Jupiter In Near-Infrared & Jupiter And Ganymede In Near-UV And Blue


Jupiter in Near-Infrared & Jupiter and Ganymede in Near-UV and Blue
Image credit: Judy Schmidt @ twitter | instagram
More Posts from Xnzda and Others
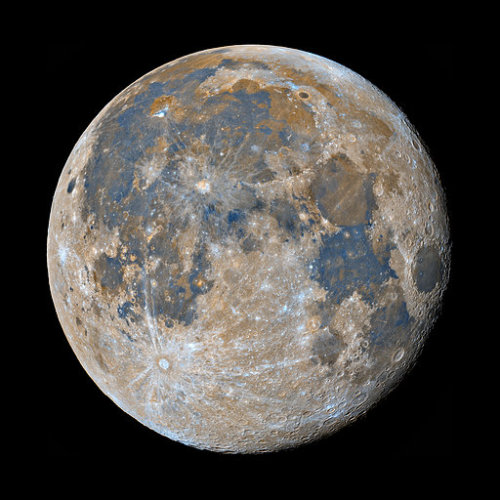
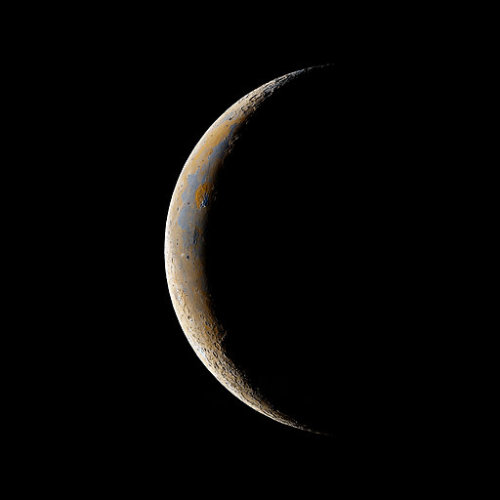


98% waning gibbous Moon | 11% waning crescent Moon
by Bartosz Wojczyński
FUCKING NASA
I’m fucking pissing myself. You know how all of Jupiter’s moons are named after his lovers and affairs? Yeah. NASA is sending a craft to check up on Jupiter. You know what the craft is called?
JUNO.
Who’s Juno?
JUPITER’S WIFE.
NASA IS SENDING JUPITER’S WIFE TO CHECK ON JUPITER AND HIS AFFAIRS AND LOVERS.
FUCKING NASA
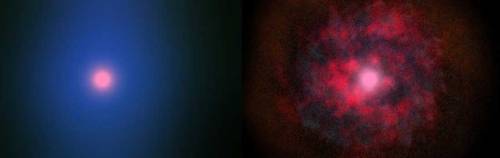
Black holes

Perseus Black hole
Black holes are objects that have collapsed under their own weight to a point, creating an object that is very small but enormously dense. It is a region of space that has a gravitational pull so strong that no imminent particle or electromagnetic radiation can escape from it. This astonishing concept of black hole was first given by John Michell in 1783.He proposed that if you take the sun and compress it to a very small volume it would have a gravitational pull so strong that you have to travel at speeds greater than the speed of light to escape it.At first black holes are thought to be theoretical concepts which do not exist. But later they turned out to be very real. So how do these giant suckers form?
In order to understand the formation of a black hole we need to understand the formation and the life cycle of stars. A star is formed when large amounts of dust and gases, mainly hydrogen gas condense and collapse under its own gravitational force. As the gas collapses, the atoms of the gas collide with each other at higher and higher speeds resulting in the heating of the gas. Ultimately the gas becomes so hot that when the hydrogen atoms collide they don’t bounce off, but fuse together to form helium atoms, same as in the hydrogen bomb. As a result a large amount of heat is released which is the reason why stars shine. This heat increases the pressure of the gas until it balances out the gravitational pull and the gas stops contracting. Hence a star is formed.
The stars are usually stable as long as they have hydrogen in them. As the hydrogen runs out, the fusion reaction stops. To keep the fusion reaction going the star turns to its helium reserve. After it runs out of helium, it switches to carbon, and then oxygen. Stars with the mass of our Sun stop at this point as they don’t have enough energy to continue the fusion process and become white dwarfs. But stars with about 5 times the mass of our sun continue further to produce silicon, aluminum, potassium so on up to iron. No further energy can be produced by fusing iron atoms so the star starts to cool down. Once the external force of radiation stops acting the gravitational pull takes over and the star begins to contract. The entire mass of the star collapses into smaller and smaller volume of space. Eventually when the star has contracted to a certain critical radius, the gravitational field at the surface becomes so strong that even light cannot escape it. And this is how a black hole is formed.
Another way of formation of black hole is when two neutron stars collide with each other. When they collide their combined mass results in a very high gravitational force that leads to a collapse and a black hole is formed.

