backstory: Develop a detailed backstory for each character, even if only a fraction of it makes it into your story. Understanding a character's past experiences, traumas, and motivations will inform their actions and decisions in the present.
Show their emotions: Allow your characters to express a range of emotions realistically. Show how they react to different situations, both internally and externally, to make them feel human and relatable.
Give them distinct voices: Each character should have a unique way of speaking, with distinct vocabulary, syntax, and speech patterns. This helps readers differentiate between characters and adds authenticity to their dialogue.
Create internal conflicts: Give your characters inner struggles and conflicting desires that they must grapple with throughout the story. Internal conflicts add depth and complexity to characters, making them more believable.
Show their relationships: Develop meaningful relationships between characters, whether they're familial, romantic, platonic, or adversarial. Show how these relationships evolve and influence the characters' development over time.
Make them evolve: Characters should grow and change over the course of the story, driven by their experiences and the challenges they face. Allow them to learn from their mistakes, overcome obstacles, and develop as individuals.
Ground them in reality: Anchor your characters in the real world by giving them relatable experiences, hobbies, jobs, or cultural backgrounds. Incorporating realistic details adds depth and authenticity to their portrayal.
Show their flaws: Imperfect characters are often the most compelling. Don't be afraid to showcase your characters' flaws and vulnerabilities; these imperfections make them more relatable and human.
Give them agency: Allow your characters to drive the plot forward through their actions, decisions, and choices. Avoid making them passive observers or mere vehicles for the story's events. Characters with agency feel more authentic and engaging to readers.
10 Non-Lethal Injuries to Add Pain to Your Writing
New Part: 10 Lethal Injury Ideas
If you need a simple way to make your characters feel pain, here are some ideas:
1. Sprained Ankle
A common injury that can severely limit mobility. This is useful because your characters will have to experience a mild struggle and adapt their plans to their new lack of mobiliy. Perfect to add tension to a chase scene.
2. Rib Contusion
A painful bruise on the ribs can make breathing difficult, helping you sneak in those ragged wheezes during a fight scene. Could also be used for something sport-related! It's impactful enough to leave a lingering pain but not enough to hinder their overall movement.
3. Concussions
This common brain injury can lead to confusion, dizziness, and mood swings, affecting a character’s judgment heavily. It can also cause mild amnesia.
I enjoy using concussions when you need another character to subtly take over the fight/scene, it's an easy way to switch POVs. You could also use it if you need a 'cute' recovery moment with A and B.
4. Fractured Finger
A broken finger can complicate tasks that require fine motor skills. This would be perfect for characters like artists, writers, etc. Or, a fighter who brushes it off as nothing till they try to throw a punch and are hit with pain.
5. Road Rash
Road rash is an abrasion caused by friction. Aka scraping skin. The raw, painful sting resulting from a fall can be a quick but effective way to add pain to your writing. Tip: it's great if you need a mild injury for a child.
6. Shoulder Dislocation
This injury can be excruciating and often leads to an inability to use one arm, forcing characters to confront their limitations while adding urgency to their situation. Good for torture scenes.
7. Deep Laceration
A deep laceration is a cut that requires stitches. As someone who got stitches as a kid, they really aren't that bad! A 2-3 inch wound (in length) provides just enough pain and blood to add that dramatic flair to your writing while not severely deterring your character.
This is also a great wound to look back on since it often scars. Note: the deeper and wider the cut the worse your character's condition. Don't give them a 5 inch deep gash and call that mild.
8. Burns
Whether from fire, chemicals, or hot surfaces, burns can cause intense suffering and lingering trauma. Like the previous injury, the lasting physical and emotional trauma of a burn is a great wound for characters to look back on.
If you want to explore writing burns, read here.
9. Pulled Muscle
This can create ongoing pain and restrict movement, offering a window to force your character to lean on another. Note: I personally use muscle related injuries when I want to focus more on the pain and sprains to focus on a lack of mobility.
10. Tendonitis
Inflammation of a tendon can cause chronic pain and limit a character's ability to perform tasks they usually take for granted. When exploring tendonitis make sure you research well as this can easily turn into a more severe injury.
This is a quick, brief list of ideas to provide writers inspiration. Since it is a shorter blog, I have not covered the injuries in detail. This is inspiration, not a thorough guide. Happy writing! :)
Looking For More Writing Tips And Tricks?
Check out the rest of Quillology with Haya; a blog dedicated to writing and publishing tips for authors!
Instagram Tiktok
19 Most Common Character Flaws in Horror Fiction
Curiosity: Characters who are overly curious may investigate dangerous situations or places, leading to their downfall.
Arrogance: Arrogant characters may underestimate threats or refuse to heed warnings, putting themselves in danger.
Recklessness: Characters who act impulsively or without considering the consequences may find themselves in perilous situations.
Naivety: Naive characters may be easily deceived or manipulated by villains or supernatural forces.
Overconfidence: Overconfident characters may believe they can handle any situation, leading them to take unnecessary risks.