In this image, information from the Chandra X-ray Observatory is combined with images from the Hubble Space Telescope. NASA believes these two black holes are spiraling toward each other and have been doing so for 30 years.
So it turns out, Pluto is red.

What color is Pluto? If you search for the dwarf planet on Google, images suggest that it’s a sort of steely blue or gray color. But now, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft is closing in on it, and has learned Mars isn’t the only red planet in our solar system. But the reason it’s red couldn’t be more different from Mars.
Stellar Winds
Stellar winds are fast moving flows of material (protons, electrons and atoms of heavier metals) that are ejected from stars. These winds are characterised by a continuous outflow of material moving at speeds anywhere between 20 and 2,000 km/s.
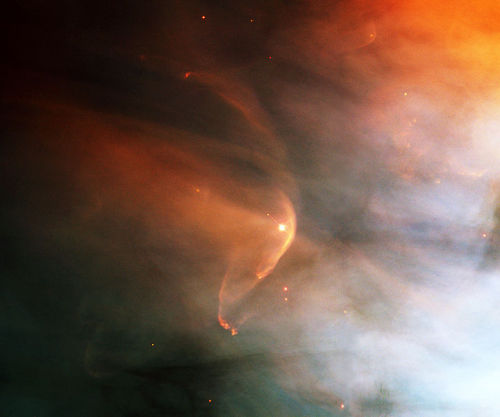

In the case of the Sun, the wind ‘blows’ at a speed of 200 to 300 km/s from quiet regions, and 700 km/s from coronal holes and active regions.
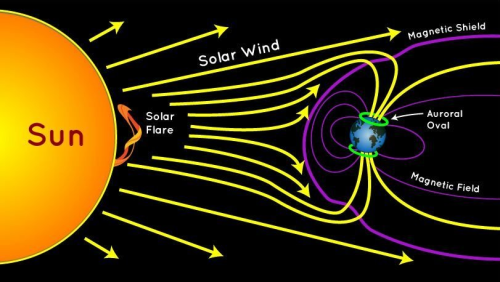
The causes, ejection rates and speeds of stellar winds vary with the mass of the star. In relatively cool, low-mass stars such as the Sun, the wind is caused by the extremely high temperature (millions of degrees Kelvin) of the corona.

his high temperature is thought to be the result of interactions between magnetic fields at the star’s surface, and gives the coronal gas sufficient energy to escape the gravitational attraction of the star as a wind. Stars of this type eject only a tiny fraction of their mass per year as a stellar wind (for example, only 1 part in 1014 of the Sun’s mass is ejected in this way each year), but this still represents losses of millions of tonnes of material each second. Even over their entire lifetime, stars like our Sun lose only a tiny fraction of 1% of their mass through stellar winds.
In contrast, hot, massive stars can produce stellar winds a billion times stronger than those of low-mass stars. Over their short lifetimes, they can eject many solar masses (perhaps up to 50% of their initial mass) of material in the form of 2,000 km/sec winds.

These stellar winds are driven directly by the radiation pressure from photons escaping the star. In some cases, high-mass stars can eject virtually all of their outer envelopes in winds. The result is a Wolf-Rayet star.
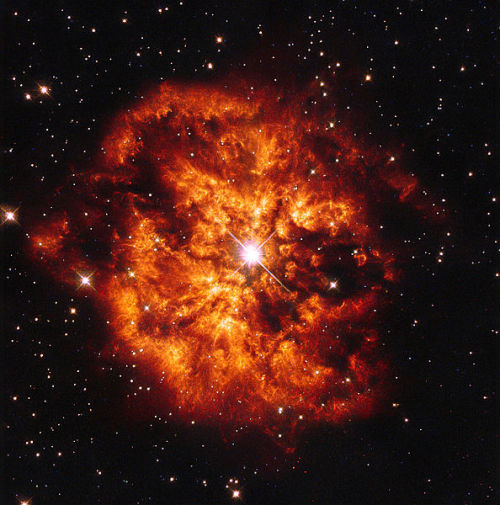

Stellar winds play an important part in the chemical evolution of the Universe, as they carry dust and metals back into the interstellar medium where they will be incorporated into the next generation of stars.
source (read more) + Wolf–Rayet star










Where Could Life Exist?
When NASA scientists announced earlier this year that they had found evidence of liquid water on Mars, imaginations ran wild with the possibility that life could exist somewhere other than here on Earth.
Scientists continue to explore the possibility that Mars once looked a lot like Earth — salty oceans, fresh water lakes, and a water cycle to go with it. That’s exciting stuff.
So where else are they looking? What exactly are they looking for?
There are nine places in our universe where scientists say life is a possibility. The locations range from a smoking hot planet like Venus to a moon that orbits Saturn called Enceladus, which looks a lot like a massive, tightly-packed ball of ice.
All of these places show signs that water is, or at least was, a possibility. They also appear to feature some kind of energy that could produce heat.
full resolution
-
 lost-poets-poetry reblogged this · 1 week ago
lost-poets-poetry reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 lost-poets-poetry liked this · 1 week ago
lost-poets-poetry liked this · 1 week ago -
 kalosdyke liked this · 1 month ago
kalosdyke liked this · 1 month ago -
 dearsvdghostt liked this · 3 months ago
dearsvdghostt liked this · 3 months ago -
 murren-606 reblogged this · 3 months ago
murren-606 reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 annita890dzmzfmh liked this · 6 months ago
annita890dzmzfmh liked this · 6 months ago -
 messstar liked this · 7 months ago
messstar liked this · 7 months ago -
 knightvelvet reblogged this · 7 months ago
knightvelvet reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 wanderlustlolita reblogged this · 8 months ago
wanderlustlolita reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 archtech-fox reblogged this · 8 months ago
archtech-fox reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 archtech-fox liked this · 8 months ago
archtech-fox liked this · 8 months ago -
 captastra reblogged this · 8 months ago
captastra reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 flapjackoctopus07 liked this · 8 months ago
flapjackoctopus07 liked this · 8 months ago -
 corvidovis liked this · 8 months ago
corvidovis liked this · 8 months ago -
 megaalodon reblogged this · 8 months ago
megaalodon reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 theehighwarlock reblogged this · 8 months ago
theehighwarlock reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 sleepy-idiot reblogged this · 8 months ago
sleepy-idiot reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 sleepy-idiot liked this · 8 months ago
sleepy-idiot liked this · 8 months ago -
 invisiblevoyager reblogged this · 8 months ago
invisiblevoyager reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 littlemusicalwitch reblogged this · 8 months ago
littlemusicalwitch reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 confused--polarity reblogged this · 8 months ago
confused--polarity reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 supahgrl reblogged this · 8 months ago
supahgrl reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 supahgrl liked this · 8 months ago
supahgrl liked this · 8 months ago -
 katebihshop reblogged this · 8 months ago
katebihshop reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 xrgesh liked this · 8 months ago
xrgesh liked this · 8 months ago -
 draven-the-great-is-not-okay liked this · 8 months ago
draven-the-great-is-not-okay liked this · 8 months ago -
 thelupines reblogged this · 8 months ago
thelupines reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 iheartkhloe liked this · 8 months ago
iheartkhloe liked this · 8 months ago -
 xyl3m liked this · 8 months ago
xyl3m liked this · 8 months ago -
 seriously-nobody reblogged this · 8 months ago
seriously-nobody reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 seriously-nobody liked this · 8 months ago
seriously-nobody liked this · 8 months ago -
 eivorsfist liked this · 8 months ago
eivorsfist liked this · 8 months ago -
 obsessivedaydreamer reblogged this · 8 months ago
obsessivedaydreamer reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 finalbarbiegirl liked this · 8 months ago
finalbarbiegirl liked this · 8 months ago -
 stripesysheaven reblogged this · 8 months ago
stripesysheaven reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 stripesysheaven liked this · 8 months ago
stripesysheaven liked this · 8 months ago -
 folklouire reblogged this · 8 months ago
folklouire reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 folklouire liked this · 8 months ago
folklouire liked this · 8 months ago -
 nadia-el-mansours liked this · 8 months ago
nadia-el-mansours liked this · 8 months ago -
 wickedwitzh reblogged this · 8 months ago
wickedwitzh reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 librariescats reblogged this · 8 months ago
librariescats reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 bi-hans liked this · 9 months ago
bi-hans liked this · 9 months ago -
 oxfordsonnets reblogged this · 9 months ago
oxfordsonnets reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 wa-ng-da-ng-sw-eet-po-on-ta-ng reblogged this · 9 months ago
wa-ng-da-ng-sw-eet-po-on-ta-ng reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 mister-kaplan liked this · 9 months ago
mister-kaplan liked this · 9 months ago -
 lovelydulcecito reblogged this · 9 months ago
lovelydulcecito reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 leo-inspo reblogged this · 10 months ago
leo-inspo reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 omgherbalicious reblogged this · 10 months ago
omgherbalicious reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 omgherbalicious liked this · 10 months ago
omgherbalicious liked this · 10 months ago -
 pokemella liked this · 11 months ago
pokemella liked this · 11 months ago