Stubbornness: Stubborn characters may refuse to listen to advice or change their course of action, even when it's clear they're in danger.
Greed: Greedy characters may prioritize personal gain over safety, leading them to make unethical or dangerous choices.
Distrust: Characters who are overly distrustful may alienate allies or miss crucial information, making them more vulnerable.
Cowardice: Cowardly characters may abandon others in dangerous situations or fail to confront threats when necessary.
Impulsiveness: Impulsive characters may act without thinking, leading to mistakes or putting themselves in harm's way.
Lack of Empathy: Characters who lack empathy may disregard the well-being of others, making them more susceptible to manipulation or isolation.
Overprotectiveness: Overprotective characters may prioritize the safety of loved ones to the detriment of their own safety or the safety of others.
Addiction: Characters who are addicted to substances or behaviors may make irrational decisions or be more easily controlled by external forces.
Obsession: Characters who are obsessed with a goal or idea may pursue it at any cost, even endangering themselves or others.
Paranoia: Paranoid characters may see threats where none exist, leading them to take extreme measures or isolate themselves unnecessarily.
Lack of Self-awareness: Characters who lack self-awareness may fail to recognize their own limitations or the impact of their actions on others.
Insecurity: Insecure characters may doubt their own abilities or judgment, making them more susceptible to manipulation or self-destructive behavior.
Ignorance: Characters who are ignorant of the true nature of the threats around them may underestimate their danger or fail to take necessary precautions.
Desperation: Characters who are desperate may make rash decisions or ally themselves with dangerous individuals or entities in hopes of achieving their goals.
-
 kikisoda liked this · 1 week ago
kikisoda liked this · 1 week ago -
 lisa2089 liked this · 1 week ago
lisa2089 liked this · 1 week ago -
 youdidnotseeme liked this · 1 week ago
youdidnotseeme liked this · 1 week ago -
 allaroundsimp liked this · 1 week ago
allaroundsimp liked this · 1 week ago -
 nyhne liked this · 1 week ago
nyhne liked this · 1 week ago -
 dahlia-scribbles reblogged this · 1 week ago
dahlia-scribbles reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 burningsilence liked this · 1 week ago
burningsilence liked this · 1 week ago -
 rahabs reblogged this · 1 week ago
rahabs reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 henry-k-emily liked this · 1 week ago
henry-k-emily liked this · 1 week ago -
 henry-k-emily reblogged this · 1 week ago
henry-k-emily reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 shamelessprincesweets liked this · 1 week ago
shamelessprincesweets liked this · 1 week ago -
 lireb-librarian liked this · 1 week ago
lireb-librarian liked this · 1 week ago -
 cremebrulee-69 reblogged this · 1 week ago
cremebrulee-69 reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 cremebrulee-69 liked this · 1 week ago
cremebrulee-69 liked this · 1 week ago -
 avt195 liked this · 1 week ago
avt195 liked this · 1 week ago -
 camrebb liked this · 1 week ago
camrebb liked this · 1 week ago -
 spidersdeservebetter liked this · 1 week ago
spidersdeservebetter liked this · 1 week ago -
 gumamelaa reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
gumamelaa reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 gumamelaa liked this · 2 weeks ago
gumamelaa liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 glitterfixation reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
glitterfixation reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 ikeberry liked this · 2 weeks ago
ikeberry liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 little-lamb-lyosha liked this · 2 weeks ago
little-lamb-lyosha liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 sandumilfshous reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
sandumilfshous reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 creative-sweets liked this · 2 weeks ago
creative-sweets liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 phlebasphoenician liked this · 2 weeks ago
phlebasphoenician liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 artbythedarkside reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
artbythedarkside reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 artbythedarkside liked this · 2 weeks ago
artbythedarkside liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 veloursdor liked this · 2 weeks ago
veloursdor liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 itzaeolian liked this · 2 weeks ago
itzaeolian liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 tideswept reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
tideswept reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 cat-tokio reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
cat-tokio reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 cat-tokio liked this · 2 weeks ago
cat-tokio liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 korbensoi liked this · 2 weeks ago
korbensoi liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 goomar-churchill liked this · 2 weeks ago
goomar-churchill liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 floppyjacks liked this · 2 weeks ago
floppyjacks liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 corvid-collector reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
corvid-collector reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 corvid-collector liked this · 2 weeks ago
corvid-collector liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 katpawzi liked this · 2 weeks ago
katpawzi liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 valkyrcat liked this · 2 weeks ago
valkyrcat liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 kmoftherose reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
kmoftherose reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 kmoftherose liked this · 2 weeks ago
kmoftherose liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 stextrovert liked this · 2 weeks ago
stextrovert liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 nicrt liked this · 2 weeks ago
nicrt liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 lycanwrites reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
lycanwrites reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 skankcreature liked this · 2 weeks ago
skankcreature liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 vampfukr reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
vampfukr reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 vampfukr liked this · 3 weeks ago
vampfukr liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 virenasalin liked this · 3 weeks ago
virenasalin liked this · 3 weeks ago
